MPI并行计算模拟N体问题
实验内容
N体问题是指找出已知初始位置、速度和质量的多个物体在经典力学情况下的后续运动。在本次实验中,你需要模拟N个物体在二维空间中的运动情况。通过计算每两个物体之间的相互作用力,可以确定下一个时间周期内的物体位置。
在本次实验中,N个小球在均匀分布在一个正方形的二维空间中,小球在运动时没有范围限制。每个小球间会且只会受到其他小球的引力作用。在计算作用力时,两个小球间的距离不会低于其半径之和,在其他的地方小球位置的移动不会受到其他小球的影响(即不会发生碰撞,挡住等情况)。你需要计算模拟一定时间后小球的分布情况,并通过MPI并行化计算过程。
实验要求
有关参数要求如下:
- 引力常数数值取6.67*10^-11
- 小球重量都为 10000kg
- 小球半径都为1cm
- 小球间的初始间隔为1cm,例:N=36时,则初始的正方形区域为5cm*5cm
- 小球初速为0.
对于时间间隔,公式:delta_t=1/timestep。其中,timestep表示在1s内程序迭代的次数,小球每隔delta_t时间更新作用力,速度,位置信息。结果中程序总的迭代次数=timestep*模拟过程经历的时间,你可以根据你的硬件环境自己设置这些数值,理论上来说,时间间隔越小,模拟的真实度越高。
算法设计与分析
不考虑小球间的碰撞;小球可重叠,但是在计算距离时最小距离为半径。
首先初始化小球的位置速度加速度
循环:
compute_force()更新加速度。加速度需要依赖于所有小球的位置
compute_velocitiescompute_positions更新位置和速度。这两项只依赖于自身的属性
并行的实现:
将小球按进程数连续地均分,每个进程计算自己的部分;在计算加速度之前要接受其他进程的小球数据,并向其他进程发送自己的小球数据
核心代码
//小球结构体:
typedef struct ball{
double px,py;
double vx,vy;
double ax,ay;
}ball;
ball ball_list[256];计算加速度:每次计算之前都初始化加速度为0,然后遍历计算每一个其他小球。首先计算小球间距离,如果小于半径就以半径计算
Index表示要计算的小球,ball_list是全局变量
void compute_force(int index){
ball_list[index].ax=0;
ball_list[index].ay=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
if(i!=index){
double dx=ball_list[i].px-ball_list[index].px;
double dy=ball_list[i].py-ball_list[index].py;
double d=(dx*dx+dy*dy);
if(d<r*r)d=r*r;
d*=sqrt(d);//^(3/2)
ball_list[index].ax+=GM*(dx)/d;
ball_list[index].ay+=GM*(dy)/d;
}
}
}计算速度:
void compute_velocities(int index){
ball_list[index].vx+=ball_list[index].ax*delta_t;
ball_list[index].vy+=ball_list[index].ay*delta_t;
}计算位置:注意小球不能超越边界,但是不考虑碰撞
void compute_positions(int index){
ball_list[index].px+=ball_list[index].vx*delta_t;
if(ball_list[index].px>((size-1)/100.0))ball_list[index].px=(size-1)/100.0;
if(ball_list[index].px<0)ball_list[index].px=0;
ball_list[index].py+=ball_list[index].vy*delta_t;
if(ball_list[index].py>((size-1)/100.0))ball_list[index].py=(size-1)/100.0;
if(ball_list[index].py<0)ball_list[index].py=0;
}核心循环:
//向所有其他线程发送本线程所拥有的数据
for(int j=0;j<numprocs;j++){
if(j!=myid)MPI_Bsend((ball_list+(N/numprocs)*myid),sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs,MPI_BYTE,j,i*10+myid,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
//从所有其他线程接收其他线程拥有的数据
for(int j=0;j<numprocs;j++){
if(j!=myid){
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Recv((ball_list+(N/numprocs)*j),sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs,MPI_BYTE,j,i*10+j,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status);
}
}
//首先计算加速度
for(int j=(N/numprocs)*myid;j<(N/numprocs)*(myid+1);j++)
compute_force(j);
//之后更新位置会影响加速度的计算,所以要等所有线程计算完之后在计算
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
//更新速度和位置
