NIO初识
Java编程中的NIO,俗称new I/O,是在JDK1.4版本之后开始引入的,在JDK1.4之前,Java服务端大多使用同步阻塞式来处理网络请求,在低流量、低并发情况还能抗住,在如今互联网时代,信息量很明显差远了,在没有NIO之前,服务器端通信模块基本被C/C++占据着,它们可以利用操作系统的原生API来处理非阻塞事件,随着java的nio类库发布,经过不断发展完善,性能也逐渐与c++媲美了,加上JAVA很多优秀的开源类库,使用更广泛了,现在,来了解一下nio的原理,做一个感官上的认识。
使用NIO,必须记住如下3个核心概念,编程实现就是围绕他们的关系的:
1. 缓冲区Buffer: 在nio编程中,读写都在基于缓冲区的,区别于之前的基于流的,根据用途,可以使用字节缓冲区、字符缓冲区等
2. 通道Channel: 在Buffer里的数据通过Channel与网络交互,是全双工的,而流数单工操作的
3. 多路复用器Selector: 管理Channel,最基本的就是读写Channel,一个线程使用Selector来轮询读写Channel,通道上有事件发生时,就会进行处理,类似一个函数指针集合,在BLE开发的底层OS上也是这样处理的,增加一个模块,只要写好模块函数,然后把函数指针放到功能数组就可以了,后面就轮询这个注册了的函数,有置位就调用指针进行操作。这种模式可以实现单线程就能支持上千万并发连接。
下面新建一个工程来测试一下:
1. 新建一个TestNIO工程,目录结构设为如下:

2. 实现服务器端,代码如下:
package cn.linjk.testnio.server; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; /**
* Created by LinJK on 19/11/2016.
*/
public class NioServer {
private static final int serverPort = 8889; public static void main(String[] argc) {
//启动一个线程来处理Selector
HelloServer helloServer = new HelloServer(serverPort);
if (!helloServer.getInitResult()) {
System.out.println("Init Error");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("Hello Server listening on localhost:" + serverPort); new Thread(helloServer).start();
} } class HelloServer implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
private ByteBuffer byteBufferWrite;
private boolean contrustorFlag; public HelloServer(int port) {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); contrustorFlag = true;
}
catch (Exception e) {
contrustorFlag = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
} public boolean getInitResult() {
return contrustorFlag;
} public void stop() {
stop = true;
} @Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
try {
selector.select(1000); //1秒轮询周期,可以按需修改 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey selectionKey = null; while (it.hasNext()) {
selectionKey = it.next();
it.remove(); try {
//handle event
handleIncomeEvent(selectionKey);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (selectionKey != null) {
selectionKey.cancel();
if (selectionKey.channel() != null) {
selectionKey.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//User set stop listening, clear something
if (selector != null) {
try {
selector.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} private void handleIncomeEvent(SelectionKey key) {
if (key.isValid()) {
//连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
try {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//监听到了连接事件,原有基础上注册监听读取用户端数据事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} //读到客户端数据事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBufferRead = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int readCnt = socketChannel.read(byteBufferRead); if (readCnt > 0) {
byteBufferRead.flip();//刷新缓冲区,然后从缓冲区读取数据 byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBufferRead.remaining()];
byteBufferRead.get(bytes); String request = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Server receive: " + request); //say hello to client
byteBufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(20);
byteBufferWrite.put("[<<-]Hello".getBytes());
byteBufferWrite.flip();//刷新数据到缓冲区
socketChannel.write(byteBufferWrite);
//避免缓冲区已满,造成写数据不全现象,注册写事件,轮询是否所有数据已写完
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
else if (readCnt < 0) {
key.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
}
else {
//
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} if (key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel(); while (byteBufferWrite.hasRemaining()){
//.....
}
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Input key unvalid");
}
}
}
3. 实现客户端,测试功能,有些异常没有写全,也没实现重连服务器机制,只把框架写了,代码如下:
package cn.linjk.testnio.client; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; /**
* Created by LinJK on 19/11/2016.
*/
public class NioClient {
private static Selector selector;
private static SocketChannel socketChannel;
private static volatile boolean stop; public static void main(String[] argc) { new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//connect to server
if (socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8889))) {
//注册监听服务器返回事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//send request to server
ByteBuffer byteBufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
byteBufferWrite.put("I am Jim".getBytes());
byteBufferWrite.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBufferWrite);
if (!byteBufferWrite.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println("Send Finish.");
}
}
else {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
} while (!stop) {
selector.select(1000); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator(); SelectionKey selectionKey = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
selectionKey = it.next();
it.remove(); if (selectionKey.isValid()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel();
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
if (socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//send data
ByteBuffer byteBufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
byteBufferWrite.put("I am Jim".getBytes());
byteBufferWrite.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBufferWrite);
if (!byteBufferWrite.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println("Send Finish.");
}
}
}
//收到服务器返回数据事件
if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer byteBufferRead = ByteBuffer.allocate(100); int readCnt = socketChannel.read(byteBufferRead);
if (readCnt > 0) {
byteBufferRead.flip(); byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBufferRead.remaining()];
byteBufferRead.get(bytes); System.out.println("Receive from server: " + new String(bytes, "UTF-8"));
stop = true;
}
else if (readCnt < 0){
selectionKey.channel();
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
} if (selector != null) {
selector.close();
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
//资源清理....
