Go LRU Cache 抛砖引玉
目录
1. LRU Cache
2. container/list.go
2.1 list 数据结构
2.2 list 使用例子
3. transport.go connLRU
4. 结尾
正文
1. LRU Cache
- package cache
- import (
- "container/list"
- "sync"
- )
- // entry 存储的实体
- type entry struct {
- key, val interface{}
- }
- // Cache 缓存结构
- type Cache struct {
- // m 保证 LRU Cache 访问线程安全
- rw sync.RWMutex
- // max 标识缓存容量的最大值, = 0 标识无限缓存
- max int
- // list 是 entry 循环双向链表
- list *list.List
- // pond entry 缓存池子 key -> entry
- pond map[interface{}]*list.Element
- }
- // New 构建 LRU Cache 缓存结构
- func New(max int) *Cache {
- return &Cache{
- max: max,
- list: list.New(),
- pond: make(map[interface{}]*list.Element),
- }
- }
- func (c *Cache) delete(key interface{}) {
- element, ok := c.pond[key]
- if ok {
- delete(c.pond, key)
- c.list.Remove(element)
- return
- }
- }
- // Set 设置缓存
- func (c *Cache) Set(key, val interface{}) {
- c.rw.Lock()
- defer c.rw.Unlock()
- // 看是否进入删除分支
- if val == nil {
- c.delete(key)
- return
- }
- element, ok := c.pond[key]
- if ok {
- // 重新设置 value 数据
- element.Value.(*entry).val = val
- // set key nil exists 进入 update 逻辑
- c.list.MoveToFront(element)
- return
- }
- // 首次添加
- c.pond[key] = c.list.PushFront(&entry{key, val})
- // 数据过多, 删除尾巴数据
- if c.list.Len() > c.max && c.max > 0 {
- delete(c.pond, c.list.Remove(c.list.Back()).(*entry).key)
- }
- }
- // Get 获取缓存
- func (c *Cache) Get(key interface{}) (val interface{}, ok bool) {
- c.rw.RLock()
- defer c.rw.RUnlock()
- if element, ok := c.pond[key]; ok {
- // 获取指定缓存值
- val, ok = element.Value.(*entry).val, true
- // 调整缓存热点
- c.list.MoveToFront(element)
- }
- return
- }
原理是 1. RWLock 做线程安全 2. list 双向链表保存时间新老关系 2. map 为了让时间复杂度到 O(1).
使用教程:
- // 创建
- c := cache.New(1)
- // 设置
- c.Set("123", "123")
- c.Set("234", "234")
- // 使用
- fmt.Println(c.Get("123"))
- fmt.Println(c.Get("234"))
- // 删除
- c.Set("123", nil)
2. container/list.go
2.1 list 数据结构
上面 LRU Cache 代码中引用了 "container/list" , 简单分析下 list, 加深基础数据结构的了解.
- // Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
- // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
- // license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
- // Package list implements a doubly linked list.
- //
- // To iterate over a list (where l is a *List):
- // for e := l.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
- // // do something with e.Value
- // }
- //
- package list
- // Element is an element of a linked list.
- type Element struct {
- // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
- // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
- // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
- // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
- // element (l.Front()).
- next, prev *Element
- // The list to which this element belongs.
- list *List
- // The value stored with this element.
- Value interface{}
- }
- // Next returns the next list element or nil.
- func (e *Element) Next() *Element {
- if p := e.next; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
- return p
- }
- return nil
- }
- // Prev returns the previous list element or nil.
- func (e *Element) Prev() *Element {
- if p := e.prev; e.list != nil && p != &e.list.root {
- return p
- }
- return nil
- }
- // List represents a doubly linked list.
- // The zero value for List is an empty list ready to use.
- type List struct {
- root Element // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
- len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
- }
它是个特殊循环双向链表数据结构, 特殊之处在于 Element::List 指向头结点(root list).
