Objective-C 中的Runtime的使用
Runtime的使用
一直以来,OC被大家冠以动态语言的称谓,其实是因为OC中包含的runtime机制。Runtime 又叫运行时,是一套底层的 C 语言 API,其为 iOS 内部的核心之一,我们平时编写的 OC 代码,底层都是基于它来实现的。这一组API可以在Xcode的runtime.h文档中看到。
关于Runtime的深层次的东西,在很多其他开发者的博客中都有介绍。比如下面这些。
http://www.cnblogs.com/ioshe/ 这篇文章对与初识runtime做了很多基础性的介绍,并就runtime一些特性做了深入的讲解。
https://github.com/ChenYilong/iOSInterviewQuestions/blob/master/01《招聘一个靠谱的iOS》面试题参考答案/《招聘一个靠谱的iOS》面试题参考答案 (上).md 这里针对一些高质量的iOS面试题做的讲解。 其中包含了很多关于runtime 的知识。 看完之后大有裨益。
在本文中,不会很会很深入的进入到Runtime,而是就我们的开发过程中,如何使用runtime来简便的实现一些功能。主要包含以下方面的内容:
- runtime 获取类与对象的信息。
- 如何动态给对象添加成员变量。
- 如何动态给成员变量添加属性。
- 如何动态的给对象添加方法。
- categroy关联属性。
- 消息转发如何实现。
- 如何替换一个已有的方法的实现。
一、runtime 获取对象的信息。
通过简单的使用runtime可以获取到有关于类和对象的一些信息。
@interface GetClassAndIvarInfo () //属性
@property (nonatomic,copy) NSString* name;
@property (nonatomic,assign) int age;
@property (nonatomic,assign) BOOL isMan; @end @implementation GetClassAndIvarInfo{
//添加的变量
NSString* _adr;
} /**
获取类相关的信息
*/
- (void)getRegisteredClassInfo{
int bufferCount = ;
bufferCount = objc_getClassList(NULL, bufferCount);
//开辟一段空间 用于存储即将获取的类。
//类型的目的是: 告诉编译器我需要多大的空间
__unsafe_unretained Class *buffer = ( __unsafe_unretained Class *)malloc(sizeof(Class) * bufferCount);
objc_getClassList(buffer, bufferCount);
for (int i = ; i < bufferCount; i++) {
//查找本类是不是在里面
if(strcmp(class_getName([self class]), class_getName(buffer[i])) == ){
NSLog(@"%s", class_getName(buffer[i]));
}
}
} /**
获取所有的属性
*/
- (void)getAllProp{
unsigned int outCount = ;
NSLog(@"属性");
objc_property_t *props = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &outCount);
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"%s",property_getName(props[i]));
}
free(props);
} /**
获取所有的变量
*/
- (void)getAllIvar{
unsigned int outCount = ;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList( object_getClass(self),&outCount);
NSLog(@"变量");
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"%s",ivar_getName(ivars[i]));
}
free(ivars);
} /**
获取所有的方法
*/
- (void)getAllMethod{
unsigned int outCount = ;
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(object_getClass(self),&outCount);
NSLog(@"方法名");
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"%s",sel_getName(method_getName(methods[i])));
}
free(methods);
}
通过上面的这些方法。 我们可以方便的做一些有关方法属性的工作了。 比如,当对某个类进行归档的时候,如果能获取累类的所有属性,运用KVC进行赋值和取值。就能用很简短的代码实现整个类的归档动作。
除了上面的几个简单的方法之外,还有很多非常实用的runtime的API:
- OBJC_EXPORT id object_getIvar(id obj, Ivar ivar) //给变量设置值 KVC通过这个方式做
- OBJC_EXPORT void object_setIvar(id obj, Ivar ivar, id value) //获取成员变量的值 KVC
- OBJC_EXPORT Class objc_getMetaClass(const char *name) //获取该类的元类, 用于分析isa指针
- Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *class_copyProtocolList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount) //获取类遵循的协议中的方法列表
- OBJC_EXPORT Class objc_getFutureClass(const char *name) //toll-free bridging. 分析中,获取转换类的名字
