mser 最大稳定极值区域(文字区域定位)算法 附完整C代码
mser 的全称:Maximally Stable Extremal Regions
第一次听说这个算法时,是来自当时部门的一个同事,
提及到他的项目用它来做文字区域的定位,对这个算法做了一些优化。
也就是中文车牌识别开源项目EasyPR的作者liuruoze,刘兄。
自那时起就有一块石头没放下,想要找个时间好好理理这个算法。
学习一些它的一些思路。
因为一般我学习算法的思路:3个做法,
第一步,编写demo示例。
第二步,进行算法移植或效果改进。
第三步,进行算法性能优化。
然后在这三个过程中,不断来回地验证,实测。
任何事情,一下子囫囵吞枣,容易呛到。
找了不少资料,mser这方面的资料还挺少。
比较不错的资料自然就是开源项目opencv以及VLFeat。
opencv用了太多依赖和封装,阅读代码非常费事。
VLFeat则友好得多。
嗯,花了点时间把mser从VLFeat抽离出来,并编写相应的测试用例。
代码注释比较详尽,写这个示例 demo 的时候,
来回翻阅官方文档无头绪,阅读代码以及注释才大致理清楚逻辑。
项目地址:https://github.com/cpuimage/mser
附完整代码:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007-12 Andrea Vedaldi and Brian Fulkerson.
* All rights reserved.
* This file is part of the VLFeat library and is made available under
* the terms of the BSD license (see the COPYING file).
*/
#define MSER_DRIVER_VERSION 0.2 #define STB_IMAGE_STATIC
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
/* ref:https://github.com/nothings/stb/blob/master/stb_image.h */
#define TJE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "tiny_jpeg.h"
/* ref:https://github.com/serge-rgb/TinyJPEG/blob/master/tiny_jpeg.h */ #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* 计时 */
#include <stdint.h>
#if defined(__APPLE__)
#include <mach/mach_time.h>
#elif defined(_WIN32)
#define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
#include <windows.h>
#else /* __linux */
#include <time.h>
#ifndef CLOCK_MONOTONIC /* _RAW */
#define CLOCK_MONOTONIC CLOCK_REALTIME
#endif
#endif
static
uint64_t nanotimer()
{
static int ever = ;
#if defined(__APPLE__)
static mach_timebase_info_data_t frequency;
if (!ever)
{
if (mach_timebase_info(&frequency) != KERN_SUCCESS)
{
return();
}
ever = ;
}
return;
#elif defined(_WIN32)
static LARGE_INTEGER frequency;
if (!ever)
{
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&frequency);
ever = ;
}
LARGE_INTEGER t;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&t);
return((t.QuadPart * (uint64_t) 1e9) / frequency.QuadPart);
#else /* __linux */
struct timespec t;
if (!ever)
{
if (clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &spec) != )
{
return();
}
ever = ;
}
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &spec);
return((t.tv_sec * (uint64_t) 1e9) + t.tv_nsec);
#endif
} static double now()
{
static uint64_t epoch = ;
if (!epoch)
{
epoch = nanotimer();
}
return((nanotimer() - epoch) / 1e9);
}; double calcElapsed(double start, double end)
{
double took = -start;
return(took + end);
} unsigned char* loadImage(const char * filename, int * width, int * height, int * depth)
{
unsigned char *output = stbi_load(filename, width, height, depth, );
*depth = ;
return(output);
} bool saveJpeg(const char * filename, int width, int height, int depth, unsigned char* bits)
{
if (!tje_encode_to_file(filename, width, height, depth, true, bits))
{
fprintf(stderr, "save JPEG fail.\n");
return(false);
} return(true);
