Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) A B C D dfs序+求两个不相交区间 最大权值和
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vladik is a competitive programmer. This year he is going to win the International Olympiad in Informatics. But it is not as easy as it sounds: the question Vladik face now is to find the cheapest way to get to the olympiad.
Vladik knows n airports. All the airports are located on a straight line. Each airport has unique id from 1 to n, Vladik's house is situated next to the airport with id a, and the place of the olympiad is situated next to the airport with id b. It is possible that Vladik's house and the place of the olympiad are located near the same airport.
To get to the olympiad, Vladik can fly between any pair of airports any number of times, but he has to start his route at the airport a and finish it at the airport b.
Each airport belongs to one of two companies. The cost of flight from the airport i to the airport j is zero if both airports belong to the same company, and |i - j| if they belong to different companies.
Print the minimum cost Vladik has to pay to get to the olympiad.
The first line contains three integers n, a, and b (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ a, b ≤ n) — the number of airports, the id of the airport from which Vladik starts his route and the id of the airport which he has to reach.
The second line contains a string with length n, which consists only of characters 0 and 1. If the i-th character in this string is 0, then i-th airport belongs to first company, otherwise it belongs to the second.
Print single integer — the minimum cost Vladik has to pay to get to the olympiad.
4 1 4
1010
1
5 5 2
10110
0
In the first example Vladik can fly to the airport 2 at first and pay |1 - 2| = 1 (because the airports belong to different companies), and then fly from the airport 2 to the airport 4 for free (because the airports belong to the same company). So the cost of the whole flight is equal to 1. It's impossible to get to the olympiad for free, so the answer is equal to 1.
In the second example Vladik can fly directly from the airport 5 to the airport 2, because they belong to the same company.
题意:n个机场 起点a 终点b 给你长度魏n的01串 符号相同表示机场属于同一家公司 相同公司通航免费 不同公司通航费用为abs(i-j) 输出最小的花费
题解:细细分析一下 相同公司的花费为零 不同公司任意点的花费为1 水
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
const int N=;
using namespace std;
int n,a,b;
char c[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&a,&b);
getchar();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%c",&c[i]);
if(c[a]==c[b])
{
printf("0\n");
return ;
}
else
{
printf("1\n");
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Chloe, the same as Vladik, is a competitive programmer. She didn't have any problems to get to the olympiad like Vladik, but she was confused by the task proposed on the olympiad.
Let's consider the following algorithm of generating a sequence of integers. Initially we have a sequence consisting of a single element equal to 1. Then we perform (n - 1) steps. On each step we take the sequence we've got on the previous step, append it to the end of itself and insert in the middle the minimum positive integer we haven't used before. For example, we get the sequence [1, 2, 1] after the first step, the sequence [1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1] after the second step.
The task is to find the value of the element with index k (the elements are numbered from 1) in the obtained sequence, i. e. after (n - 1) steps.
Please help Chloe to solve the problem!
The only line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 50, 1 ≤ k ≤ 2n - 1).
Print single integer — the integer at the k-th position in the obtained sequence.
3 2
2
4 8
4
In the first sample the obtained sequence is [1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1]. The number on the second position is 2.
In the second sample the obtained sequence is [1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 4, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1]. The number on the eighth position is 4.
题意:按照题目要求生成序列 问第k个数是什么
题解:将k转换为二进制 可以发现结果为末尾零的个数加一
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
const int N=;
using namespace std;
ll n,k;
int main()
{
scanf("%I64d %I64d",&k,&n);
ll ans=;
while(((n>>ans)&)==) ans++;
printf("%d\n",ans+);
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vladik and Chloe decided to determine who of them is better at math. Vladik claimed that for any positive integer n he can represent fraction  as a sum of three distinct positive fractions in form
as a sum of three distinct positive fractions in form 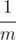 .
.
Help Vladik with that, i.e for a given n find three distinct positive integers x, y and z such that 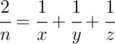 . Because Chloe can't check Vladik's answer if the numbers are large, he asks you to print numbers not exceeding 109.
. Because Chloe can't check Vladik's answer if the numbers are large, he asks you to print numbers not exceeding 109.
If there is no such answer, print -1.
The single line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 104).