二、runtime 给类添加成员变量
oc中,我们还可以给一个类动态的添加成员变量。 但是有一个前提是:被添加成员变量的类必须是动态创建的类。曾经有个人问我,对于已经编译的类,能否使用运行时添加成员变量, 答案是不行的。 好,下面的代码演示如何创建一个动态的类。
/*
1. 创建一个类。比如: Car,继承自NSObjest
2. 给这个类添加两个成员变量,分别是: 车身的颜色 bodyColor 和 车的最高速度 maxSpeed
3. 添加一些方法。以便可以访问两个成员变量。
3. 使用这个类创建对象,并对对象的成员属性进行访问。
*/
NSString *bodyColorName = @"bodyColor"; //类型为 UIcolor
NSString *maxSpeedName = @"maxSpeed"; // 类型为 NSString
NSString *className = @"Car";
Class Car = objc_getClass([className UTF8String]);
if (!Car)
{
Class superClass = [NSObject class];
Car = objc_allocateClassPair(superClass, [className UTF8String], );
//添加成员变量的代码必须放在这里
objc_registerClassPair(Car); //注册到运行时 }
这些代码演示添加成员变量
if(class_addIvar([Car class],[maxSpeedName UTF8String], sizeof(NSString *), log2(_Alignof(NSString *)), @encode(NSString *))){
NSLog( @"添加最高速度成功。");
}
if(class_addIvar([Car class],[bodyColorName UTF8String], sizeof(UIColor *), log2(_Alignof(UIColor *)), @encode(UIColor *))){
NSLog( @"添加车身速颜色成功。");
}
虽然每次添加成功之后,会打印相关的提示文字,何不验证一下呢?运用上一节的内容,打印一下car的所有的成员变量吧
id car = [[Car alloc]init];
unsigned int outCount = ;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList( object_getClass(car),&outCount); NSLog(@"变量");
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"%s",ivar_getName(ivars[i]));
}
free(ivars);
结果是:
2017-05-12 11:11:31.784 runtimeTest[3072:90675] 添加最高速度成功。
2017-05-12 11:11:31.784 runtimeTest[3072:90675] 添加车身速颜色成功。
2017-05-12 11:11:31.784 runtimeTest[3072:90675] maxSpeed
2017-05-12 11:11:31.784 runtimeTest[3072:90675] bodyColor
看来对了。
如何访问添加的变量? 通过runtime可以做到。
unsigned int outCount = ;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList( object_getClass(car),&outCount); NSLog(@"变量");
//runtime 赋值
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"%s",ivar_getName(ivars[i])); if(strcmp(ivar_getName(ivars[i]), [bodyColorName UTF8String])){
object_setIvar(car, ivars[i] , [UIColor blueColor]);
}
if(strcmp(ivar_getName(ivars[i]), [maxSpeedName UTF8String])){
object_setIvar(car, ivars[i] ,@"205.5 km/h");
}
} //runtime 取值
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
if(strcmp(ivar_getName(ivars[i]), [bodyColorName UTF8String])){ NSLog(@"车的颜色是%@", object_getIvar(car, ivars[i]));
}
if(strcmp(ivar_getName(ivars[i]), [maxSpeedName UTF8String])){
object_getIvar(car, ivars[i]);
NSLog(@"速度是%@",object_getIvar(car, ivars[i]));
}
}
free(ivars);
当然这样每次写起来实在是不怎么友好。 其实又个更简单的办法,利用KVC。
//利用KVC赋值 取值
[car setValue:[UIColor redColor] forKey:bodyColorName];
[car setValue:@"199.6 km/h" forKey:maxSpeedName];
NSLog(@"车的颜色是%@, 速度是%@",[car valueForKey:bodyColorName],[car valueForKey:maxSpeedName]);
三、如何动态的给成员变量添加属性。
刚才我创建了一个类,并给他添加了成员变量,并且做到了如何进行访问。 接下来我还希望能给这些成员变量添加添加的属性,以便编译器更好的帮我们做内存的管理等。比如nonatomic、copy之类的属性。
比如我们要为成员变量 maxSpeedName 添加 nonatomic、copy属性。看这些代码.
