Android学习笔记-事件处理之Handler消息传递机制
内容摘要:Android Handler消息传递机制的学习总结、问题记录
Handler消息传递机制的目的:
1.实现线程间通信(如:Android平台只允许主线程(UI线程)修改Activity里的UI组件,而实际开发时会遇到新开的线程要改变界面组件属性的情况,这时就要有一种办法通知主线程更新UI)。Handler消息传递机制可用于线程间传递消息。
2.实现消息的异步处理。
机制的实现:(工作原理涉及Handler、Looper、Message(消息)、MessageQueue(消息队列);代码分消息接收方,发送方2处)
原理说明(本人理解有限,比较好的Handler说明看这篇):
Handler可发送Message到MessageQueue或处理从Looper收到的Message。
Message消息对象,在整个机制中传递。
MessageQueue是一个以先进先出方式管理Message的队列。
Looper管理MessageQueue,它把从MessageQueue里取到的Message分发给相应的Handler。
原理图:

注意:
1.Handler是建立在Looper上,实现Thread的消息系统处理模型,实现消息异步处理的;
2.MessageQueue会在Looper(Looper()构造函数)初始化时创建关联;
3.一个线程最多只能有一个Looper对象(Looper.prepare()方法创建Looper对象,规定了这个);
4.主线程(UI线程)系统已经帮初始化了一个Looper对象(简单分析看这,主线程源码详细分析看这),因此程序直接创建Handler即可;程序员自己启动的线程必须先创建Looper对象并启动(调用Looper.loop()),然后才能向该线程的消息队列发消息。
Looper源码参考:
prepare()方法保证每个线程最多只有一个Looper对象,loop()方法使用一个死循环不断取出MessageQueue中的消息,并把取出的消息分给对应的Handler处理。
//Looper初始化时创建并关联MessageQueue
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
//一个线程最多一个Looper,调用prepare()方法创建Looper对象
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
} private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
/**
* Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an
* application's main looper. The main looper for your application
* is created by the Android environment, so you should never need
* to call this function yourself. See also: {@link #prepare()}
*/
//主UI线程初始化Looper对象调用的方法
public static void prepareMainLooper() {
prepare(false);
synchronized (Looper.class) {
if (sMainLooper != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");
}
sMainLooper = myLooper();
}
}
/**
* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.
*/
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); //使用一个死循环不断从MessageQueue取Message,并发给对应Handler
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
} // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
final Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
} final long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs; final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;
if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag)) {
Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));
}
final long start = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long end;
try {
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
end = (slowDispatchThresholdMs == 0) ? 0 : SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} finally {
if (traceTag != 0) {
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
}
}
if (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0) {
final long time = end - start;
if (time > slowDispatchThresholdMs) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Dispatch took " + time + "ms on "
+ Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", h=" +
msg.target + " cb=" + msg.callback + " msg=" + msg.what);
}
} if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
} // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
} msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
原理总结到这,下面看看在代码中具体如何实现
代码示例(只是一种实现,更多Handler用法总结看这):
1.消息接收方线程先调用Looper.prepare()创建Looper对象,然后创建Handler对象并定义处理消息的方法,接下来调用Looper.loop()启动Looper。
class CallbackThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == 123) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "get message!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}
2.消息发送方线程通过调用Handler类相关方法向接收方线程的Handler对象发送消息,可用的方法有:

callbackThread = new CallbackThread();
callbackThread.start(); //发空消息
callbackThread.mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(123); //创建消息发送
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = 123;
callbackThread.mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
以上是Handler学习总结,接下来是学习过程中遇到的问题记录。
问题记录
1.代码示例中接收消息的线程是先调用Looper.prepare(),再创建Handler实现消息处理方法,最后再Looper.loop()。为什么是prepare->Handler->loop这个顺序?可不可以换?
