CS229 6.11 Neurons Networks implements of self-taught learning
在machine learning领域,更多的数据往往强于更优秀的算法,然而现实中的情况是一般人无法获取大量的已标注数据,这时候可以通过无监督方法获取大量的未标注数据,自学习( self-taught learning)与无监督特征学习(unsupervised feature learning)就是这种算法。虽然同等条件下有标注数据蕴含的信息多于无标注数据,但是若能获取大量的无标注数据并且计算机能够加以利用,计算机往往可以取得比较良好的结果。
通过自学习与无监督特征学习,可以得到大量的无标注数据,学习出较好的特征描述,在尝试解决一个具体的分类问题时,可以基于这些学习出的特征描述和任意的(可能比较少的)已标注数据,使用有监督学习方法在标注数据上完成分类。
在拥有大量未标注数据和少量已标注数据的场景下,通过对所有x(i)进行特征学习得到a(i),在标注数据中用a(i)替原始的输入x(i)得到新的训练样本{a(i) ,y(i) }(i=1...m),即可取得很好的效果,即使在只有标注数据的情况下,本算法依然能取得很好的效果。
autoencoder可以在无标注数据集中学习特征,给定一个无标注的训练数据集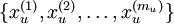 (下标
(下标 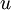 代表“不带类标”),首先进行预处理,比如pca或者白化,然后训练一个sparse autoencoder:
代表“不带类标”),首先进行预处理,比如pca或者白化,然后训练一个sparse autoencoder:
 '
'
通过训练得到的模型参数 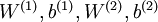 ,给定任意的输入数据
,给定任意的输入数据 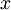 ,可以计算隐藏单元的激活量(activations)
,可以计算隐藏单元的激活量(activations) 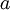 。相比原始输入
。相比原始输入 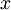 来说,
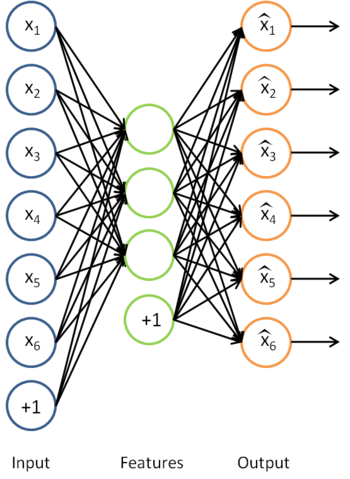
来说,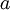 可能是一个更好的特征描述。下图的神经网络描述了特征(激活量
可能是一个更好的特征描述。下图的神经网络描述了特征(激活量 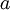 )的计算:
)的计算:
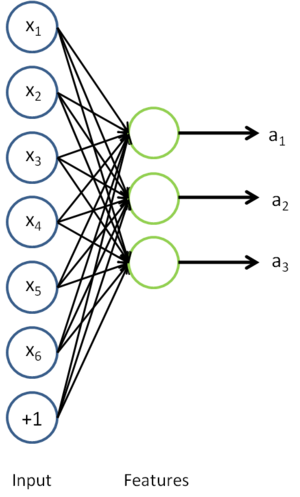
对应之前所提到的,假定有 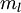 个 已标注训练集
个 已标注训练集 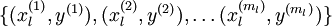 (下标
(下标 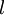 表示“带类标”),现在可以为输入数据找到更好的特征描述。将
表示“带类标”),现在可以为输入数据找到更好的特征描述。将 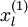 输入到稀疏自编码器,得到隐藏单元激活量
输入到稀疏自编码器,得到隐藏单元激活量 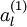 。接下来,可以直接使用
。接下来,可以直接使用 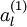 来代替原始数据
来代替原始数据 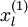 (“替代表示”,Replacement Representation)。也可以合二为一,使用新的向量
(“替代表示”,Replacement Representation)。也可以合二为一,使用新的向量 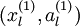 来代替原始数据
来代替原始数据 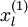 (“级联表示”,Concatenation Representation)。
(“级联表示”,Concatenation Representation)。
经过变换后,训练集就变成 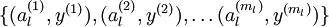 或者是
或者是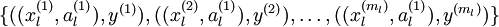 (取决于使用
(取决于使用 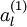 替换
替换 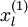 还是将二者合并)。在实践中,将
还是将二者合并)。在实践中,将 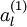 和
和 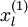 合并通常表现的更好。考虑到内存和计算的成本,也可以使用替换操作。
合并通常表现的更好。考虑到内存和计算的成本,也可以使用替换操作。
最终,可以训练出一个有监督学习算法(例如 svm, logistic regression 等),得到一个判别函数对 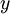 值进行预测。预测过程如下:给定一个测试样本
值进行预测。预测过程如下:给定一个测试样本 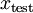 ,重复之前的过程,将其送入稀疏自编码器,得到
,重复之前的过程,将其送入稀疏自编码器,得到 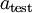 。然后将