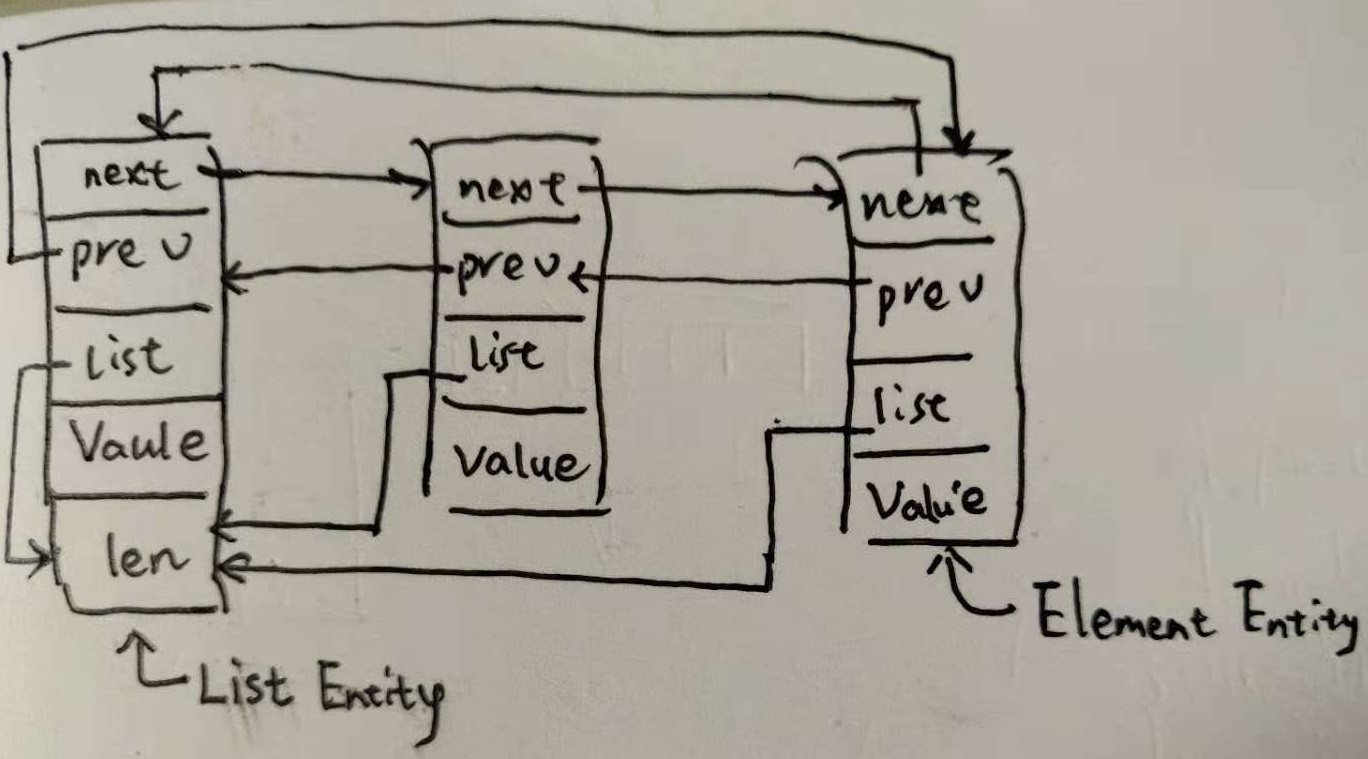
关于业务 list.go 具体实现部分我们不表.
2.2 list 使用例子
- func Test_List_Demo(t *testing.T) {
- // Persion 普通人
- type Persion struct {
- Name string
- Age int
- }
- pers := list.New()
- // 链表数据填充
- pers.PushBack(&Persion{Name: "wang", Age: 31})
- pers.PushFront(&Persion{Name: "zhi", Age: 31})
- fmt.Printf("List Len() = %d\n", pers.Len())
- if pers.Len() != 2 {
- t.Fatal("pers.Len() != 2 data faild")
- }
- // 开始遍历数据
- for element := pers.Front(); element != nil; element = element.Next() {
- per, ok := element.Value.(*Persion)
- if !ok {
- panic(fmt.Sprint("Persion list faild", element.Value))
- }
- fmt.Println(per)
- }
- // 数据删除
- for element := pers.Front(); element != nil; {
- next := element.Next()
- pers.Remove(element)
- element = next
- }
- fmt.Printf("List Len() = %d\n", pers.Len())
- if pers.Len() != 0 {
- t.Fatal("pers.Len() != 0 data faild")
- }
- }
单元测试结果:
- Running tool: /usr/local/go/bin/go test -timeout 30s -run ^Test_List_Demo$ demo/src/container/list -v -count=1
- === RUN Test_List_Demo
- List Len() = 2
- &{zhi 31}
- &{wang 31}
- List Len() = 0
- --- PASS: Test_List_Demo (0.00s)
- PASS
- ok demo/src/container/list 0.002s
3. transport.go connLRU
抛一段 Go 源码中一处应用, 小学以小用
- //
- // src/net/http/transport.go
- //
- // persistConn wraps a connection, usually a persistent one
- // (but may be used for non-keep-alive requests as well)
- type persistConn struct {
- ...
..
.- }
- type connLRU struct {
- ll *list.List // list.Element.Value type is of *persistConn
- m map[*persistConn]*list.Element
- }
- // add adds pc to the head of the linked list.
- func (cl *connLRU) add(pc *persistConn) {
- if cl.ll == nil {
- cl.ll = list.New()
- cl.m = make(map[*persistConn]*list.Element)
- }
- ele := cl.ll.PushFront(pc)
- if _, ok := cl.m[pc]; ok {
- panic("persistConn was already in LRU")
- }
- cl.m[pc] = ele
- }
- func (cl *connLRU) removeOldest() *persistConn {
- ele := cl.ll.Back()
- pc := ele.Value.(*persistConn)
- cl.ll.Remove(ele)
- delete(cl.m, pc)
- return pc
- }
- // remove removes pc from cl.