/* 添加成员变量的属性 */
//在添加之前,需要先编辑属性。 //这里给 maxSpeed成员变量添加属性。 这些属性的 encode 可以官网看到。
objc_property_attribute_t type = { "T", [[NSString stringWithFormat:@"@\"%@\"",NSStringFromClass([car class])] UTF8String] };
objc_property_attribute_t ownership = { "&", "N" };
objc_property_attribute_t ownership0 = { "C", "" }; // C = copy
objc_property_attribute_t ownership1 = { "N", "" }; // N = nonatomic
objc_property_attribute_t backingivar = { "V", [[NSString stringWithFormat:@"_%@", maxSpeedName] UTF8String] };
//这里需要注意的是: type和backingivar 必须放在头部和尾部 不然会有意想不到的后果
objc_property_attribute_t attrs[] = { type, ownership,ownership0,ownership1,backingivar};
//参数的描述分别是: 对象的类,属性的预设名字,属性数组,属性的个数
if(class_addProperty([car class], [maxSpeedName UTF8String], attrs, )){
NSLog(@"添加属性maxSpeedName 成功");
//打印下
unsigned int outCount = ;
NSLog(@"属性");
objc_property_t *props = class_copyPropertyList([car class], &outCount);
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"名字:%s",property_getName(props[i]));
//属性值
NSLog(@"属性值:%s",property_getAttributes(props[i]));
}
free(props);
添加属性之后,如果设置setter和getter方法,那么这些操作需要根据不同的属性进行设置,比如,storeWeak 就表示对带有weak属性的变量进行存储。
四、如何动态的给对象添加方法。
添加属性之后,我们最好还是能添加响应的个体和set方法,这是OC一贯的风格。
//添加get和set方法
class_addMethod([car class], NSSelectorFromString(maxSpeedName), (IMP)getter, "@@:");
class_addMethod([car class], NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"set%@:",[maxSpeedName capitalizedString]]), (IMP)setter, "v@:@");
outCount = ;
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(object_getClass(car),&outCount);
NSLog(@"方法名");
for (int i = ; i < outCount; i++) {
NSLog(@"%s",sel_getName(method_getName(methods[i])));
NSLog(@"%p",sel_getName(method_getImplementation(methods[i]))); }
free(methods); //调用
[self setMaxSpeed:@"300km/h" target:car];
NSLog(@"%@",[self maxSpeedWithTarget:car]);
- (void)setMaxSpeed:(NSString *)maxSpeed target:(NSObject*)car{
// 动态添加的方法,需要使用performselector调用。 因为在注册的类中,我们还没有设置改变类的变量布,也没有设置方法列表。
if([car respondsToSelector:NSSelectorFromString(@"setMaxspeed:" )]){
[car performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(@"setMaxspeed:") withObject:@"300 km/h"];
}
}
- (NSString *)maxSpeedWithTarget:(NSObject*)car{
//这里不仅判断有可能报错的
if([car respondsTOSelector:NSSelectorFromString:(@"maxspeed")]){
return [car performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(@"maxspeed")];
