quota - linux磁盘配额管理
磁盘管理系列
linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html
linux磁盘管理系列二:软RAID的实现 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_041_raid.html
linux磁盘管理系列三:LVM的使用 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_042_lvm.html
1 前言
在linux系统中,由于是多用户、多任务的环境,如果有少数几个用户大量使用磁盘空间,导致其他用户的正常使用,因此需要对各个用户的磁盘空间进行管理和限定。
2 quota的用途
限制某一个用户的最大磁盘配额
3 quota的使用限制
- 仅能针对整个文件系统
- 内核必须支持
- 只对一般用户生效
- 这里提供一个样例,针对样例对quota的配置管理做个描述
4 案例讲解
4.1案例描述
- 创建5个用户user1,user2,user3,user4,user5,密码和用户名相同,初始组为usergrp组。
- 5个用户都可以取得300M的磁盘使用空间,文件数量不限。超过250M,给于提示。
- usergrp这个组内成员最大使用空间1GB。
- 如果有用户超过soft限制,给14天的宽限时间。
4.2 准备磁盘

- [root@mail ~]# fdisk -l #查看磁盘情况
- Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
- Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0x000bd275
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
- /dev/sda2 2099200 83886079 40893440 8e Linux LVM
- Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors
- Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- Disk /dev/mapper/cl-root: 39.7 GB, 39720058880 bytes, 77578240 sectors
- Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- Disk /dev/mapper/cl-swap: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
- Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- [root@mail ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb #对sdb这个盘进行分区,这里就分一个区
- Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
- Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
- Be careful before using the write command.
- Device does not contain a recognized partition table
- Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xbcd17d69.
- Command (m for help): n
- Partition type:
- p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
- e extended
- Select (default p): p
- Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
- First sector (2048-20971519, default 2048):
- Using default value 2048
- Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-20971519, default 20971519):
- Using default value 20971519
- Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 10 GiB is set
- Command (m for help): p
- Disk /dev/sdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors
- Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
- Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- Disk label type: dos
- Disk identifier: 0xbcd17d69
- Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
- /dev/sdb1 2048 20971519 10484736 83 Linux
- Command (m for help): w
- The partition table has been altered!
- Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
- Syncing disks.
- [root@mail ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
- mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
- Filesystem label=
- OS type: Linux
- Block size=4096 (log=2)
- Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
- Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
- 655360 inodes, 2621184 blocks
- 131059 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
- First data block=0
- Maximum filesystem blocks=2151677952
- 80 block groups
- 32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
- 8192 inodes per group
- Superblock backups stored on blocks:
- 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
- Allocating group tables: done
- Writing inode tables: done
- Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
- Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
- [root@mail ~]# mkdir /mnt/home #创建一个目录
- [root@mail ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/home #测试挂载下

4.4.创建用户

- [root@mail ~]# vim adduserbat.sh #创建一个添加用户的脚本
- [root@mail ~]# cat adduserbat.sh #确认下脚本
- #!/bin/bash
- groupadd usergrp
- for user in user1 user2 user3 user4 user5
- do
- useradd -g usergrp -b /mnt/home $user
- echo $user |passwd --stdin $user
- done
- [root@mail ~]# sh adduserbat.sh #运行脚本去创建用户
- useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
- Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
- Creating mailbox file: File exists
- Changing password for user user1.
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
- Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
- Creating mailbox file: File exists
- Changing password for user user2.
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
- Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
- Creating mailbox file: File exists
- Changing password for user user3.
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
- Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
- Creating mailbox file: File exists
- Changing password for user user4.
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- useradd: warning: the home directory already exists.
- Not copying any file from skel directory into it.
- Creating mailbox file: File exists
- Changing password for user user5.
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- [root@mail ~]# finger user1 #查看用户信息,确保家目录在/dev/sdb1的挂载目录上。
- Login: user1 Name:
- Directory: /mnt/home/user1 Shell: /bin/bash
- Never logged in.
- No mail.
- No Plan.
- [root@mail ~]# id user1 #查看用户信息
- uid=2531(user1) gid=2532(usergrp) groups=2532(usergrp)