- func (cl *connLRU) remove(pc *persistConn) {
- if ele, ok := cl.m[pc]; ok {
- cl.ll.Remove(ele)
- delete(cl.m, pc)
- }
- }
- // len returns the number of items in the cache.
- func (cl *connLRU) len() int {
- return len(cl.m)
- }
4. 结尾
很多代码, 很多事情也都平淡无奇, 但凡事种种都离不开用心, 反复琢磨 ~ 方能长久
欢迎批评指正交流 ~ good luckly ~
Go LRU Cache 抛砖引玉的更多相关文章
- 从 LRU Cache 带你看面试的本质
前言 大家好,这里是<齐姐聊算法>系列之 LRU 问题. 在讲这道题之前,我想先聊聊「技术面试究竟是在考什么」这个问题. 技术面试究竟在考什么 在人人都知道刷题的今天,面试官也都知道大家会 ...
- [LeetCode] LRU Cache 最近最少使用页面置换缓存器
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the fol ...
- 【leetcode】LRU Cache
题目简述: Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support t ...
- LeetCode:LRU Cache
题目大意:设计一个用于LRU cache算法的数据结构. 题目链接.关于LRU的基本知识可参考here 分析:为了保持cache的性能,使查找,插入,删除都有较高的性能,我们使用双向链表(std::l ...
- LRU Cache实现
最近在看Leveldb源码,里面用到LRU(Least Recently Used)缓存,所以自己动手来实现一下.LRU Cache通常实现方式为Hash Map + Double Linked Li ...
- 【leetcode】LRU Cache(hard)★
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the fol ...
- [LintCode] LRU Cache 缓存器
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the fol ...
- LRU Cache [LeetCode]
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the fol ...
- 43. Merge Sorted Array && LRU Cache
Merge Sorted Array OJ: https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/merge-sorted-array/ Given two sorted integer ...
随机推荐
- DMS是临时解决方案?
DMS是临时解决方案? Who Says DMS Is an Interim Solution? 现在是认真对待DMS驱动程序监控系统的时候了. 特斯拉(Tesla)在台湾高速公路上撞上翻倒卡车的镜头 ...
- GPU端到端目标检测YOLOV3全过程(下)
GPU端到端目标检测YOLOV3全过程(下) Ubuntu18.04系统下最新版GPU环境配置 安装显卡驱动 安装Cuda 10.0 安装cuDNN 1.安装显卡驱动 (1)这里采用的是PPA源的安装 ...
- C语言代码区错误以及编译过程
C语言代码区错误 欲想了解C语言代码段会有如何错误,我们必须首先了解编译器是如何把C语言文本信息编译成为可以执行的机器码的. 背景介绍 测试使用的C语言代码 导入标准库,定义宏变量,定义结构体,重命名 ...
- Java8 Lambda表达式、Optional类浅析
1.概念 Lambda是一个匿名函数,可以将其理解为一段可以传递的代码(将代码像数据一样进行传递)可以写出更简洁.更灵活的代码.作为一种更紧凑的代码风格,使得java语言的表达能利得到了提升. 2. ...
- 【VBA】日期时间
当前日期: Sub 测试() Debug.Print Date End Sub 当前时间: Sub 测试() Debug.Print Date End Sub 几月: Sub 测试() Debug.P ...
- 【SQLite】教程05-SQLite创建数据库、附加、分离数据库
创建数据库 .quit命令 退出sqlite 提示符 .quit .dump 命令 使用 SQLite .dump 点命令来导出完整的数据库在一个文本文件中,如下所示: sqlite3 Test.db ...
- 【题解】codeforces 8c Looking for Order 状压dp
题目描述 Lena喜欢秩序井然的生活.一天,她要去上大学了.突然,她发现整个房间乱糟糟的--她的手提包里的物品都散落在了地上.她想把所有的物品都放回她的手提包.但是,这里有一点问题:她一次最多只能拿两 ...
- Vue(5)计算属性computed
前言 一般情况下属性都是放到data中的,但是有些属性可能是需要经过一些逻辑计算后才能得出来,那么我们可以把这类属性变成计算属性.比如以下: <div id="example" ...
- 【LeetCode每日一题 Day 5】5. 最长回文子串
大家好,我是编程熊,今天是LeetCode每日一题的第五天,一起学习LeetCode第五题<最长回文子串>. 题意 给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串. 示例 输入:s = & ...
- 02 jumpserver系统设置
2.系统设置: (1)基本设置: (2)邮件设置: 1)163邮箱设置: 2)在jumpserver上填写邮箱信息: 3)邮件测试信息如下: (3)邮件内容设置: (4)终端设置: (5)安全设置:
