从浏览器发送请求给SpringBoot后端时,是如何准确找到哪个接口的?(下篇)
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行
注意: 本文 SpringBoot 版本为 2.5.2; JDK 版本 为 jdk 11.
前言:
前文:你了解SpringBoot启动时API相关信息是用什么数据结构存储的吗?(上篇)
写文的原因,我前文说过就不再复述了。
问题大致如下:
为什么浏览器向后端发起请求时,就知道要找的是哪一个接口?采用了什么样的匹配规则呢?
SpringBoot 后端是如何存储 API 接口信息的?又是拿什么数据结构存储的呢?
@ResponseBody@GetMapping("/test")public String test(){return "test";}
说实话,听他问完,我感觉我又不够卷了,简直灵魂拷问,我一个答不出来。我们一起去了解了解吧!
如果文章中有不足之处,请你一定要及时批正!在此郑重感谢。
一、请求流程
其他的不看了,我们就直接从 DispatcherServlet 处入手了.
我们只看我们关注的,不是我们关注的,我们就不做多讨论了.
这边同样也画了一个流程图给大家参考:
1.1、DispatcherServlet
我们都熟悉SpringMVC 处理请求的模式,就不多讨论了.直接肝了.0
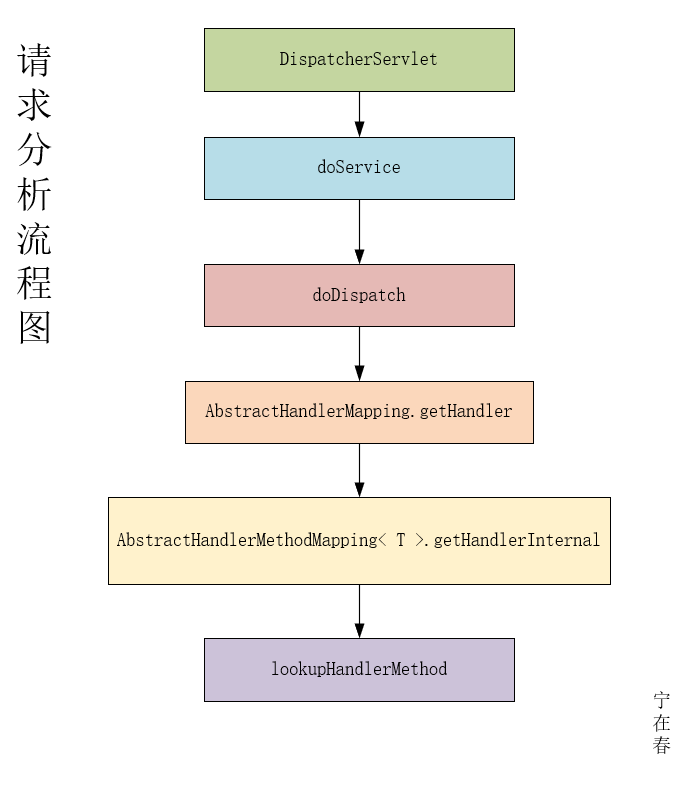
1)doService
@Overrideprotected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {logRequest(request);// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));}}}// 使框架对象可用于处理程序和视图对象。request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());if (this.flashMapManager != null) {FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);if (inputFlashMap != null) {request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));}request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);}RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;if (this.parseRequestPath) {previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);}try {// 从这里去下一步.doDispatch(request, response);}finally {if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.if (attributesSnapshot != null) {restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);}}if (this.parseRequestPath) {ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);}}}
2)doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// Determine handler for the current request.// 获取匹配的执行链 这里就是我们下一处入口了mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}//返回此处理程序对象的 HandlerAdapter。HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}// Actually invoke the handler.//使用给定的处理程序来处理此请求。 在这里面反射执行业务方法mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {dispatchException = ex;}catch (Throwable err) {// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);}processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);}catch (Exception ex) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);}catch (Throwable err) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));}finally {if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletionif (mappedHandler != null) {mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);}}else {// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.if (multipartRequestParsed) {cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);}}}}
