OpenCV 之 霍夫变换
Hough 变换,对图像中直线的残缺部分、噪声、以及其它的共存结构不敏感,因此,具有很强的鲁棒性。
它常用来检测 直线和曲线 (圆形),识别图像中的几何形状,甚至可用来分割重叠或有部分遮挡的物体。
1 平面坐标和极坐标
1) 平面坐标的点 <=> 极坐标(平面化)的曲线
所谓极坐标平面化是指, 将 ρ-θ 的关系像 x-y 那样在平面内展开。
公式推导: x-y坐标中的点 (x0, y0), 代入极坐标 ρ-θ 中得
$\quad \begin{align*}\rho = x_{0}\: cos\theta + y_{0}\: sin\theta = \sqrt{x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}}\:\left (\frac{x_{0}}{\sqrt{x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}}}\: cos\theta + \frac{y_{0}}{\sqrt{x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}}}\:sin\theta\right )
= \sqrt{x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}} \; sin(\varphi_{0} +\theta ) \end{align*} $
其中, $sin\varphi_{0} = \frac{x_{0}}{\sqrt{x_{0}^{2}+y_{0}^{2}}}$
由上述公式可以明显的看出ρ与θ之间的函数关系。
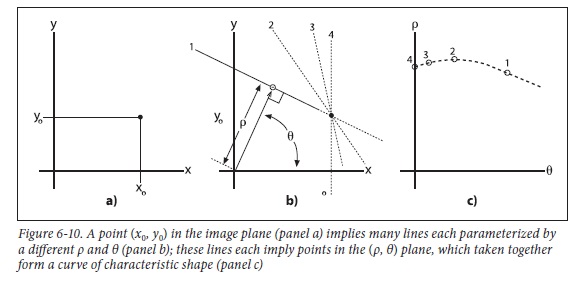
2) 极坐标的点 <=> 平面坐标的直线
公式推导: ρ-θ 极坐标中的点 (ρ0, θ0), 代入平面坐标 x-y 中得
$\quad y = ( -\tfrac{cos\theta_{0} }{sin\theta_{0}} )\:x + \tfrac{\rho_{0} }{sin\theta_{0}}$
由此可知, 极坐标中的一个定点(ρ0, θ0), 对应于平面坐标内的一条直线。若极坐标中有N条曲线相交于一点(如下左图), 则说明在平面坐标中, 该点对应的直线包含N条曲线对应的N个点, 也即这N个点组成了一条直线。


上面左图中, 是平面坐标中的三个点 (8,6), (4, 9), (12,3) 分别对应的三条曲线。
因此, 霍夫变换的目的是将平面坐标内的直线检测, 转换为极坐标内的交点检测, 显然寻找一个交点要比寻找直线(实际上是寻找许多点)容易得多了。
2 OpenCV中的函数
1) HoughLines
void cv::HoughLines(
InputArray image, // 输入图像
OutputArray lines, // 输出位直线数组
double rho, // 用像素个数表示的长度分辨率
double theta, // 用像素个数表示的角度分辨率
int threshold, // 累加器阈值 (只有大于该阈值的才有足够的投票)
double srn = , // 若 srn = stn = 0,则使用的是经典霍夫变换
double stn =,
double min_theta = , // 取值为 0 ~ max_theta
double max_theta = CV_PI // 取值为 min_theta ~ CV_PI
);
未完待续-源代码留待以后剖析:
/*
Here image is an input raster;
step is it's step; size characterizes it's ROI;
rho and theta are discretization steps (in pixels and radians correspondingly).
threshold is the minimum number of pixels in the feature for it
to be a candidate for line. lines is the output
array of (rho, theta) pairs. linesMax is the buffer size (number of pairs).
Functions return the actual number of found lines.