If the answer exists, print 3 distinct numbers x, y and z (1 ≤ x, y, z ≤ 109, x ≠ y, x ≠ z, y ≠ z). Otherwise print -1.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
3
2 7 42
7
7 8 56
题意:公式题目
题解:我是莫名其妙暴力出来的
看了别人的题解 是直接分解式子的 2/n=1/n+1/(n+1)+1/n*(n+1)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
const int N=;
using namespace std;
int n;
ll x1,x2,x3;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int i=n;
while(i)
{
if(*i>n)
{
x1=i;
break;
}
i++;
}
ll zi1,mu1;
zi1=*x1-n;
mu1=n*x1;
i=x1+;
while(i)
{
if(zi1*i>mu1)
{
x2=i;
break;
}
i++;
}
ll zi2,mu2;
zi2=zi1*x2-mu1;
mu2=mu1*x2;
if(mu2%zi2==)
{
x3=mu2/zi2;
if(x1!=x3&&x2!=x3)
{
cout<<x1<<" "<<x2<<" "<<x3<<endl;
return ;
}
}
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Generous sponsors of the olympiad in which Chloe and Vladik took part allowed all the participants to choose a prize for them on their own. Christmas is coming, so sponsors decided to decorate the Christmas tree with their prizes.
They took n prizes for the contestants and wrote on each of them a unique id (integer from 1 to n). A gift i is characterized by integer ai — pleasantness of the gift. The pleasantness of the gift can be positive, negative or zero. Sponsors placed the gift 1 on the top of the tree. All the other gifts hung on a rope tied to some other gift so that each gift hung on the first gift, possibly with a sequence of ropes and another gifts. Formally, the gifts formed a rooted tree with n vertices.
The prize-giving procedure goes in the following way: the participants come to the tree one after another, choose any of the remaining gifts and cut the rope this prize hang on. Note that all the ropes which were used to hang other prizes on the chosen one are not cut. So the contestant gets the chosen gift as well as the all the gifts that hang on it, possibly with a sequence of ropes and another gifts.
Our friends, Chloe and Vladik, shared the first place on the olympiad and they will choose prizes at the same time! To keep themselves from fighting, they decided to choose two different gifts so that the sets of the gifts that hang on them with a sequence of ropes and another gifts don't intersect. In other words, there shouldn't be any gift that hang both on the gift chosen by Chloe and on the gift chosen by Vladik. From all of the possible variants they will choose such pair of prizes that the sum of pleasantness of all the gifts that they will take after cutting the ropes is as large as possible.
Print the maximum sum of pleasantness that Vladik and Chloe can get. If it is impossible for them to choose the gifts without fighting, print Impossible.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of gifts.
The next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the pleasantness of the gifts.
The next (n - 1) lines contain two numbers each. The i-th of these lines contains integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi) — the description of the tree's edges. It means that gifts with numbers ui and vi are connected to each other with a rope. The gifts' ids in the description of the ropes can be given in arbirtary order: vi hangs on ui or ui hangs on vi.
It is guaranteed that all the gifts hang on the first gift, possibly with a sequence of ropes and another gifts.
If it is possible for Chloe and Vladik to choose prizes without fighting, print single integer — the maximum possible sum of pleasantness they can get together.
Otherwise print Impossible.
8
0 5 -1 4 3 2 6 5
1 2
2 4
2 5
1 3
3 6
6 7
6 8
25
4
1 -5 1 1
1 2
1 4
2 3
2
1
-1
Impossible
题意:给你一颗树 树有点权 现在找到两个不关联的子树 输出最大的子树点权和
题解:dfs序将子树转化为区间 在n个区间中选取两个不相交的区间 输出最大的权值和。(具体看代码)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define dazhi 2147483647
using namespace std;
int n;
ll a[];
int u,v;
int pre[];
ll d[];
int in[];
int out[];
ll dp[];
int nedge=;
struct node
{
int from;
int to;
}N[];
struct xx
{
int l;
int r;
ll w;
}M[];
void add(int from ,int to)
{
nedge++;
N[nedge].to=to;
N[nedge].from=pre[from];
pre[from]=nedge;
}
int dfn=;
ll sum=;
map<int,int> mp;
map<int,int>mpp;
void getdfs(int root)
{
sum+=a[root];
in[root]=++dfn;
d[dfn]=sum;
mp[dfn]=root;
mpp[root]=;
