音视频八股文(11)-- ffmpeg avio 内存输入和内存输出。内存输出有完整代码,网上很少有的。
1.avio介绍
avio是FFmpeg中的一个模块,用于实现多种输入输出方式的封装。
avio提供了一系列API,可以将数据从内存读取到缓冲区中,也可以将缓冲区中的数据写入到内存中。其实现依赖于IOContext结构体,该结构体定义了当前输入/输出事件的状态、数据、回调函数等信息,并支持通过自定义回调函数实现不同的输入/输出方式。
内存输入(Memory Input)是指将数据从内存中读取到缓冲区中,常见的应用场景包括:从内存中读取音视频数据进行解码或处理。在使用avio实现内存输入时,需要首先创建一个AVIOContext结构体,并将内存数据缓冲区作为参数传递给avio_open函数进行初始化。之后,可以使用avio_read函数从缓冲区中读取数据,直至读取完成。
内存输出(Memory Output)是指将数据从缓冲区中写入到内存中,常见的应用场景包括:将音视频数据编码并保存到内存中。在使用avio实现内存输出时,需要首先创建一个AVIOContext结构体,并将内存数据缓冲区和缓冲区大小作为参数传递给avio_open函数进行初始化。之后,可以使用avio_write函数将数据写入缓冲区中,并在完成输出后调用avio_close函数关闭AVIOContext结构体。
总的来说,内存输入和输出是指在使用FFmpeg进行音视频处理时,将数据从内存中读取或写入到内存中的一种方式。使用avio模块可以方便地实现这种输入输出方式,并支持自定义回调函数以满足不同的应用需求。
2.为什么要用avio?
使用FFmpeg的avio模块实现内存输入和输出有以下几个优点:
2.1.灵活性高
传统的音视频处理方式往往需要将音视频数据保存到文件中,然后再进行读取和处理。而使用avio模块可以将数据直接读取或写入到内存中,从而提高了音视频处理的灵活性。这种方式可以避免繁琐的文件IO操作,节省磁盘空间。
2.2.扩展性强
内存输入和输出功能可以方便地扩展为其他更高级的应用程序,例如:流媒体服务器、实时音视频采集与处理等。这是因为内存输出能够较为轻松地将音视频数据编码并存储到内存缓冲区中,进而交由网络传输;内存输入则可直接从内存缓冲区获取音视频数据,快速响应用户请求。
2.3.可定制性好
FFmpeg的avio模块提供了一系列API,可以通过设置回调函数实现各种自定义功能。例如:自定义网络协议传输方式、增加错误重试机制、实现多路复用等。这使得处理器可以根据自己的需求对avio模块进行灵活配置,以最大限度地满足不同场景下的业务需求。
因此,使用FFmpeg的avio模块实现内存输入和输出可以提高音视频处理的效率,增加程序的灵活性和扩展性,同时还具有良好的可定制性。
3.内存区作为输入
3.1.回调函数何时被回调呢?
所有需要从输入源中读取数据的时刻,都将调用回调函数。和输入源是普通文件相比,只不过输入源变成了内存区,其他各种外在表现并无不同。
如下各函数在不同的阶段从输入源读数据,都会调用回调函数:
avformat_open_input() 从输入源读取封装格式文件头
avformat_find_stream_info() 从输入源读取一段数据,尝试解码,以获取流信息
av_read_frame() 从输入源读取数据包
3.2.该示例作用是统计mp4文件的视频帧数,代码如下:
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#include <libavformat/avio.h>
#include <libavutil/file.h>
#define INPUT_FILE "1.mp4"
struct buffer_data {
uint8_t* ptr;
size_t size; ///< size left in the buffer
};
static int read_packet(void* opaque, uint8_t* buf, int buf_size)
{
struct buffer_data* bd = (struct buffer_data*)opaque;
buf_size = FFMIN(buf_size, bd->size);
