JavaScript EventLoop
转自:http://cek.io/blog/2015/12/03/event-loop/
What is JavaScript
What is JavaScript anyway? Some words:
- It’s a single-threaded, non-blocking, asynchronous, concurrent language”
- It has a call stack, an event loop, a callback queue, some other apis and stuff
If you’re like me (or Philip Roberts, it seems), these words themselves don’t mean a ton. So let’s parse that out.
JavaScript Runtimes
JavaScript runtimes (like V8) have a heap (memory allocation) and stack (execution contexts). But they don’t have setTimeout, the DOM, etc. Those are web APIs in the browser.
JavaScript as we know it
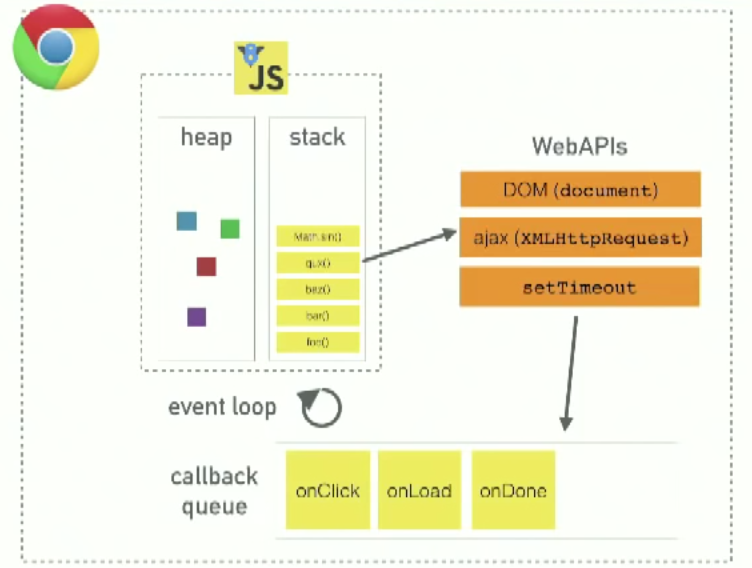
JavaScript in the browser has:
- a runtime like V8 (heap/stack)
- Web APIs that the browser provides, like the DOM, ajax, and
setTimeout - a callback queue for events with callbacks like
onClick,onLoad,onDone - an event loop
What’s the call stack?
JavaScript is single-threaded, meaning it has a single call stack, meaning it can do one thing at a time. The call stack is basically a data structure which records where in the program we are. If we step into a function, we push something onto the stack. If we return from a function, we pop off the top of the stack.
When our program throws an error, we see the call stack in the console. We see the state of the stack (which functions have been called) when that error happened.
Blocking
An important question that this relates to: what happens when things are slow? In other words, blocking. Blocking doesn’t have a strict definition; really it’s just things that are slow. console.log isn’t slow, but while loops from 1 to 1,000,000,000, image processing, or network requests are slow. Those things that are slow and on the stack are blocking.
Since JS is single-threaded, we make a network request and have to wait until it’s done. This is a problem in the browser—while we wait on a request, the browser is blocked (can’t click things, submit forms, etc.). The solution is asynchronous callbacks.
Concurrency, where we realize there’s a lie above
It’s a lie that JavaScript can only do one thing at a time. It’s true: JavaScript the runtime can only do one thing at a time. It can’t make an ajax request while doing other code. It can’t do a setTimeout while doing other code. But we can do things concurrently, because the browser is more than the runtime (remember the grainy image above).
The stack can put things into web APIs, which (when done) push callbacks onto task queue, and then…the event loop. Finally we get to the event loop. It’s the simplest little piece in this equation, and it has one very simple job. Look at the stack and look at the task queue; if the stack is empty, it takes the first thing off of the queue and pushes it onto the stack (back in JS land, back inside V8).
Louping it all together
Philip built an awesome tool to visualize all of this, called Loupe. It’s a tool that can visualize the JavaScript runtime at runtime.
Let’s use it to look at a simple example: logging a few things to the console, with one console.log happening asynchronously in a setTimeout.