System.exit(1);
}
}
}).start();
} }
4. 代码分析:
对比服务端和客户端的代码逻辑,有如下两点相似:
a. 程序启动后创建一个线程来管理Selctor
b. 都配置为非阻塞操作,然后注册SelctionKey到SocketChanell,然后在线程的run()函数里轮询哪个事件发生了再进行操作
流程都相似,稍微有点不一样,看代码并运行一下就明白了。
5. 运行结果:
先运行Server端,然后运行Client端,二者输出分别如下:
Server:

Client:
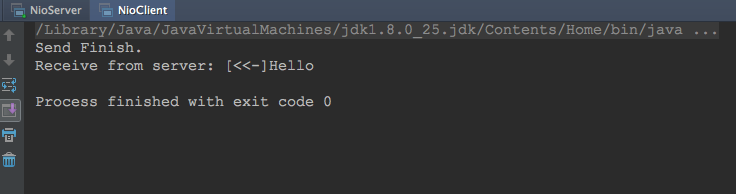
6. 总结:
NIO和IO直接最大区别就是,NIO是面向缓冲区的,IO是面向流的,面向缓冲区数据处理比较灵活,数据处理速度与吞吐量更大,同时保证数据完整性比较重要,前面提到缓冲区满时,需要检测"半包"也是这个意思,使用NIO的非阻塞避免了因网络情况阻塞造成的高并发环境下时延问题,在高并发通讯情况下,可以使用它来处理通信还是很好的。
NIO初识的更多相关文章
- java核心技术-NIO
1.reactor(反应器)模式 使用单线程模拟多线程,提高资源利用率和程序的效率,增加系统吞吐量.下面例子比较形象的说明了什么是反应器模式: 一个老板经营一个饭店, 传统模式 - 来一个客人安排一个 ...
- Java NIO学习与记录(一):初识NIO
初识 工作中有些地方用到了netty,netty是一个NIO框架,对于NIO却不是那么熟悉,这个系列的文章是我在学习NIO时的一个记录,也期待自己可以更好的掌握NIO. 一.NIO是什么? 非阻塞式I ...
- Java NIO (一) 初识NIO
Java NIO(New IO / Non-Blocking IO)是从JDK 1.4版本开始引入的IO API , 可以替代标准的Java IO API .NIO与原来标准IO有同样的作用和目的,但 ...
- 初识Java NIO
原文链接:http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/index.html Java NIO是java 1.4之后新出的一套IO接口,这里的新是相对于原有标准的Java ...
- 深入理解Java NIO
初识NIO: 在 JDK 1. 4 中 新 加入 了 NIO( New Input/ Output) 类, 引入了一种基于通道和缓冲区的 I/O 方式,它可以使用 Native 函数库直接分配堆外内存 ...
- DotNetty网络通信框架学习之初识Netty
p{ text-align:center; } blockquote > p > span{ text-align:center; font-size: 18px; color: #ff0 ...
- Java NIO学习与记录(二):FileChannel与Buffer用法与说明
FileChannel与Buffer用法与说明 上一篇简单介绍了NIO,这一篇将介绍FileChannel结合Buffer的用法,主要介绍Buffer FileChannel的简单使用&Buf ...
- 从 BIO、NIO 聊到 Netty,最后还要实现个 RPC 框架!
大家好,我是 「后端技术进阶」 作者,一个热爱技术的少年. 觉得不错的话,欢迎 star!ღ( ´・ᴗ・` )比心 Netty 从入门到实战系列文章地址:https://github.com/Snai ...
- Netty与NIO
初识Netty Netty是由JBoss提供的一个Java的开源框架,是GitHub上的独立项目. Netty是一个异步的,基于事件驱动的网络应用框架,用于快速开发高性能.高可靠的网络IO程序. Ne ...
随机推荐
- SignalR主动通知订阅者示例
html代码: <script src="~/Scripts/jquery.signalR-2.2.0.min.js"></script> <scri ...
- JS数组转字符串和字符串转数组
主要用到以下两个函数 join();//将数组转换成字符串split();//将字符串转换成数组 <script type="text/javascript"> var ...
- bzoj2064[和谐社会模拟赛]分裂
题意:给定一个初始集合和目标集合,有两种操作:1.合并集合中的两个元素,新元素为两个元素之和 2.分裂集合中的一个元素,得到的两个新元素之和等于原先的元素.要求用最小步数使初始集合变为目标集合,求最小 ...
- 基于Linux平台的libpcap源码分析和优化
目录 1..... libpcap简介... 1 2..... libpcap捕包过程... 2 2.1 数据包基本捕包流程... 2 2.2 libpcap捕包过程... ...
- xpth 字符串截取
<xsl:value-of select="substring(//div[@class='infos'],1,27)"/>
- JS控制flash的方法
JS控制flash的一些方法:Play() ---------------------------------------- 播放动画 StopPlay()---------------------- ...
- %我的 tex 模版
%我的 tex 模版 \documentclass[UTF8,a1paper,landscape]{ctexart}%UTF8 中文支持,a1paper 纸张大小,landscape 横向版面,cte ...
- 多光谱图像数据库, Multispectral images databses
1. https://scien.stanford.edu/index.php/hyperspectral-image-data/ 2. http://www.cs.columbia.edu/CAVE ...
- thinkphp3.2与phpexcel带图片生成 完美案例
thinkphp3.2与phpexcel完美案例 // 导出exl public function look_down(){ $id = I('get.id'); $m = M ('offer_goo ...
- mysql常用操作语句
mysql常用操作语句 1.mysql -u root -p 2.mysql -h localhost -u root -p database_name 2.列出数据库: 1.show datab ...