for(int j=(N/numprocs)*myid;j<(N/numprocs)*(myid+1);j++){
compute_velocities(j);
compute_positions(j);
}
//位置的更新会影响下一个循环的加速度的计算,所以要同步
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);实验结果
| 规模 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| N=64/时间/s | 1.636738 | 1.097428 | 0.956398 |
| 加速比 | 1 | 1.491430873 | 1.711357 |
| N=256/时间/s | 22.832278 | 13.928187 | 11.09423 |
| 加速比 | 1 | 1.639285716 | 2.058031 |
小球的位置:
初始:
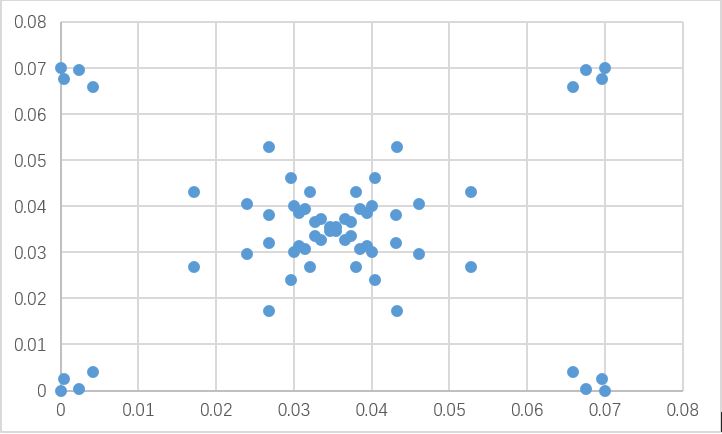
2000周期,Timestep=10000
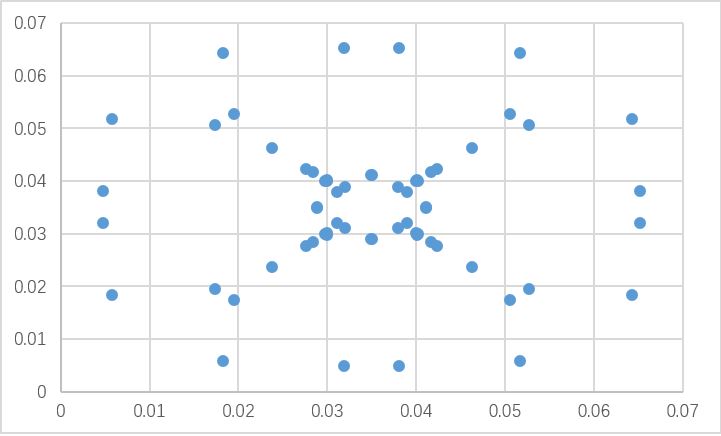
为什么在四个角落里会有小球:在调试中发现,timestep设置的过小会因为数据精度不足导致位置无法更新,将timestep设置为100就不会出现这种情况
2000周期,Timestep=100
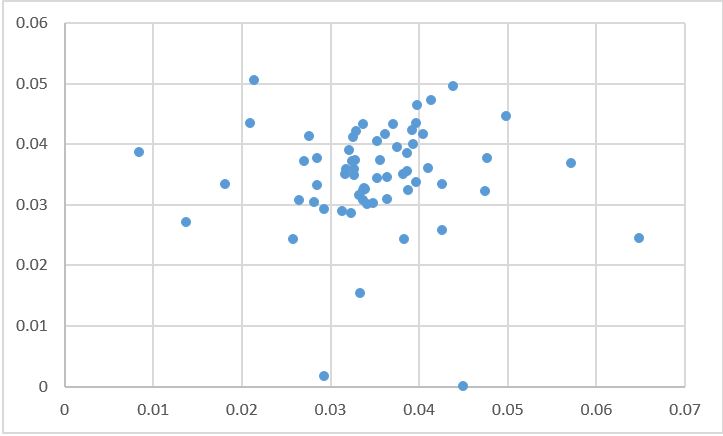
20000周期,timestep=100
分析与总结
MPI是基于进程通信的并行计算,所以进程间不会共享数据,要使用其他进程的数据的时候需要进行通信
源程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <mpi.h>
typedef struct ball
{
double px,py;
double vx,vy;
double ax,ay;
}ball;
ball ball_list[256];
const int N=256;
const double GM=6.67E-7;//G*M
int timestep=100;
double delta_t=0.0;
double r=0.01;//球的半径
int cycle_times=20000;//周期数
int size=0;//方阵宽
FILE* fp;
char* filename[4]={"result1.txt","result2.txt","result3.txt","result4.txt"};
void compute_force(int index)
{
ball_list[index].ax=0;
ball_list[index].ay=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
if(i!=index)
{
double dx=ball_list[i].px-ball_list[index].px;
double dy=ball_list[i].py-ball_list[index].py;
double d=(dx*dx+dy*dy);
if(d<r*r)d=r*r;
d*=sqrt(d);//^(3/2)
ball_list[index].ax+=GM*(dx)/d;
ball_list[index].ay+=GM*(dy)/d;
//printf("%lf %lf ",dx,dy);
}
}
//printf("%d a: %lf %lf\n",index,ball_list[index].ax,ball_list[index].ay);
}
void compute_velocities(int index)
{
ball_list[index].vx+=ball_list[index].ax*delta_t;
ball_list[index].vy+=ball_list[index].ay*delta_t;
//printf("%d v: %lf %lf\n",index,ball_list[index].vx,ball_list[index].vy);
}
void compute_positions(int index)
{
ball_list[index].px+=ball_list[index].vx*delta_t;
if(ball_list[index].px>((size-1)/100.0))ball_list[index].px=(size-1)/100.0;
if(ball_list[index].px<0)ball_list[index].px=0;
ball_list[index].py+=ball_list[index].vy*delta_t;
if(ball_list[index].py>((size-1)/100.0))ball_list[index].py=(size-1)/100.0;
if(ball_list[index].py<0)ball_list[index].py=0;
//printf("%d p: %lf %lf\n",index,ball_list[index].px,ball_list[index].py);
}
void print()
{
//int table[16][16]={0};
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
//table[(int)(ball_list[i].px*100)][(int)(ball_list[i].py*100)]++;
fprintf(fp,"%lf\n",ball_list[i].px);
}
fprintf(fp,"\n");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
//table[(int)(ball_list[i].px*100)][(int)(ball_list[i].py*100)]++;