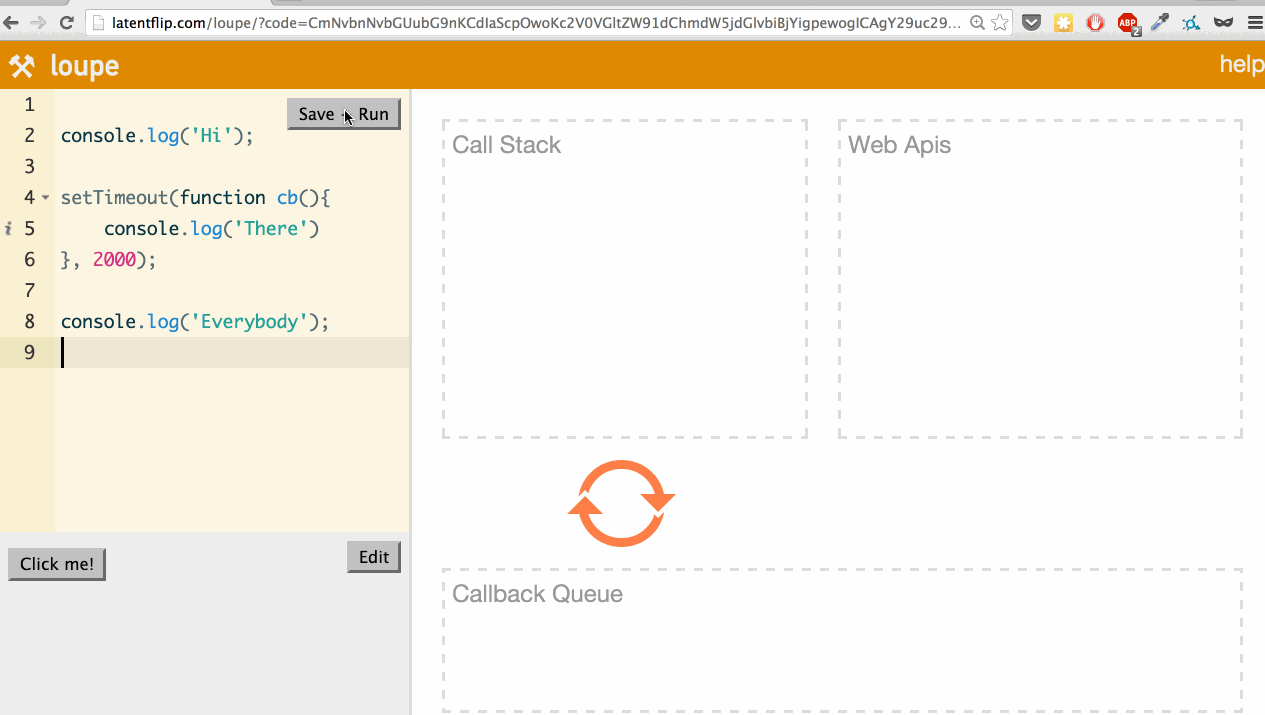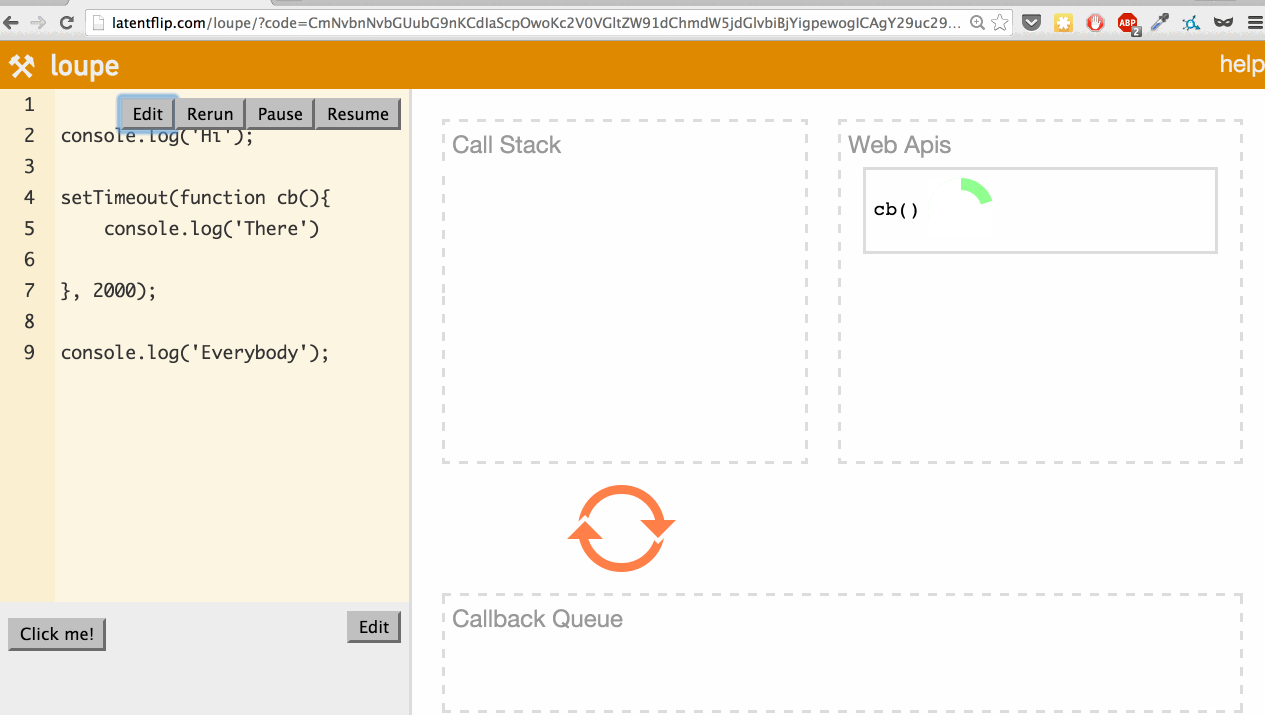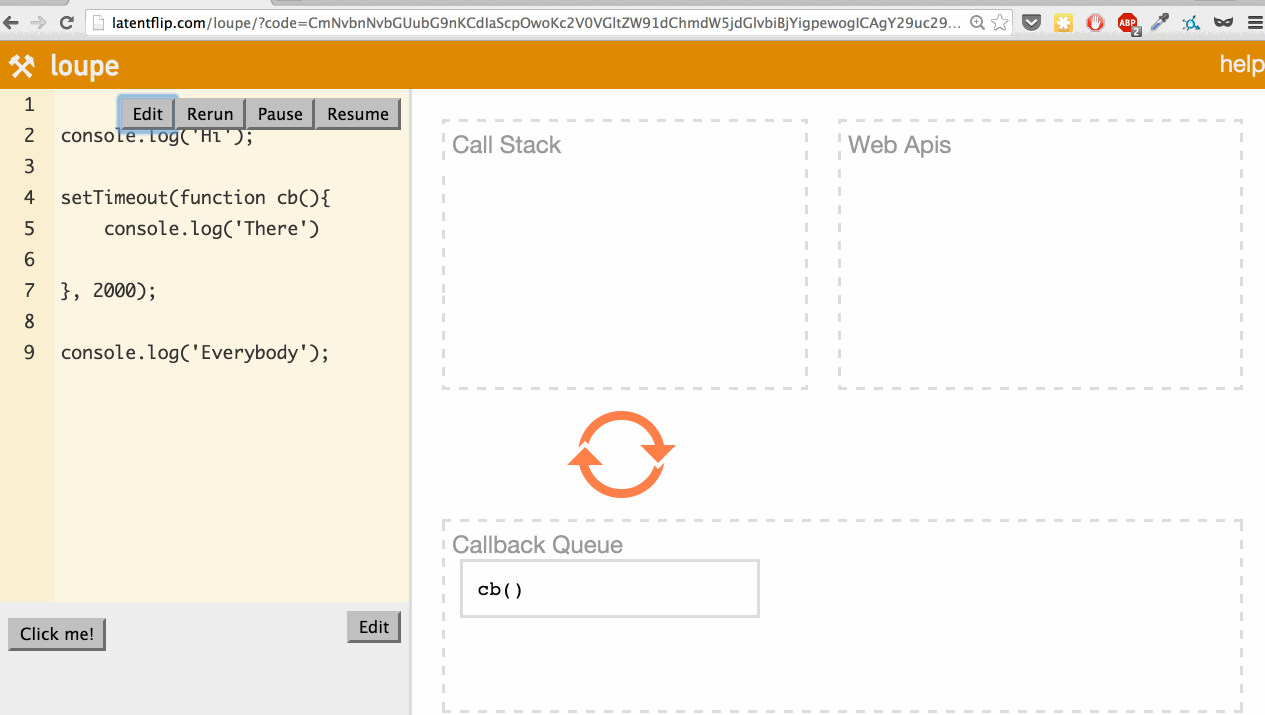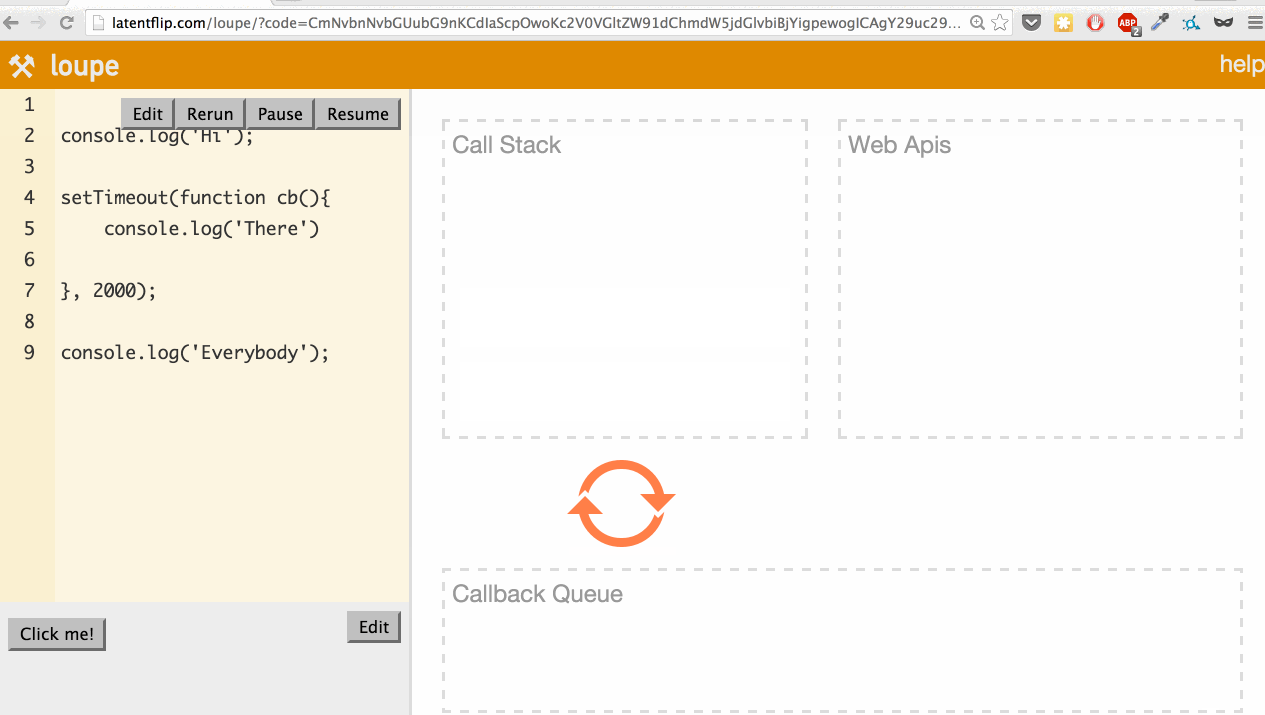
What’s actually happening here? Let’s go through it:
- We step into the
console.log('Hi');function, so it’s pushed onto the call stack. console.log('Hi');returns, so it’s popped off the top of the stack.- We step into the
setTimeoutfunction, so it’s pushed onto the call stack. setTimeoutis part of the web API, so the web API handles that and times out the 2 seconds.- We continue our script, stepping into the
console.log('Everybody')function, pushing it onto the stack. console.log('Everybody')returns, so it’s popped off the stack.- The 2-second timeout completes, so the callback moves to the callback queue.
- The event loop checks if the call stack is empty. If it were not empty, it would wait. Because it is empty, the callback is pushed onto the call stack.
console.log('Everybody')returns, so it’s popped off the call stack.
An interesting aside: setTimeout(function(...), 0). setTimeout with 0 isn’t necessarily intuitive, except when considered in the context of call stack and event loop. It basically defers something until the stack is clear.
JavaScript EventLoop的更多相关文章
- 对javascript EventLoop事件循环机制不一样的理解
前置知识点: 浏览器原理,浏览器内核5种线程及协作,JS引擎单线程设计推荐阅读: 从浏览器多进程到JS单线程,JS运行机制最全面的一次梳理 [FE]浏览器渲染引擎「内核」 js异步编程,Promise ...
- 初识JavaScript EventLoop
Event Loop指的是计算机系统的一种运行机制.JavaScript采用此机制解决单线程引发相关问题 在浏览器中的web应用会涉及到.JavaScript引擎.WebAPI.Event Loop. ...
