1-11 RHLE7-重定向和文件查找
在Linux 系统中,一切皆设备
Linux系统中使用文件来描述各种硬件,设备资源等
例如:以前学过的硬盘和分区,光盘等设备文件
sda1 sr0
============================================
1、Linux中的重定向的作用
重定向的含义:
在实际的Linux维护中,可以改变输入输出内容的方向.
不使用默认的标准输入输出设备,即重定向.
当我们在调试或安装时,希望将一些不必要的信息不显示出来,
或者是需要将调试信息保存下来时,我们可以使用重点向
>(覆盖输出),>>(追加输出),<(输入) 符号,
将需要的信息打印到对应的文件中
============================================
2、文件描述符 0、1、2
文件描述符是一个简单的整数,
用以标明每一个被进程所打开的文件
第一个打开的文件是0,第二个是1,以此类推
先查看LINUX默认的文件描述符:# ulimit -n
[root@xiaogan ~]# ulimit -n
1024
用户通过操作系统处理信息的过程中,使用的交互设备文件

在Linux系统中,在一个程序运行时,会打开很多文件,
其中默认打开前三个文件,
以此为标准输入文件、标准输出文件、标准错误文件
标准输入文件 STDIN 文件描述符为0 默认为键盘
标准输出文件 STDOUT 文件描述符为1 默认为显示器
标准错误文件 STDERR 文件描述符为2 默认为显示器
STDIN 标准输入 默认的设备是键盘 文件编号为:0
命令将从标准输入文件中 读取 在执行过程中的 需要的 输入数据.
数据来源于文件
STDOUT 标准输出 默认的设备是 显示器 文件编号为:1
命令执行后的输出结果,发送到标准输出文件.
结果输出到文件
STDERR 标准错误 默认的设备是显示器 文件编号为:2
命令将执行期间的各种错误信息发送到标准错误文件.
错误信息发送到文件
标准输入,标准输出和标准错误默认使用键盘和显示器作为关联设备
与操作系统进行交互完成最基本的输入,输出操作.
============================================
3、输入输出重定向,管道使用的方式
输入输出重点向可使用重定向符号 >、>>、<符号来实现
> 以覆盖的方式将输出重定向到文件
>> 以追加的方式将输出重定向到文件
<输入重定向到文件
注:若重定向的输出的文件不存在,则会新建这个文件
当使用覆盖重定向时,文件中原本的内容将丢失
重定向输出就将结果输出到文件中
实验:
查看当前主机的CPU的类型保存到kernel.txt文件中(而不是直接显示到屏幕上)
uname -p 查看cpu类型信息
将内核 的版本信息追加到kernel.txt
uname -r 查看内核版本信息
- [root@xiaogan ~]# uname -p #查看CPU类型
- x86_64
- [root@xiaogan ~]# uname -p >kernel.txt #将cpu类型信息保存到kernel.txt文件中
- [root@xiaogan ~]# ls
- Desktop Documents Downloads kernel.txt Music Pictures Public Templates Videos
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat kernel.txt #查看kernel.txt信息
- x86_64
- [root@xiaogan ~]# uname -r >>kernel.txt #将内核版本信息追加保存到kernel.txt文件中
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat kernel.txt
- x86_64
- 3.10.-.el7.x86_64
- [root@xiaogan ~]# uname -r > kernel.txt
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat kernel.txt
- 3.10.-.el7.x86_64
- [root@xiaogan ~]#
重定向输入
将命令中接收输入的途径由默认的键盘改为其他文件.
