Python CRM项目八
自定义用户认证
目的:实现Django自定义的认证系统,在生产环境都是根据此代码进行定制的
步骤:
1.在settings文件中配置要使用的类
#命名规则 app名称.类名
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'crm.UserProfile'
2.在crm app下的models文件中加入Django官方的用户认证
from django.contrib.auth.models import (
BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser,PermissionsMixin
)
from django.utils.safestring import mark_safe
from django.utils.translation import ugettext_lazy as _
class UserProfileManager(BaseUserManager):
def create_user(self, email, name, password=None):
#创建用户根据UserProfile中的字段,输入
if not email:
raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') user = self.model(
email=self.normalize_email(email),
name=name,
) user.set_password(password)
user.save(using=self._db)
return user def create_superuser(self, email, name, password):
#创建超级用户根据UserProfile中的字段,输入
user = self.create_user(
email,
password=password,
name=name,
)
user.is_admin = True
user.save(using=self._db)
return user class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser,PermissionsMixin):
#使用Django自带的登录系统,可以自定义一些字段,例如邮箱,密码,用户名
email = models.EmailField(
verbose_name='email address',
max_length=255,
unique=True,
)
password = models.CharField(_('password'), max_length=128,help_text = mark_safe('<a href="password/">修改密码</a>')) name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True)
is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False)
#在创建用户的时候调用该方法进行用户的创建
objects = UserProfileManager() USERNAME_FIELD = 'email'
REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] def get_full_name(self):
# The user is identified by their email address
return self.email def get_short_name(self):
# The user is identified by their email address
return self.email def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2
return self.email def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None):
"Does the user have a specific permission?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True def has_module_perms(self, app_label):
"Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?"
# Simplest possible answer: Yes, always
return True @property
def is_staff(self):
"Is the user a member of staff?"
# Simplest possible answer: active users are staff
return self.is_active class Meta:
verbose_name_plural = '用户'
3.在crm app下的admin中
from django import forms
from django.contrib.auth.models import Group
from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin as BaseUserAdmin
from django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashField
from crm.models import UserProfile class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm):
#在Django Admin页面中用户创建的表单展示
"""A form for creating new users. Includes all the required
fields, plus a repeated password."""
password1 = forms.CharField(label='Password', widget=forms.PasswordInput)
password2 = forms.CharField(label='Password confirmation', widget=forms.PasswordInput) class Meta:
#展示的model对象和字段
model = UserProfile
fields = ('email', 'name') def clean_password2(self):
#判断两次输入的密码是否一致
# Check that the two password entries match
password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1")
password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2")
if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2:
raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don't match")
return password2 def save(self, commit=True):
#保存用户到数据库
# Save the provided password in hashed format
user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False)
user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"])
if commit:
user.save()
return user class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm):
#在Django Admin页面中用户修改的表单展示
"""A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on
the user, but replaces the password field with admin's
password hash display field.
"""
password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField() class Meta:
#展示的model对象和字段
model = UserProfile
fields = ('email', 'password', 'name', 'is_active', 'is_admin') def clean_password(self):
# Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value.
# This is done here, rather than on the field, because the
# field does not have access to the initial value
return self.initial["password"] class UserProfileAdmin(BaseUserAdmin):
#在在Django Admin页面中配置的admin_class
# The forms to add and change user instances
form = UserChangeForm #调用修改用户的表单
add_form = UserCreationForm #调用创建用户的表单 # The fields to be used in displaying the User model.
# These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin
# that reference specific fields on auth.User.
list_display = ('email', 'name', 'is_admin')
list_filter = ('is_admin',)
fieldsets = (
(None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}),
('Personal info', {'fields': ('name',)}),
('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_admin','is_active','user_permissions',)}),
)
