Spring的aop思想
1、AOP思想
面向切面编程,采取横向抽取的方式,取代了纵向继承体系代码的重复性。底层采用代理的机制进行实现,是面向对象编程的延续,使得业务的耦合性降低,提高了程序的可重用性
应用:
事务管理、性能监控、安全检查、缓存、日志等
(1)在解决中文乱码的应用:
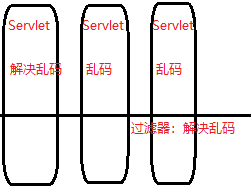
一般情况下如果在Servlet中要解决中文乱码问题需要在每一个Servlet中书写解决乱码的代码,但是,在运用了过滤器之后,就不再需要每一个Servlet中都写解决乱码的函数,减少了代码量。
AOP思想又叫做“面向切面编程”,过滤器就是面向每一个Servlet的,每一个Servlet都需要执行过滤器。
(2)动态代理:

代理类的那部分代码被固定下来了,不会因为业务的增加而逐渐庞大。
(3)拦截器:
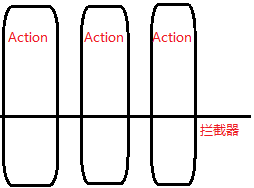
不需要在每一个Action中书写拦截器的代码,只需要在Action需要的时候在配置文件中将相应的拦截器配置进去即可。
2、Spring中的AOP
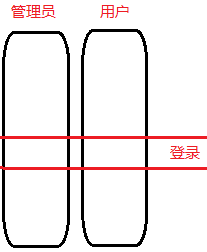
Spring能够为容器中管理的对象生成动态代理对象。这样做是有好处的,如果把登录功能写在每一个业务中当需要修改代码的时候,就需要对每一个业务进行修改,但是,如果把登录功能抽取出来形成独立的模块,问题就迎刃而解了。
3、Spring实现aop的原理
(1)动态代理(优先使用):被代理对象必须要实现接口,才能产生代理对象,如果没有接口将不能实现动态代理。

假如登录需要分为登录前、登录、登录后三部分,也就是说登录部分是相同的代码,而登录前和登录后的代码根据用户的不同进行不同的操作,那么,登录接口可以这样写:
public class LoginService {
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("登录前的操作");
System.out.println("登录");
System.out.println("登录后的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("登录前的操作");
System.out.println("登录");
System.out.println("登录后的操作");
}
}
这样写的话不仅会造成代码的冗余,而且,如果要修改登录的代码的话两个都要分别作出修改,可以使用动态代理的方式将公共部分抽取出来:
定义登录接口:
public interface LoginService {
public void userLogin();
public void managerLogin();
}
定义接口的实现类:
public class LoginProxyImp implements LoginService{
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("普通用户登录前的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("管理员登录前的操作");
}
}
创建代理类:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class LoginProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private LoginService ls;
public LoginProxy(LoginService ls) {
super();
this.ls = ls;
}
public LoginService getloginProxy(){
LoginService loginService= (LoginService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LoginService.class.getClassLoader(),//创建接口实例
LoginProxyImp.class.getInterfaces(),//与目标对象有相同的类加载器
this); //被代理的类所实现的接口(可以是多个)
return loginService;//产生代理对象
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] arg2) throws Throwable {
Object invoke=method.invoke(ls,arg2);
System.out.println("登录");//抽取出来的公共部分
return invoke;
}
}
测试类:
public class TestProxy {
public static void main(String [] args){
LoginService loginService=new LoginProxyImp();
LoginProxy loginProxy=new LoginProxy(loginService);
LoginService loginService1=loginProxy.getloginProxy();
loginService1.userLogin();
}
}
(2)cglib技术:可以对任何类生成代理对象,原理是对目标对象进行继承代理,如果该目标对象被final修饰,将无法使用cglib技术
登录接口:
public interface LoginService {
public void userLogin();
public void managerLogin();
}
接口的实现类:
public class LoginProxyImp implements LoginService{
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("普通用户登录前的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("管理员登录前的操作");
}
}
创建代理类:
public class LoginProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
public LoginService getLoginServiceProxy(){
Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer();//帮我们生成代理对象
enhancer.setSuperclass(LoginProxyImp.class);//设置对谁进行代理,即确定父类
enhancer.setCallback(this);//代理要做什么,即设定回调函数
LoginService loginService=(LoginService) enhancer.create();//创建代理对象
return loginService;
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
//前三个参数和jdk方式的代理相同
Object invokeSuper = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o,objects);
return invokeSuper;
}
}
测试类:
public class TestProxy {
public static void main(String [] args){
LoginProxy loginProxy=new LoginProxy();
LoginService loginService=loginProxy.getLoginServiceProxy();
loginService.userLogin();
System.out.println("登录");
}
}