}
}
id getter(id self1, SEL _cmd1) {
NSString *key = NSStringFromSelector(_cmd1);
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self1 class], [key cStringUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]);
NSString *s = object_getIvar(self1, ivar);
return s;
}
void setter(id self1, SEL _cmd1, id newValue) {
//移除set
NSString *key = [NSStringFromSelector(_cmd1) stringByReplacingCharactersInRange:NSMakeRange(, ) withString:@""];
//首字母小写
NSString *head = [key substringWithRange:NSMakeRange(, )];
head = [head lowercaseString];
key = [key stringByReplacingCharactersInRange:NSMakeRange(, ) withString:head];
//移除后缀 ":"
key = [key stringByReplacingCharactersInRange:NSMakeRange(key.length - , ) withString:@""];
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self1 class], [key cStringUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]);
object_setIvar(self1, ivar, newValue);
}
对于 BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types), 几个参数相信很容易理解。 cls是要操作的类,name方法的名字,imp实现函数的指针,types是方法的类型。像文中的 "v@:@" 它是方法的类型,是一种缩写,有利于编译时提升效率。 我们还可以通过
- method_copyReturnType
method_copyArgumentType
这两个runtime API获取对应的方法type。 当然去苹果官网了解下相信会更明白。
这里就不详细介绍。
五、categroy关联属性。
刚开始接触的OC的时候,大部分都会有这么一个认知,category是不能添加属性的,只能添加成员变量,并在私有中使用。但是可以使用runtime来添加属性,使得属性可在 public中使用,这种操作也即是关联属性。
static const NSString* addProp = @"addName"; @implementation NSObject (ClassInfo) /**
设置get方法 @return value
*/
- (NSString *)name{ return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, [addProp UTF8String]);
} /**
设置set方法 @param name newVlaue
*/
- (void)setName:(NSString *)name{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, [addProp UTF8String], name, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); }
之后就可以直接调用这个变量了。这种方法用的非常多。不仅可以使得category增加属性,还特别的简洁明了。
[self setName:@"test000000"];
NSLog(@"%@",self.name);
六、消息发送/转发是如何实现。
我们知道。OC中所有的调用其实就是消息的传递。在使用OC方法的时候,实际上在runtime中是将放啊放转化成了C语言的 API :
id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL op, ...) //这里包含消息的发送者,方法名,方法的类型。举个简单的例子: 如果我们要执行一个方法:
[self setName:@"小明"]; ----> objc_msgSend(self,method_getName(method),method_getTypeEncoding(method))
除了 objc_msgSend 还有如下几个发送消息的API
- objc_msgSend(self,sel); // 发送着为本类的实例对象 如果返回的是常用的类型值的时候,调用
- objc_msgSendSuper(); // 发送着是 超类的实例对象的时候 返回常用类型 调用
- objc_msgSend_stret(); // 发送者是 本类的实例对象, 返回一个结构体 调用
- objc_msgSendSuper_stret(); // 发送者是 超类的实例对象, 返回一个结构体 调用