# add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin
# overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user.
add_fieldsets = (
(None, {
'classes': ('wide',),
'fields': ('email', 'name', 'password1', 'password2')}
),
)
search_fields = ('email',)
ordering = ('email',)
filter_horizontal = ('groups','user_permissions') admin.site.unregister(Group)
#把models对象中的model对象和admin_class对象组合起来
admin.site.register(models.UserProfile,UserProfileAdmin)
4.在king_admin中实现修改密码的功能
在king_admin的urls.py中配置
url(r'^(\w+)/(\w+)/(\d+)/change/password/$',views.password_reset,name='password_reset'),
在king_admin中的king_admin.py中配置
class UserAdmin(BaseAdmin):
list_display = ['email','name'] #首页展示的字段
readonly_fields = ['password',] #只读字段
modelfrom_exclude_fields = ['last_login','is_superuser','groups','user_permissions'] #不展示的字段
在views函数中开发该模块
def password_reset(request,app_name,table_name,obj_id):
'''动态修改密码'''
#获取admin_class类和要修改密码的对象
admin_class = king_admin.enabled_admins[app_name][table_name]
model_obj = admin_class.model.objects.get(id=obj_id)
errors = {}
if request.method == 'POST':
#获取前端页面的两个值,密码和新密码
_password1 = request.POST.get('password1')
_password2 = request.POST.get('password2')
#如果两次密码相同,并且长度大于5位,则调用父类的方法保存密码,同时入库,最后返回到展示页面
if _password1 == _password2:
if len(_password2) > 5:
model_obj.set_password(_password1)
model_obj.save()
#保存成功则跳转到展示页面进行展示
return redirect(request.path.rstrip('password/'))
else:
errors['invalid_password'] = '密码长度不足6位'
else:
errors['invalid_password'] = '两次密码不一致'
return render(request,'king_admin/password_reset.html',{'model_obj':model_obj})
5.在forms.py中将不需要展示的字段写到exclude上
class Meta:
model = admin_class.model
fields = '__all__'
exclude = admin_class.modelfrom_exclude_fields #排除的字段
6.前端页面
本质上是一个form表达,展示用户的用户名,然后用户填写密码和新密码之后提交到views的方法中进行修改密码的操作
{% extends 'king_admin/table_index.html' %}
{% block container %}
<div class="row">
<div class="panel panel-info">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h3 class="panel-title">重置用户{{ model_obj.name }}密码</h3>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<form method="post" class="form-horizontal">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-1" style="font-weight:normal">
用户名:
</label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<input class="form-control" type="text" value="{{ model_obj.email }}" disabled>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-1" style="font-weight:normal">
密码:
</label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<input class="form-control" type="password" name="password1">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-1" style="font-weight:normal">
重复密码:
</label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<input class="form-control" type="password" name="password2">
</div>
</div>
<div>
<ul style="color:red">
{% for k,v in errors.items %}
<li>{{ k }}-{{ v }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-info" style="margin-left:110px" value="提交">
<input type="reset" class="btn btn-danger" style="margin-left:30px" value="重置">
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
自定义用户登录
目的:利用Django提供的组件,实现自己的用户认证系统,包括登录,登出和利用装饰器实现方法的登录校验
1.在settings文件中配置登录url的路径
LOGIN_URL = '/'
2.在入口的app中配置url
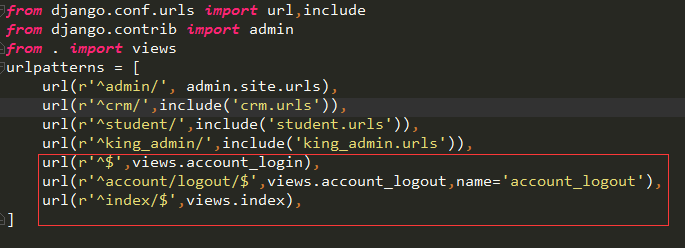
3.在views中开发登录,登出和首页的模块
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect
from django.contrib.auth import login,authenticate,logout
# Create your views here. def account_login(request):
errors = {}
if request.method == 'POST':
#获取前端表单的值
_email = request.POST.get('email')
_password = request.POST.get('password')
#使用Django自带的用户认证
user = authenticate(username=_email,password=_password)
if user:
#登录成功则进行跳转,如果有next_url则跳转到下一个页面,否则跳转到首页
login(request,user)
next_url = request.GET.get('next','')
if next_url:
return redirect(next_url)
else:
return redirect('/index/')
else:
errors['error'] = '用户名密码不正确'
return render(request,'login.html',{'errors':errors}) def account_logout(request):
#用户登出
logout(request)
return redirect('/account/login/') def index(request):
return render(request,'index.html')
4.在需要登录校验的方法上,加上@login_required装饰器
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required @login_required
def index(request):
return render(request, 'king_admin/table_index.html',{'table_list':king_admin.enabled_admins})
5.前端页面,form表单以post的方式向后台发送用户名和密码,后端的views中相应的方法进行校验
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block body %}
<div class="row">
<div class="panel panel-info">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h3 class="panel-title">登录CRM系统</h3>
</div>
<div class="panel-body ">
<form class="form-horizontal" method="post">{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-1" style="font-weight:normal">
邮箱:
</label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<input type="email" name="email" id="inputEmail" class="form-control" placeholder="Email address" required autofocus>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-1" style="font-weight:normal">
密码:
</label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<input type="password" name="password" id="inputPassword" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" required>
</div>
</div>
{% if errors %}
<span style="color: red">{{ errors.error }}</span>
{% endif %}
<button class="btn btn-info" style="margin-left:113px" type="submit">登陆</button>
<button class="btn btn-danger" type="reset">清空</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
6.在index首页集成用户登出同时生成动态的菜单链接,点击跳转到相应的页面
登出
<li class="dropdown">
<a href="#" class="dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown" aria-expanded="false">{{ request.user.name }}</a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu" role="menu">
<li><a href="{% url 'account_logout' %}">注销</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
动态菜单生成
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-3 col-md-2 sidebar">
<ul class="nav nav-sidebar"> {% for role in request.user.roles.all %}
{% for menu in role.menus.all %}
<li>
{# 如果是绝对路径的url type=1,直接显示url的名称,如果是相对路径的url type=0,则动态根据url的别名来获取url #}
<a href="{% if menu.url_type == 0 %}{% url menu.url_name %}{% else %}{{ menu.url_name }}{% endif %}">{{ menu.name }}</a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
</ul> </div>
<div class="col-sm-9 col-sm-offset-3 col-md-10 col-md-offset-2 main">
{% block page-content %} {% endblock %}
</div>
</div>
</div>
Python CRM项目八的更多相关文章
- Python CRM项目二
一.准备工作 如果没有配置基本的项目,请参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/luhuajun/p/7771196.html 当我们配置完成后首先准备我们的app 创建2个app分别对应 ...