3)getHandler
返回此请求的 HandlerExecutionChain。
按顺序尝试所有处理程序映射。
@Nullableprotected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {if (this.handlerMappings != null) {for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {//返回 HandlerExecutionChain 我们从这里继续往下HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);if (handler != null) {return handler;}}}return null;}
1.2、HandlerMapping
public interface HandlerMapping {//... 剩余了其他的代码/**返回此请求的处理程序和任何拦截器。 可以根据请求 URL、会话状态或实现类选择的任何因素进行选择。返回的 HandlerExecutionChain 包含一个处理程序对象,而不是标签接口,因此处理程序不受任何方式的约束。例如,可以编写 HandlerAdapter 以允许使用另一个框架的处理程序对象。如果未找到匹配项,则返回null 。这不是错误。DispatcherServlet 将查询所有已注册的 HandlerMapping beans 以找到匹配项,只有在没有找到处理程序时才确定有错误*/@NullableHandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;}
1.3、AbstractHandlerMapping
AbstractHandlerMapping:HandlerMapping 实现的抽象基类。 支持排序、默认处理程序、处理程序拦截器,包括由路径模式映射的处理程序拦截器。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupportimplements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {//..../**查找给定请求的处理程序,如果没有找到特定的处理程序,则回退到默认处理程序。*/@Override@Nullablepublic final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {// 查找给定请求的处理程序,如果未找到特定请求,则返回null 。// 我们主要看这个方法,接着跟进去Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);if (handler == null) {handler = getDefaultHandler();}if (handler == null) {return null;}// Bean name or resolved handler?if (handler instanceof String) {String handlerName = (String) handler;handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);}// 确保存在拦截器和其他人的缓存查找路径if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {initLookupPath(request);}//getHandlerExecutionChain():为给定的处理程序构建一个HandlerExecutionChain ,包括适用的拦截器。HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);// 跨域相关 没有去细看了if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);}if (config != null) {config.validateAllowCredentials();}executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);}return executionChain;}// ...}
getHandlerInternal 方法定义在 AbstractHandlerMapping,但它是个抽象方法,我们往下看它实现,才知晓它做了什么。
/**查找给定请求的处理程序,如果未找到特定请求,则返回null 。如果设置了一个null返回值将导致默认处理程序。*/@Nullableprotected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
我们往下看他的实现:
1.4、AbstractHandlerMethodMapping< T >
1.4.1、getHandlerInternal
/*** 查找给定请求的处理程序方法。*/@Override@Nullableprotected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {//initLookupPath方法的实现在上层类中 AbstractHandlerMapping 中// 方法解释为:初始化用于请求映射的路径。// lookupPath 变量见名思义,我们可以知道,其实它就是 查找路径String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();try {//查找当前请求的最佳匹配处理程序方法。 如果找到多个匹配项,则选择最佳匹配项// 这里就关系到了我们是如何进行匹配的啦。HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);}finally {this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();}}
1.4.2、lookupHandlerMethod (匹配接口代码)
需要注意的是匹配方法时,是根据 @RequestMapping 里面的value路径来匹配的,如果匹配到的有多个,如你配置了通配符,也配置了精确配置,他都会匹配到放在一个集合中,根据规则排序,然后取集合的第一个元素。有兴趣的可以看看这个排序的规则,理论上肯定是路径越精确的会优先,具体代码实现如下:
/**查找当前请求的最佳匹配处理程序方法。 如果找到多个匹配项,则选择最佳匹配项。我们看这个doc 注释,就知道这是个重点啦*/@Nullableprotected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();//返回给定 URL 路径的匹配项。List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);if (directPathMatches != null) {// 下文addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);}if (matches.isEmpty()) {addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);}if (!matches.isEmpty()) {// 这里也取出第一个,当没有多个匹配时,直接使用这个Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);if (matches.size() > 1) {//排序规则Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));//进行排序matches.sort(comparator);// 取出第一个bestMatch = matches.get(0);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);}// 跨域相关if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {for (Match match : matches) {if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;}}}else {Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();String uri = request.getRequestURI();throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");}}}//这句代码分析图在下面。request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());// 这句方法注释上就一句 在找到匹配的映射时调用。具体作用没有搞懂handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();}else {return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);}}
第二句中的 this.mappingRegistry,它就是一个private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry();
它的方法getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath) 方法,真实调用如下:
/**返回给定 URL 路径的匹配项。 */@Nullablepublic List<T> getMappingsByDirectPath(String urlPath) {return this.pathLookup.get(urlPath);}
hxdm,看到这个 this.mappingRegistry 和 this.pathLookup 有没有一股子熟悉感啊,它就是我们启动时存储信息的类和数据结构啊,xd。
那这结果就非常明了了啊。