4.5.检查操作系统支持
前面提到了quota仅仅针对整个文件系统来进行规划的。需要确认我们为各个用户提供存储的位置是独立的文件系统。
- [root@mail ~]# df -h /mnt/home #查看我们的挂载点是否是独立文件系统
- Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
- /dev/sdb1 9.8G 37M 9.2G 1% /mnt/home
- [root@mail ~]# mount |grep /mnt/home #查看我们的文件系统
- /dev/sdb1 on /mnt/home type ext4 (rw,relatime,data=ordered)
4.6.让文件系统支持quota设置

- [root@mail ~]# mount -o remount,usrquota,grpquota /mnt/home #重新挂载/mnt/home 支持usrquota,grpquota
- [root@mail ~]# mount |grep /mnt/home #确认下
- /dev/sdb1 on /mnt/home type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
- [root@mail ~]# tail -n 1 /etc/mtab >> /etc/fstab #追加到/etc/fstab中去,确保开机启用quota
- [root@mail ~]# cat /etc/fstab #确保fstab文件正确性
- #
- # /etc/fstab
- # Created by anaconda on Fri Feb 10 03:56:55 2017
- #
- # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
- # See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
- #
- /dev/mapper/cl-root / xfs defaults 0 0
- UUID=dd4c6743-bdf5-4899-a43b-814cbe75c618 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
- /dev/mapper/cl-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
- /dev/sr0 /mnt/cdrom iso9660 ro,relatime,uid=0,gid=0,iocharset=utf8,mode=0400,dmode=0500 0 0
- /dev/sdb1 /mnt/home ext4 rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered 0 0

4.7.扫描文件系统并新建quota的配置文件

- [root@mail ~]# quotacheck -avug
- quotacheck: Your kernel probably supports journaled quota but you are not using it. Consider switching to journaled quota to avoid running quotacheck after an unclean shutdown.
- quotacheck: Scanning /dev/sdb1 [/mnt/home] done
- quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file /mnt/home/aquota.user: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
- quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file /mnt/home/aquota.group: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
- quotacheck: Cannot stat old user quota file /mnt/home/aquota.user: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
- quotacheck: Cannot stat old group quota file /mnt/home/aquota.group: No such file or directory. Usage will not be subtracted.
- quotacheck: Checked 30 directories and 20 files
- quotacheck: Old file not found.
- quotacheck: Old file not found.

主要参数
- -a: 扫描所有在/etc/mtab内含有quota参数的文件系统
- -u: 针对用户扫描文件与目录的使用情况,会新建一个aquota.user文件
- -g: 针对用户组扫描文件与目录的使用情况,会新增一个aquota.group文件
- -v: 显示扫描过程的信息
4.8 启用quota
- [root@mail ~]# quotaon -avug #启用quota
- /dev/sdb1 [/mnt/home]: group quotas turned on
- /dev/sdb1 [/mnt/home]: user quotas turned on
这个命令(quotaon) 几乎只需要在第一次启动quota时才需要进行,因为下次等你重新启动时,系统的/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit这个初始化脚本就会自动执行这个命令。
如果想关闭可以使用quotaoff -avug
4.9.编辑账户的的限值
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -u user1
会打开一个vi编辑器,修改我们的设置如下图。

- 软限制: 这个值超过了基本上没事,还是可以创建文件继续使用文件,但是在指定grace天过后就不能在创建文件了。
- 硬限值: 这个值不能超过。
执行如下命令将user1的设置应用到其他用户上
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user2 #-p 指定参考用户,这句话的意思就是将user1的quota信息赋值给user2
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user3
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user4
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -p user1 -u user5
4.10.编辑组的设置
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -g usergrp
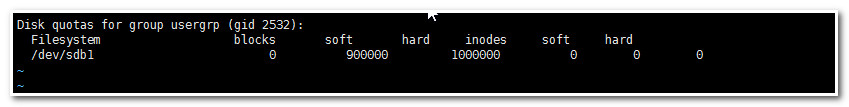
4.11.修改宽限时间
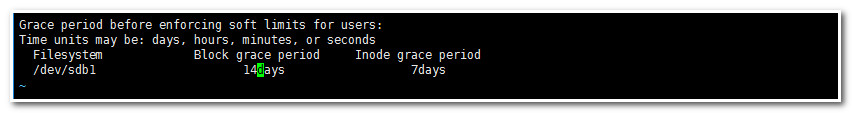
- [root@mail ~]# edquota -t
4.12.对用户和组合quota限制查看

