What is Double Spending & How Does Bitcoin Handle It?
https://coinsutra.com/bitcoin-double-spending/
Bitcoin is gaining rapid popularity and adoption across the globe. It is re-defining the way we use money by being the world’s first fully functional digital currency.
You might be surprised to know that even before Bitcoin, there were attempts to create a sustainable digital monetary system. But all those attempts failed because an obvious problem with digital money is that transactions can be copied and spent twice.
Let me simply the concept…
Bitcoin has been able to survive and thrive because it solves the “double spending”problem.
What Does Double Spending Mean?
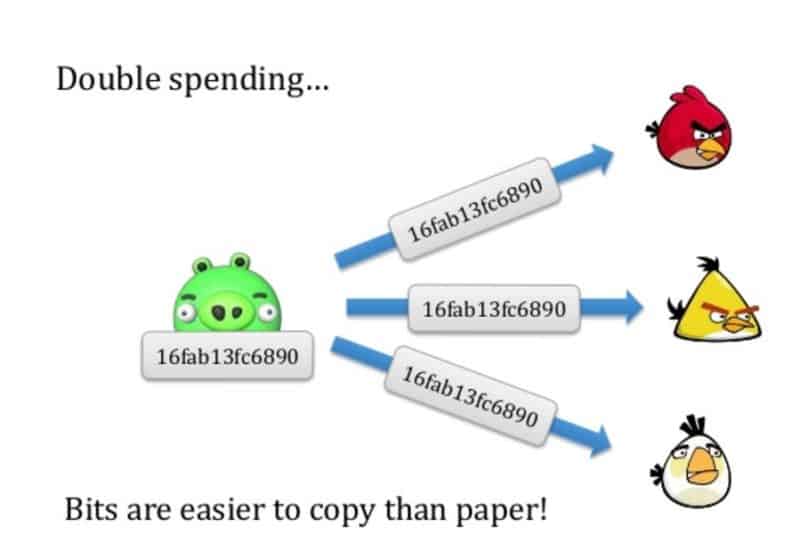
Double spending means spending the same money twice.
Let’s consider this example:
You go to Starbucks and order a cappuccino worth $10. You pay in cash. Now that $10 in cash is in the cash vault of Starbucks. By all means, you simply cannot spend the same $10 somewhere else to make another purchase.
Unless you steal it…!!!
As you paid with your $10 bill, the service provider at Starbucks instantly confirmed that you have paid, and you received your coffee in exchange for the money.
But Bitcoin is digital money, not physical cash. Hence, Bitcoin transactions have a possibility of being copied and rebroadcasted. This opens up the possibility that the same BTC could be spent twice by its owner.
How?
In our Starbucks example, you paid cash, so the payment was confirmed and verified instantly by another human. But with digital currency like BTC, if this verification mechanism is missing, it can lead to double spending.
Anyone can just copy that digital money and pay somewhere else.
And here is where the unique invention lies…
Bitcoin, although being digital currency, solves the problem of being copied and getting spent twice.
How Bitcoin Handles The Double Spending Problem

Bitcoin manages the double spending problem by implementing a confirmation mechanism and maintaining a universal ledger (called “blockchain”), similar to the traditional cash monetary system.
Bitcoin’s blockchain maintains a chronologically-ordered, time-stamped transaction ledger from the very start of its operation in 2009.
Every 10 mins, a block (i.e. a group of transactions) is added to the ledger. And all the nodes on the Bitcoin network keep a copy of this global ledger (the blockchain).
Let’s see how the Bitcoin network prevents double spending:
Let’s suppose you have 1 BTC which you try to spend twice.
You made the 1 BTC transaction to a merchant. Now, you again sign and send the same 1 BTC on another Bitcoin address to try and trick the merchant.
Both transactions go into the unconfirmed pool of transactions. But only your first transaction got confirmations and was verified by miners in the next block. Your second transaction could not get enough confirmations because the miners judged it as invalid, so it was pulled from the network.
But wait… what if both the transactions are taken simultaneously by the miners?
When miners pull the transactions simultaneously from the pool, then whichever transaction gets the maximum number of confirmations from the network will be included in the blockchain, and the other one will be discarded.
You might say that this is unfair for the merchant, as the transaction might fail in getting confirmations. Yeah, this can happen!!!
That’s why it is recommended for merchants to wait for a minimum of 6 confirmations.
Here, “6 confirmations” simply means that after a transaction was added to the blockchain, 6 more blocks containing several other transactions were added after it.
“Confirmations” are nothing but more blocks containing more transactions being added to the blockchain. Each transaction and blocks are mathematically related to the previous one.
All these confirmations and transactions are time-stamped on the blockchain, making them irreversible and impossible to tamper with.
So if a merchant receives his/her minimum number of confirmations, he/she can be positive it was not a double spend by the sender.
Why can the merchant be assured?
Because to be able to double spend that coin, the sender has to go back and reverse all transactions in the 6 blocks that have been added after their transaction, which is computationally impossible.
How Double-Spend Attacks Can Happen
- Attack 51%
If somehow an attacker captures 51% of the hash power of the network, double spending can happen.
“Hash power” means the computational power which verifies transactions and blocks. If an attacker has this control, he/she can reverse any transaction and make a private blockchain which everyone will consider as real.
But so far, no such attack has happened because controlling 51% of the network is highly cost intensive. It depends on the present difficulty of mining, the hardware price, and the electricity cost, all of which is infeasible to acquire.