- objc_msgSend_fpret(); // 本类的实例对象, 返回一个浮点类型 调用
这些方法调用的流程是什么呢? 通过一副图片了解下。当一个msgSend执行的时候,经过以下几个步骤:
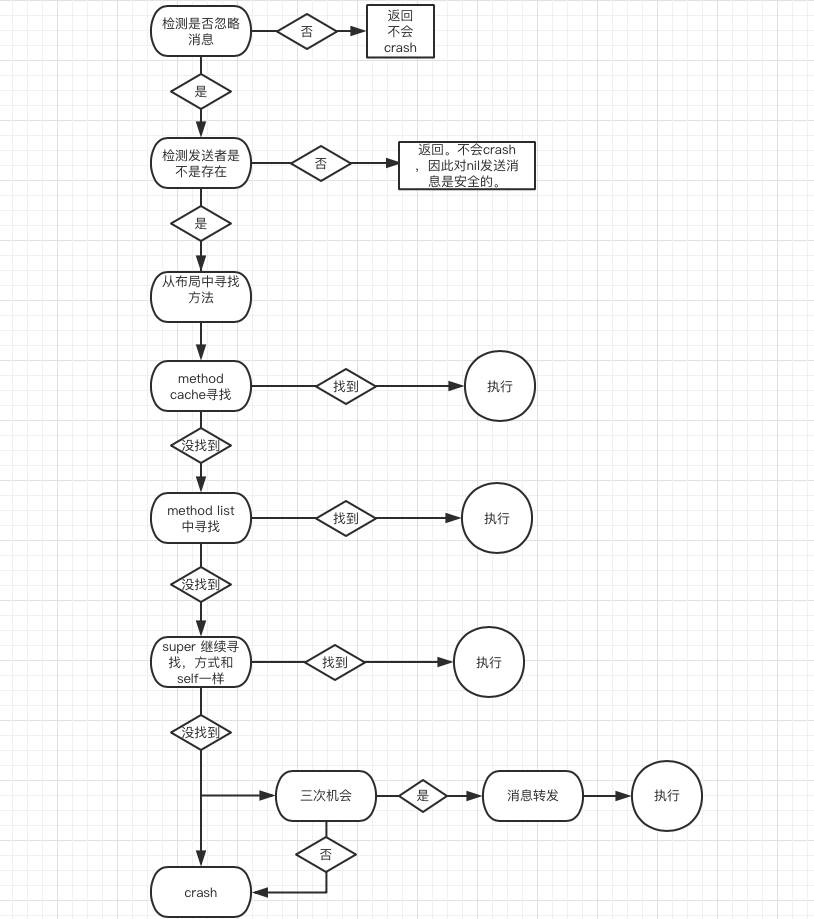
1.检测消息类型是否被忽略,mac上的retain等操作是被忽略的。
2.检测发送者是不是空指针,如果是,直接retrun ,这里不会产生Crash。
3.在mothod cache 中寻找对应的IMP,有则执行。没有进行下一步。
4.在mothod list 中寻找IMP ,有则执行,没有则下一步。 执行之后会将IMP放入cache,以便下次访问提升效率。
5.在父类中继续寻找。有则执行,没有则进行下一步/ 执行之后会将IMP放入cache,以便下次访问提升效率。
6.进入消息转发,或者crash 抛出异常。
在这里详细讲一下消息的转发。一张示意图。
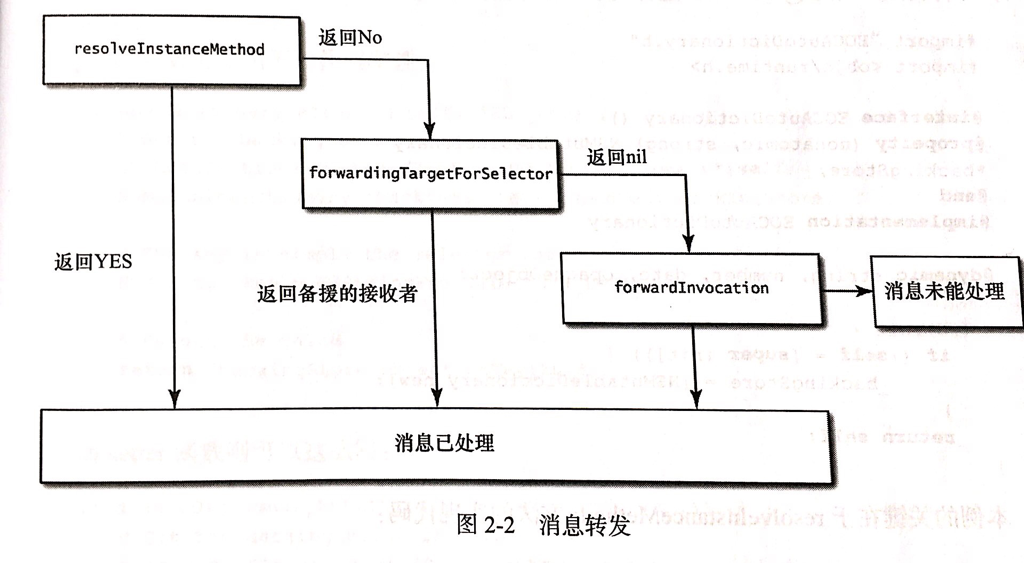
在上面的那副图中,消息转发的类型有两大类,一类是 对象方法,也就是我们说的 - 方法。另一类是 类方法,即 + 方法。-方法 有三次机会可以进行消息的转发,但是对于 + 方法,只有一次。
我们先看看 +方法。 如果想要转发+方法,只需要重写 + (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel 即可。如下
// runtime中的消息
- (void)testTwo{
//我们随便发送一个没有定义过的方法
[[self class] performSelector:@selector(classMethodTest)];
} + (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel{
//针对类方法
//第一种 使用自定义方法制作IMP 进行转发
class_addMethod(objc_getMetaClass([NSStringFromClass([self class]) UTF8String]), NSSelectorFromString(@"classMethodTest"), (IMP)classForwardFunc,"V@:" );
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel]; //第二种 使用制作block的方法得到IMP 进行转发
methodBlock ablock = ^{
NSLog(@"使用 block的 IMP 接到消息的转发");
};
IMP amethod = imp_implementationWithBlock(ablock);
class_addMethod(objc_getMetaClass([NSStringFromClass([self class]) UTF8String]), NSSelectorFromString(@"classMethodTest"), amethod,"V@:" );
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
} void classForwardFunc(id self1, SEL _cmd1) {
NSLog(@"类消息转发成功");
}
classMethodTest在self 中是没有定义的,如果我们强行调用,会提示警报,并且运行会crash. 如果重写 resolveClassMethod ,会先进入这个方法中,我们在这里进行 IMP的添加替换,注意这里操作的对象是self的元类, 因为在OC的内存布局中,元类中存放静态方法。如果这里不进行转发,接下来程序将回崩溃。
对于- 方法有所不同,它有三次机会进行消息的转发。第一种有点类似的,- 方法也有一个方法用于替换IMP的。
// runtime中的消息
- (void)testTwo{
//我们随便发送一个没有定义过的方法
[self performSelector:@selector(instanceMethodTest)];
// [[self class] performSelector:@selector(classMethodTest)];
} + (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
//针对实例方法 // 1.
class_addMethod([self class], NSSelectorFromString(@"instanceMethodTest"), (IMP)instanceForwardFunc,"V@:" );
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel]; // 2.
//同样可以使用block方法得到IMP 进行转发
methodBlock ablock = ^{
NSLog(@"使用 block的 IMP 接到消息的转发");
};
IMP amethod = imp_implementationWithBlock(ablock);
class_addMethod(objc_getMetaClass([NSStringFromClass([self class]) UTF8String]), NSSelectorFromString(@"instanceMethodTest"), amethod,"V@:" );