*/
static void
HoughLinesStandard( const Mat& img, float rho, float theta,
int threshold, std::vector<Vec2f>& lines, int linesMax,
double min_theta, double max_theta )
{
int i, j;
float irho = / rho; CV_Assert( img.type() == CV_8UC1 ); const uchar* image = img.ptr();
int step = (int)img.step;
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows; if (max_theta < min_theta ) {
CV_Error( CV_StsBadArg, "max_theta must be greater than min_theta" );
}
int numangle = cvRound((max_theta - min_theta) / theta);
int numrho = cvRound(((width + height) * + ) / rho); #if defined HAVE_IPP && !defined(HAVE_IPP_ICV_ONLY) && IPP_VERSION_X100 >= 810 && IPP_DISABLE_BLOCK
CV_IPP_CHECK()
{
IppiSize srcSize = { width, height };
IppPointPolar delta = { rho, theta };
IppPointPolar dstRoi[] = {{(Ipp32f) -(width + height), (Ipp32f) min_theta},{(Ipp32f) (width + height), (Ipp32f) max_theta}};
int bufferSize;
int nz = countNonZero(img);
int ipp_linesMax = std::min(linesMax, nz*numangle/threshold);
int linesCount = ;
lines.resize(ipp_linesMax);
IppStatus ok = ippiHoughLineGetSize_8u_C1R(srcSize, delta, ipp_linesMax, &bufferSize);
Ipp8u* buffer = ippsMalloc_8u(bufferSize);
if (ok >= ) ok = ippiHoughLine_Region_8u32f_C1R(image, step, srcSize, (IppPointPolar*) &lines[], dstRoi, ipp_linesMax, &linesCount, delta, threshold, buffer);
ippsFree(buffer);
if (ok >= )
{
lines.resize(linesCount);
CV_IMPL_ADD(CV_IMPL_IPP);
return;
}
lines.clear();
setIppErrorStatus();
}
#endif AutoBuffer<int> _accum((numangle+) * (numrho+));
std::vector<int> _sort_buf;
AutoBuffer<float> _tabSin(numangle);
AutoBuffer<float> _tabCos(numangle);
int *accum = _accum;
float *tabSin = _tabSin, *tabCos = _tabCos; memset( accum, , sizeof(accum[]) * (numangle+) * (numrho+) ); float ang = static_cast<float>(min_theta);
for(int n = ; n < numangle; ang += theta, n++ )
{
tabSin[n] = (float)(sin((double)ang) * irho);
tabCos[n] = (float)(cos((double)ang) * irho);
} // stage 1. fill accumulator
for( i = ; i < height; i++ )
for( j = ; j < width; j++ )
{
if( image[i * step + j] != )
for(int n = ; n < numangle; n++ )
{
int r = cvRound( j * tabCos[n] + i * tabSin[n] );
r += (numrho - ) / ;
accum[(n+) * (numrho+) + r+]++;
}
} // stage 2. find local maximums
for(int r = ; r < numrho; r++ )
for(int n = ; n < numangle; n++ )
{
int base = (n+) * (numrho+) + r+;
if( accum[base] > threshold &&
accum[base] > accum[base - ] && accum[base] >= accum[base + ] &&
accum[base] > accum[base - numrho - ] && accum[base] >= accum[base + numrho + ] )
_sort_buf.push_back(base);
} // stage 3. sort the detected lines by accumulator value
std::sort(_sort_buf.begin(), _sort_buf.end(), hough_cmp_gt(accum)); // stage 4. store the first min(total,linesMax) lines to the output buffer
linesMax = std::min(linesMax, (int)_sort_buf.size());
double scale = ./(numrho+);
for( i = ; i < linesMax; i++ )
{
LinePolar line;
int idx = _sort_buf[i];
int n = cvFloor(idx*scale) - ;
int r = idx - (n+)*(numrho+) - ;
line.rho = (r - (numrho - )*0.5f) * rho;
line.angle = static_cast<float>(min_theta) + n * theta;
lines.push_back(Vec2f(line.rho, line.angle));
}
}
2) HoughLinesP
void cv::HoughLinesP ( InputArray image, OutputArray lines,
double rho, double theta, int threshold,
double minLineLength=, double maxLineGap= )
/*
1) image
8-bit, single-channel binary source image. The image may be modified by the function.
2) lines
Output vector of lines. Each line is represented by a 4-element vector x1, y1, x2,y2), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the ending points of each detected line segment.
3) rho
Distance resolution of the accumulator in pixels.
4) theta
Angle resolution of the accumulator in radians.
5) threshold
Accumulator threshold parameter. Only those lines are returned that get enough votes(>threshold).
6) minLineLength
Minimum line length. Line segments shorter than that are rejected.
7) MaxLineGap
Maximum allowed gap between points on the same line to link them. */
Progressive Probabilistic Hough Transform Algorithm Outline:
/* 摘自文献 J. Matas, Robust Detection of Lines Using the Progressive Probabilistic Hough Transform
1. Check the input image; if it is empty then finish.
2. Update the accumulator with a single pixel randomly selected from the input image.
3. Remove the selected pixel from input image.
4. Check if the highest peak in the accumulator that was modified by the new pixel is higher than threshold thr(N). If not then goto 1.
5. Look along a corridor specified by the peak in the accumulator, and find the longest segment that either is continuous
or exhibits a gap not exceeding a given threshold.
6. Remove the pixels in the segment from input image.
7. “Unvote” from the accumulator all the pixels from the line that have previously voted.
