[概念理解] UML类建模
Class Diagram
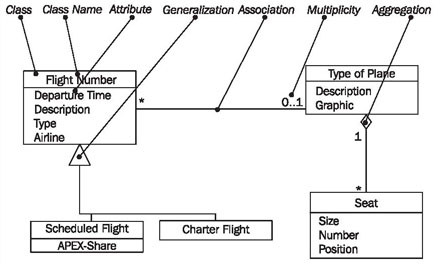
In class diagrams, as shown in Figure 4.30, we work with the following elements:
Class
A class represents a relevant concept from the domain, a set of persons, objects, or ideas that are depicted in the IT system:
Examples of classes are passengers, planes, or tickets.
Attribute
An attribute of a class represents a characteristic of a class that is of interest for the user of the IT system:
Characteristics of interest of a passenger, for example, are name and age.
Generalization
Generalization is a relationship between two classes: a general class and a special class:

Refer to Generalization, Specialization, and Inheritance.
Association
An association represents a relationship between two classes:

An association indicates that objects of one class have a relationship with objects of another class, in which this connection has a specifically defined meaning (for example, "is flown with").
Multiplicity
A multiplicity allows for statements about the number of objects that are involved in an association:
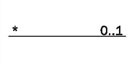
Also see Figure 4.32.
Aggregation
An aggregation is a special case of an association (see above) meaning "consists of":
The diamond documents this meaning; a caption is unnecessary.
Reading Class Diagrams
Figure 4.31 shows a class diagram from our case study with the classes customer, ticket, and coupon, their attributes, and their associations:
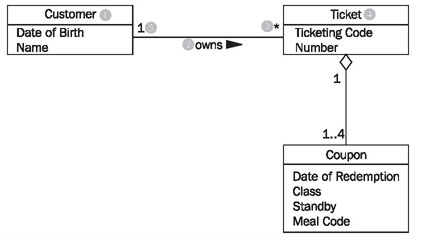
Looking at the class diagram in Figure 4.31, you can read the association between the classes customer and ticket as follows:
- One (this sentence always begins with "one") object of the first class has an association with a number of objects of the second class.
The appropriate values from the diagram have to be inserted into this first abstract formulation, which can be universally applied. The name of one class is customer (1); the name of the other class is ticket (4). The name of the association is owns (2):
- A customer (1) owns (2) * (3) ticket (4).
If the asterisk is exchanged with its meaning, a regular English sentence is created:
- A customer (1) owns (2) zero, one or several (3) ticket(s) (4).
Since associations usually are not directional, meaning usually go both directions, our association also has a meaning in the other direction:
- A ticket (4) is owned by (2) exactly one (5) customer (1).
The small triangle next to the name of the association (2) indicates in which direction the name of the association holds true. We can read all the associations in the class diagram in this way.
The specification of the number of objects of the second class (you always start with one object of the first class) is called the multiplicity. The course of action should always be according to the same pattern:
First, a statement of the lower limit (minimum number) followed by two periods (..) and a statement of the upper limit (maximum number).
Figure 4.32 shows the most common possibilities:
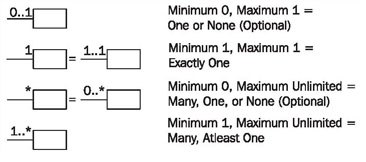
However, in UML it is also possible to insert any values as the lower and upper limits, e.g., 2 .. 4 or 6 .. *.
The association's name is necessary for understanding the domain meaning of the association. In contrast to the association itself, which applies to both directions, the name of the association applies to only one direction, which is indicated by a black triangle. If the association is not labeled, its meaning has to be derived from the domain context, or it takes on a general meaning such as has or belongs to. In case of doubt it is better to label associations too much than too little. Many diagrams that we have encountered in our practical experience were incomprehensible because associations were not labeled.
Associations can also be viewed as the implementation of static business rules (see Static and Dynamic Business Rules). Statements such as "a ticket belongs to exactly one customer" are documented in the class diagram by associations.
Roles are another possible way in UML to give relationships between classes a domain meaning. In this way, we can state what role an object of one class plays for the objects of another class:
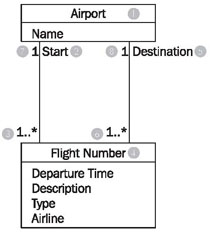
Looking at the class diagram in Figure 4.33, we can read the left association with roles between the classes flight number and airport as follows:
- An airport (1) is a start (location) (2) for one or more (3) flightnumbers (4).
There is another association between the two classes flight number and airport:
- An airport (1) is a destination (5) for one or more flight numbers (4).
These two associations also have inversions, even though roles are only stated for one direction:
- A flight number (4) has as start (location) (2) exactly one (7) airport (1).
- A flight number (4) has as destination (5) exactly one (8) airport (1).
This records that a certain flight number has a departure airport and a destination airport. An example of a flight number is LX317, a daily flight of the Swiss airline Crossair from London to Zurich.
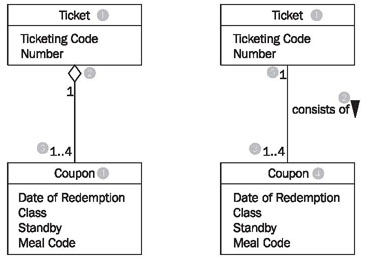
Among the many domain meanings that an association can have there is one that can be signified with UML by its own symbol: the whole-part relationship or aggregation. This type of relationship is always used when objects of one class are a part of objects of another class.
In the class diagram in Figure 4.34 aggregation is used on the left side (the white diamond), which can be read as follows:
- A ticket (1) consists of (2) 1 to 4 (3) coupons (4).
or the other way around:
- A coupon (4) is part of (2) exactly one (5) ticket (1).
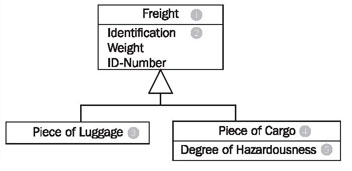
The example without a diamond, but with a name for the association, has exactly the same meaning! The last missing element of UML that we use to model class diagrams is generalization/specialization, which serves to depict the relationship between a superclass and a subclass. The generalization/specialization in Figure 4.35 can be read from top to bottom or bottom to top. If you begin at the top, you find a class Freight (1) with the attributes: Identification, Weight, and ID-number (2). This class has two specializations, Piece of Luggage (3) and Piece of Cargo (4). The class Piece of Cargo has an additional attribute: Degree of Hazardousness (5).
If you begin at the bottom you will find the classes Piece of Luggage (3) and Piece of Cargo(4). These have a superclass, the class Freight (1), which contains the shared attributes (and functions) of the subclasses.
[概念理解] UML类建模的更多相关文章
- UML类建模(强烈推荐-思路很清晰)
UML类建模(强烈推荐-思路很清晰) 2016年10月23日 15:17:47 mbshqqb 阅读数:2315 标签: uml面向对象设计模式 更多 个人分类: 面向对象程序设计 UML的构造快 ...
- UML类图关系大全
UML类图关系大全 1.关联 双向关联: C1-C2:指双方都知道对方的存在,都可以调用对方的公共属性和方法.在GOF的设计模式书上是这样描述的:虽然在分析阶段这种关系是适用的,但我们觉得它对于描述设 ...
- UML类图关系大全【转】
UML类图关系大全 1.关联 双向关联:C1-C2:指双方都知道对方的存在,都可以调用对方的公共属性和方法. 在GOF的设计模式书上是这样描述的:虽然在分析阶段这种关系是适用的,但我们觉得它对于描述设 ...
- Java 大黑话讲解设计模式 -- UML类图
目录 1.啥是UML类图? 2.UML类图有啥用? 3.正式理解UML类图 4.使用idea画第一个UML类图 5.类之间的关系图[必须牢记] 6.类之间的关系 6.1.依赖 6.2.泛化 6.3.实 ...