- Race Attack
When an attacker sends the same coin in rapid succession to two different addresses, the obvious outcome is that only one of them will get included.
Now, if you as a merchant don’t wait for confirmations of payment, then in a case like this, there’s a 50% chance you got the double spent coin (and you won’t receive that money).
Let’s see how…
Your customer can trick you if he/she sends the same coins again to his/her address.
Once the customer does both transactions, both transactions go to an unconfirmed pool of transactions. Whichever transaction gets verified first and gets 6 confirmations will be accepted, and the other will be discarded.
As a merchant, you might get the 6 confirmations first, but if the attacker gets the confirmations first, then you won’t receive your funds. That’s why it is said to wait for a minimum of 6 confirmations.
So far, in the 8-year history of Bitcoin, no such attack has been successful. The Bitcoin mechanism of maintaining a universal transaction ledger based on confirmations has yet to be tricked.
What is Double Spending & How Does Bitcoin Handle It?的更多相关文章
- Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System Satoshi Nakamoto October 31, 2008 Abstract A purely p ...
- How the Bitcoin protocol actually works
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&a ...
- 比特币_Bitcoin 简介
2008-11 Satoshi Nakamoto Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System http://p2pbucks.com/?p=99 ...
- p3.BTC-协议
数字货币是文件,难伪造,但是容易复制,不像实体货币,花出去就没了,数字货币存在double spending attack,双花攻击. 去中心化的货币,需要解决两个问题: 1.货币的发行 挖矿 2.交 ...
- Blockchain technology and Application
BTC-密码学原理 比特币本质:crypto currency[加密货币] 比特币用到的两个功能: 1.哈希 crypto graphic hash function 2.签名(非对称加密) 哈希cr ...
- Block Chain Learning Notes
区块链是什么 区块链技术是由比特币创造的,本文也将从比特币开始进行引导,一步一步告诉大家什么是区块链.如果你想立马知道区块链是什么,也可以直接转到文章末尾的区块链定义. 区块链,可能是当下最有前景又充 ...
- [No00009E]几种常见的命名规则
变量命名规则 必须遵循的命名规则 1. 变量名首字母必须为字母(a-z A-Z),下划线(_),或者美元符号($)开始php编程中所有变量必须以$开始. 2. 变量名只能是字母(a-z A ...
- effectiveC++ 内存管理 学习笔记
1.尽量使用初始化列表而不要再构造函数里赋值,初始化顺序和声明的顺序一致,一些类型如const,引用等,必须使用初始化.对于非内部数据类型成员对象应当采用初始化表,以获取更高的效率.example:B ...
- Delphi编程建议遵守的规范2---命名规范
1.1.形参命名建议 所有形参的名称都应当表达出它的用途.如果合适的话,形参的名称最好以字母a 为前缀,例如: procedure SomeProc(aUserName:string; aUserAg ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ4816】【SDOI2017】数字表格 [莫比乌斯反演]
数字表格 Time Limit: 50 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB[Submit][Status][Discuss] Description Doris刚刚学习了fibonac ...
- 「6月雅礼集训 2017 Day10」perm(CodeForces 698F)
[题目大意] 给出一个$n$个数的序列$\{a_n\}$,其中有些地方的数为0,要求你把这个序列填成一个1到$n$的排列,使得: $(a_i, a_j) = 1$,当且仅当$(i, j) = 1$.多 ...
- [Unity]插件Node Editor介绍 实现类似状态机画布的扩展
Unity自带的动画状态机有一套对策划非常友好的UI.但是Unity官方没有公开这些控件的api.除了Asset Store里一些已有的方案,我在这里介绍一个在github上的开源项目,封装了底层,但 ...
- 更新ubuntu15.10后触摸板点击功能消失
问题描述: 昨天升级了ubuntu15.10,升级之后很多15.04让人不爽的东西消失了,大快人心,但是突然发现自己的触摸板不怎么好用了,原来可以点击,双指点击代表右键,三指点击代表鼠标中键的功能不见 ...
- Java 关于微信公众号支付总结附代码
很多朋友第一次做微信支付的时候都有蒙,但当你完整的做一次就会发现其实并没有那么难 业务流程和应用场景官网有详细的说明:https://pay.weixin.qq.com/wiki/doc/api/js ...
- 前端—css
css css概述 CSS是Cascading Style Sheets的简称,中文称为层叠样式表,用来控制网页数据的表现,可以使网页的表现与数据内容分离. 一.css的四种引入方式: 1.行内式 ...
- sk_buff结构
sk_buff结构用来描述已接收或者待发送的数据报文信息:skb在不同网络协议层之间传递,可被用于不同网络协议,如二层的mac或其他链路层协议,三层的ip,四层的tcp或者udp协议,其中某些成员变量 ...
- smb windows中使用的文件共享协议(主要用于与windows互通)
主要是samba服务. SMB协议又成为CIFS(Common Internet File System)协议 samba服务功能: 1文件共享 2打印共享 3加入windows2000/2003/2 ...
- win7旗舰版64位缺失tbb.dll文件
win7旗舰版64位缺失tbb.dll文件 https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/688589990330312804.html 到好的电脑中复制一个,黏贴到下同的路径下 ...
- c#导出文件,下载文件,命名下载后的文件名
Page.Response.AppendHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + HttpU ...
