JAVA设计模式:装饰模式
前面我们学习了代理模式:
代理模式主要使用了java的多态,干活的是被代理类,代理类主要是接活,你让我干活,好,我交给幕后的类去干,你满意就成,那怎么知道被代理类能不能干呢?同根就成,大家知根知底,你能做啥,我能做啥都清楚得很,同样一个接口。
本次我们学习下装饰模式:
装饰模式又称为包装模式,装饰模式以对客户端透明的方式扩展对象功能,相对于代理而言,代理是不让客户端知道真实对象的信息,装饰模式是基层关系的一个替代方案。
装饰模式是采用对客户端透明的方式动态的给一个对象添加了更多职责,对于原来被装饰的对象而言在装饰前和后并没有什么不同。装饰模式可以在不使用创造更多子类的情况下扩展对象的功能。
类图如下:
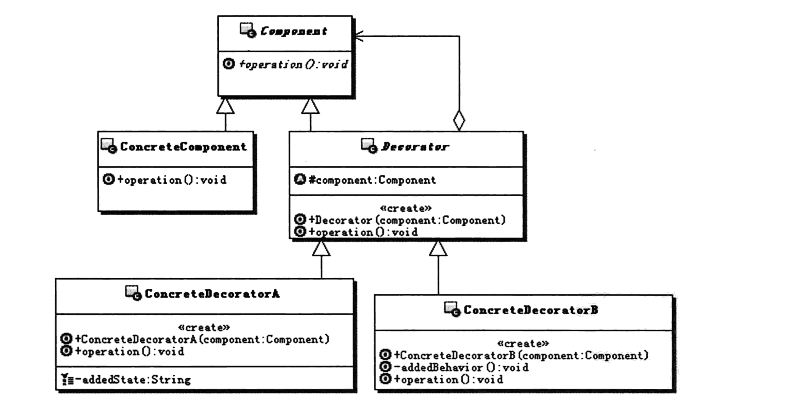
Component:组件对象的接口,规范那些准备添加附加功能类的对象。
ConcreateComponent:具体的组件对象,实现组件对象接口,通常就是被装饰的原始对象,也就是可以给这个对象添加附加的功能。
Decorator:所有装饰器的抽象父类,需要定义一个与组件对象一致的接口,并且持有一个Component对象,其实就是原始对象,被装饰的对象。
ConcreateDecorator:实际的装饰对象,实现具体要像被装饰对象添加的功能。
抽象的接口:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public interface Component {
public void operation();
}
原始对象,即需要被装饰的对象:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class ConcreateComponent implements Component{
public ConcreateComponent(){};
@Override
public void operation()
{
System.out.println("开车");
}
}
所有装饰对象的父类:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public abstract class Decorator implements Component {
private Component component;
public Decorator(Component component)
{
this.component = component;
}
public void operation()
{
this.component.operation();
}
}
实际装饰对象A:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class ConCreateDecoratorA extends Decorator {
public ConCreateDecoratorA(Component component) {
super(component);
}
public void addedOperation()
{
System.out.println("晚上");
}
public void operation()
{
addedOperation();
super.operation();
}
}
实际装饰对象B:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class ConCreateDecoratorB extends Decorator {
public ConCreateDecoratorB(Component component) {
super(component);
}
public void addedOperation()
{
System.out.println("兜风");
}
public void operation()
{
super.operation();
addedOperation();
}
}
客户端:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator; public class Client
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
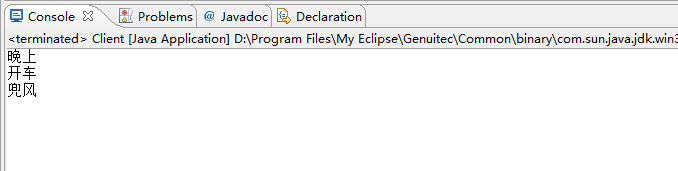
Component component = new ConcreateComponent(); Decorator decorator = new ConCreateDecoratorB(new ConCreateDecoratorA(component));
decorator.operation();
} }
测试结果:
装饰模式的定义 : 透明的给一个对象添加功能,并能够实现功能的动态组合.
在装饰模式的实现中,为了能够实现和原来使用被装饰对象的代码无缝结合,是通过定义一个抽象类,让这个类实现与被装饰对象相同的接口,然后在具体的实现类中,转调被装饰的对象,在转调的前后添加新的功能,这就实现了给被装饰对象增加功能.
