Redis配置文件(1)units/includes/GENERAL/SECURITY/LIMITS
redis.conf文件
在Linux进行文件的查看!
units单位:
# Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify
# it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth:
#
# 1k => bytes
# 1kb => bytes
# 1m => bytes
# 1mb => * bytes
# 1g => bytes
# 1gb => ** bytes
#
# units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same.
################################## INCLUDES ##############################
# Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you
# have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need
# to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include
# other files, so use this wisely.
#
# Notice option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE"
# from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed
# line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes
# at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runti me.
#
# If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration
# options, it is better to use include as the last line.
#
# include /path/to/local.conf
GENERAL
# If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup
# and removes it at exit.
#
# When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is
# specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid fi le
# is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid".
#
# Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it
# nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally.
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
# By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
# Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemoniz ed.
daemonize yes
# Accept connections on the specified port, default is (IANA #).
# If port is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket.
port 6379
# TCP listen() backlog.
#
# In high requests-per-second environments you need an high backlog in order
# to avoid slow clients connections issues. Note that the Linux kernel
# will silently truncate it to the value of /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn so
# make sure to raise both the value of somaxconn and tcp_max_syn_backlog
# in order to get the desired effect.
tcp-backlog 511 tcp-backlog
设置tcp的backlog,backlog其实是一个连接队列,backlog队列总和=未完成三次握手队列 + 已经完成三次握手队列。
在高并发环境下你需要一个高backlog值来避免慢客户端连接问题。注意Linux内核会将这个值减小到
/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn的值,所以需要确认增大somaxconn和tcp_max_syn_backlog两个值
来达到想要的效果
# Close the connection after a client is idle for N seconds ( to disable)
timeout
# IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES
# JUST COMMENT THE FOLLOWING LINE.
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
bind 127.0.0.1
# On Linux, the specified value (in seconds) is the period used to send ACKs.
# Note that to close the connection the double of the time is needed.
# On other kernels the period depends on the kernel configuration.
#
# A reasonable value for this option is seconds, which is the new
# Redis default starting with Redis 3.2..
tcp-keepalive 300
单位为秒,如果设置为0,则不会进行Keepalive检测,建议设置成60
# Specify the server verbosity level.
# This can be one of:
# debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
loglevel notice
日志级别
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
# Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
# output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
logfile ""
日志的名字
# Set the number of databases. The default database is DB , you can select
# a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT <dbid> where
# dbid is a number between and 'databases'-
databases 16
系统默认的库16个
默认使用0库
# To enable logging to the system logger, just set 'syslog-enabled' to yes,
# and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs.
# syslog-enabled no 是否把日志输出到syslog中
系统日志默认时关着
# Specify the syslog identity.
# syslog-ident redis 指定syslog里的日志标志
设备以redis开头
# Specify the syslog facility. Must be USER or between LOCAL0-LOCAL7.
# syslog-facility local0
指定syslog设备,值可以是USER或LOCAL0-LOCAL7
默认使用local0
SECURITY安全
访问密码的查看、设置和取消
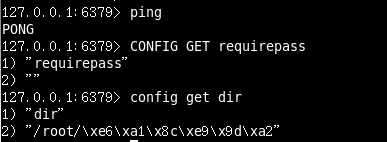
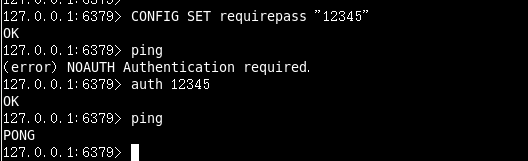
设置密码:
config set requirepass " "
;
改为空的时候默认没有密码!
################################## SECURITY ################################### # Require clients to issue AUTH <PASSWORD> before processing any other
# commands. This might be useful in environments in which you do not trust
# others with access to the host running redis-server.
要求必须auth + password 在任何命令之前
设置redis同时可以与多少个客户端进行连接。默认情况下为10000个客户端。当你
无法设置进程文件句柄限制时,redis会设置为当前的文件句柄限制值减去32,因为redis会为自
身内部处理逻辑留一些句柄出来。如果达到了此限制,redis则会拒绝新的连接请求,并且向这
些连接请求方发出“max number of clients reached”以作回应。
maxmemory
设置redis可以使用的内存量。一旦到达内存使用上限,redis将会试图移除内部数据,移除规则可以通过maxmemory-policy来指定。
如果redis无法根据移除规则来移除内存中的数据,或者设置了“不允许移除”,
那么redis则会针对那些需要申请内存的指令返回错误信息,比如SET、LPUSH等。
但是对于无内存申请的指令,仍然会正常响应,比如GET等。如果你的redis是主redis(说明你的redis有从redis),
那么在设置内存使用上限时,需要在系统中留出一些内存空间给同步队列缓存,只有在你设置的是“不移除”的情况下,才不用考虑这个因素
()volatile-lru:使用LRU算法移除key,只对设置了过期时间的键
()allkeys-lru:使用LRU算法移除key
()volatile-random:在过期集合中移除随机的key,只对设置了过期时间的键
()allkeys-random:移除随机的key
()volatile-ttl:移除那些TTL值最小的key,即那些最近要过期的key
()noeviction:不进行移除。针对写操作,只是返回错误信息
LRU 算法或者 TTL 算法都是不是很精确算法,而是 个近似算法。

maxmemory-samples
设置样本数量,LRU算法和最小TTL算法都并非是精确的算法,而是估算值,所以你可以设置样本的大小,
redis默认会检查这么多个key并选择其中LRU的那个
Redis配置文件(1)units/includes/GENERAL/SECURITY/LIMITS的更多相关文章
- redis深入学习(二)-----redis配置文件、持久化
redis配置文件 地址 units单位 a 配置大小单位,开头定义了一些基本的度量单位,只支持bytes,不支持bitb 对大小写不敏感 GENERAL通用 1.daemonize 2.pidf ...
- linux资源使用配置文件 /etc/security/limits.conf和ulimit
limits.conf文件实际上是linux PAM中pam_limits.so的配置文件,而且只针对于单个会话. limits.conf的格式如下: <domain> <type& ...
- Linux资源使用配置文件 /etc/security/limits.conf
Linux资源使用配置文件 /etc/security/limits.conf http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-05/59489.htm Linux就这个范儿P5 ...
- /etc/security/limits.conf配置文件详解
这个文件主要是用来限制用户对系统资源的使用.是/lib64/security/pam_limits.so模块对应的/etc/serurity/pam_limits的配置文件. # /etc/secur ...
- Redis 配置文件详解
# Redis 配置文件 # 当配置中需要配置内存大小时,可以使用 1k, 5GB, 4M 等类似的格式,其转换方式如下(不区分大小写)## 1k => 1000 bytes# 1kb => ...
- 4 Redis 配置文件介绍
2016-12-22 14:28:39 该系列文章链接NoSQL 数据库简介Redis的安装及及一些杂项基础知识Redis 的常用五大数据类型(key,string,hash,list,set,zse ...
- windows下redis 配置文件参数说明
1.先看redis.windows.conf 文件 # Redis configuration file example # Note on units: when memory size is ne ...
- Redis配置文件redis.conf详解
一.Redis配置文件redis.conf详解 # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specifiy # it ...
- redis配置文件redis.conf翻译、解释以及常用注意事项(持续更新中...)
# Redis configuration file example. #Redis 配置文件的示例 #如何利用配置文件启动Redis # Note that in order to read the ...
随机推荐
- [转]How to use an Area in ASP.NET Core
本文转自:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/36535511/how-to-use-an-area-in-asp-net-core Q: How does one ...
- golang学习之go简单博客应用
先说说golang的语法吧,个人觉得有以下特点: 简洁,不管是变量.方法声明,还是代码编写,均十分简洁,效率也比较高 非纯粹面向对象,但是go的struct类似c的struct,go的结构体还可以进行 ...
- 一:HttpClient知识整理
一:httpclient 简介 HttpClient 是 Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,可以用来提供高效的.最新的.功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支 ...
- tomcat启动编码等部署遇到问题
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明文章链接.https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoanzi123/article/details/58254318 2017-02-27 21:01 ...
- 流畅的python和cookbook学习笔记(六)
1.同时迭代多个序列(zip(函数)) 使用zip()函数可以同时迭代多个序列. >>> X = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] >>> Y = [121, ...
- 一、python简单爬取静态网页
一.简单爬虫框架 简单爬虫框架由四个部分组成:URL管理器.网页下载器.网页解析器.调度器,还有应用这一部分,应用主要是NLP配合相关业务. 它的基本逻辑是这样的:给定一个要访问的URL,获取这个ht ...
- PL/SQL: numeric or value error: character to number conversion error
在最简单的plsql块编程中出现这个错误,是因为 DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('the x is '+x);这里面不能用“+”,而是要用“||” DECLARE x number; ; ...
- ImportError: No module named bs4错误解决方法
前言:毕业论文打算用Python做爬虫爬一些数据,最近开始入门Python: 在学习的时候遇到一个问题,按照看的文章安装了Python,也配置了相应的环境(使用window系统),使用pycharm编 ...
- org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
1. 问题描述 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'xxxx ...
- bootstrap-datepicker汉化
bootstrap-datepicker 是一个非常优秀的时间选择插件,默认是英文显示日期的,通过下面几个小修改让其支持默认中文 1.首先将 bootstrap-datepicker.js 另存为 u ...