8. If the line segment is longer than the minimum length add it into the output list.
9. Goto 1. */
3) HoughCircles
void cv::HoughCircles ( InputArray image, OutputArray circles,
int method, double dp, double minDist,
double param1 = , double param2 = ,
int minRadius = , int maxRadius = )
/*
1) image
8-bit, single-channel, grayscale input image.
2) circles
Output vector of found circles. Each vector is encoded as a 3-element floating-point vector (x, y, radius).
3) method
Detection method, see cv::HoughModes. Currently, the only implemented method is HOUGH_GRADIENT
4) dp
Inverse ratio of the accumulator resolution to the image resolution.
For example, if dp=1 , the accumulator has the same resolution as the input image.
If dp=2 , the accumulator has half as big width and height.
5) minDist
Minimum distance between the centers of the detected circles.
If the parameter is too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one.
If it is too large, some circles may be missed.
6) param1
First method-specific parameter.
In case of CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the higher threshold of the two passed to the Canny edge detector (the lower one is twice smaller).
7) param2
Second method-specific parameter.
In case of CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT , it is the accumulator threshold for the circle centers at the detection stage.
The smaller it is, the more false circles may be detected. Circles, corresponding to the larger accumulator values, will be returned first.
8) minRadius
Minimum circle radius.
9) maxRadius
Maximum circle radius. */
3 代码示例
在进行霍夫变换之前,首先要对图像进行"边缘检测"的预处理。
3.1 检测直线 (带滑动条)
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp" using namespace cv;
using namespace std; // 全局变量
Mat src, src_gray, edges;
Mat standard_hough, probabilistic_hough;
int min_threshold = ;
int max_trackbar = ; const char* probabilistic_name = "Probabilistic Hough Lines"; int p_trackbar = max_trackbar; void Probabilistic_Hough( int, void* ); // 函数声明
int main( int, char** argv )
{
// 读图
src = imread("line_demo.png");
if(src.empty())
return -; // 灰度图
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY); // cany 边缘检测
Canny(src_gray, edges, , , ); // 阈值滑动条
char thresh_label[];
sprintf( thresh_label, "Thres: %d + input", min_threshold ); namedWindow(probabilistic_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
createTrackbar(thresh_label, probabilistic_name, &p_trackbar, max_trackbar, Probabilistic_Hough); // 回调函数
Probabilistic_Hough(, ); waitKey();
} void Probabilistic_Hough(int, void*)
{
vector<Vec4i> p_lines;
// gray -> rgb
cvtColor(edges, probabilistic_hough, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
// Probabilistic Hough Transform
HoughLinesP(edges, p_lines, , CV_PI/, min_threshold + p_trackbar, , );
// 显示
for( size_t i = ; i < p_lines.size(); i++ ) {
Vec4i l = p_lines[i];
line(probabilistic_hough, Point(l[], l[]), Point(l[], l[]), Scalar(,,), , LINE_AA);
}
imshow( probabilistic_name, probabilistic_hough );
}
3.2 检测圆形 (不带滑动条)
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp> using namespace cv;
using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 读图
Mat src, src_gray;
src = imread("circle_demo.png");
if(src.empty())
return -; // 灰度图 + 高斯滤波
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
GaussianBlur(src_gray, src_gray, Size(, ), , ); // 画圆
vector<Vec3f> circles;
HoughCircles(src_gray, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT, , src_gray.rows/, , );
for(size_t i=; i<circles.size(); ++i)
{
Point center(cvRound(circles[i][]), cvRound(circles[i][]));
int radius = cvRound(circles[i][]);
circle(src, center, , Scalar(,,), -, , ); // 圆心
circle(src, center, radius, Scalar(,,), , , ); // 圆形
} // 窗体
namedWindow("circles", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("circles", src); waitKey();
}
参考资料:
<图像处理、分析与机器视觉> 第4版, 6.2.6 Hough 变换
OpenCV Tutorials / Image Processing (imgproc module) / Hough Line Transform
OpenCV Tutorials / Image Processing (imgproc module) / Hough Circle Transform
OpenCV 之 霍夫变换的更多相关文章
- 【OpenCV新手教程第14】OpenCVHough变换:霍夫变换线,霍夫变换圆汇编
本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品.转载请注明出处. 文章链接:http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/26977557 作者:毛星云(浅墨) ...
- 【OpenCV入门教程之十四】OpenCV霍夫变换:霍夫线变换,霍夫圆变换合辑
http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/26977557 本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处. 文章链接:http://blog ...