我们获取到的List<T> directPathMatches 的这个 list 就是我们启动时扫描到的所有接口,之后再经过排序,取第一个,找到最匹配的。
xdm,我们完事了啊。
1.4.3、addMatchingMappings
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {for (T mapping : mappings) {//检查映射是否与当前请求匹配,并返回一个(可能是新的)映射与当前请求相关的条件。T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);if (match != null) {// 我看注释 Match 就是 已经匹配的HandlerMethod 及其映射的包装器,用于在当前请求的上下文中将最佳匹配与比较器进行比较。//这里的 this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations() 返回的就是项目启动时注册的 被 RequestMapping 注解修饰的方法相关信息//private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();// 后面跟的 .get(mapping) 就是获取到我们向后端请求的方法// 这里的mapping 就是我们请求的 url、方式 等。matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping)));}}}
这么说还是不太好说清楚,我们直接去方法调用处,看它改变了什么了吧。
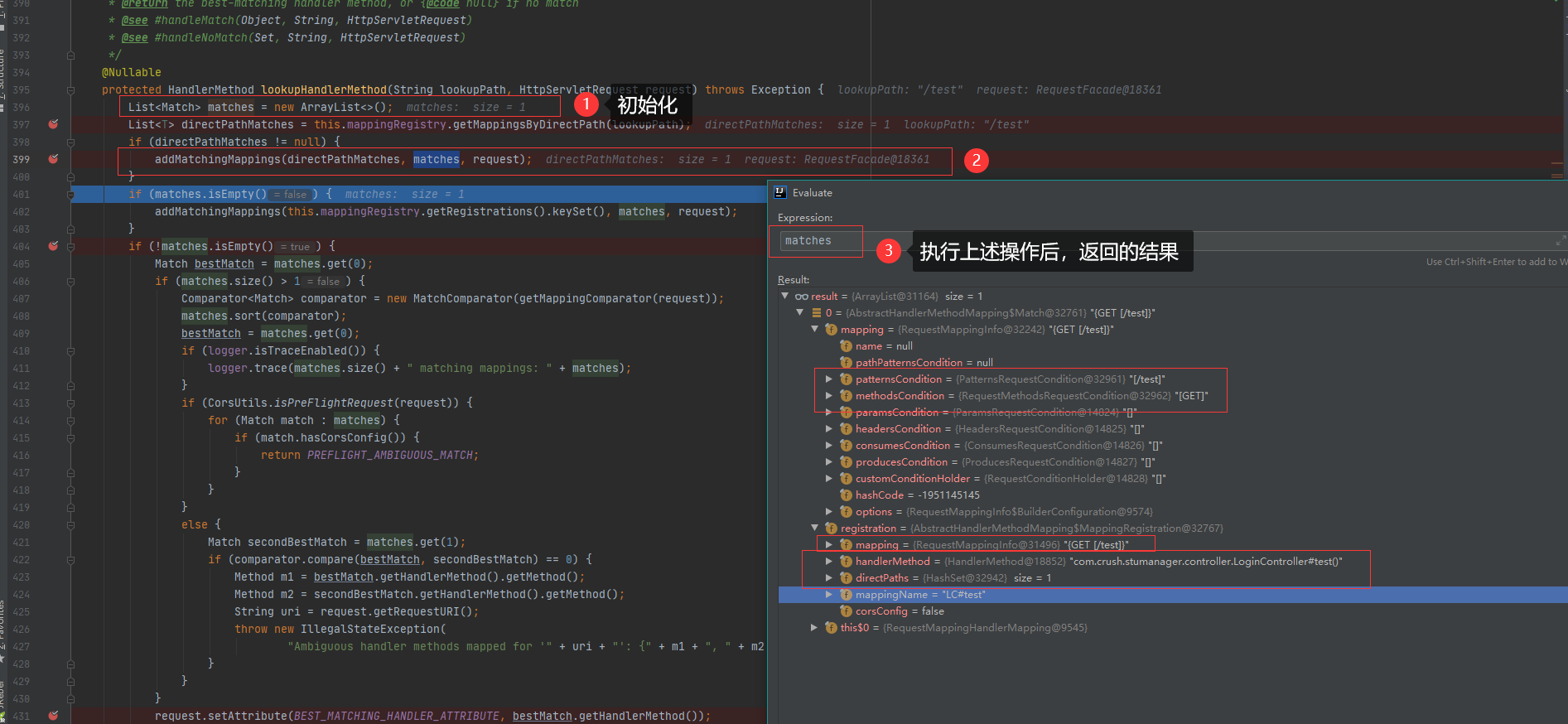
简单说就是将信息存储到 matches 变量中了。还有就是将匹配HandlerMethod的实例取出来了。
二、小结
- 扫描所有注册的Bean
- 遍历这些Bean,依次判断是否是处理器,并检测其HandlerMethod
- 遍历Handler中的所有方法,找出其中被@RequestMapping注解标记的方法。
- 获取方法method上的@RequestMapping实例。
- 检查方法所属的类有没有@RequestMapping注解
- 将类层次的RequestMapping和方法级别的RequestMapping结合 (createRequestMappingInfo)
- 当请求到达时,去urlMap中需找匹配的url,以及获取对应mapping实例,然后去handlerMethods中获取匹配HandlerMethod实例。
- 后续就是SpringMVC 执行流程了。
- 将RequestMappingInfo实例以及处理器方法注册到缓存中。
写到这里基本可以回答完文前所说的三个问题了。
他问的是为什么浏览器在向后端发起请求的时候,就知道要找的是哪一个API 接口,你们 SpringBoot 后端框架是如何存储API接口的信息的?是拿什么数据结构存储的呢?
第一个答案:将所有接口信息存进一个HashMap,请求时,取出相关联的接口,排序之后,匹配出最佳的 接口。
第二个答案:大致就是和MappingRegistry 这个注册表类相关了。
第三个答案:我们之前看到存储信息时,都是 HashMap 相关的类来存储的,那么我们可以知道它底层的数据结构就是 数组+链表+红黑树
三、后语
若不是小伙伴提起那三问,我想我也不会有如此兴致,去一步一步Debug阅读相关源码,此文多半可能会胎死腹中了。
在此非常感谢 @小宇。不瞒大家,他又邀请我一起去读 ORM 框架源码了。不过得好好等上一段时间了。
个人所谈:阅读源码的过程中,其实真的是充满有趣和枯燥的。
读懂了一些关键东西,就开心的不得了;而像“又忘记debug到哪了,思路又凉了",就会开始满心抱怨(我常常骂完一两句),然后就继续的去看。
大家好,我是博主
宁在春:主页一名喜欢文艺却踏上编程这条道路的小青年。
希望:
我们,待别日相见时,都已有所成。
另外就只能说是在此提供一份个人见解。因文字功底不足、知识缺乏,写不出十分术语化的文章,望见谅。
如果觉得本文让你有所收获,希望能够点个赞,给予一份鼓励。
也希望大家能够积极交流。如有不足之处,请大家及时批正,在此郑重感谢大家。
从浏览器发送请求给SpringBoot后端时,是如何准确找到哪个接口的?(下篇)的更多相关文章
- 使用HttpClient配置代理服务器模拟浏览器发送请求调用接口测试
在调用公司的某个接口时,直接通过浏览器配置代理服务器可以请求到如下数据: 请求url地址:http://wwwnei.xuebusi.com/rd-interface/getsales.jsp?cid ...
- vue-cli3.x中使用axios发送请求,配合webpack中的devServer编写本地mock数据接口(get/post/put/delete)
vue-cli3.x中使用axios发送请求,配合webpack中的devServer编写本地mock数据接口(get/post/put/delete) 手把手式笔记 Axios配置 安装 axios ...
- 20200726_java爬虫_使用HttpClient模拟浏览器发送请求
浏览器获取数据: 打开浏览器 ==> 输入网址 ==> 回车查询 ==> 返回结果 ==> 浏览器显示结果数据 HttpClient获取数据: 创建HttpClient ==& ...