} /** @brief Maximum value
**
** Maximum value of the integer type ::unsigned char.
**/
#define MSER_PIX_MAXVAL 256 /** @brief MSER Filter
**
** The MSER filter computes the Maximally Stable Extremal Regions of
** an image.
**
** @sa @ref mser
**/
typedef struct _MserFilt MserFilt; /** @brief MSER filter statistics */
typedef struct _MserStats MserStats; /** @brief MSER filter statistics definition */
struct _MserStats
{
int num_extremal; /**< number of extremal regions */
int num_unstable; /**< number of unstable extremal regions */
int num_abs_unstable; /**< number of regions that failed the absolute stability test */
int num_too_big; /**< number of regions that failed the maximum size test */
int num_too_small; /**< number of regions that failed the minimum size test */
int num_duplicates; /**< number of regions that failed the duplicate test */
}; /** @name Construction and Destruction
** @{
**/
MserFilt* mser_new(int ndims, int const* dims); void mser_delete(MserFilt *f); /** @} */ /** @name Processing
** @{
**/
void mser_process(MserFilt *f,
unsigned char const *im); void mser_ell_fit(MserFilt *f); /** @} */ /** @name Retrieving data
** @{
**/
unsigned int mser_get_regions_num(MserFilt const *f); unsigned int const* mser_get_regions(MserFilt const *f); float const* mser_get_ell(MserFilt const *f); unsigned int mser_get_ell_num(MserFilt const *f); unsigned int mser_get_ell_dof(MserFilt const *f); MserStats const* mser_get_stats(MserFilt const *f); /** @} */ /** @name Retrieving parameters
** @{
**/
unsigned char mser_get_delta(MserFilt const *f); float mser_get_min_area(MserFilt const *f); float mser_get_max_area(MserFilt const *f); float mser_get_max_variation(MserFilt const *f); float mser_get_min_diversity(MserFilt const *f); /** @} */ /** @name Setting parameters
** @{
**/
void mser_set_delta(MserFilt *f, unsigned char x); void mser_set_min_area(MserFilt *f, float x); void mser_set_max_area(MserFilt *f, float x); void mser_set_max_variation(MserFilt *f, float x); void mser_set_min_diversity(MserFilt *f, float x); /** @} */ /* ====================================================================
* INLINE DEFINITIONS
* ================================================================== */ /** @internal
** @brief MSER accumulator data type
**
** This is a large integer type. It should be large enough to contain
** a number equal to the area (volume) of the image by the image
** width by the image height (for instance, if the image is a square
** of side 256, the maximum value is 256 x 256 x 256).
**/
typedef float mser_acc; /** @internal @brief Basic region flag: null region */
#ifdef COMPILER_MSC
#define MSER_VOID_NODE ( (1ui64 << 32) - 1)
#else
#define MSER_VOID_NODE ( (1ULL << 32) - 1)
#endif /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @internal
** @brief MSER: basic region (declaration)
**
** Extremal regions and maximally stable extremal regions are
** instances of image regions.
**
** There is an image region for each pixel of the image. Each region
** is represented by an instance of this structure. Regions are
** stored into an array in pixel order.
**
** Regions are arranged into a forest. MserReg::parent points to
** the parent node, or to the node itself if the node is a root.
** MserReg::parent is the index of the node in the node array
** (which therefore is also the index of the corresponding
** pixel). MserReg::height is the distance of the fartest leaf. If
** the node itself is a leaf, then MserReg::height is zero.
**
** MserReg::area is the area of the image region corresponding to
** this node.
**
** MserReg::region is the extremal region identifier. Not all
** regions are extremal regions however; if the region is NOT
** extremal, this field is set to ....
**/
struct _MserReg
{
unsigned int parent; /**< points to the parent region. */
unsigned int shortcut; /**< points to a region closer to a root. */
unsigned int height; /**< region height in the forest. */
unsigned int area; /**< area of the region. */
}; /** @internal @brief MSER: basic region */
typedef struct _MserReg MserReg; /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @internal