- 学习 opencv---(13)opencv霍夫变换:霍夫线变换,霍夫圆变换
在本篇文章中,我们将一起学习opencv中霍夫变换相关的知识点,以及了解opencv中实现霍夫变换的HoughLines,HoughLinesP函数的使用方法,实现霍夫圆变换的HoughCircles ...
- 【OpenCV新手教程之十四】OpenCV霍夫变换:霍夫线变换,霍夫圆变换合辑
本系列文章由@浅墨_毛星云 出品,转载请注明出处. 文章链接:http://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/26977557 作者:毛星云(浅墨) ...
- OpenCV-Python教程(9、使用霍夫变换检测直线)
相比C++而言,Python适合做原型.本系列的文章介绍如何在Python中用OpenCV图形库,以及与C++调用相应OpenCV函数的不同之处.这篇文章介绍在Python中使用OpenCV的霍夫变换 ...
- opencv-霍夫直线变换与圆变换
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/26977557 一.引言 在图像处理和计算机视觉领域中,如何从当前的图像中提取所需要的特征信 ...
- OpenCV探索之路(七):霍夫变换
我们如何在图像中快速识别出其中的圆和直线?一个非常有效的方法就是霍夫变换,它是图像中识别各种几何形状的基本算法之一. 霍夫线变换 霍夫线变换是一种在图像中寻找直线的方法.OpenCV中支持三种霍夫线变 ...
- C++ Opencv HoughLines()用霍夫变换在二元图像中寻线
一.霍夫变换简介 参考http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/hough.htm 二.HoughLines()函数详解 该函数接受的输入矩阵只能是8位单通道的二 ...
- opencv 霍夫变换 实现图片旋转角度计算
在OCR实际开发中,证件照采集角度有很大的偏差,需要将图片进行旋转校正, 效果图: 在应用中发现应该加入高斯模糊,可以极大减少误差线条. 知道线条后 通过求斜率 得旋转角度 .(x1-x2)/(y1- ...
随机推荐
- es2015(es6)学习总结
1.三种声明方式 var:它是variable的简写,可以理解成变量的意思. let:它在英文中是“让”的意思,也可以理解为一种声明的意思. const:它在英文中也是常量的意思,在ES6也是用来声明 ...
- cuda8.0 百度云盘分享
因为深度学习的需要,装了ubuntu16系统,同时也装了cuda,在下载cuda的时候发现教育网下载的速度不忍直视,故换了更快的网下载,结果发现10兆宽带下载速度依然很慢,不过总算还是下载了,故把千辛 ...
- Loj#6432「PKUSC2018」真实排名(二分查找+组合数)
题面 Loj 题解 普通的暴力是直接枚举改或者不改,最后在判断最后对哪些点有贡献. 而这种方法是很难优化的.所以考虑在排序之后线性处理.首先先假设没有重复的元素 struct Node { int p ...
- CDH-hive支持insert、update、delete操作
开发要求hive支持update操作,搞张临时表测试下,报错如下: 配置hive-site.xml CDH进入hive配置页,选择高级,找到hive-site.xml的HIve客户端高级配置段代码段, ...
- python队列、线程、进程、协程(转)
原文地址: http://www.cnblogs.com/wangqiaomei/p/5682669.html 一.queue 二.线程 #基本使用 #线程锁 #自定义线程池 #生产者消费者模型(队列 ...
- JZYZOJ1390【noi2001】炮兵阵地 状压DP
http://172.20.6.3/Problem_Show.asp?id=1390 需要储存该行和上一行两个状态.通过观察规则可以发现条件允许的状态很少(相邻两个至少空两格),据此可以减少状态数量, ...
- [Lydsy1704月赛] 最小公倍佩尔数
4833: [Lydsy1704月赛]最小公倍佩尔数 Time Limit: 8 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 202 Solved: 99[Submit][St ...
- RMI(Remote Method Invocation ) 概念恢复
1.RMI是远程方法调用的简称,像其名称暗示的那样,它能够帮助我们查找并执行远程对象,通俗的说,远程调用就像一个class放在A机器上,然后在B机器中调用这个class的方法. 2.EMI术语 在研究 ...
- 浅谈分布式CAP定理
互联网发展到现在,由于数据量大.操作并发高等问题,大部分网站项目都采用分布式的架构.而分布式系统最大的特点数据分散,在不同网络节点在某些时刻(数据未同步完,数据丢失),数据会不一致. 在2000年,E ...
- SpringBoot使用Gradle构建war包
Spring Boot默认将应用打包成可执行的jar包.有时候需要打包成war包部署在tomcat等容器.下面简单介绍下打包的步骤. 一.修改gradle.build文件 1.1 添加如下配置 app ...