if (!buf_size)
return AVERROR_EOF;
printf("ptr:%p size:%zu\n", bd->ptr, bd->size);
/* copy internal buffer data to buf */
memcpy(buf, bd->ptr, buf_size);
bd->ptr += buf_size;
bd->size -= buf_size;
return buf_size;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
AVFormatContext* fmt_ctx = NULL;
AVIOContext* avio_ctx = NULL;
uint8_t* buffer = NULL, * avio_ctx_buffer = NULL;
size_t buffer_size, avio_ctx_buffer_size = 4096;
char* input_filename = NULL;
int ret = 0;
struct buffer_data bd = { 0 };
int videoStreamIndex = -1;
AVCodecParameters* avCodecPara = NULL;
const AVCodec* codec = NULL;
AVCodecContext* codecCtx = NULL;
AVPacket* pkt = NULL;
input_filename = INPUT_FILE;
/* slurp file content into buffer */
ret = av_file_map(input_filename, &buffer, &buffer_size, 0, NULL);
if (ret < 0)
goto end;
/* fill opaque structure used by the AVIOContext read callback */
bd.ptr = buffer;
bd.size = buffer_size;
if (!(fmt_ctx = avformat_alloc_context())) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
avio_ctx_buffer = av_malloc(avio_ctx_buffer_size);
if (!avio_ctx_buffer) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
avio_ctx = avio_alloc_context(avio_ctx_buffer, avio_ctx_buffer_size,
0, &bd, &read_packet, NULL, NULL);
if (!avio_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
fmt_ctx->pb = avio_ctx;
ret = avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open input\n");
goto end;
}
ret = avformat_find_stream_info(fmt_ctx, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find stream information\n");
goto end;
}
//av_dump_format(fmt_ctx, 0, input_filename, 0);
printf("完成\n");
//循环查找视频中包含的流信息,直到找到视频类型的流
//便将其记录下来 保存到videoStreamIndex变量中
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < fmt_ctx->nb_streams; i++) {
if (fmt_ctx->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