- UML类图关系全面剖析
UML的类图关系分为: 关联.聚合/组合.依赖.泛化(继承).而其中关联又分为双向关联.单向关联.自身关联:下面就让我们一起来看看这些关系究竟是什么,以及它们的区别在哪里. 1.关联 双向关联:C1- ...
- UML类图关系-转
1.关联 双向关联: C1-C2:指双方都知道对方的存在,都可以调用对方的公共属性和方法. 在GOF的设计模式书上是这样描述的:虽然在分析阶段这种关系是适用的,但我们觉得它对于描述设计模式内的类关系来 ...
- UML类图关系大全-转
1.关联 双向关联: C1-C2:指双方都知道对方的存在,都可以调用对方的公共属性和方法. 在GOF的设计模式书上是这样描述的:虽然在分析阶段这种关系是适用的,但我们觉得它对于描述设计模式内的类关系来 ...
- UML类图关系表示
UML 之 C++类图关系全面剖析 分类: 软件设计与架构2008-10-16 08:52 5165人阅读 评论(3) 收藏 举报 umlc++borderclasscblog UML的类图关系分为: ...
- 我对uml类图关系的理解
uml类图的关系: 泛化关系也就是继承. 实现关系就是一个类实现另外一个接口. 依赖关系就是一个类使用了另外一个类,是一种使用关系,在这个类的某个服务中需要另外一个类来协助. 关联关系就是一类拥有另外 ...
随机推荐
- 如何用 CSS 创作一个立体滑动 toggle 交互控件
效果预览 在线演示 按下右侧的"点击预览"按钮在当前页面预览,点击链接全屏预览. https://codepen.io/zhang-ou/pen/zjoOgX 可交互视频教程 此视 ...
- 在不使用ssr的情况下解决Vue单页面SEO问题
遇到的问题: 近来在写个人博客的时候遇到了大家可能都会遇到的问题 Vue单页面在SEO时显得很无力,尤其是百度不会抓取动态脚本 Vue-Router配合前后端分离无法让meta标签在蜘蛛抓取时动态填充 ...
- 杭电 5326 Work (并查集求子结点为k的结点数)
Description It’s an interesting experience to move from ICPC to work, end my college life and start ...
- 数据结构实验7:实现二分查找、二叉排序(查找)树和AVL树
实验7 学号: 姓名: 专业: 7.1实验目的 (1) 掌握顺序表的查找方法,尤其是二分查找方法. (2) 掌握二叉排序树的建立及查找. 查找是软件设计中的最常用的运算,查找所涉及到 ...
- PhotoshopCS6
download: http://www.playnext.cn/photoshop-cs6.html cracker: http://www.playnext.cn/adobe-cs6-crack. ...
- 洛谷 P3800 Power收集
题目背景 据说在红雾异变时,博丽灵梦单身前往红魔馆,用十分强硬的手段将事件解决了. 然而当时灵梦在Power达到MAX之前,不具有“上线收点”的能力,所以她想要知道她能收集多少P点,然而这个问题她答不 ...
- Ubuntu安装sublime Text 3并配置可以输入中文
使用Ubuntu系统后,想找一个顺手的编辑器,sublime作为我的首选编辑器,在安装和配置可输入中文时遇到各种个样的问题,总结一些: 1:问题: 我的系统是Ubuntu 18.04 LTS,尝试多次 ...
- firefox自动化测试的常用插件
1.firebug 2.firepath 3.firefinder 5.WebDriver Element Locator 提供多种语言的xpath路径
- VS Code 列编辑功能说明
新版本v1.13.1或者附近的版本中的列编辑功能已经调整. 一.多光标插入功能 Alt+鼠标左键,添加多光标输入 二.自由多行选择 Alt键+鼠标左键拖动选择各行的部分内容 三.列选择 Shift+A ...
- php的错误控制运算符
php的错误控制运算符 PHP中提供了一个错误控制运算符“@”. 可以将@放置在一个PHP表达式之前,该表达式可能产生的任何错误信息都被忽略掉: 如果开启了php.ini 中的 track_error ...