for(int i=pre[root];i;i=N[i].from)
{
if(mpp[N[i].to])
continue;
getdfs(N[i].to);
}
out[root]=dfn;
}
bool cmp(struct xx aa,struct xx bb)
{
return aa.r<bb.r;
}
int main()
{
memset(pre,,sizeof(pre));
mp.clear();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
for(int i=;i<=n-;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
add(u,v);
add(v,u);
}
getdfs();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
M[i].l=in[i];
M[i].r=out[i];
M[i].w=d[out[i]]-d[in[i]]+a[mp[in[i]]];
}
sort(M+,M++n,cmp);
ll ans=-1e18-;
ll maxn=-1e18-;
int flag=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
dp[i]=-1e18-;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
maxn=max(M[i].w,maxn);
dp[M[i].r]=maxn;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(dp[i]<=dp[i-])
dp[i]=dp[i-];
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
ans=max(ans,M[i].w+dp[M[i].l-]);
if(dp[M[i].l-]!=(-1e18-))
flag=;
}
if(flag==)
printf("Impossible\n");
else
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return ;
}
/*
10
-1 2 -2 -3 -1 -1 0 -4 -5 -4
4 6
6 9
1 2
6 2
7 8
7 9
5 10
6 3
10 1
*/
Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) A B C D dfs序+求两个不相交区间 最大权值和的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1) D. Water Tree(dfs序加线段树)
思路: dfs序其实是很水的东西. 和树链剖分一样, 都是对树链的hash. 该题做法是:每次对子树全部赋值为1,对一个点赋值为0,查询子树最小值. 该题需要注意的是:当我们对一棵子树全都赋值为1的 ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) E. Vladik and cards 状压dp
E. Vladik and cards 题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/743/problem/E 题面 Vladik was bored on his way ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2)D - Chloe and pleasant prizes 树形dp
D - Chloe and pleasant prizes 链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/743/problem/D 题面 Generous sponsors of ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) C. Vladik and fractions 构造题
C. Vladik and fractions 题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/743/problem/C 题面 Vladik and Chloe decided ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2)B. Chloe and the sequence 数学
B. Chloe and the sequence 题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/743/problem/B 题面 Chloe, the same as Vla ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) A. Vladik and flights 水题
A. Vladik and flights 题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/743/problem/A 题面 Vladik is a competitive pr ...
- Codeforces Round #384(div 2)
A 题意:有n个机场处于一直线上,可两两到达,每个机场只可能属于两家公司中的一家(用0,1表示),现在要从a机场到b机场,可任意次转机.若机场i与机场j从属同一公司,则费用为0,否则费用为1.问最小费 ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) C. Vladik and fractions(构造题)
传送门 Description Vladik and Chloe decided to determine who of them is better at math. Vladik claimed ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2) B. Chloe and the sequence(规律题)
传送门 Description Chloe, the same as Vladik, is a competitive programmer. She didn't have any problems ...
随机推荐
- vs2017 asp.net FriendlyUrls 新特性
这个包如何使用呢?其实很简单,只需将nuget包添加到项目中,再调用routes.EnableFriendlyUrls(),你就可以通过/Foo来访问/Foo.aspx了!你也能够利用URL片段将更多 ...
- leetcode个人题解——#48 rotage image
思路:本题要求不能利用额外的二维数组实现旋转,所以重点在于弄清矩阵旋转的数学方法. 我的方法是,首先按照副对角线进行对称,然后按照水平中轴线进行对称即可. class Solution { publi ...
- [T-ARA][HUE]
歌词来源:http://music.163.com/#/song?id=22704406 wa du seu mo geum to yo do ga tae 어딜가도 스페셜한게 없어 [eo-dil ...
- 标准版 Eclipse (Eclipse standard 4.3.3) 添加 Tomcat 支持
步骤1:下载 Eclipse Tomcat 插件最新版:tomcatPluginV33.zip,官网下载最新版:http://www.eclipsetotale.com/tomcatPlugin.ht ...
- JS - Promise使用详解--摘抄笔记
第一部分: JS - Promise使用详解1(基本概念.使用优点) 一.promises相关概念 promises 的概念是由 CommonJS 小组的成员在 Promises/A 规范中提出来的. ...
- Beta周王者荣耀交流协会第三次Scrum会议
1.立会照片 成员王超,高远博,冉华,王磊,王玉玲,任思佳,袁玥全部到齐. master:王玉玲 2.时间跨度: 2017年11月12日 18:00 — 18:20 ,总计20分钟. 3.地点: 一食 ...
- 0324操作系统cmd功能的扩展
需求:1.实现清屏功能 2.实现不区分大小写功能 3.添加功能能添加新的命令符 设计:1.使用system("cls")清屏. 2.使用strlwr()函数把大写都变成小写 3.( ...
- SpringMVC 应知应会
springMVC 是表现层技术,可以用来代替 struts2,下面是简略图:主要是处理器和视图,只有这两个部分需要编写代码. springMVC 三大组件:处理器映射器,处理器适配器,视图解析器. ...
- IP地址转换32为长整型
Programming Question: Convert an IPv4 address in the format of null-terminated C string into a 32-bi ...
- python的N个小功能(更新文件)
########################################################################## #对于第二份文件:第一份与第二份不相同,以第二份为 ...