videoStreamIndex = i;
break;//找到视频流就退出
}
}
//如果videoStream为-1 说明没有找到视频流
if (videoStreamIndex == -1) {
printf("cannot find video stream\n");
goto end;
}
//================================= 查找解码器 ===================================//
avCodecPara = fmt_ctx->streams[videoStreamIndex]->codecpar;
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(avCodecPara->codec_id);
if (codec == NULL) {
printf("cannot find decoder\n");
goto end;
}
//根据解码器参数来创建解码器内容
codecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
avcodec_parameters_to_context(codecCtx, avCodecPara);
if (codecCtx == NULL) {
printf("Cannot alloc context.");
goto end;
}
//================================ 打开解码器 ===================================//
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, NULL)) < 0) { // 具体采用什么解码器ffmpeg经过封装 我们无须知道
printf("cannot open decoder\n");
goto end;
}
//=========================== 分配AVPacket结构体 ===============================//
int i = 0;//用于帧计数
pkt = av_packet_alloc(); //分配一个packet
av_new_packet(pkt, codecCtx->width * codecCtx->height); //调整packet的数据
//=========================== 读取视频信息 ===============================//
while (av_read_frame(fmt_ctx, pkt) >= 0) { //读取的是一帧视频 数据存入一个AVPacket的结构中
if (pkt->stream_index == videoStreamIndex) {
i++;//只计算视频帧
}
av_packet_unref(pkt);//重置pkt的内容
}
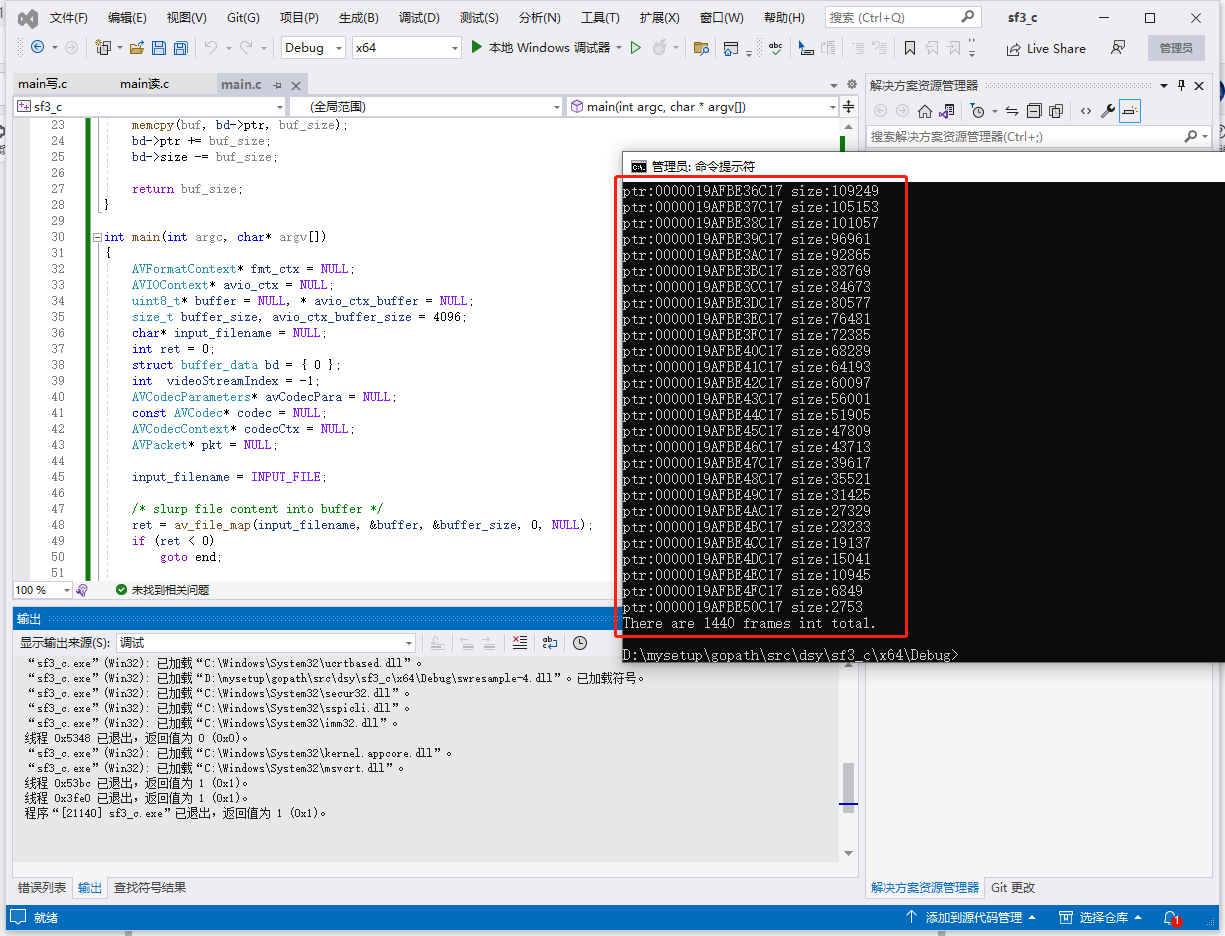
printf("There are %d frames int total.\n", i);
end:
avformat_close_input(&fmt_ctx);
/* note: the internal buffer could have changed, and be != avio_ctx_buffer */
if (avio_ctx)
av_freep(&avio_ctx->buffer);
avio_context_free(&avio_ctx);
av_packet_free(&pkt);
avcodec_close(codecCtx);
av_file_unmap(buffer, buffer_size);
avformat_free_context(fmt_ctx);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error occurred: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
4.内存区作为输出
4.1.回调函数何时被回调呢?