** @brief MSER: extremal region (declaration)
**
** Extremal regions (ER) are extracted from the region forest. Each
** region is represented by an instance of this structure. The
** structures are stored into an array, in arbitrary order.
**
** ER are arranged into a tree. @a parent points to the parent ER, or
** to itself if the ER is the root.
**
** An instance of the structure represents the extremal region of the
** level set of intensity MserExtrReg::value and containing the
** pixel MserExtReg::index.
**
** MserExtrReg::area is the area of the extremal region and
** MserExtrReg::area_top is the area of the extremal region
** containing this region in the level set of intensity
** MserExtrReg::area + @c delta.
**
** MserExtrReg::variation is the relative area variation @c
** (area_top-area)/area.
**
** MserExtrReg::max_stable is a flag signaling whether this extremal
** region is also maximally stable.
**/
struct _MserExtrReg
{
int parent; /**< index of the parent region */
int index; /**< index of pivot pixel */
unsigned char value; /**< value of pivot pixel */
unsigned int shortcut; /**< shortcut used when building a tree */
unsigned int area; /**< area of the region */
float variation; /**< rel. area variation */
unsigned int max_stable; /**< max stable number (=0 if not maxstable) */
}; /** @internal
** @brief MSER: extremal region */
typedef struct _MserExtrReg MserExtrReg; /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @internal
** @brief MSER filter
** @see @ref mser
**/
struct _MserFilt
{
/** @name Image data and meta data @internal */
/*@{*/
int ndims; /**< number of dimensions */
int *dims; /**< dimensions */
int nel; /**< number of image elements (pixels) */
int *subs; /**< N-dimensional subscript */
int *dsubs; /**< another subscript */
int *strides; /**< strides to move in image data */
/*@}*/ unsigned int *perm; /**< pixel ordering */
unsigned int *joins; /**< sequence of join ops */
int njoins; /**< number of join ops */ /** @name Regions */
/*@{*/
MserReg *r; /**< basic regions */
MserExtrReg *er; /**< extremal tree */
unsigned int *mer; /**< maximally stable extremal regions */
int ner; /**< number of extremal regions */
int nmer; /**< number of maximally stable extr. reg. */
int rer; /**< size of er buffer */
int rmer; /**< size of mer buffer */
/*@}*/ /** @name Ellipsoids fitting */
/*@{*/
float *acc; /**< moment accumulator. */
float *ell; /**< ellipsoids list. */
int rell; /**< size of ell buffer */
int nell; /**< number of ellipsoids extracted */
int dof; /**< number of dof of ellipsoids. */ /*@}*/ /** @name Configuration */
/*@{*/
int verbose; /**< be verbose */
int delta; /**< delta filter parameter */
float max_area; /**< badness test parameter */
float min_area; /**< badness test parameter */
float max_variation; /**< badness test parameter */
float min_diversity; /**< minimum diversity */
/*@}*/ MserStats stats; /** run statistic */
}; /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get delta
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return value of @c delta.
**/
unsigned char
mser_get_delta(MserFilt const *f)
{
return(f->delta);
} /** @brief Set delta
** @param f MSER filter.
** @param x value of @c delta.
**/
void
mser_set_delta(MserFilt *f, unsigned char x)
{
f->delta = x;
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get minimum diversity
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return value of @c minimum diversity.
**/
float
mser_get_min_diversity(MserFilt const *f)
{
return(f->min_diversity);
} /** @brief Set minimum diversity
** @param f MSER filter.
** @param x value of @c minimum diversity.
**/
void
mser_set_min_diversity(MserFilt *f, float x)
{
f->min_diversity = x;
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get statistics
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return statistics.
**/
MserStats const*
mser_get_stats(MserFilt const *f)
{
return(&f->stats);
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get maximum region area
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return maximum region area.
**/
float
mser_get_max_area(MserFilt const *f)
{
return(f->max_area);
} /** @brief Set maximum region area
** @param f MSER filter.
** @param x maximum region area.
**/
void
mser_set_max_area(MserFilt *f, float x)
{
f->max_area = x;
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get minimum region area
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return minimum region area.
