《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example6.29

代码:
% The following funciton computes the filter
% coefficients shown in Table 6.2
b = firpm(30, [0, 0.3, 0.5, 1], [1, 1, 0, 0]);
w = [0:500]*pi/500; H = freqz(b, 1, w);
magH = abs(H); magHdb = 20*log10(magH); % 16-bit word-length quantization
N1 = 15; [bhat1, L1, B1] = QCoeff(b, N1);
TITLE1 = sprintf('%i-bits (1+%i+%i) ', N1+1, L1, B1);
%bhat1 = bahat(1, :); ahat1 = bahat(2, :);
Hhat1 = freqz(bhat1, 1, w); magHhat1 = abs(Hhat1);
magHhat1db = 20*log10(magHhat1); zhat1 = roots(bhat1); % 8-bit word-length quantization
N2 = 7; [bhat2, L2, B2] = QCoeff(b, N2);
TITLE2 = sprintf('%i-bits (1+%i+%i) ', N2+1, L2, B2);
%bhat2 = bahat(1, :); ahat2 = bahat(2, :);
Hhat2 = freqz(bhat2, 1, w); magHhat2 = abs(Hhat2);
magHhat2db = 20*log10(magHhat2); zhat2 = roots(bhat2); % Comparison of Magnitude Plots
Hf_1 = figure('paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 5], 'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 6.29');
%figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 6.26a')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); % Comparison of Log-Magnitude Response: 16 bits
subplot(2, 2, 1); plot(w/pi, magHdb, 'g', 'linewidth', 1.5); axis([0, 1, -80, 5]);
hold on; plot(w/pi, magHhat1db, 'r', 'linewidth', 1); hold off;
xlabel('Digital Frequency in \pi units', 'fontsize', 10);
ylabel('Decibels', 'fontsize', 10); grid on;
title(['Log-mag Plot: ', TITLE1], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); % Comparison of Pole-Zero Plots: 16 bits
subplot(2, 2, 3); [HZ, HP, Hl] = zplane([b], [1]); axis([-2, 2, -2, 2]); hold on;
set(HZ, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
set(HP, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
plot(real(zhat1), imag(zhat1), 'r+', 'linewidth', 1); grid on;
title(['PZ Plot: ' TITLE1], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); hold off; % Comparison of Log-Magnitude Response: 8 bits
subplot(2, 2, 2); plot(w/pi, magHdb, 'g', 'linewidth', 1.5); axis([0, 1, -80, 5]);
hold on; plot(w/pi, magHhat2db, 'r', 'linewidth', 1); hold off;
xlabel('Digital Frequency in \pi units', 'fontsize', 10);
ylabel('Decibels', 'fontsize', 10); grid on;
title(['Log-mag Plot: ', TITLE2], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); % Comparison of Pole-Zero Plots: 8 bits
subplot(2, 2, 4); [HZ, HP, Hl] = zplane([b], [1]); axis([-2, 2, -2, 2]); hold on;
set(HZ, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
set(HP, 'color', 'g', 'linewidth', 1, 'markersize', 4);
plot(real(zhat2), imag(zhat2), 'r+', 'linewidth', 1); grid on;
title(['PZ Plot: ' TITLE2], 'fontsize', 10, 'fontweight', 'bold'); hold off;
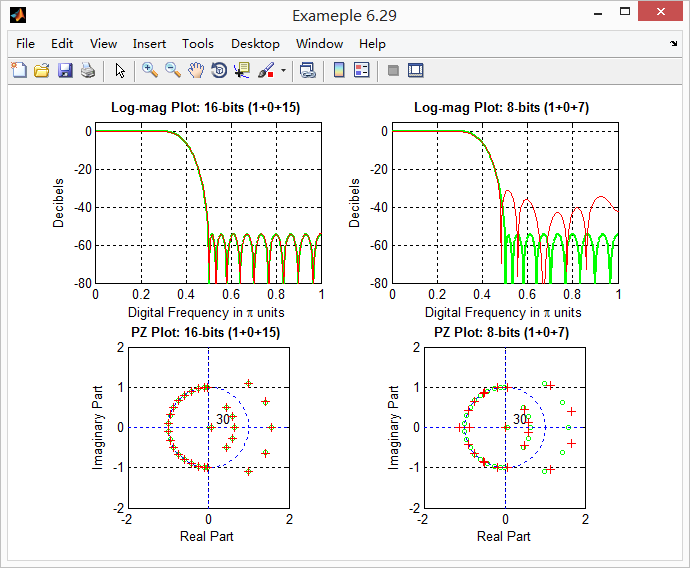
运行结果:
《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example6.29的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
随机推荐
- class文件直接修改_反编译修改class文件变量
今天笔者同事遇到一个问题,客户同事的数据库连接信息直接写在代码中,连接的密码改了,但是又没有源代码,所以只能直接修改Java class文件. 记录一下修改步骤: 1.下载JClassLib_wind ...
- transform对定位元素的影响
1.温故知新 absolute:生成绝对定位的元素,相对于除position:static 定位以外的第一个有定位属性的父元素进行定位,若父元素没有定位属性则相对于浏览器窗口的左上角定位,定位的元素不 ...
- JS正则表达式入门,看这篇就够了
前言 在正文开始前,先说说正则表达式是什么,为什么要用正则表达式?正则表达式在我个人看来就是一个浏览器可以识别的规则,有了这个规则,浏览器就可以帮我们判断某些字符是否符合我们的要求.但是,我们为什么要 ...
- MVVM模式的3种command总结[2]--RelayCommand
MVVM模式的3种command总结[2]--RelayCommand RelayCommand本来是WPF下面用的一种自定义的command,主要是它用到了事件管理函数,这个SL下面是没有的.不过这 ...
- AngularJS 教程 - CodePreject
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1065838/AngularJS-Tutorial Article Series Tutorial 1: Angular JS ...
- Wannafly挑战赛14E无效位置
https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/81/E 给一个1-base数组{a},有N次操作,每次操作会使一个位置无效.一个区间的权值定义为这个区间里选出一些数的异或和 ...
- HDU 4696 Answers (脑补+数形结合)
题意 给一个图,每个点的出度为1,每个点的权值为1或者2.给Q个询问,问是否能找到一条路径的权值和M. 思路 由于每个点的出度为1,所以必然存在环.又因为c[i]只能取1或者2,可以组成任意值,所以只 ...
- linux---网络相关配置,ssh服务,bash命令及优先级,元字符
- 二:临时配置网络(ip,网关,dns)+永久配置 临时配置: [root@nfs-server ~]# ifconfig ens32: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUN ...
- h5开发中,利用微信或者QQ登陆以后获取用户头像在canvas画布显示问题
在实际开发上先的h5页面产品中,总会遇到各种坑,好多坑都是安卓和iPhone端兼容的问题(用电脑谷歌浏览器输入 chrome://inspect/#devices可以用手机USB调试,打开) eg: ...
- New Concept English Two 34 game over
$课文95 纯属虚构 1049. When the Ambassador or Escalopia returned home for lunch, his wife got a shock. 当艾 ...