fprintf(fp,"%lf\n",ball_list[i].py);
}
fprintf(fp, "end of printing\n\n");
}
void main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//init
delta_t=1.0/timestep;
//printf("%lf\n",delta_t);
size=(int)sqrt(N);
//printf("%d\n",size);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
ball_list[i].px=0.01*(i%size);
ball_list[i].py=0.01*(i/size);
ball_list[i].vx=0;
ball_list[i].vy=0;
ball_list[i].ax=0;
ball_list[i].ay=0;
}
int myid, numprocs;
clock_t starttime,endtime;
int namelen;
MPI_Init(&argc,&argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&numprocs);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myid);
double* mpi_buffer=malloc(sizeof(double)*1000000);
MPI_Buffer_attach(mpi_buffer,sizeof(double)*1000000);
//模拟开始
//if(myid==0)print();
starttime=clock();
for(int i=0;i<cycle_times;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<numprocs;j++)
{
if(j!=myid)
MPI_Bsend((ball_list+(N/numprocs)*myid),sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs,MPI_BYTE,j,i*10+myid,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
for(int j=0;j<numprocs;j++)
{
if(j!=myid)
{
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Recv((ball_list+(N/numprocs)*j),sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs,MPI_BYTE,j,i*10+j,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status);
}
}
for(int j=(N/numprocs)*myid;j<(N/numprocs)*(myid+1);j++)
{
compute_force(j);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
for(int j=(N/numprocs)*myid;j<(N/numprocs)*(myid+1);j++)
{
compute_velocities(j);
compute_positions(j);
}
//printf("\n");
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
endtime=clock();
printf("rank=%d time:%lf\n",myid,(double)(endtime-starttime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
//printf("id %d\n",myid);
if(myid!=0)
{
//printf("sid %d %d %d\n",myid,ball_list+(N/numprocs)*myid,sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs);
MPI_Send((ball_list+(N/numprocs)*myid),sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs,MPI_BYTE,0,myid,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
if(myid==0)
{
fp = fopen(filename[numprocs-1],"w");
for(int i=1;i<numprocs;i++)
{
MPI_Status status;
//printf("rid %d %d %d\n",myid,ball_list+(N/numprocs)*myid,sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs);
MPI_Recv((ball_list+(N/numprocs)*i),sizeof(ball)*N/numprocs,MPI_BYTE,i,i,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status);
}
print();
fclose(fp);
}
MPI_Finalize();
}
MPI并行计算模拟N体问题的更多相关文章
- 矩阵乘法的MPI并行计算
1.问题描述 矩阵乘法问题描述如下: 给定矩阵A和B,其中A是m*p大小矩阵,B是p*n大小的矩阵.求C = A*B. 求解这个问题最简单的算法是遍历A的行和B的列,求得C的相应元素,时间复杂度O(m ...