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
} void instanceForwardFunc(id self1, SEL _cmd1) {
NSLog(@"对象消息转发成功");
}
跟+方法很类似的。
第二种情况 ,替换消息发送者转发。 如果self 中没有对应的方法,除了替换IMP达到转发的目的,替换self也是可以的。这个动作将在下面的方法中实现。
// 这是消息发送者转发阶段
-(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
NSLog(@"FlyElephant-http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaofeixiang/");
NSLog(@"forwardingTargetForSelector");
if (aSelector == @selector(instanceMethodTest)) { //对象方法
return [[Other alloc] init];
}return self;
}
@interface Other : NSObject - (void)instanceMethodTest;
@end @implementation Other
- (void)instanceMethodTest{ NSLog(@"更换对象转发 对象 消息成功");
}
@end
如果前面两种情况我们都没有使用,苹果还提供了一种方式用语转发: 完整转发! 意思就是将IMP和self都替换掉。 看下面的代码。
//如果第二种情况还是没有转发 第三种情况 整体转发
- (NSMethodSignature*)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)selector
{ // 返回一个签名
// 只有包含了selector方法的对象的签名才是有效的
//用另一个实现了seletor的对象 创建si。
Another *another = [[Another alloc] init]; NSMethodSignature * si = [another methodSignatureForSelector:selector];
if(si){
return si;
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:selector];
} - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{ [anInvocation setSelector:anInvocation.selector];
//这里有点小技巧, 这里的 selector 是可以更改的,只需要确保another的method list包含这个selecor
// 比如:
[anInvocation setSelector:NSSelectorFromString(@"anotherFunc")]; [anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[Another alloc] init]]; }
@interface Another : NSObject
- (void)instanceMethodTest;
- (void)anotherFunc; @end @implementation Another
- (void)instanceMethodTest{
NSLog(@"更换对象转发 对象 消息成功 Another对象");
}
- (void)anotherFunc{
NSLog(@"消息转发 同时更改方法名字 Another对象");
} @end
如果将Another的所有的方法都使用这种方式转发,包括它的属性的set和get,那么就做到类似于继承的效果。 再者,对于多个类做到同样的效果, 就有了OC的多继承实现了。
七、如何替换一个已有的方法的实现。
替换一个已有的方法的实现,使用继承加上重写就可以做到,但是我今天来说下使用runtime做到不继承的情况下,实现方法实现的替换。也就是大名鼎鼎的 method swizzling的做法。
首先我们来看看metodSwizzling的原理是什么。
在runtime中,method 的结构体大概是这样的。
typedef struct objc_ method {
SEL method_name; 方法名 SEL
char *method_types; 方法类型, 包括了参数和返回值类型 通过method_getTypeEncoding获得
IMP method_imp; 方法实现的函数指针 IMP
};
在runtime中有几个API:
- IMP method_getImplementation(Method m) //获取某个方法的函数的实现
- IMP method_setImplementation(Method m, IMP imp) //设置某个方法的函数的实现
- void method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2) //改变某个方法的函数的实现