- Python CRM项目一
开发环境: 语言Python3.X以上 MTV WEB框架 Django 前端框架 jQuery+bootstrap 数据库 MySQL 运行环境 安装Python3.x 安装Django 除IE8以 ...
- Python CRM项目三
1.分页: 分页使用Django内置的分页模块来实现 官方的分页案例 from django.core.paginator import Paginator, EmptyPage, PageNotAn ...
- python实践项目八:生成随机试卷文件
描述:匹配美国50个州的首府. 下面是程序需要完成的任务: • 创建35 份不同的测验试卷. • 为每份试卷创建50 个多重选择题,次序随机. • 为每个问题提供一个正确答案和3 个随机的错误答案,次 ...
- Python CRM项目七
仿照Django Admin实现对readonly的字段进行设置 功能点: 1.页面不可进行更改 2.如果改变html代码中的值,则需要进行后端的数据库数据校验 3.可以对某些字段进行自定制校验规则 ...
- Python CRM项目六
自定义Django Admin的action 在Django Admin中,可以通过action来自定义一些操作,其中默认的action的功能是选中多条数据来进行删除操作 我们在king_admin中 ...
- Python CRM项目四
实现Django Admin的多对多的复选框效果 效果:左边显示的是未选中的字段,右边显示的是已选中的字段,两边点击的标签可以互相更换 首先在king_admin.py中增加filter_horizo ...
- 2015老男孩Python培训第八期视频教程
2015老男孩Python培训第八期视频教程,希望您通过本教程的学习,能学会常用方法和技巧.教程从基础知识开始讲解一直到后期的案例实战,完全零基础学习,从初学者的角度探讨分析问题,循序渐进由易到难,确 ...
- Python Tutorial 学习(八)--Errors and Exceptions
Python Tutorial 学习(八)--Errors and Exceptions恢复 Errors and Exceptions 错误与异常 此前,我们还没有开始着眼于错误信息.不过如果你是一 ...
随机推荐
- SQLAlchemy框架用法详解
介绍 SQLAlchemy是一个基于Python实现的ORM框架.该框架建立在 DBAPI之上,使用关系对象映射进行数据库操作,简言之便是:将类和对象转换成SQL,然后使用数据API执行SQL并获取执 ...
- Gym 101667I Slot Machines
原题传送门 题意:给定n(n≤106)个数,要求将它化为混偱环小数的形式,即前k个数不参与循环,之后所有数以p为循环节长度进行循环.求k和p,要求k+p尽量小,k+p相等时要求p尽量小. 样例1 输入 ...
- C语言单向链表
1,为什么要用到链表 数组作为存放同类数据的集合,给我们在程序设计时带来很多的方便,增加了灵活性.但数组也同样存在一些弊病.如数组的大小在定义时要事先规定,不能在程序中进行调整,这样一来,在程序设计中 ...
- UE4 字符串的转换
创建Fstring: FString TestHUDString = FString(TEXT("This is my test FString.")); FString,FNam ...
- .25-浅析webpack源码之事件流compilation(3)
这一节跑下一批plugin. compiler.apply( new EnsureChunkConditionsPlugin(), new RemoveParentModulesPlugin(), n ...
- Linux 离线安装Rubygems详解
很多时候我们会发现,真实的生成环境很多都没有外网,只有内网环境,这个时候我们又需要安装RubyGems,则不能提供yum命令进行在线安装了,这个时候我们就需要下载安装包进行离线安装.本文主要简单介绍如 ...
- error: Failed dependencies:解决
error: Failed dependencies:解决 使用rpma安装安装包时,会出现 error: Failed dependencies: 意思是 失败的依赖 解决方法: 在安装包后面加两个 ...
- 从零开始学习前端JAVASCRIPT — 2、JavaScript基础ES5
1:ES5简介 ECMAScript 5.1 (或仅 ES5) 是ECMAScript(基于JavaScript的规范)标准的修正. 与HTML5规范进程本质类似,ES5通过对现有JavaScript ...
- Redis 数据结构与内存管理策略(下)
Redis 数据结构与内存管理策略(下) 标签: Redis Redis数据结构 Redis内存管理策略 Redis数据类型 Redis类型映射 Redis 数据类型特点与使用场景 String.Li ...
- Html5+js测试题【完整版】
一.闭包的理解:使用闭包主要是为了设计私有的方法和变量.闭包的优点是可以避免全局变量的污染,缺点是闭包会常驻内存,会增大内存使用量,使用不当很容易造成内存泄露.闭包三个特性: 1.函数嵌套函数 ; 2 ...