- JavaScript的sleep实现--Javascript异步编程学习
一.原始需求 最近在做百度前端技术学院的练习题,有一个练习是要求遍历一个二叉树,并且做遍历可视化即正在遍历的节点最好颜色不同 二叉树大概长这个样子: 以前序遍历为例啊, 每次访问二叉树的节点加个sle ...
- JavaScript Concurrency model and Event Loop 并发模型和事件循环机制
原文地址:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/EventLoop JavaScript 有一个基于 event loop 的 ...
- javascript运行时中的堆栈和队列
下面是一个理论上的模型,js引擎着重实现和优化了描述的这几个语义 可视化描述 栈(stack) var a = 10; function bar(x) { var b = 5; fn(x + b); ...
- JavaScript 异步和单线程
JavaScript语言本身是单线程的,所以它自身不可能是异步.所谓单线程,就必然意味着:所有任务需要排队,前一个任务结束,才会执行后一个任务. 但js的宿主环境(比如浏览器,Node)是多线程的.宿 ...
- 【JavaScript】要点知识的个人总结(1)
米娜桑,哦哈哟~ 该篇章主要基于链接中的参考内容和代码测试得出的结论,面向具有一定基础的前端开发者.如有错误,请指出与包涵. 原型链的解释 https://juejin.im/post/5aa78fe ...
- js的单线程和异步
前言 说到js的单线程(single threaded)和异步(asynchronous),很多同学不禁会想,这不是自相矛盾么?其实,单线程和异步确实不能同时成为一个语言的特性.js选择了成为单线程的 ...
- 【 js 基础 】【 源码学习 】 setTimeout(fn, 0) 的作用
在 zepto 源码中,$.fn 对象 有个 ready 函数,其中有这样一句 setTimeout(fn,0); $.fn = { ready: function(callback){ // don ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces Round #257 (Div. 2) B
B. Jzzhu and Sequences time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- So easy Webservice 8.spring整合CXF 发布WS
1.添加jar包(cxf的jar包中包含了spring的jar包),添加spring配置文件 2.web.xml中配置CXFServlet,过滤WS服务的地址 <!-- 配置CXFServlet ...
- python_way day17 html-day3 前端插件(fontawsome,easyui,bootstrap,jqueryui,bxslider,jquerylazyload),web框架
python_way day17 一.模板插件 图标的插件 fontawsome: 后台管理: easyui jqueryui 很多网站都会用: bootstrap :引入jQuery:(2.x,1. ...
- .NET在后置代码中输入JS提示语句(背景不会变白)
来源:http://niunan.iteye.com/blog/248256 Page.ClientScript.RegisterStartupScript(Page.GetType(), " ...
- git学习笔记08-分支管理策略-实际上我们应该怎么应用分支
Git用Fast forward模式(快进模式),但这种模式下,删除分支后,会丢掉分支信息. 如果要强制禁用Fast forward模式,Git就会在merge时生成一个新的commit,这样,从分支 ...
- javascript中的计时器
javascript中的定时器有两种:一种是一次性定时器,一种是可以持续使用的定时器: 1:一次性定时器setTimeout(a,b):兼容ie的任何版本 该方法接受两个参数,第一个是要执行的代码,第 ...
- Redis实践操作之—— keyspace notification(键空间通知)
一.需求分析: 设置了生存时间的Key,在过期时能不能有所提示? 如果能对过期Key有个监听,如何对过期Key进行一个回调处理? 如何使用 Redis 来实现定时任务? 二.序言: 本文所说的定时任务 ...
- 基础2 JVM
1. 内存模型以及分区,需要详细到每个区放什么. //运行时数据区域 方法区 Method Area 各个线程共享的内存区域 存储已被虚拟机加载的类信息 常量 静态变量 即时编译器编译后的代码 虚拟机 ...
- 转:strcmp函数实现及分析
转自:strcmp函数实现及详解 strcmp函数是C/C++中基本的函数,它对两个字符串进行比较,然后返回比较结果,函数形式如下:int strcmp(constchar*str1,constcha ...
- 牛客网 --java问答题
http://www.nowcoder.com/ 主要是自己什么都不怎么会.在这里可以学习很多的! 第一天看题自己回答,第二天看牛客网的答案! 1 什么是Java虚拟机?为什么Java被称作是“平台无 ...