。然后将 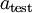 (或者
(或者 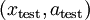 )送入分类器中,得到预测值。
)送入分类器中,得到预测值。
从未标注训练集 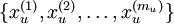 中学习这一过程中可能计算了各种数据预处理参数。例如计算数据均值并且对数据做均值标准化(mean normalization);或者对原始数据做主成分分析(PCA),然后将原始数据表示为
中学习这一过程中可能计算了各种数据预处理参数。例如计算数据均值并且对数据做均值标准化(mean normalization);或者对原始数据做主成分分析(PCA),然后将原始数据表示为 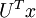 (又或者使用 PCA 白化或 ZCA 白化)。这样的话,有必要将这些参数保存起来,并且在后面的训练和测试阶段使用同样的参数,以保证新来(测试)数据进入稀疏自编码神经网络之前经过了同样的变换。例如,如果对未标注数据集进行PCA预处理,就必须将得到的矩阵
(又或者使用 PCA 白化或 ZCA 白化)。这样的话,有必要将这些参数保存起来,并且在后面的训练和测试阶段使用同样的参数,以保证新来(测试)数据进入稀疏自编码神经网络之前经过了同样的变换。例如,如果对未标注数据集进行PCA预处理,就必须将得到的矩阵 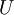 保存起来,并且应用到有标注训练集和测试集上;而不能使用有标注训练集重新估计出一个不同的矩阵
保存起来,并且应用到有标注训练集和测试集上;而不能使用有标注训练集重新估计出一个不同的矩阵 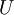 (也不能重新计算均值并做均值标准化),否则的话可能得到一个完全不一致的数据预处理操作,导致进入自编码器的数据分布迥异于训练自编码器时的数据分布。
(也不能重新计算均值并做均值标准化),否则的话可能得到一个完全不一致的数据预处理操作,导致进入自编码器的数据分布迥异于训练自编码器时的数据分布。
有两种常见的无监督特征学习方式,区别在于有什么样的未标注数据。自学习(self-taught learning) 是其中更为一般的、更强大的学习方式,它不要求未标注数据 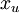 和已标注数据
和已标注数据 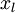 来自同样的分布。另外一种带限制性的方式也被称为半监督学习,它要求
来自同样的分布。另外一种带限制性的方式也被称为半监督学习,它要求 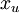 和
和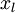 服从同样的分布。下面通过例子解释二者的区别。
服从同样的分布。下面通过例子解释二者的区别。
假定有一个计算机视觉方面的任务,目标是区分汽车和摩托车图像;也即训练样本里面要么是汽车的图像,要么是摩托车的图像。哪里可以获取大量的未标注数据呢?最简单的方式可能是从互联网上下载一些随机的图像数据集,在这些数据上训练出一个稀疏自编码器,从中得到有用的特征。这个例子里,未标注数据完全来自于一个和已标注数据不同的分布(未标注数据集中,或许其中一些图像包含汽车或者摩托车,但是不是所有的图像都如此)。这种情形被称为自学习。
相反,如果有大量的未标注图像数据,要么是汽车图像,要么是摩托车图像,仅仅是缺失了类标号(没有标注每张图片到底是汽车还是摩托车)。也可以用这些未标注数据来学习特征。这种方式,即要求未标注样本和带标注样本服从相同的分布,有时候被称为半监督学习。在实践中,常常无法找到满足这种要求的未标注数据(到哪里找到一个每张图像不是汽车就是摩托车,只是丢失了类标号的图像数据库?)因此,自学习在无标注数据集的特征学习中应用更广。
下面通过自学习的方法,整合sparse autoencoder 与 softmax regression 来构建一个手写数字的分类。
算法步骤:
1)把MNIST数据库的数据分为labeled(0-4) 与 unlabeled(5-9),并且把labeled data 分为 test data 与 train data,一半用来测试,一般用来训练
2)用unlabeled data (5-9)训练一个 sparse autoencoder,得到所有参数W(1) W(2) b(1) b(2) ,记做 θ ,展示第一层参数W(1),展示效果如下:
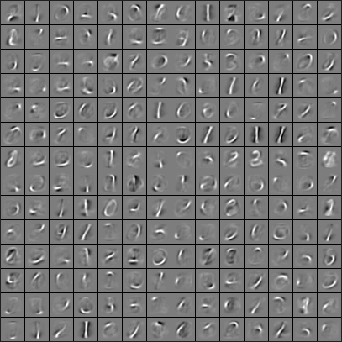
3)使用上面的sparse autoencoder 训练出来的W(1)对labeled data(0-4)训练得到其隐层输出a(2),这样不适用原来的像素值,而使用学到的特征来对0-4进行分类。
4)用上述学到的特征a(2)(i)代替原始输入x(i),现在的样本为{(a(1) ,y(1))(a(2) ,y(2))...(a(m) ,y(m))},用该样本来训练我们的softmax分类器。
5)用训练好的softmax进行预测,在labeled data 中的 test data 进行测试即可。准确率讲道理的话应该有98%以上。
一下是matlab代码。部分代码直接调用到之前章节的:
- %% CS294A/CS294W Self-taught Learning Exercise
- % Instructions
- % ------------
- %
- % This file contains code that helps you get started on the
- % self-taught learning. You will need to complete code in feedForwardAutoencoder.m
- % You will also need to have implemented sparseAutoencoderCost.m and