所有输出数据的时刻,都将调用回调函数。和输出是普通文件相比,只不过输出变成了内存区,其他各种外在表现并无不同。
如下各函数在不同的阶段会输出数据,都会调用回调函数:
avformat_write_header() 将流头部信息写入输出区
av_interleaved_write_frame() 将数据包写入输出区
av_write_trailer() 将流尾部信息写入输出区
4.2.该示例作用是提取mp4文件的视频帧为h264文件,输出采用write_packet回调,代码如下:
//https://www.cnblogs.com/leisure_chn/p/10318145.html
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#define INPUT_FILE "1.mp4"
#define OUTPUT_FILE "output.h264"
typedef struct {
FILE* fp;
} OutputContext;
static int write_packet(void* opaque, uint8_t* buf, int buf_size)
{
OutputContext* output_ctx = (OutputContext*)opaque;
FILE* fp = output_ctx->fp;
fwrite(buf, 1, buf_size, fp);
return buf_size;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
AVFormatContext* input_ctx = NULL;
AVOutputFormat* output_fmt = NULL;
AVFormatContext* output_ctx = NULL;
OutputContext* output_opaque = NULL;
int ret = avformat_open_input(&input_ctx, INPUT_FILE, NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not open input file: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
ret = avformat_find_stream_info(input_ctx, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not find stream information: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
output_fmt = av_guess_format("h264", NULL, NULL);
if (!output_fmt) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not guess output format.\n");
ret = AVERROR_MUXER_NOT_FOUND;
goto end;
}
ret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&output_ctx, output_fmt, NULL, OUTPUT_FILE);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not allocate output context: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
AVStream* in_video_stream = NULL;
AVCodecParameters* in_codec_params = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < input_ctx->nb_streams; i++) {
AVStream* stream = input_ctx->streams[i];
if (stream->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
in_video_stream = stream;
in_codec_params = stream->codecpar;
break;
}
}
if (!in_video_stream) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not find video stream.\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOSYS);
goto end;
}
AVStream* out_video_stream = avformat_new_stream(output_ctx, NULL);
if (!out_video_stream) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not create new stream.\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
ret = avcodec_parameters_copy(out_video_stream->codecpar, in_codec_params);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not copy codec parameters: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
out_video_stream->codecpar->codec_tag = 0;
output_opaque = av_malloc(sizeof(OutputContext));
if (!output_opaque) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not allocate output context.\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
fopen_s(&output_opaque->fp, OUTPUT_FILE, "wb");