答:顺序不能换。首先prepare是肯定要在loop之前,因为prepare()方法源码注释中有这样一句话(Be sure to call* {@link #loop()} after calling this method),那就按它的来(因为我没看源码......)。可还有两种顺序是吧,一个个试下。Handler->prepare->loop不行,现象是发出的消息没被接收。prepare->loop->Handler也不可以,现象是导致APP退出。我(zhao)的(chao)理(wang)解(shang)是Handler要想正常工作首先要保证当前线程中有Looper对象(why?可能是能发消息首先要有消息队列?),所以先要prepare创建Looper对象;然后Looper.loop()使用死循环取消息,且当没有消息时会阻塞,这样的话放在它之后的代码——创建Handler的代码不会执行,当调用该Handler对象的sendMessage()一类方法时便会产生NullPointerException,如下(AV画质):
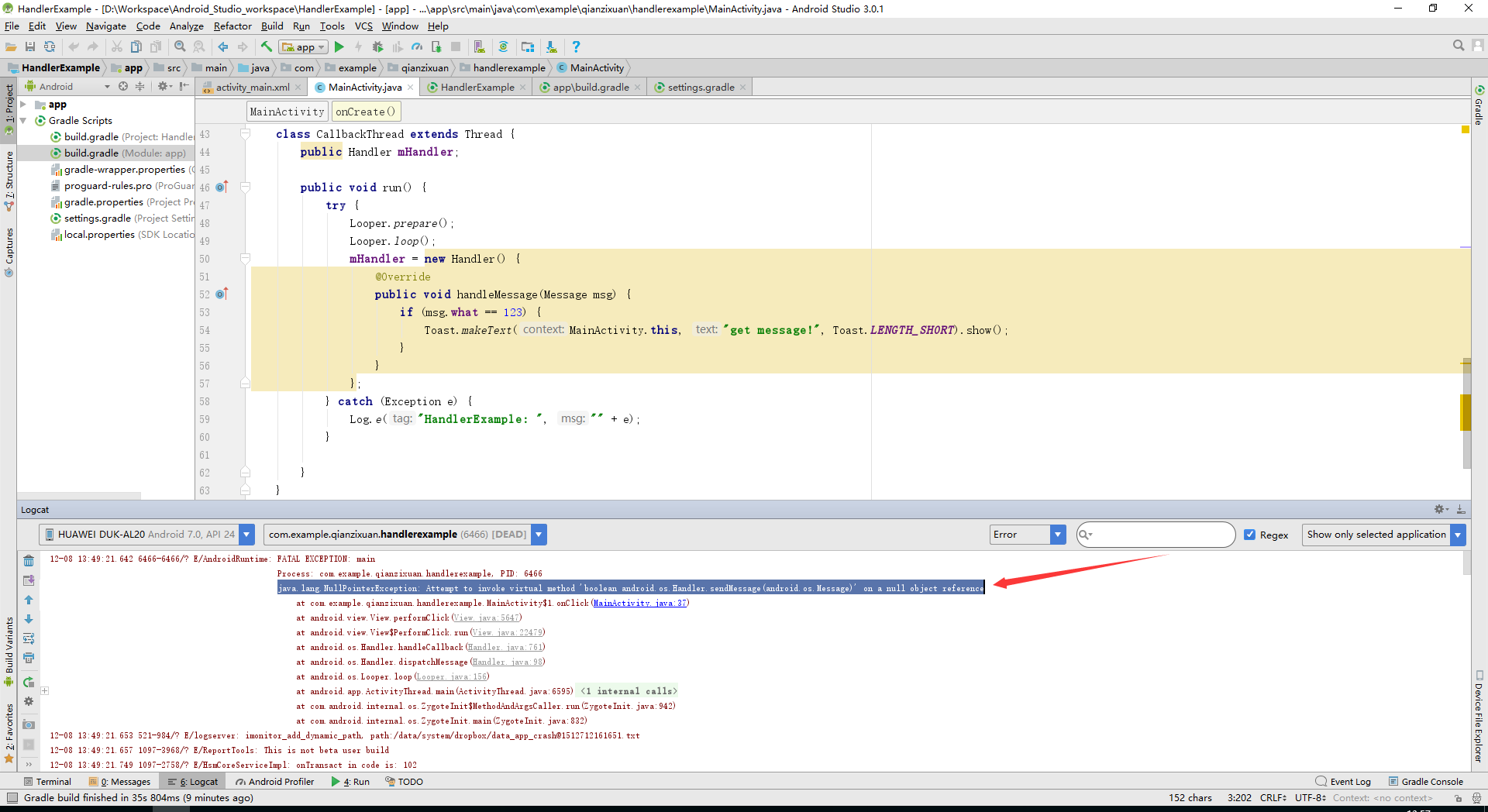
2.不是说只有UI线程能对UI组件操作,为什么当上面截图中代码把创建Handler对象放在prepare和loop之间时,子线程使用Toast不报错还能显示?
答:首先子线程直接用Toast是不行的,不会弹出Toast只会报错......之后我上网找啊找啊找到这篇,只是后面得出结论的时候说“Toast可能是属于修改UI界面”???这几个意思???于是我又找啊找啊,知乎找到这个问题,天啊!用了Toast这么久难道它不是更新UI操作,可能正如知乎上大佬说的——“吐司操作的是window,不属于checkThread抛主线程不能更新UI异常的管理范畴”?信息量太大,我能力有限还没理解,先存疑记录//Todo。总之,现在知道Toast要在子线程中使用可以借助Looper。
3.Looper.loop()使用死循环取消息难道不会很耗资源吗?
答:并不会,具体看这篇。简而言之,死循环中调用queue.next()读取下一条消息(在loop调用的线程中),如果读取到了就msg.target.dispatchMessage(),否则queue.next()则会一直阻塞到超过超时时间。
4.主线程Looper也调用了loop(),会不会也阻塞?
答:也会有阻塞,但不会卡死,其实和问题3是一个道理,MessageQueue没消息了都会阻塞进入休眠,之后会被句柄写操作唤醒epoll.wait。参考:知乎问题,CSDN文章(虽然文章标题和结论矛盾)。
5.queue.next()的阻塞是怎么实现的?