- 【并行计算】用MPI进行分布式内存编程(一)
通过上一篇关于并行计算准备部分的介绍,我们知道MPI(Message-Passing-Interface 消息传递接口)实现并行是进程级别的,通过通信在进程之间进行消息传递.MPI并不是一种新的开发语 ...
- 浅说CPU并行计算与GPU并行计算
最近在学一门课,叫做“C++与并行计算”.要用到多CPU(进程)并行的原理,实现语言是C++的MPI接口.联想到上学期用到CUDA C/C++来做并行计算,就对这两门语言做一个总结,分享下自己关于并行 ...
- 关于mpi的理论知识以及编写程序来实现数据积分中的梯形积分法。
几乎所有人的第一个程序是从“hello,world”程序开始学习的 #include "mpi.h" #include <stdio.h> int main(int a ...
- VMware workstation运维实践系列博客导航
第一章:VMware workstation虚拟化1.1 VMware workstation计算网络存储介绍1.2 VMware workstation其他功能特性介绍1.3 VMware work ...
- [.net 多线程] Interlocked实现CAS操作
Interlocked:为多个线程共享的变量提供原子操作. Interlocked.Increment(ref value) 数值加一(原子性操作) Interlocked.Decrement(ref ...
- 高性能集群(HPC
串行计算与并行计算1.串行计算串行计算是指在单个计算机(拥有单个中央独立单元) 上执行软件写操作.CPU 逐个使用一系列指令解决问题.为了加快处理速度,在原有的串行计算的基础上演变出并行计算2.并行计 ...
- 基于MPI的并行计算—矩阵向量乘
以前没接触过MPI编程,对并行计算也没什么了解.朋友的期末课程作业让我帮忙写一写,哎,实现结果很一般啊.最终也没完整完成任务,惭愧惭愧. 问题大概是利用MPI完成矩阵和向量相乘.输入:Am×n,Bn× ...
- MPI n 体问题
▶ <并行程序设计导论>第六章中讨论了 n 体问题,分别使用了 MPI,Pthreads,OpenMP 来进行实现,这里是 MPI 的代码,分为基本算法和简化算法(引力计算量为基本算法的一 ...
随机推荐
- Windows 10 Mobile 演示:插入耳机自动执行 APP
Windows Mobile 10 新特性:插入外部设备自动动作(如插入耳机执行 APP.打开小工具):另外可以找到最后一次使用设备地点和时间: http://www.tudou.com/progra ...
- C#调用webservice(一)
最近一直在搞网络编程,这篇是关于webservice的,准备写两篇例子这篇是实现手机号码归宿地查询,下篇准备写实现机票查询. 这个网站(http://www.webxml.com.cn/zh_cn/i ...
- Android 实现下拉刷新和上拉加载更多的RECYCLERVIEW和SCROLLVIEW
PullRefreshRecyclerView.java /** * 类说明:下拉刷新上拉加载更多的RecyclerView * Author: gaobaiq * Date: 2016/5/9 18 ...
- 阿里巴巴战略投资印度最大支付平台Paytm
腾讯科技讯 9月29日,据路透社报道,阿里巴巴和印度最大移动支付和商务平台Paytm今天发布联合声明,宣布阿里巴巴集团及其旗下金融子公司蚂蚁金服将向Paytm注入新资金.阿里称这是一项“战略性的”投资 ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(3)----Spring Cloud Netflix之深入理解Eureka
1. Eureka服务端的启动过程 1.1 入口类EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration类, public void start() { (new Thread(n ...
- Dapper优秀资料
dapper extensions (predicates) https://www.cnblogs.com/starluck/p/4542370.html
- js对象追加到数组里
描述:将一个点击事件得到的对象追加到数组里 做法:全局声明一个数组,,在对象的点击事件里将得到的对象追加到数组 change(a){ arr.push(a) console.log(arr) var ...
- JSON.stringify(),JSON.parse(),eval(string)
JSON.stringify()用于从一个对象解析出字符串 : var obj = {"name":"week","age":" ...
- POJ-1062 昂贵的聘礼 有限制的最短路
题目链接:https://cn.vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1062 题意 虽然是中文题,还是简单复述一下吧 我们想要酋长的女儿作为老婆.作为交换,酋长想要点钱. 酋长提出可以用其他 ...
- 洛谷 P1417 烹调方案 (01背包拓展)
一看到这道题就是01背包 但是我注意到价值和当前的时间有关. 没有想太多,直接写,0分 然后发现输入方式不对-- 改了之后只有25分 我知道wa是因为时间会影响价值,但不知道怎么做. 后来看了题解,发 ...