而不是等待从键盘输入
从文件读取数据
操作符: “<”
通过重定向输入可以
使一些交互式操作过程能够通过读取文件来完成
例如:使用passwd 设置密码时.每次都根据提示输入密码比较烦琐
改用重定向输入将可以忽略交互式的过程.而自动完成密码设置
(结合--stdin 选项来识别标准的输入)
通过文件中的内容作为输入的数据
实验:使用非交互式的去执行设置密码
- [root@xiaogan ~]# echo "" > passwd.txt #将密码输出到文件
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat passwd.txt #查看密码文件
- [root@xiaogan ~]# tail - /etc/passwd
- apache:x:::Apache:/usr/share/httpd:/sbin/nologin
- [root@xiaogan ~]# tail - /etc/passwd
- gan:x:::Gan:/home/gan:/bin/bash
- nginx:x::::/home/nginx:/sbin/nologin
- apache:x:::Apache:/usr/share/httpd:/sbin/nologin
- [root@xiaogan ~]# useradd xiaogan #新建用户
- [root@xiaogan ~]# passwd xiaogan --stdin <passwd.txt #使用无交互式执行设置密码
- Changing password for user xiaogan.
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- [root@xiaogan ~]#
执行成功!!!

错误重定向:
将命令执行过程中出现的错误信息 (选项或参数错误) 保存到指定的文件,而不是直接显示到显示器
错误信息保存到文件
操作符: 使用2>
2指的是错误文件的编号
(在使用标准的输入和输出省略了1 0 编号)
在实际应用中.
错误重定向可以用来收集执行的错误信息.为排错提供依据;
对于shell脚本还可以将无关紧要的错误信息重定向到空文件/dev/null中
以保持脚本输出的简洁
使用”2>”操作符时,会想使用”>”一样覆盖目标文件的内容,
若追加而不覆盖文件的内容即可使用”2>>”操作符
例如: 使用tar命令进行备份的时候出新的错误信息保存到err.log文件中
- [root@xiaogan ~]# tar -cf asdf.tar /asdf
- tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
- tar: /asdf: Cannot stat: No such file or directory
- tar: Exiting with failure status due to previous errors
- [root@xiaogan ~]# tar -cf asdf.tar /asdf >err.log #将错误信息输出到err.log文件
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat err.log
- tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
- tar: /asdf: Cannot stat: No such file or directory
- tar: Exiting with failure status due to previous errors
- [root@xiaogan ~]#

把/dev/null看作"黑洞".
它等价于一个只写文件. 所有写入它的内容都会永远丢失.
而尝试从它那儿读取内容则什么也读不到.
然而, /dev/null对命令行和脚本都非常的有用.
可使用
echo $?
命令,查看上一条命令的执行结果,0为执行成功
- [root@xiaogan ~]# tar -cf asdf.tar /asdf >/dev/null
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat /dev/null
- [root@xiaogan ~]# tar -cf asdf.tar /asdf >/dev/null
- [root@xiaogan ~]# echo $?
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat /dev/null
- [root@xiaogan ~]# echo $?
- [root@xiaogan ~]#

& 表示等同于的意思
正确的写到一个文件,错误的在写到一个文件
[root@xuegod63 ~]# ls /tmp/ /nginx 1> a.txt 2>b.txt
当我们希望将标准输出,与标准错误文件混合输出是可以使用如下命令:
[root@xiaogan ~]# ls /tmp /asdf 1>a.txt 2>&1
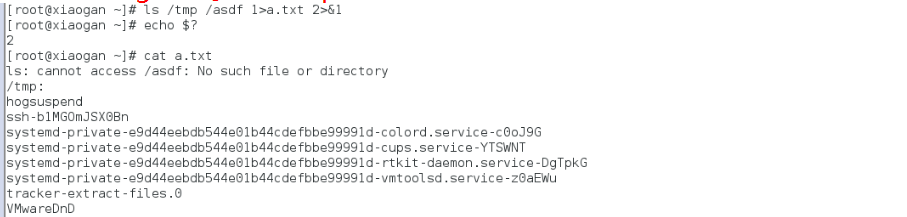
&> 混合输出
不分正确的还是错误的
[root@xiaogan ~]# ls /tmp /asdf &>a.txt

管道的作用:
前面的输出作为后面的输入
(可以将两条命令连接起来)
4、常用文件查找命令简介
tee which whereis locate find grep
4.1 tee命令
详解
功能:读取标准输入的数据,并将其内容输出成文件。
语法:tee [-a][--help][--version][文件...]