- Method class_getInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL name) //通过方法名获取 method
// runtime的方法交换
- (void)testThree{ Method methodA = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], NSSelectorFromString(@"funcA"));
Method methodB = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], NSSelectorFromString(@"funcB")); IMP impA = method_getImplementation(methodA);
IMP impB = method_getImplementation(methodB); method_setImplementation(methodA, impB);
method_setImplementation(methodB, impA); if([self funcA]){
NSLog(@"执行了 方法A");
} if([self funcB]){
NSLog(@"执行了 方法B");
}
} //定义方法A
- (BOOL)funcA{ NSLog( @"我是方法A");
return YES;
} //定义方法B
- (BOOL)funcB{ NSLog( @"我是方法B");
return YES;
}
打印:
2017-05-12 11:11:35.595 runtimeTest[3072:90675] 我是方法B
2017-05-12 11:11:35.595 runtimeTest[3072:90675] 执行了方法A
2017-05-12 11:11:35.595 runtimeTest[3072:90675] 我是方法A
2017-05-12 11:11:35.595 runtimeTest[3072:90675] 执行了方法B
方法被交换。
如果使用的 method_exchangeImplementations 也是等效的 ,代码如下:
Method methodA = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], NSSelectorFromString(@"funcA"));
Method methodB = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], NSSelectorFromString(@"funcB")); // IMP impA = method_getImplementation(methodA);
// IMP impB = method_getImplementation(methodB); // method_setImplementation(methodA, impB);
// method_setImplementation(methodB, impA); //使用 method_exchangeImplementations 等效
method_exchangeImplementations(methodA, methodB); if([self funcA]){
NSLog(@"执行了 方法A");
} if([self funcB]){
NSLog(@"执行了 方法B");
}
仔细想想,这个方式的作用非常有效,我们如果需要替换某个系统的方法的时候,盲目的重写可能带来无法预知的后果,并且维护起来也很困难。 使用方法替换可做到一次替换,一直有效,并可在局部进行。 正常情况下,我们会在
+(void)load{
//执行替换
}
替换方法,原因是,再不主动调用的情况下,load只会执行一次,并且不会收到超类或者类别的影响。 当然为了防止程序员手动调用,执行了过多次数的替换,可以把替换的代码使用 GCD 的oncetime_t中扩写。这样保证了绝对的一次调用。(偶数次的调用会回到没有替换的状态)。
以上的代码在https://github.com/lufubinGit/runtimeTest上
相关链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/ioshe/p/5489086.html
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20160121/15076.html
http://blog.sunnyxx.com/2015/09/13/class-ivar-layout/
Objective-C 中的Runtime的使用的更多相关文章
- 理解Objective C 中id
什么是id,与void *的区别 id在Objective C中是一个类型,一个complier所认可的Objective C类型,跟void *是不一样的,比如一个 id userName, 和vo ...
- 浅谈Objective—C中的面向对象特性
Objective-C世界中的面向对象程序设计 面向对象称程序设计可能是现在最常用的程序设计模式.如何开发实际的程序是存在两个派系的-- 面向对象语言--在过去的几十年中,很多的面向对象语言被发明出来 ...