**/
float
mser_get_min_area(MserFilt const *f)
{
return(f->min_area);
} /** @brief Set minimum region area
** @param f MSER filter.
** @param x minimum region area.
**/
void
mser_set_min_area(MserFilt *f, float x)
{
f->min_area = x;
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get maximum region variation
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return maximum region variation.
**/
float
mser_get_max_variation(MserFilt const *f)
{
return(f->max_variation);
} /** @brief Set maximum region variation
** @param f MSER filter.
** @param x maximum region variation.
**/
void
mser_set_max_variation(MserFilt *f, float x)
{
f->max_variation = x;
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get maximally stable extremal regions
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return array of MSER pivots.
**/
unsigned int const *
mser_get_regions(MserFilt const* f)
{
return(f->mer);
} /** @brief Get number of maximally stable extremal regions
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return number of MSERs.
**/
unsigned int
mser_get_regions_num(MserFilt const* f)
{
return(f->nmer);
} /* ----------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** @brief Get ellipsoids
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return ellipsoids.
**/
float const *
mser_get_ell(MserFilt const* f)
{
return(f->ell);
} /** @brief Get number of degrees of freedom of ellipsoids
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return number of degrees of freedom.
**/
unsigned int
mser_get_ell_dof(MserFilt const* f)
{
return(f->dof);
} /** @brief Get number of ellipsoids
** @param f MSER filter.
** @return number of ellipsoids
**/
unsigned int
mser_get_ell_num(MserFilt const* f)
{
return(f->nell);
} /*MSER */ /** -------------------------------------------------------------------
** @brief Advance N-dimensional subscript
**
** The function increments by one the subscript @a subs indexing an
** array the @a ndims dimensions @a dims.
**
** @param ndims number of dimensions.
** @param dims dimensions.
** @param subs subscript to advance.
**/ void adv(int ndims, int const *dims, int *subs)
{
int d = ;
while (d < ndims)
{
if (++subs[d] < dims[d])
return;
subs[d++] = ;
}
} /** -------------------------------------------------------------------
** @brief Climb the region forest to reach aa root
**
** The function climbs the regions forest @a r starting from the node
** @a idx to the corresponding root.
**
** To speed-up the operation, the function uses the
** MserReg::shortcut field to quickly jump to the root. After the
** root is reached, all the used shortcut are updated.
**
** @param r regions' forest.
** @param idx stating node.
** @return index of the reached root.
**/ unsigned int climb(MserReg* r, unsigned int idx)
{
unsigned int prev_idx = idx;
unsigned int next_idx;
unsigned int root_idx; /* move towards root to find it */
while ()
{
/* next jump to the root */
next_idx = r[idx].shortcut; /* recycle shortcut to remember how we came here */
r[idx].shortcut = prev_idx; /* stop if the root is found */
if (next_idx == idx)
break; /* next guy */
prev_idx = idx;
idx = next_idx;
} root_idx = idx; /* move backward to update shortcuts */
while ()
{
/* get previously visited one */
prev_idx = r[idx].shortcut; /* update shortcut to point to the new root */
r[idx].shortcut = root_idx; /* stop if the first visited node is reached */
if (prev_idx == idx)
break; /* next guy */
idx = prev_idx;
} return(root_idx);