tee指令会从标准输入设备读取数据,将其内容输出到标准输出设备,同时保存成文件。
参 数:
-a或 --append 追加
-i 无视中断信号
--help 在线帮助。
--version 显示版本信息
- [root@xiaogan ~]# who
- root : -- : (:)
- root pts/ -- : (:)
- [root@xiaogan ~]# who | tee who.txt
- root : -- : (:)
- root pts/ -- : (:)
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat who.txt
- root : -- : (:)
- root pts/ -- : (:)
- [root@xiaogan ~]# who -uH | tee -a who.txt
- NAME LINE TIME IDLE PID COMMENT
- root : -- : ? (:)
- root pts/ -- : . (:)
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat who.txt
- root : -- : (:)
- root pts/ -- : (:)
- NAME LINE TIME IDLE PID COMMENT
- root : -- : ? (:)
- root pts/ -- : . (:)
- [root@xiaogan ~]#

which命令 查找二进制可执行文件的绝对路径
whereis命令 查找本地二进制可执行文件、源码及帮助的路径

- [root@xiaogan ~]# whereis --help #whereis命令帮助信息
- Usage:
- whereis [options] file
- Options:
- -b search only for binaries
- -B <dirs> define binaries lookup path
- -m search only for manuals
- -M <dirs> define man lookup path
- -s search only for sources
- -S <dirs> define sources lookup path
- -f terminate <dirs> argument list
- -u search for unusual entries
- -l output effective lookup paths
- =========================================================
- [root@xiaogan ~]# which --help #which命令帮助信息
- Usage: /usr/bin/which [options] [--] COMMAND [...]
- Write the full path of COMMAND(s) to standard output.
- --version, -[vV] Print version and exit successfully.
- --help, Print this help and exit successfully.
- --skip-dot Skip directories in PATH that start with a dot.
- --skip-tilde Skip directories in PATH that start with a tilde.
- --show-dot Don't expand a dot to current directory in output.
- --show-tilde Output a tilde for HOME directory for non-root.
- --tty-only Stop processing options on the right if not on tty.
- --all, -a Print all matches in PATH, not just the first
- --read-alias, -i Read list of aliases from stdin.
- --skip-alias Ignore option --read-alias; don't read stdin.
- --read-functions Read shell functions from stdin.
- --skip-functions Ignore option --read-functions; don't read stdin.
- Recommended use is to write the output of (alias; declare -f) to standard
- input, so that which can show aliases and shell functions. See which() for
- examples.
- If the options --read-alias and/or --read-functions are specified then the
- output can be a full alias or function definition, optionally followed by
- the full path of each command used inside of those.
- Report bugs to <which-bugs@gnu.org>.
locate #结合本地数据库,查找文件
- [root@xiaogan ~]# locate --help
- Usage: locate [OPTION]... [PATTERN]...
- Search for entries in a mlocate database.
- -A, --all only print entries that match all patterns
- -b, --basename match only the base name of path names
- -c, --count only print number of found entries
- -d, --database DBPATH use DBPATH instead of default database (which is
- /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db)
- -e, --existing only print entries for currently existing files
- -L, --follow follow trailing symbolic links when checking file
- existence (default)
- -h, --help print this help
- -i, --ignore-case ignore case distinctions when matching patterns
- -l, --limit, -n LIMIT limit output (or counting) to LIMIT entries
- -m, --mmap ignored, for backward compatibility
- -P, --nofollow, -H don't follow trailing symbolic links when checking file
- existence
- -, --null separate entries with NUL on output
- -S, --statistics don't search for entries, print statistics about each
- used database
- -q, --quiet report no error messages about reading databases
- -r, --regexp REGEXP search for basic regexp REGEXP instead of patterns
- --regex patterns are extended regexps
- -s, --stdio ignored, for backward compatibility
- -V, --version print version information
- -w, --wholename match whole path name (default)
- Report bugs to mitr@redhat.com.