if (!output_opaque->fp) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not open output file.\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOENT);
goto end;
}
AVIOContext* pb = NULL;
pb = avio_alloc_context((unsigned char*)av_malloc(32768), 32768, 1, output_opaque, NULL, &write_packet, NULL);
if (!pb) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not allocate output IO context.\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
output_ctx->pb = pb;
ret = avformat_write_header(output_ctx, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not write header: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
AVPacket packet = { 0 };
while (av_read_frame(input_ctx, &packet) >= 0) {
if (packet.stream_index == in_video_stream->index) {
av_packet_rescale_ts(&packet, in_video_stream->time_base, out_video_stream->time_base);
packet.stream_index = out_video_stream->index;
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(output_ctx, &packet);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not write frame: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
}
av_packet_unref(&packet);
}
ret = av_write_trailer(output_ctx);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Could not write trailer: %s.\n", av_err2str(ret));
goto end;
}
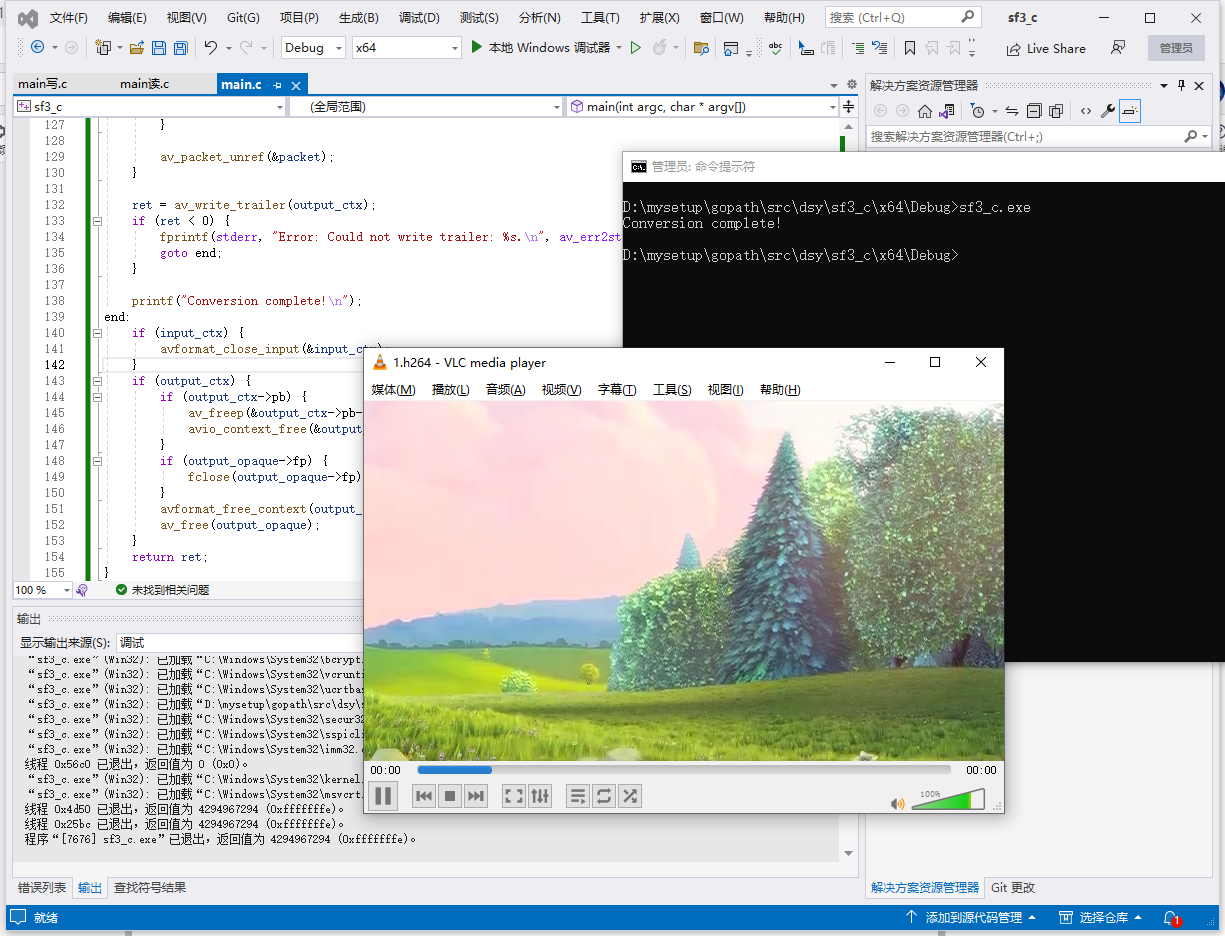
printf("Conversion complete!\n");
end:
if (input_ctx) {
avformat_close_input(&input_ctx);
}
if (output_ctx) {
if (output_ctx->pb) {
av_freep(&output_ctx->pb->buffer);
avio_context_free(&output_ctx->pb);
}
if (output_opaque->fp) {
fclose(output_opaque->fp);
}
avformat_free_context(output_ctx);
av_free(output_opaque);
}
return ret;
}
5.内存IO模式非常重要的一个函数:avio_alloc_context()
/**
* Allocate and initialize an AVIOContext for buffered I/O. It must be later
* freed with avio_context_free().
*
* @param buffer Memory block for input/output operations via AVIOContext.
* The buffer must be allocated with av_malloc() and friends.
* It may be freed and replaced with a new buffer by libavformat.
* AVIOContext.buffer holds the buffer currently in use,
* which must be later freed with av_free().
* @param buffer_size The buffer size is very important for performance.
* For protocols with fixed blocksize it should be set to this blocksize.
* For others a typical size is a cache page, e.g. 4kb.
* @param write_flag Set to 1 if the buffer should be writable, 0 otherwise.
* @param opaque An opaque pointer to user-specific data.
* @param read_packet A function for refilling the buffer, may be NULL.
* For stream protocols, must never return 0 but rather
* a proper AVERROR code.
* @param write_packet A function for writing the buffer contents, may be NULL.
* The function may not change the input buffers content.
* @param seek A function for seeking to specified byte position, may be NULL.
*
* @return Allocated AVIOContext or NULL on failure.