下面举一个实际的例子:
定义一个接口:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator; /**
* 定义被装饰者 和 装饰者 共同的接口
* @author Pony
*
*/
public interface Human
{
public void wearClothes(); public void walkToWhere();
}
定义原始对象:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator; /**
* 定义被装饰者,被装饰者初始状态有些自己的装饰
* @author Pony
*
*/
public class Person implements Human { @Override
public void walkToWhere() {
System.out.println("穿什么呢。。"); } @Override
public void wearClothes() {
System.out.println("去哪里呢。。");
} }
定义装饰对象:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class DecoratorHuman implements Human {
private Human human;
public DecoratorHuman(Human human) {
this.human = human;
}
public void wearClothes() {
human.wearClothes();
}
public void walkToWhere() {
human.walkToWhere();
}
}
下面定义三种装饰,这是第一个,第二个第三个功能依次细化,即装饰者的功能越来越多
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class Decorator_zero extends DecoratorHuman {
public Decorator_zero(Human human) {
super(human);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public void goHome() {
System.out.println("进房子。。");
}
public void findMap() {
System.out.println("书房找找Map。。");
}
@Override
public void wearClothes() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.wearClothes();
goHome();
}
@Override
public void walkToWhere() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.walkToWhere();
findMap();
}
}
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class Decorator_first extends DecoratorHuman {
public Decorator_first(Human human) {
super(human);
}
public void goClothespress() {
System.out.println("去衣柜找找看。。");
}
public void findPlaceOnMap() {
System.out.println("在Map上找找。。");
}
@Override
public void wearClothes() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.wearClothes();
goClothespress();
}
@Override
public void walkToWhere() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.walkToWhere();
findPlaceOnMap();
}
}
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class Decorator_two extends DecoratorHuman {
public Decorator_two(Human human) {
super(human);
}
public void findClothes() {
System.out.println("找到一件D&G。。");
}
public void findTheTarget() {
System.out.println("在Map上找到神秘花园和城堡。。");
}
@Override
public void wearClothes() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.wearClothes();
findClothes();
}
@Override
public void walkToWhere() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.walkToWhere();
findTheTarget();
}
}
客户端:
package com.njupt.study.designmodle.decorator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Human person = new Person();
DecoratorHuman decorator = new Decorator_two(new Decorator_first(
new Decorator_zero(person)));
decorator.wearClothes();
decorator.walkToWhere();
}
}
测试结果:
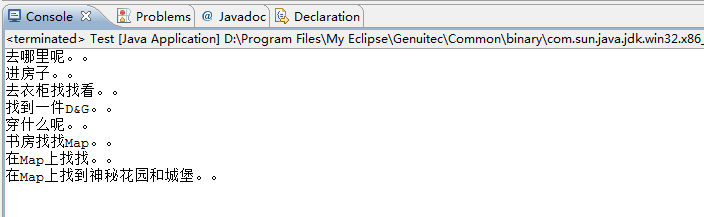
其实就是进房子找衣服,然后找地图这样一个过程,通过装饰者的三层装饰,把细节变得丰富。
关键点:
1、Decorator抽象类中,持有Human接口,方法全部委托给该接口调用,目的是交给该接口的实现类即子类进行调用。
2、Decorator抽象类的子类(具体装饰者),里面都有一个构造方法调用super(human),这一句就体现了抽象类依赖于子类实现即抽象依赖于实现的原则。因为构造里面参数都是Human接口,只要是该Human的实现类都可以传递进去,即表现出Decorator dt = new Decorator_second(new Decorator_first(new Decorator_zero(human)));这种结构的样子。所以当调用dt.wearClothes();dt.walkToWhere()的时候,又因为每个具体装饰者类中,都先调用super.wearClothes和super.walkToWhere()方法,而该super已经由构造传递并指向了具体的某一个装饰者类(这个可以根据需要调换顺序),那么调用的即为装饰类的方法,然后才调用自身的装饰方法,即表现出一种装饰、链式的类似于过滤的行为。
3、具体被装饰者类,可以定义初始的状态或者初始的自己的装饰,后面的装饰行为都在此基础上一步一步进行点缀、装饰。
4、装饰者模式的设计原则为:对扩展开放、对修改关闭,这句话体现在我如果想扩展被装饰者类的行为,无须修改装饰者抽象类,只需继承装饰者抽象类,实现额外的一些装饰或者叫行为即可对被装饰者进行包装。所以:扩展体现在继承、修改体现在子类中,而不是具体的抽象类,这充分体现了依赖倒置原则,这是自己理解的装饰者模式。
JAVA设计模式:装饰模式的更多相关文章
- Java设计模式---装饰模式
装饰模式又名包装(Wrapper)模式.装饰模式以对客户端透明的方式扩展对象的功能,是继承关系的一个替代方案. 装饰模式的结构 装饰模式以对客户透明的方式动态地给一个对象附加上更多的责任.换言之,客户 ...