在使用本地数据库查找新建文件时,是查找不到的,这是需要使用命令:
updatedb #更新数据库

grep #过滤信息
-v 反转
-i 忽略大小写
^#以#开头
#$ 以#结尾
^$ 空行
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt
- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
- AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
- bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt |grep #查找文档中有2的行
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep -v #过滤掉文档中的2那一行
- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
- AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
- bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep -i a #-i 忽略大小写
- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep ^a #以a开头的行
- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep ^B #以B开头的行
- BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep B$ #以B结尾的行
- BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep a$ #以a结尾的行
- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep ^$ #空行
- [root@xiaogan ~]# cat test.txt | grep -v ^$ #过滤掉空行
- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
- AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
- bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
- [root@xiaogan ~]#
- [root@xiaogan ~]# grep --help
- Usage: grep [OPTION]... PATTERN [FILE]...
- Search for PATTERN in each FILE or standard input.
- PATTERN is, by default, a basic regular expression (BRE).
- Example: grep -i 'hello world' menu.h main.c
- Regexp selection and interpretation:
- -E, --extended-regexp PATTERN is an extended regular expression (ERE)
- -F, --fixed-strings PATTERN is a set of newline-separated fixed strings
- -G, --basic-regexp PATTERN is a basic regular expression (BRE)
- -P, --perl-regexp PATTERN is a Perl regular expression
- -e, --regexp=PATTERN use PATTERN for matching
- -f, --file=FILE obtain PATTERN from FILE
- -i, --ignore-case ignore case distinctions
- -w, --word-regexp force PATTERN to match only whole words
- -x, --line-regexp force PATTERN to match only whole lines
- -z, --null-data a data line ends in byte, not newline
- Miscellaneous:
- -s, --no-messages suppress error messages
- -v, --invert-match select non-matching lines
- -V, --version display version information and exit
- --help display this help text and exit
- Output control:
- -m, --max-count=NUM stop after NUM matches
- -b, --byte-offset print the byte offset with output lines
- -n, --line-number print line number with output lines
- --line-buffered flush output on every line
- -H, --with-filename print the file name for each match
- -h, --no-filename suppress the file name prefix on output
- --label=LABEL use LABEL as the standard input file name prefix
- -o, --only-matching show only the part of a line matching PATTERN
- -q, --quiet, --silent suppress all normal output
- --binary-files=TYPE assume that binary files are TYPE;
- TYPE is 'binary', 'text', or 'without-match'
- -a, --text equivalent to --binary-files=text
- -I equivalent to --binary-files=without-match
- -d, --directories=ACTION how to handle directories;
- ACTION is 'read', 'recurse', or 'skip'
- -D, --devices=ACTION how to handle devices, FIFOs and sockets;
- ACTION is 'read' or 'skip'
- -r, --recursive like --directories=recurse
- -R, --dereference-recursive
- likewise, but follow all symlinks
- --include=FILE_PATTERN
- search only files that match FILE_PATTERN
- --exclude=FILE_PATTERN
- skip files and directories matching FILE_PATTERN
- --exclude-from=FILE skip files matching any file pattern from FILE
- --exclude-dir=PATTERN directories that match PATTERN will be skipped.
- -L, --files-without-match print only names of FILEs containing no match
- -l, --files-with-matches print only names of FILEs containing matches
- -c, --count print only a count of matching lines per FILE
- -T, --initial-tab make tabs line up (if needed)
- -Z, --null print byte after FILE name
- Context control:
- -B, --before-context=NUM print NUM lines of leading context
- -A, --after-context=NUM print NUM lines of trailing context
- -C, --context=NUM print NUM lines of output context
- -NUM same as --context=NUM
- --group-separator=SEP use SEP as a group separator
- --no-group-separator use empty string as a group separator
- --color[=WHEN],
- --colour[=WHEN] use markers to highlight the matching strings;
- WHEN is 'always', 'never', or 'auto'
- -U, --binary do not strip CR characters at EOL (MSDOS/Windows)
- -u, --unix-byte-offsets report offsets as if CRs were not there
- (MSDOS/Windows)
- 'egrep' means 'grep -E'. 'fgrep' means 'grep -F'.