- Java基础教程——模拟浏览器发送请求
JAVA访问网页 分别测试使用get和post方法访问网页,可以收到服务器的请求,并写入到html文件中. import java.io.*; import java.net.*; import ja ...
- [基础架构]PeopleSoft工作原理(从浏览器发送请求开始)
PeopleSoft体系结构是由几大组成部分构成,之前文章已经详细讲过,了解这几大组成部分是怎么协同工作的更为重要.在本文中将帮助您了解PeopleSoft的工作原理以及用户发送的请求是如何被解析以及 ...
- telnet客户端模拟浏览器发送请求
telnet 客户端 telnet客户端能够发出请求去连接服务器(模拟浏览器) 使用telnet之前,需要开启telnet客户端 1.进入控制面板 2.进入程序和功能,选择打开或关闭windows功能 ...
- java模拟浏览器发送请求
package test; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOExcep ...
- 服务器获取浏览器发送请求中的cookies,选取自己需要的cookie
String cookieName = “userID”; // 设置自己需要的cookie名 Cookie cookies[] = request.getCookies(); // 获取请求中的所有 ...
- htmlunit爬虫工具使用--模拟浏览器发送请求,获取JS动态生成的页面内容
Htmlunit是一款模拟浏览抓取页面内容的java框架,具有js解析引擎(rhino),可以解析页面的js脚本,得到完整的页面内容,特殊适合于这种非完整页面的站点抓取. 下载地址: https:// ...
随机推荐
- 各种插值法的python实现
一维插值 插值不同于拟合.插值函数经过样本点,拟合函数一般基于最小二乘法尽量靠近所有样本点穿过.常见插值方法有拉格朗日插值法.分段插值法.样条插值法. 拉格朗日插值多项式:当节点数n较大时,拉格朗日插 ...
- Python 利用GDAL对图像进行几何校正
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27045589/article/details/81062586 一.几何校正方法 图像校正本质是建立一种从原始图像行列号到某种投影的数学 ...
- openswan协商流程之(二):main_inI1_outR1()
主模式第二包:main_inI1_outR1() 文章目录 主模式第二包:main_inI1_outR1() 1. 序言 2. `main_inI1_outR1()`处理流程图 3. `main_in ...
- JS008. 跳转缓存滚动条高度并返回时过渡动画(window.pageYOffset & window.scrollTo & SessionStorage)
业务场景 从列表跳转详情页,通过操作返回列表页时,滚动条仍然处于跳转前的高度,并加上 ease-out 的过渡动画. 由于sessionStorage是随页面即关即消的,所以比起VUEX.localS ...
- freeswitch的网关配置
vim /usr/local/freeswitch/conf/sip_profiles/external/weihu1.xml 1 <!-- 点对点式 --> 2 <!-- 3 & ...
- ❤️❤️用最简单的方法在Webstorm中打开已存在项目 和 新建Vue项目 (亲测实用)❤️❤️
目录 一:打开已存在项目时 二:新建一个vue项目 使用webstorm创建vue项目创建vue项目各个公司用的工具都不一样 最常见的有HBuilder X,WebStorm,Visual Stu ...
- 截断误差VS舍入误差
截断误差:是指计算某个算式时没有精确的计算结果,如积分计算,无穷级数计算等,使用极限的形式表达的,显然我们只能截取有限项进行计算,此时必定会有误差存在,这就是截断误差. 舍入误差:是指由于计算机表示 ...
- 一些PHP选项参数相关的函数
关于 PHP 的配置,我们大多数情况下都是去查看 php.ini 文件或者通过命令行来查询某些信息,其实,PHP 的一些内置函数也可以帮助我们去查看或操作这些配置参数.比如之前我们学习过的 关于php ...
- npm WARN ajv-keywords@2.1.1 requires a peer of ajv@^5.0.0 but none is installed. You must install peer dependencies yourself.
解决: npm install -g npm-install-peers npm install -g npm npm i ajv 但是好像没啥用
- TP5缩放图片加水印
// 给图片增加水印文字 试验缩放图片,放大图片,加水印,加文字功能 public function doCreateImage1($data,$path) { $basePath = ROOT_PA ...