- Java设计模式-装饰模式(Decorator)
顾名思义,装饰模式就是给一个对象增加一些新的功能,而且是动态的,要求装饰对象和被装饰对象实现同一个接口,装饰对象持有被装饰对象的实例,关系图如下: Source类是被装饰类,Decorator类是一个 ...
- Java设计模式—装饰模式
装饰模式是一种比较常见的模式. 定义为:动态的给一个对象添加一些额外的职责.就增加功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更加灵活. 装饰模式的通用类图如下: 装饰模式的构成: 1) 抽象构件(Component ...
- Java设计模式——装饰模式
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/xu__cg/article/details/53024490 抽象构件 public interface CarInterface { void m ...
- Java设计模式学习记录-装饰模式
前言 装饰模式也是一种结构型模式,主要是目的是相对于类与类之间的继承关系来说,使用装饰模式可以降低耦合度.JDK中有不少地方都使用到了装饰模式,例如Java的各种I/O流,javax.swing包中一 ...
- Java设计模式(7)装饰模式(Decorator模式)
Decorator常被翻译成"装饰",我觉得翻译成"油漆工"更形象点,油漆工(decorator)是用来刷油漆的,那么被刷油漆的对象我们称decoratee.这 ...
- Java设计模式(三) 抽象工厂模式
原创文章,同步发自作者个人博客,转载请注明出处 http://www.jasongj.com/design_pattern/abstract_factory/ 抽象工厂模式解决的问题 上文<工厂 ...
- Java设计模式(十二) 策略模式
原创文章,同步发自作者个人博客,http://www.jasongj.com/design_pattern/strategy/ 策略模式介绍 策略模式定义 策略模式(Strategy Pattern) ...
- Java设计模式(二) 工厂方法模式
本文介绍了工厂方法模式的概念,优缺点,实现方式,UML类图,并介绍了工厂方法(未)遵循的OOP原则 原创文章.同步自作者个人博客 http://www.jasongj.com/design_patte ...
- Java设计模式(一) 简单工厂模式不简单
摘要:本文介绍了简单工厂模式的概念,优缺点,实现方式,以及结合Annotation和反射的改良方案(让简单工厂模式不简单).同时介绍了简单工厂模式(未)遵循的OOP原则.最后给出了简单工厂模式在JDB ...
随机推荐
- jQuery-ui datepicker的使用演示代码
这两天使用jquery做一个web端展示的工具,遇到了不少问题也学到了不少知识.其中有一个就是在页面中显示日期选择器的功能,通过百度直接使用的是jquery datepicker 看到一篇使用说明很不 ...
- jsp发布后应用根目录
1.发布到tomcat后获取应用的根目录 ServletContext s1=this.getServletContext(); String temp=s1.getRealPath("/& ...
- Run Loop简介 分类: ios技术 ios相关 2015-03-11 22:21 73人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
做了一年多的IOS开发,对IOS和Objective-C深层次的了解还十分有限,大多还停留在会用API的级别,这是件挺可悲的事情.想学好一门语言还是需要深层次的了解它,这样才能在使用的时候得心应手,出 ...
- 更深入一点理解switch语句及c/c++对const的处理
首先看一到用 c 编写的程序/* -------------------- filename : ta.c --------------- */int switch_test_first( int x ...
- 关于jquery的$each((Object, function(p1, p2)用法
通过它,你可以遍历对象.数组的属性值并进行处理. 使用说明 each函数根据参数的类型实现的效果不完全一致: 1.遍历对象(有附加参数) $.each(Object, function(p1, p2) ...
- VMWare虚拟机启动报错物理内存不足
尝试了三种修改 1.说是微软补丁KB2995388冲突-->>失败 2.修改win8.1高级环境性能更改设置-->>失败 3.修改config.ini文件-->>成 ...
- windows Vista-Server 2016系列激活脚本.cmd
@ECHO OFFTITLE Windows 全版本系统激活ECHO 检测 操作系统版本...SET RQR=REG QUERY "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windo ...
- Practice Round China New Grad Test 2014 报告
今天有Google of Greater China Test for New Grads of 2014的练习赛,主要是为了过几天的校园招聘测试做练习用的,帮助熟悉平台,题目嘛,个人觉得除了A题外, ...
- 学习笔记::LCT
今天听见茹大神20分钟讲完了LCT,10分钟讲完平衡树,5分钟讲完树剖,感觉自己智商还不及他一半... 还有很多不懂:2017/1/15 的理解: access是干什么用的? 不知道,只知道他是用来把 ...
- arcgis 瓦片图加载规则(转载)
arcgis 瓦片图加载规则 最近需要做地图离线的功能,要能下载指定区域的瓦片图,我们都知道如何加载谷歌和天地图的加载规则,但是网上貌似没有找到如何加载arcgis自己发布的瓦片图规则,好不容易找到一 ...