- Direct invocation as either 'egrep' or 'fgrep' is deprecated.
- When FILE is -, read standard input. With no FILE, read . if a command-line
- -r is given, - otherwise. If fewer than two FILEs are given, assume -h.
- Exit status is if any line is selected, otherwise;
- if any error occurs and -q is not given, the exit status is .
- Report bugs to: bug-grep@gnu.org
- GNU Grep home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/grep/>
- General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>
find命令:通过硬盘查询文件名称
- [root@xiaogan ~]# man find
- [root@xiaogan ~]# ls
- append.txt a.txt Documents err.log Music Pictures Templates usr who.txt
- asdf.tar Desktop Downloads kernel.txt passwd.txt Public test.txt Videos
- [root@xiaogan ~]# ls /opt
- abcde.txt rh
- [root@xiaogan ~]# find / -name abcde.txt
- /opt/abcde.txt
- [root@xiaogan ~]# find asdf.tar
- asdf.tar
- [root@xiaogan ~]#
- #help命令帮助信息
- [root@xiaogan ~]# find --help
- Usage: find [-H] [-L] [-P] [-Olevel] [-D help|tree|search|stat|rates|opt|exec] [path...] [expression]
- default path is the current directory; default expression is -print
- expression may consist of: operators, options, tests, and actions:
- operators (decreasing precedence; -and is implicit where no others are given):
- ( EXPR ) ! EXPR -not EXPR EXPR1 -a EXPR2 EXPR1 -and EXPR2
- EXPR1 -o EXPR2 EXPR1 -or EXPR2 EXPR1 , EXPR2
- positional options (always true): -daystart -follow -regextype
- normal options (always true, specified before other expressions):
- -depth --help -maxdepth LEVELS -mindepth LEVELS -mount -noleaf
- --version -xautofs -xdev -ignore_readdir_race -noignore_readdir_race
- tests (N can be +N or -N or N): -amin N -anewer FILE -atime N -cmin N
- -cnewer FILE -ctime N -empty -false -fstype TYPE -gid N -group NAME
- -ilname PATTERN -iname PATTERN -inum N -iwholename PATTERN -iregex PATTERN
- -links N -lname PATTERN -mmin N -mtime N -name PATTERN -newer FILE
- -nouser -nogroup -path PATTERN -perm [-/]MODE -regex PATTERN
- -readable -writable -executable
- -wholename PATTERN -size N[bcwkMG] -true -type [bcdpflsD] -uid N
- -used N -user NAME -xtype [bcdpfls]
- -context CONTEXT
- actions: -delete -print0 -printf FORMAT -fprintf FILE FORMAT -print
- -fprint0 FILE -fprint FILE -ls -fls FILE -prune -quit
- -exec COMMAND ; -exec COMMAND {} + -ok COMMAND ;
- -execdir COMMAND ; -execdir COMMAND {} + -okdir COMMAND ;
- Report (and track progress on fixing) bugs via the findutils bug-reporting
- page at http://savannah.gnu.org/ or, if you have no web access, by sending
- email to <bug-findutils@gnu.org>.
1-11 RHLE7-重定向和文件查找的更多相关文章
- Linux输入输出重定向和文件查找值grep命令
Linux输入输出重定向和文件查找值grep命令 一.文件描述符Linux 的shell命令,可以通过文件描述符来引用一些文件,通常使用到的文件描述符为0,1,2.Linux系统实际上有12个文件描述 ...
- <实训|第十一天>学习一下linux中的进程,文件查找,文件压缩与IO重定向
[root@localhost~]#序言 在今后的工作中,运维工程师每天的例行事务就是使用free -m,top,uptime,df -h...每天都要检查一下服务器,看看是否出现异常.那么今天我们就 ...
- 分享一个文件查找、替换制定的字符或数字之CS程序、附带源码
首先就上操作流程图: 图--登陆界面.登陆密码:alidoing.com 图--界面说明(一看就懂) 图--文件查找到再替换 图--文件替换成功 图--替换后的文件 代码开始: 登陆的代码就非常简单. ...