这种方式是代理对象继承了被代理对象。
4、aop中的名词
(1)连接点(Joinpoint):目标对象中可以增强的的方法
public class LoginProxyImp implements LoginService{
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("普通用户登录前的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("管理员登录前的操作");
}
}
该方法还可以通过动态代理增加登录的功能。
(2)切入点(PointCut):目标对象已经增强的方法
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("普通用户登录前的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("管理员登录前的操作");
}
例如:上述两个登录的方法通过动态代理已经增强的方法。
(3)advice(通知 / 增强):Spring中一共有五种通知类型
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] arg2) throws Throwable {
Object invoke=method.invoke(ls,arg2);
System.out.println("登录");//抽取出来的公共部分
return invoke;
}
加入了登录的功能,这部分代码是advice。
(4)Target(目标对象):
被代理的对象。
(5)weaving(织入):
将通知应用到切入点的形成代理类的过程。
(6)proxy(代理):
将通知织入到目标对象以后,形成代理对象
(7)切面(aspect):切入点加通知

5、Spring中的aop演示
(1)导包:
(2)对配置文件进行配置:
需要先导入aop约束:
(3)创建接口:
public interface LoginService {
public void userLogin();
public void managerLogin();
}
(4)创建目标对象:
public class LoginServiceImp {
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("普通用户登录前的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("管理员登录前的操作");
}
}
(5)创建通知类:
public class LoginServiceImp {
public void userLogin(){
System.out.println("普通用户登录前的操作");
}
public void managerLogin(){
System.out.println("管理员登录前的操作");
}
}
(6)配置Spring的配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean name="loginserviceTarget" class="pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp"></bean><!--配置目标对象-->
<bean name="myadvice" class="pers.zhb.test.MyAdvice"></bean><!--配置通知对象-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())" id="pointcut"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myadvice">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterException" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config> </beans>
(1)配置目标对象,即被代理的对象。
(2)配置通知对象,即需要加入的那部分代码。
(3)将通知织入目标对象:需要先配置接入点,即:userLogin(),将通知对象加入目标对象。
好处:通过配置文件的形式实现aop的开发,我们就不需要手动书写动态代理的代码了,可以进行任何类的代理,不需要接口也可以。
6、使用注解完成Spring的aop配置
配置文件的书写:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean name="loginserviceTarget" class="pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp"></bean><!--配置目标对象-->
<bean name="myadvice" class="pers.zhb.test.MyAdvice"></bean><!--配置通知对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy><!--开启使用注解完成织入-->
</beans>
使用注解配置:
package pers.zhb.test;
//通知类,即用于增强目标对象的代码
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; @Aspect//表示该类是一个通知类
public class MyAdvice {
@Before("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")//指定切入点(前置通知)
public void before(){
System.out.println("我是前置通知!");
}
@Around("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!");
Object process=proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();//环绕通知
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分!");
return process;
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")
public void afterException(){
System.out.println("异常出现了!");
}
@After("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")
public void after(){
System.out.println("后置通知,出现异常也能被调用!");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")
public void AfterReturning(){
System.out.println("我是后置通知,出现异常不会执行!!");
}
}