*/
AVIOContext *avio_alloc_context(
unsigned char *buffer,
int buffer_size,
int write_flag,
void *opaque,
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence));
这是FFmpeg中用于创建AVIOContext结构体的函数 avio_alloc_context 的代码注释。
该函数具有以下参数:
buffer:存储音视频数据的内存缓冲区指针,必须通过 av_malloc() 等函数分配。该内存块会被 AVIOContext 结构体引用,不能在生命周期内被释放。
buffer_size:缓冲区大小,对于固定块大小的协议需要设置为固定块大小,对于其他协议可以设置为典型缓存页大小,例如 4KB。
write_flag:标记是否可写,1 表示可写,0 表示只读。
opaque:用户指定的不透明指针,用于在回调函数中携带自定义数据。
read_packet:read_packet 回调函数,用于本地文件或网络流传输时从输入源中读取数据。当 buffer 中的数据被消耗完后,调用此函数填充缓冲区。
write_packet:write_packet 回调函数,在可写模式下用于将缓冲区中的数据写入输出源,例如本地文件或网络流。
seek:seek 回调函数,用于跳转到指定字节位置。
该函数主要用于在 FFmpeg 内部创建一个 AVIOContext 结构体,该结构体用于管理读取或写入内存缓冲区的音视频数据,并提供了一些 API 函数用于处理缓冲区数据。一旦创建了 AVIOContext 结构体,就可以通过调用 avio_open2() 函数来打开对应的输入或输出资源,然后即可开始读写数据。
在使用完毕后,需要通过调用 avio_context_free() 函数来释放 AVIOContext 结构体占用的内存空间。
6.两个示例的环境
操作系统:win10 64位
开发环境:VS2022
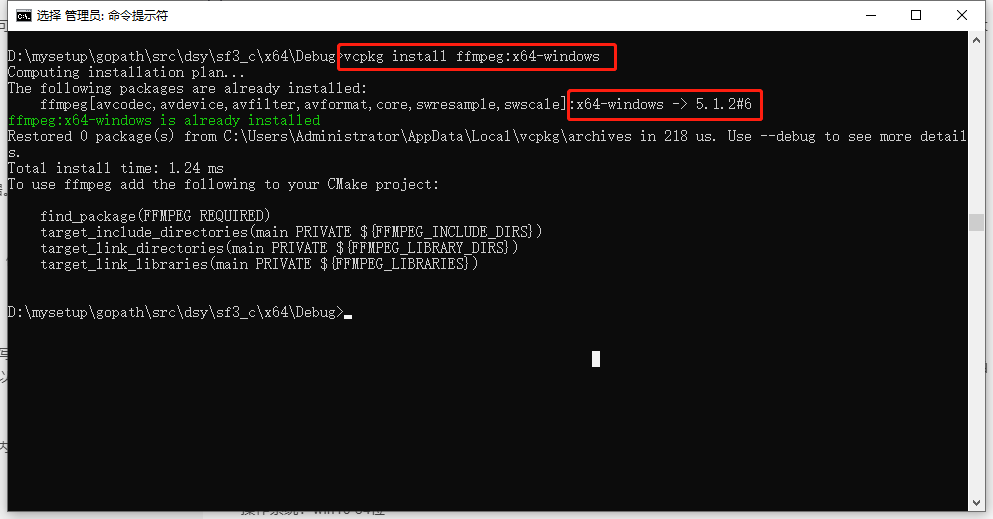
vcpkg命令:
vcpkg install ffmpeg:x64-windows
音视频八股文(11)-- ffmpeg avio 内存输入和内存输出。内存输出有完整代码,网上很少有的。的更多相关文章
- 音视频处理之FFmpeg封装格式20180510
一.FFMPEG的封装格式转换器(无编解码) 1.封装格式转换 所谓的封装格式转换,就是在AVI,FLV,MKV,MP4这些格式之间转换(对应.avi,.flv,.mkv,.mp4文件). 需要注意的 ...
- 音视频】5.ffmpeg命令分类与使用
GT其实平时也有一些处理音视频的个人或者亲人需求,熟练使用ffmpeg之后也不要借助图示化软件,一个命令基本可以搞定 G: 熟练使用ffmpeg命令!T :不要死记硬背,看一遍,自己找下规律,敲一遍, ...
- Android 音视频深入 十一 FFmpeg和AudioTrack播放声音(附源码下载)
项目地址,求starhttps://github.com/979451341/AudioVideoStudyCodeTwo/tree/master/FFmpeg%E6%92%AD%E6%94%BE%E ...
- 音视频处理之FFmpeg+SDL视频播放器20180409
一.FFmpeg视频解码器 1.视频解码知识 1).纯净的视频解码流程 压缩编码数据->像素数据. 例如解码H.264,就是“H.264码流->YUV”. 2).一般的视频解码流程 视频码 ...