- % softmaxCost.m from previous exercises.
- %
- %% ======================================================================
- % STEP : Here we provide the relevant parameters values that will
- % allow your sparse autoencoder to get good filters; you do not need to
- % change the parameters below.
- inputSize = * ;
- numLabels = ;
- hiddenSize = ;
- sparsityParam = .; % desired average activation of the hidden units.
- % (This was denoted by the Greek alphabet rho, which looks like a lower-case "p",
- % in the lecture notes).
- lambda = 3e-; % weight decay parameter
- beta = ; % weight of sparsity penalty term
- maxIter = ;
- %% ======================================================================
- % STEP : Load data from the MNIST database
- %
- % This loads our training and test data from the MNIST database files.
- % We have sorted the data for you in this so that you will not have to
- % change it.
- % Load MNIST database files
- mnistData = loadMNISTImages('mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte');
- mnistLabels = loadMNISTLabels('mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte');
- % Set Unlabeled Set (All Images)
- % Simulate a Labeled and Unlabeled set
- labeledSet = find(mnistLabels >= & mnistLabels <= );
- unlabeledSet = find(mnistLabels >= );
- %把labeled set分为训练数据 和 测试数据
- numTrain = round(numel(labeledSet)/);
- trainSet = labeledSet(:numTrain);
- testSet = labeledSet(numTrain+:end);
- unlabeledData = mnistData(:, unlabeledSet);
- trainData = mnistData(:, trainSet);
- trainLabels = mnistLabels(trainSet)' + 1; % Shift Labels 0-4 to the Range 1-5
- testData = mnistData(:, testSet);
- testLabels = mnistLabels(testSet)' + ; % Shift Labels 0-4 to the Range 1-5
- % Output Some Statistics
- fprintf('# examples in unlabeled set: %d\n', size(unlabeledData, ));
- fprintf('# examples in supervised training set: %d\n\n', size(trainData, ));
- fprintf('# examples in supervised testing set: %d\n\n', size(testData, ));
- %% ======================================================================
- % STEP : Train the sparse autoencoder
- % This trains the sparse autoencoder on the unlabeled training
- % images.
- % Randomly initialize the parameters
- theta = initializeParameters(hiddenSize, inputSize);
- %% ----------------- YOUR CODE HERE ----------------------
- % Find opttheta by running the sparse autoencoder on
- % unlabeledTrainingImages
- %theta 现再是以个展开的向量,对应[W1,W2,b1,b2]的长向量
- opttheta = theta;
- opttheta = theta;
- addpath minFunc/
- options.Method = 'lbfgs';
- options.maxIter = ;
- options.display = 'on';
- [opttheta, loss] = minFunc( @(p) sparseAutoencoderLoss(p, ...