- Objective-C中的runtime的原理和用法
一.runtime介绍 runtime翻译就是运行时,我们称为运行时机制.在OC中最重要的体现就是消息发送机制. 1)在C语言中,程序在编译过程中就决定调用哪个函数. 2)在OC中,编译的时候不会决定 ...
- Vugen 和controller 中的run-time setting区别
Vugen 和controller 中的run-time setting有什么不同?
- objective C中的字符串NSStirng常用操作
objective C中的字符串操作 在OC中创建字符串时,一般不使用C的方法,因为C将字符串作为字符数组,所以在操作时会有很多不方便的地方,在Cocoa中NSString集成的一些方法,可以很方便的 ...
- 抽取vs2010安装包中vc++ runtime
写于2015-3-21 16:59 由qq空间转过来,格式有点乱 之前遇到一个问题,c++\cli的程序部署在服务器上面,程序运行后没有反应就退出了,日志管理器中记录两个错误信息分别如下: ...
- Objective C中的ARC的修饰符的使用---- 学习笔记九
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> @interface Test : NSObject /** * 默认的就是__strong,这里只是做示范,实际使用时 ...
- Objective-C 中基于RunTime实现的反射
一.反射 反射,一般表现在字符串和Class转换,字符串和内部方法转换,字符串和属性的转换(取值和赋值). 二.Objective-C中的反射 OC的反射是基于其Runtime实现的. 以执行某个函数 ...
- Objective - C中属性和点语法的使用
一.属性 属性是Objective—C 2.0定义的语法,为实例变量提供了setter.getter方法的默认实现能在一定程度上简化程序代码,并且增强实例变量的访问安全性 ...
- 结合 category 工作原理分析 OC2.0 中的 runtime
绝大多数 iOS 开发者在学习 runtime 时都阅读过 runtime.h 文件中的这段代码: struct objc_class { Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILI ...
随机推荐
- JS实现弹性势能效果(弹力球效果[实现插件封装])
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 使用mingw制作dll文件
使用mingw制作dll文件 安装mingw 准备math.c文件 //math.c #include<stdio.h> int add(int a,int b){ return a+b; ...
- common daemon
http://zdsyouxiang.iteye.com/blog/1940202 http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-daemon/procrun.ht ...
- php实现 查找输入整数二进制中1的个数
php实现 查找输入整数二进制中1的个数 一.总结 一句话总结: 1.if($j&intval($num)){}的作用是什么? 1 <?php 2 while($num=trim(fge ...
- UVA 11367 - Full Tank? dijkstra+DP
传送门:http://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem&a ...
- LA 5902 - Movie collection 树状数组(Fenwick树)
看题传送门 题目大意:XXX喜欢看电影,他有好多好多的影碟,每个影碟都有个独立的编号.开始是从下往上影碟的顺序是n~1,他每次拿出影碟的时候,你需要输出压在该影碟上的有几个.(拿出后其他影碟顺序不变) ...
- 10.3、android输入系统_必备Linux编程知识_任意进程双向通信(scoketpair+binder)
3. 任意进程间通信(socketpair_binder) 进程每执行一次open打开文件,都会在内核中有一个file结构体表示它: 对每一个进程在内核中都会有一个task_struct表示进程,这个 ...
- 几款用jQuery写的h5小游戏
人人都说前端用来做游戏是一件很困难的事情,遇到这些js的逻辑性问题,是不是有点懵?其实,做完一款游戏之后就会发现,没啥难的地方,差不多都是换汤不换药,作为爱玩游戏的我,也总结收集了几款比较流行的小软件 ...
- Nginx content cache Nginx内容缓存
原文地址:http://nginx.com/resources/admin-guide/caching/ Nginx content cache Nginx内容缓存 This chapter desc ...
- 使用C#版本的gdal库打开hdf文件
作者:朱金灿 来源:http://blog.csdn.net/clever101 最近应同事的请求帮忙研究下使用C#版的gdal库读取hdf文件,今天算是有一点成果,特地做一些记录. 首先是编译C#版 ...