答:参考3,4中的链接。关键字:Linux pipe/epoll机制,loop()的queue.next()中的nativePollOnce()方法。
感想:第一篇博客花了我一晚上一早上加半个下午,妈呀!那些大佬都怎么这么高产的。问题其实还有更多的,但一部分忘了记录下来,一部分太不成熟,再就是还存在没发现的问题......越来越懵逼了,完全没有豁然开朗的感觉???主要是知道的太少了,一次性见识到这么多新的事物消化不来,学习笔记也很乱,毕竟第一次写博客,慢慢学吧,Android之路长着呢,嘻嘻嘻!
Android学习笔记-事件处理之Handler消息传递机制的更多相关文章
- Android学习笔记-事件处理
第三章 Android的事件处理 Android提供两种事件处理方式,基于回调和基于监听器.前者常用于传统图形界面编程中,而后者在AWT/Swing开发中常用. 3.1 事件处理概述 对于基于回调的事 ...
- Android学习笔记(十三)——广播机制
//此系列博文是<第一行Android代码>的学习笔记,如有错漏,欢迎指正! Android 中的每个应用程序都可以对自己感兴趣的广播进行注册,这样该程序就只会接收到自己所关心的广播内容 ...
- Android(java)学习笔记202:Handler消息机制的原理和实现
联合学习 Android 异步消息处理机制 让你深入理解 Looper.Handler.Message三者关系 1. 首先我们通过一个实例案例来引出一个异常: (1)布局文件activity_m ...
- Android(java)学习笔记145:Handler消息机制的原理和实现
联合学习 Android 异步消息处理机制 让你深入理解 Looper.Handler.Message三者关系 1. 首先我们通过一个实例案例来引出一个异常: (1)布局文件activity_m ...
- android学习笔记25——事件处理Handler
Handler消息传递机制 ==> android消息机制是另一种形式的“事件处理”,这种机制主要是为了解决android应用的多线程问题. ——android平台不允许Activity新启动的 ...
- android学习笔记24——事件处理
事件处理 android提供了两种事件处理机制: 1.基于回调的事件处理 2.基于监听器的事件处理(通过绑定特定事件监听器) 注意: android对于基于回调的事件处理而言,主要做法就是重写andr ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(八八):了解Handler(2):什么是Handler
文章转载只能用于非商业性质,且不能带有虚拟货币.积分.注册等附加条件.转载须注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/flowingflying/ 之前我们有一篇很好的博文<Andro ...
- 事件处理机制与Handler消息传递机制
一.基于监听的事件处理机制 基于监听的时间处理机制模型: 事件监听机制中由事件源,事件,事件监听器三类对象组成 处理流程如下: Step 1:为某个事件源(组件)设置一个监听器,用于监听用户操作 St ...
- Android学习笔记之JSON数据解析
转载:Android学习笔记44:JSON数据解析 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,为Web应用开发提供了一种 ...
随机推荐
- OC基础:Date
NSDate 日期类,继承自NSObject,代表一个时间点 NSDate *date=[NSDate date]; NSLog(@"%@",date); //格林尼治时间, ...
- 什么是cookie?session和cookie的区别?
1.cookie数据存放在客户的浏览器上,session数据放在服务器上. 2.cookie不是很安全,别人可以分析存放在本地的COOKIE并进行COOKIE欺骗 考虑到安全应当使用session ...
- gsm model二次开发C#短信猫开发/长短信
加QQ:83014588 向我索要,开发包 开发人员淘宝:http://t.cn/RhOj8W8 短信猫:http://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=686.1000925 ...
- Java中去除字符串中的所有空格
JAVA中去掉空格 1. String.trim() trim()是去掉首尾空格 2.str.replace(" ", ""); ...
- POJ - 3468 A Simple Problem with Integers(线段树区间更新,区间查询)
1.给出了一个序列,你需要处理如下两种询问. "C a b c"表示给[a, b]区间中的值全部增加c (-10000 ≤ c ≤ 10000). "Q a b" ...
- I.MX6 mkuserimg.sh 使用
/*********************************************************************** * I.MX6 mkuserimg.sh 使用 * 说 ...
- Sleep示例分析
sleep让"当前线程"由“运行状态”进入到“休眠(阻塞)状态”,sleep结束,线程重新被唤醒时,它会由“阻塞状态”变成“就绪状态”,从而等待cpu的调度执行. 示例分析: pu ...
- ionic2 angular2 模板指令补充
向div中插入带有html标签的数据 [innerHTML]="item.content" 字符串截取指令 {{item.de ...
- css覆盖select样式并添加小箭头
.select { border-radius: 5px; border: 1px #F4A627 solid; -webkit-appearance: none;//清除默认样式 backgroun ...
- 结对测试vs随机测试
在接口测试过程中,最关键的是对参数的各种情况进行测试. 随机测试是指随机选择一些参数值来测. 结对测试是指parewise算法生成较高"性价比"的组合情况来测. 随机测试存在的问题 ...