- inputSize, hiddenSize, ...
- lambda, sparsityParam, ...
- beta, unlabeledData), ...
- theta, options);
- %% -----------------------------------------------------
- % Visualize weights,展示W1'(28*28 * 200的矩阵)
- % 把该矩阵的每一列展示为一个28*28的图片,来看效果
- W1 = reshape(opttheta(1:hiddenSize * inputSize), hiddenSize, inputSize);
- display_network(W1');
- %%======================================================================
- %% STEP : Extract Features from the Supervised Dataset
- %
- % You need to complete the code in feedForwardAutoencoder.m so that the
- % following command will extract features from the data.
- trainFeatures = feedForwardAutoencoder(opttheta, hiddenSize, inputSize, ...
- trainData);
- testFeatures = feedForwardAutoencoder(opttheta, hiddenSize, inputSize, ...
- testData);
- %%======================================================================
- %% STEP : Train the softmax classifier
- softmaxModel = struct;
- % Use softmaxTrain.m from the previous exercise to train a multi-class
- % classifier.
- % Use lambda = 1e- for the weight regularization for softmax
- % You need to compute softmaxModel using softmaxTrain on trainFeatures and
- % trainLabels
- lambda = 1e-;
- inputSize = hiddenSize;
- numClasses = numel(unique(trainLabels));%unique为找出向量中的非重复元素并进行排序
- options.maxIter = ;
- %注意这里的数据不是x^(i),而是a^().
- softmaxModel = softmaxTrain(inputSize, numClasses, lambda, ...
- trainFeatures, trainLabels, options);
- %% -----------------------------------------------------
- %%======================================================================
- %% STEP : Testing
- % Compute Predictions on the test set (testFeatures) using softmaxPredict
- % and softmaxModel
- [pred] = softmaxPredict(softmaxModel, testFeatures);
- %% -----------------------------------------------------
- % Classification Score
- fprintf('Test Accuracy: %f%%\n', *mean(pred(:) == testLabels(:)));
- % (note that we shift the labels by , so that digit now corresponds to
- % label )
- %
- % Accuracy is the proportion of correctly classified images
- % The results for our implementation was:
- %
- % Accuracy: .%
- %
- %
- %%%%%%%%%%%%% 以下对应STEP ,%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
- function [activation] = feedForwardAutoencoder(theta, hiddenSize, visibleSize, data)
- % theta: trained weights from the autoencoder
- % visibleSize: the number of input units (probably )
- % hiddenSize: the number of hidden units (probably )
- % data: Our matrix containing the training data as columns. So, data(:,i) is the i-th training example.
- % We first convert theta to the (W1, W2, b1, b2) matrix/vector format, so that this
- % follows the notation convention of the lecture notes.
- W1 = reshape(theta(:hiddenSize*visibleSize), hiddenSize, visibleSize);
- b1 = theta(*hiddenSize*visibleSize+:*hiddenSize*visibleSize+hiddenSize);
- %% ---------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------------------------
- % Instructions: Compute the activation of the hidden layer for the Sparse Autoencoder.
- %计算隐层输出a^()
- activation = sigmoid(W1*data+repmat(b1,[,size(data,)]));
- %-------------------------------------------------------------------
- end
- %-------------------------------------------------------------------
- % Here's an implementation of the sigmoid function, which you may find useful
- % in your computation of the costs and the gradients. This inputs a (row or
- % column) vector (say (z1, z2, z3)) and returns (f(z1), f(z2), f(z3)).
- function sigm = sigmoid(x)
- sigm = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-x));
- end
CS229 6.11 Neurons Networks implements of self-taught learning的更多相关文章
- CS229 6.10 Neurons Networks implements of softmax regression
softmax可以看做只有输入和输出的Neurons Networks,如下图: 其参数数量为k*(n+1) ,但在本实现中没有加入截距项,所以参数为k*n的矩阵. 对损失函数J(θ)的形式有: 算法 ...
- (六)6.11 Neurons Networks implements of self-taught learning
在machine learning领域,更多的数据往往强于更优秀的算法,然而现实中的情况是一般人无法获取大量的已标注数据,这时候可以通过无监督方法获取大量的未标注数据,自学习( self-taught ...