- Linux正则表达式、shell基础、文件查找及打包压缩
Linux正则表达式.shell基础.文件查找及打包压缩 一.正则表达式 Linux正则表达式分为2类: 1.基本正则表达式(BRE) 2.扩展正则表达式(ERE) 两者的区别: 1.使用扩展正则表达 ...
- Linux操作系统的文件查找工具locate和find命令常用参数介绍
Linux操作系统的文件查找工具locate和find命令常用参数介绍 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.非实时查找(数据库查找)locate工具 locate命 ...
- Linux文件查找工具之find “大宝剑”--转载
原文地址:http://xinzong.blog.51cto.com/10018904/1749465 一.文件查找工具常用软件 locate: locate命令其实是find -name的另一种写法 ...
- find——文件查找命令 linux一些常用命令
find 命令eg: 一般文件查找方法: 1. find /home -name file , 在/home目录下查找文件名为file的文件2. find /home -name '*file ...
- 【C语言】重定向和文件
重定向和文件 一.相关基础知识 重定向:在计算机领域,重定向是大多数命令行解释器所具有的功能,包括各种可以将标准流重定向用户规定地点的Unix shells. 输入重定向:可以使程序能够使用文件代替键 ...
- (大数据工程师学习路径)第一步 Linux 基础入门----环境变量与文件查找
环境变量与文件查找 本节介绍环境变量的作用与用法,及几种搜索文件的方法.学会这些技巧高效地使用 Linux. 一.环境变量 1.变量 要解释环境变量,得先明白变量是什么,准确的说应该是 Shell 变 ...
- linux下文件查找工具--find
常用的文件查找命令有:which,locate,find 1.which命令 查找二进制数或二进制命令,由PATH给出 2.loacte 特点: 1.非实时,每天在系统上生成数据库,通过数据库查询 2 ...
随机推荐
- 【转】js获取当前日期时间“yyyy-MM-dd HH:MM:SS”
获取当前的日期时间 格式“yyyy-MM-dd HH:MM:SS” 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 function getNowFormatD ...
- Java 对比Hashtable、Hashmap、Treemap有什么不同?
①基本理解 Hashtable.Hashmap.Treemap都是最常见的一些Map实现,是以键值对的形式存储和操作数据的容器类型. Hashtable是Java类库提供的一个哈希实现,本身是同步的, ...
- win 7 64 安装 MondgoDB 3.4
https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/f3e34a12ac10cef5eb653583.html mongod --dbpath "D:\Program Fil ...
- 通过Java编码获取String分行字符串的内容
代码案列: import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.IOException ...
- iOS开发之plist文件操作
之前在想用代码去实现很多界面上能用interface builder可以拖进去的功能,现在想想真是够无知的啊.不仅效率低下,而且对于代码的维护带来不少麻烦,这段时间一直在反思看了design+code ...
- java中数组以及集合
java中数组: 数组在Java里是一种特殊类型,有别于普通的“类的实例”的对象.但实际数组也是一种对象类型,int[]a = new int[5] a是在java栈中分配的引用变量,类型是int[ ...
- GRUB2 分析 (三)
接上一篇 从地址0x8200开始的是lzma_decompress.img.这是由startup_raw.S编译生成的.这个文件稍微复杂点.首先一开始就是个跳转指令: ljmp $0, $ABS(LO ...
- Python面试题之Python中type和object的关系
知乎上看到的提问: 两个是互为实例的关系,但不是互为子类的关系,只有type是object的子类,反之则不成立. 大牛说两者是蛋生鸡鸡生蛋的关系,但我还是不明白,有懂的麻烦解释一下, 希望不要给出外文 ...
- spring手动配置
本文总结自:https://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/7183408.html SpringBoot中免除了大部分配置,但是对于一些特定的情况,还是需要我们进行手动配置的. ...
- ThinkPHP将上传问件添加到数据库
<?php namespace Home\Controller; /***************** use Think\Controller; ****命名空间****/ class Mes ...