- [root@mail ~]# quota -uvs user1 #查看user1的限制信息
- Disk quotas for user user1 (uid 2531):
- Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
- /dev/sdb1 28K 245M 293M 7 0 0
- [root@mail ~]# quota -gvs usergrp
- Disk quotas for group usergrp (gid 2532): #查看usergrp的限制信息
- Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
- /dev/sdb1 0K 879M 977M 0 0 0

参数说明
- -u: 指定用户
- -g: 指定用户组
- -s: 以1024为倍数来指定单位,显示M之类的单位
- -v: 显示用户在文件系统的quota值
4.13对文件系统quota限制查看

- [root@mail ~]# repquota -as
- *** Report for user quotas on device /dev/sdb1 #这里看到是针对/dev/sdb1的文件系统的
- Block grace time: 14days; Inode grace time: 7days
- Space limits File limits
- User used soft hard grace used soft hard grace
- ----------------------------------------------------------------------
- root -- 20K 0K 0K 2 0 0
- zhao -- 52K 0K 0K 13 0 0
- user1 -- 28K 245M 293M 7 0 0
- user2 -- 28K 245M 293M 7 0 0
- user3 -- 28K 245M 293M 7 0 0
- user4 -- 28K 245M 293M 7 0 0
- user5 -- 28K 245M 293M 7 0 0

4.14.quota测试

- [user1@mail ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=bigfile bs=1M count=270 #先创建一个270M的文件看看
- sdb1: warning, user block quota exceeded. #这里提示警告了。 也就是我们超过了软限制的值250了。
- 270+0 records in
- 270+0 records out
- 283115520 bytes (283 MB) copied, 0.715086 s, 396 MB/s
- [user1@mail ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=bigfile2 bs=1M count=40 #这里我们创建一个40M的文件
- sdb1: write failed, user block limit reached. #提示错误了。超出限制了。
- dd: error writing ‘bigfile2’: Disk quota exceeded
- 23+0 records in
- 22+0 records out
- 24035328 bytes (24 MB) copied, 0.1165 s, 206 MB/s
- [user1@mail ~]$ du -sk #查看两个文件占用情况
- 300000 .

4.12脚本设置quota信息
上面我们对用户和组的设置,它会启动一个vi编辑器,修改保存才生效。需要交互。如果我们想使用script方式快速设置,那就需要使用setquota命令了。
命令使用 setquota [ -u | -g ] 用户名或者组名 块大小软限制 块大小硬限制 文件数量软限制 文件数量大小硬限制 文件系统

- [root@mail ~]# quota -usv user1 #查看user1的quota信息
- Disk quotas for user user1 (uid 2531):
- Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
- /dev/sdb1 293M* 245M 293M 13days 14 0 0
- [root@mail ~]# setquota -u user1 400000 500000 100 200 /dev/sdb1 #使用setquota修改
- [root@mail ~]# quota -usv user1 #再次查看quota信息
- Disk quotas for user user1 (uid 2531):
- Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace
- /dev/sdb1 293M 391M 489M 14 100 200