但是,用上面的方法配置的注解不利于修改,可以进行下面的配置:
package pers.zhb.test;
//通知类,即用于增强目标对象的代码
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; @Aspect//表示该类是一个通知类
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")
public void pc(){ }
@Before("MyAdvice.pc()")//指定切入点(前置通知)
public void before(){
System.out.println("我是前置通知!");
}
@Around("MyAdvice.pc()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!");
Object process=proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();//环绕通知
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分!");
return process;
}
@AfterThrowing("MyAdvice.pc()")
public void afterException(){
System.out.println("异常出现了!");
}
@After("MyAdvice.pc()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("后置通知,出现异常也能被调用!");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* pers.zhb.test.LoginServiceImp.userLogin())")
public void AfterReturning(){
System.out.println("我是后置通知,出现异常不会执行!!");
}
}
Spring的aop思想的更多相关文章
- [ SSH框架 ] Spring框架学习之二(Bean的管理和AOP思想)
一.Spring的Bean管理(注解方式) 1.1 什么是注解 要使用注解方式实现Spring的Bean管理,首先要明白什么是注解.通俗地讲,注解就是代码里的特殊标记,使用注解可以完成相应功能. 注解 ...
- spring(二) AOP之AspectJ框架的使用
前面讲解了spring的特性之一,IOC(控制反转),因为有了IOC,所以我们都不需要自己new对象了,想要什么,spring就给什么.而今天要学习spring的第二个重点,AOP.一篇讲解不完,所以 ...
- Spring框架AOP学习总结(下)
目录 1. AOP 的概述 2. Spring 基于AspectJ 进行 AOP 的开发入门(XML 的方式): 3.Spring 基于AspectJ 进行 AOP 的开发入门(注解的方式): 4.S ...
- Spring框架学习之注解配置与AOP思想
上篇我们介绍了Spring中有关高级依赖关系配置的内容,也可以调用任意方法的返回值作为属性注入的值,它解决了Spring配置文件的动态性不足的缺点.而本篇,我们将介绍Spring的又一大核心 ...
- Spring框架系列之AOP思想
微信公众号:compassblog 欢迎关注.转发,互相学习,共同进步! 有任何问题,请后台留言联系! 1.AOP概述 (1).什么是 AOP AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Progra ...
- spring框架学习(四)AOP思想
什么是AOP 为什么需要AOP 从Spring的角度看,AOP最大的用途就在于提供了事务管理的能力.事务管理就是一个关注点,你的正事就是去访问数据库,而你不想管事务(太烦),所以,Spring在你访问 ...
- spring框架中AOP思想与各种配置详解
Spring中提供两种AOP支持: 1.基于代理的经典AOP 2.Aspectj注解配置AOP 首先我们先了解什么是AOP,AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming ...
- 【Spring Framework】Spring入门教程(五)AOP思想和动态代理
本文主要讲解内容如下: Spring的核心之一 - AOP思想 (1) 代理模式- 动态代理 ① JDK的动态代理 (Java官方) ② CGLIB 第三方代理 AOP概述 什么是AOP(面向切面编程 ...
- 深入理解Spring AOP思想
什么是AOP?AOP解决了什么问题? 在传统的开发模式中,以下层次的是非常常见的一种,业务层每一个方法都要有重复的事务代码 如何改善这个问题? AOP希望将A.B 这些分散在各个业务逻辑中的相同代码, ...
随机推荐
- $bzoj4237$稻草人 $cdq$分治
正解:$cdq$分治 解题报告: 传送门$QwQ$ $umm$总感觉做过这题的亚子,,,? 先把坐标离散化,然后把所有点先按$x$排序$QwQ$,然后用类似平面最近点对的方法,先分别解决$mid$两侧 ...
- IDEA 连接Docker 并部署
安装docker 之前先更新系统: yum update 安装docker: yum install docker 启动docker: systemctl start docker docker 远程 ...
- (httpd、php)
(一)http协议介绍 http: 超文本传输协议,http协议是应用层协议,实现http协议的软件都监听的TCP的80端口之上.http协议也是一种文本协议,是基于TCP协议实现 http协议有几个 ...
- Good Bye 2019(前五题题解)
这套也是后来补得. 我太菜了,第三题就卡着了.想了好久才做出来,要是参加了绝对掉分. D题是人生中做完的第一道交互题,不容易. 比赛传送门 A.Card Game 题目大意:一共有n张互不相同的牌,玩 ...
- linux下卸载旧版本cmake安装新版本cmake
1.看当前cmake版本 cmake --version 2.卸载旧版本下的cmake apt-get autoremove cmake 3.安装新版面cmake http://www.cnblogs ...
- C# DataTable数据类型判断
当我们从数据中获取到数据,一般会使用 DataTable 接收,然后会遍历每行数据.由于从数据库中读取的数据可能为空,比如我们的编译代码如下: foreach (DataRow datarow in ...
- EntityFramework Core一劳永逸动态加载模型,我们要知道些什么呢?
前言 这篇文章源于一位问我的童鞋:在EntityFramework Core中如何动态加载模型呢?在学习EntityFramwork时关于这个问题已有对应园友给出答案,故没有过多研究,虽然最后解决了这 ...
- 让vue-router渲染为指定的标签
<router-link :to="{name:'cart'}" tag="li"> cart </router-link> 在rout ...
- 从头学pytorch(二十):残差网络resnet
残差网络ResNet resnet是何凯明大神在2015年提出的.并且获得了当年的ImageNet比赛的冠军. 残差网络具有里程碑的意义,为以后的网络设计提出了一个新的思路. googlenet的思路 ...
- HTML中使用Vue+Dhtmlxgantt制作任务进度图
HTML中使用Vue+Dhtmlxgantt制作任务进度图 Dhtmlxgantt官网: https://dhtmlx.com/docs/products/dhtmlxGantt/ 参考文章 甘特图配 ...