- CS229 6.13 Neurons Networks Implements of stack autoencoder
对于加深网络层数带来的问题,(gradient diffuse 局部最优等)可以使用逐层预训练(pre-training)的方法来避免 Stack-Autoencoder是一种逐层贪婪(Greedy ...
- CS229 6.8 Neurons Networks implements of PCA ZCA and whitening
PCA 给定一组二维数据,每列十一组样本,共45个样本点 -6.7644914e-01 -6.3089308e-01 -4.8915202e-01 ... -4.4722050e-01 -7.4 ...
- CS229 6.5 Neurons Networks Implements of Sparse Autoencoder
sparse autoencoder的一个实例练习,这个例子所要实现的内容大概如下:从给定的很多张自然图片中截取出大小为8*8的小patches图片共10000张,现在需要用sparse autoen ...
- (六)6.10 Neurons Networks implements of softmax regression
softmax可以看做只有输入和输出的Neurons Networks,如下图: 其参数数量为k*(n+1) ,但在本实现中没有加入截距项,所以参数为k*n的矩阵. 对损失函数J(θ)的形式有: 算法 ...
- CS229 6.1 Neurons Networks Representation
面对复杂的非线性可分的样本是,使用浅层分类器如Logistic等需要对样本进行复杂的映射,使得样本在映射后的空间是线性可分的,但在原始空间,分类边界可能是复杂的曲线.比如下图的样本只是在2维情形下的示 ...
- CS229 6.16 Neurons Networks linear decoders and its implements
Sparse AutoEncoder是一个三层结构的网络,分别为输入输出与隐层,前边自编码器的描述可知,神经网络中的神经元都采用相同的激励函数,Linear Decoders 修改了自编码器的定义,对 ...
- CS229 6.17 Neurons Networks convolutional neural network(cnn)
之前所讲的图像处理都是小 patchs ,比如28*28或者36*36之类,考虑如下情形,对于一副1000*1000的图像,即106,当隐层也有106节点时,那么W(1)的数量将达到1012级别,为了 ...
随机推荐
- COLUMN_FORMAT 的值:FIXED、DYNAMIC、DEFAULT 的区别(待补充)
参考===MySQL 建表语句 create table 中的列定义: column_definition: data_type [NOT NULL | NULL] [DEFAULT default_ ...
- SpringBoot入门学习笔记
SpringBoot是SpringMVC的升级版,SpringBoot的特点: application.properties文件配置: server.port = 8080端口配置 server.co ...
- AXI_LITE源码学习笔记
AXI_LITE源码学习笔记 1. axi_awready信号的产生 准备接收写地址信号 // Implement axi_awready generation // axi_awready is a ...
- GTX的生成(包括COMMON)
GTX的生成(包括COMMON) 1.每一个GTX Quad需要一个GTX common,同时GTX common只包含有QPLL,不包含CPLL. 2.kintex-7设备只支持GTX 3.参考时钟 ...
- Video Timing Controller v6.1软件调试记录
Video Timing Controller v6.1软件调试记录 GUI配置: . case XVTC_VMODE_PAL: //576i@50 { TimingPtr->Interlace ...
- IK分词器的使用
1.下载 根据自己的版本进行下载 https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases wget https://github.com ...
- NP完全性理论与近似算法
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/chinazhangjie/archive/2010/12/06/1898070.html 一.图灵机 根据有限状态控制器的当前状态及每个读写头读到 ...
- C/S,B/S的应用区别
C/S,B/S的应用区别 C/S即大家熟知的客服机和服务器结构通过它可以充分利用两端硬件环境的优势,将任务合理分配到Client端和Server端来实现,降低了系统的通讯开销 B/S结构即浏览器和服务 ...
- 基于vue.js实现远程请求json的select控件
基本思路 前端把需要的参数类型编码传到后台,后台返回相应的参数列表json,前端利用vue渲染select控件 具体实现 前端代码 <select v-model="template. ...
- JIRA 资源
https://www.**.com/article/2015/8/7/22532.html e_v_g_e_t JIRA使用教程:在Windows上安装JIRAJIRA使用教程:在Linux上安装J ...