quota - linux磁盘配额管理的更多相关文章
- linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理
磁盘管理系列 linux磁盘管理系列一:磁盘配额管理 http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaojiedi1992/p/zhaojiedi_linux_040_quota.html l ...
- Linux quota命令参数及用法详解---Linux磁盘配额限制设置和查看命令
功能说明:显示磁盘已使用的空间与限制. 语 法:quota [-quvV][用户名称...] 或 quota [-gqvV][群组名称...] 补充说明:执行quota指令,可查询磁盘空间的限制,并得 ...
- Linux 磁盘配额(XFS & EXT4)
若是在Linux中搭建了FTP服务器,为了安全性,就要考虑磁盘配额,以防服务器磁盘空间被恶意占满. 磁盘配额概述 1.作用范围:只在指定的分区有效. 2.限制对象:主要针对用户.组进行限制,对组账号限 ...
- Linux fdisk命令参数及用法详解---Linux磁盘分区管理命令fdisk
fdisk 命令 linux磁盘分区管理 用途:观察硬盘之实体使用情形与分割硬盘用. 使用方法: 一.在 console 上输入 fdisk -l /dev/sda ,观察硬盘之实体使用情形. 二.在 ...
- Linux磁盘系统——管理磁盘的命令
Linux磁盘系统——管理磁盘的命令 摘要:本文主要学习了Linux系统中管理磁盘的命令,包括查看磁盘使用情况.磁盘挂载相关.磁盘分区相关.磁盘格式化等操作. df命令 df命令用于显示Linux系统 ...
- Linux磁盘管理系列 — 磁盘配额管理
一.磁盘管理的概念 Linux系统是多用户任务操作系统,在使用系统时,会出现多用户共同使用一个磁盘的情况,如果其中少数几个用户占用了大量的磁盘空间,势必压缩其他用户的磁盘的空间和使用权限.因此,系统管 ...
- Linux磁盘配额与LVM
一.LVM概述 逻辑卷管理 Logical Volume Manager二.LVM机制的基本概念三.LVM的管理命令 ① 主要命令 ② ==LVM逻辑卷操作流程== ③ 举例四.磁盘配额概述 ...
- Linux磁盘配额实验
1.实现磁盘限额的条件 *需要Linux内核支持 *安装quota软件包2.Linux磁盘限额的特点 作用范围:针对指定 文件系统(分区) 限制对象:普通用户帐号.组帐号 限制类型:磁盘容量(默认单位 ...
- linux 磁盘配额配置
1. 添加一块新磁盘 ,分区 .格式化 .(mkfs.etx3 /dev/sdc5/) 2.设置开机自动挂载(vi /etc/fstab) 添加磁盘配额支持 (用户配额usrquota.组配额grpq ...
随机推荐
- java String 常用方法
String方法 class CeShi{ public static void main(String[] args) { //toCharArray char chararraryone[]=&q ...
- qr.h
创建二维码 QRCodeCreate vc++
- WTL 9.0的变化 - atlcrack.h
atlcrack.h中是一些对消息映射的简化,9.0版本中只增加了一个WM_MOUSEWHEEL的响应,而且要求windows vista. #if (_WIN32_WINNT >= 0x060 ...
- vmware中桥接模式,NAT模式,主机模式的区别
桥接模式 在桥接模式下,VMWare虚拟出来的操作系统就像是局域网中的一台独立的主机(主机和虚拟机处于对等地 位),它可以访问网内任何一台机器.在桥接模式下,我们往往需要为虚拟主机配置IP地址.子网掩 ...
- 20180610模拟赛T1——脱离地牢
Description 在一个神秘的国度里,年轻的王子Paris与美丽的公主Helen在一起过着幸福的生活.他们都随身带有一块带磁性的阴阳魔法石,身居地狱的魔王Satan早就想着得到这两块石头了,只要 ...
- ZROI 暑期高端峰会 A班 Day2 线性代数
高斯消元 很普及组,不讲了 当主元没有逆的时候可以辗转相除. 如果也没有带余数除法--没救了 逆矩阵 我们定义矩阵 \(A\) 的逆矩阵为 \(A^{-1}\),满足 \(AA^{-1}=A^{-1} ...
- matplotlib 柱状图
222 # coding utf-8 # import matplotlib import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import mat ...
- Unchecked runtime.lastError: The message port closed before a response was received.
这是由于某个 Chrome 扩展程序造成的. 打开 chrome://extensions/,逐一关闭排查.我这边是由于“迅雷下载支持”这个扩展引起的,将其关闭即可.
- Hbase安装使用
启动Hadoop 启动Hbase jps 进入shell 建立表及使用
- #lua中编写shader的方式
lua中编写shader的方式 1. 字符串拼接 类似于下面这种 vertDefaultSource = "\n".."\n" .. "attribu ...