- Android 音视频深入 九 FFmpeg解码视频生成yuv文件(附源码下载)
项目地址,求star https://github.com/979451341/Audio-and-video-learning-materials/tree/master/FFmpeg(MP4%E8 ...
- Android 音视频深入 十 FFmpeg给视频加特效(附源码下载)
项目地址,求starhttps://github.com/979451341/Audio-and-video-learning-materials/tree/master/FFmpeg(AVfilte ...
- 音视频处理之FFmpeg+SDL+MFC视频播放器20180411
一.FFmpeg+SDL+MFC视频播放器 1.MFC知识 1).创建MFC工程的方法 打开VC++ 文件->新建->项目->MFC应用程序 应用程序类型->基于对话框 取消勾 ...
- Android 音视频深入 十七 FFmpeg 获取RTMP流保存为flv (附源码下载)
项目地址https://github.com/979451341/RtmpSave 这个项目主要代码我是从雷神那弄过来的,不愧是雷神,我就配个环境搞个界面就可以用代码了. 这一次说的是将RTMP流媒体 ...
- 音视频处理之FFmpeg程序的介绍与使用20180302
一.FFMPEG程序介绍与使用 主要介绍一下ffmpeg工程包含的三个exe的使用方法. 1. FFMPEG程序介绍 1.1.下载 ffmpeg的官方网站是:http://ffmpeg.org/ 下载 ...
- 多媒体音视频处理及FFmpeg使用技巧总结
截图 ffmpeg -ss 00:02:06 -i input.mp4 -f image2 -y poster.jpg 连续截图 ffmpeg -y -i input.mp4 -vf "fp ...
随机推荐
- 第二节 printf语句和C++中的判断结构
第二节 printf语句和C++中的判断结构 1.1printf语句作用 保留几位小数:%.4lf 保留四位小数 %.3lf 保留三位小数, 格式化输出:整数:printf("%5d!&qu ...
- Python第十章实验报告
一.实验对象:<零基础学Python>6道实例和2道实战 二.实验环境:IDLE Shell 3.9.7 三.实验目的:学习如何在Python中进行文件和目录的相关操作 四.实验过程: 实 ...
- Axure RP Extension for Chrome 0.6.2安装和详解
1.当我们用网页访问一个本地页面时就会出现这种问题,提示你要安装浏览器的扩展程序包,以下有搜狗浏览器如何安装,qq浏览器
- Nodejs 发送 TCP 消息的正确姿势
最近使用 NODE-RED 跟 TCP 打交道.NODE-RED 里内建了一个节点叫"tcp-out",看文档呢使用这个节点可以很方便的把 payload 用 TCP 协议发送出去 ...
- rosetta Resfile语法和约束
介绍 参考:https://www.rosettacommons.org/docs/latest/rosetta_basics/file_types/resfiles resfile包含输入到Pack ...
- Trino Master OOM 排查记录
背景 最近线上的 trino 集群 master 节点老是因为 OOM crash,我们注意到 trino crash 前集群正在运行的查询数量正常,不太像是因为并发查询数据太多导致的 OOM.遂配置 ...
- ElasticSearch 实现分词全文检索 - delete-by-query
目录 ElasticSearch 实现分词全文检索 - 概述 ElasticSearch 实现分词全文检索 - ES.Kibana.IK安装 ElasticSearch 实现分词全文检索 - Rest ...
- 关于EasyExcel的数据导入和单sheet和多sheet导出
读写Excel基本代码 直接复制不一定能用 实体类 @ExcelIgnore 在导出操作中不会被导出 @ExcelProperty 在导入过程中 可以根据导入模板自动匹配字段, 在导出过程中可用于设置 ...
- 基于springboot实现SSM整合
(1)SpringBoot整合Spring(不存在) (2)SpringBoot整合SpringMVC(不存在) (3)SpringBoot整合MyBatis(主要) 一.新建springboot项目 ...
- 【译】使用 ChatGPT 和 Azure Cosmos DB 构建智能应用程序
原文 | Mark Brown 翻译 | 郑子铭 随着对智能应用程序的需求不断增长,开发人员越来越多地转向人工智能(AI)和机器学习(ML),以增强其应用程序的功能.聊天机器人已经成为提供对话式人工智 ...