} /** -------------------------------------------------------------------
** @brief Create a new MSER filter
**
** Initializes a new MSER filter for images of the specified
** dimensions. Images are @a ndims -dimensional arrays of dimensions
** @a dims.
**
** @param ndims number of dimensions.
** @param dims dimensions.
**/ MserFilt*
mser_new(int ndims, int const* dims)
{
MserFilt* f = (MserFilt *)calloc(sizeof(MserFilt), ); f->ndims = ndims;
f->dims = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * ndims);
f->subs = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * ndims);
f->dsubs = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * ndims);
f->strides = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * ndims);
/* shortcuts */
if (f->dims != NULL && f->subs != NULL && f->dsubs != NULL && f->strides != NULL)
{
int k = ; /* copy dims to f->dims */
memcpy(f->dims, dims, sizeof(int) * ndims); /* compute strides to move into the N-dimensional image array */
f->strides[] = ;
for (k = ; k < ndims; ++k)
{
f->strides[k] = f->strides[k - ] * dims[k - ];
} /* total number of pixels */
f->nel = f->strides[ndims - ] * dims[ndims - ]; /* dof of ellipsoids */
f->dof = ndims * (ndims + ) / + ndims; /* more buffers */
f->perm = (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int) * f->nel);
f->joins = (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int) * f->nel);
f->r = (MserReg *)malloc(sizeof(MserReg) * f->nel); f->er = ;
f->rer = ;
f->mer = ;
f->rmer = ;
f->ell = ;
f->rell = ; /* other parameters */
f->delta = ;
f->max_area = 0.75f;
f->min_area = 3.0f / f->nel;
f->max_variation = 0.25f;
f->min_diversity = 0.2f;
}
return(f);
} /** -------------------------------------------------------------------
** @brief Delete MSER filter
**
** The function releases the MSER filter @a f and all its resources.
**
** @param f MSER filter to be deleted.
**/ void
mser_delete(MserFilt* f)
{
if (f)
{
if (f->acc)
free(f->acc);
if (f->ell)
free(f->ell); if (f->er)
free(f->er);
if (f->r)
free(f->r);
if (f->joins)
free(f->joins);
if (f->perm)
free(f->perm); if (f->strides)
free(f->strides);
if (f->dsubs)
free(f->dsubs);
if (f->subs)
free(f->subs);
if (f->dims)
free(f->dims); if (f->mer)
free(f->mer);
free(f);
}
} #define MAX( x, y ) ( ( (x) > (y) ) ? (x) : (y) ) /** -------------------------------------------------------------------
** @brief Process image
**
** The functions calculates the Maximally Stable Extremal Regions
** (MSERs) of image @a im using the MSER filter @a f.
**
** The filter @a f must have been initialized to be compatible with
** the dimensions of @a im.
**
** @param f MSER filter.
** @param im image data.
**/ void
mser_process(MserFilt* f, unsigned char const* im)
{
/* shortcuts */
unsigned int nel = f->nel;
unsigned int *perm = f->perm;
unsigned int *joins = f->joins;
int ndims = f->ndims;
int *dims = f->dims;
int *subs = f->subs;
int *dsubs = f->dsubs;
int *strides = f->strides;
MserReg *r = f->r;
MserExtrReg *er = f->er;
unsigned int *mer = f->mer;
int delta = f->delta; int njoins = ;
int ner = ;
int nmer = ;
int nbig = ;
int nsmall = ;
int nbad = ;
int ndup = ; int i, j, k; /* delete any previosuly computed ellipsoid */
f->nell = ; /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Sort pixels by intensity
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ {
unsigned int buckets[MSER_PIX_MAXVAL]; /* clear buckets */
memset(buckets, , sizeof(unsigned int) * MSER_PIX_MAXVAL); /* compute bucket size (how many pixels for each intensity
* value) */
for (i = ; i < (int)nel; ++i)
{
unsigned char v = im[i];
++buckets[v];
} /* cumulatively add bucket sizes */
for (i = ; i < MSER_PIX_MAXVAL; ++i)
{
buckets[i] += buckets[i - ];
} /* empty buckets computing pixel ordering */
for (i = nel; i >= ; )
{
unsigned char v = im[--i];
unsigned int j = --buckets[v];
perm[j] = i;
}
} /* initialize the forest with all void nodes */
for (i = ; i < (int)nel; ++i)
{
r[i].parent = MSER_VOID_NODE;
} /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Compute regions and count extremal regions
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ /*
* In the following:
* idx : index of the current pixel
* val : intensity of the current pixel
* r_idx : index of the root of the current pixel
* n_idx : index of the neighbors of the current pixel
* nr_idx : index of the root of the neighbor of the current pixel
*/ /* process each pixel by increasing intensity */
for (i = ; i < (int)nel; ++i)
{
/* pop next node xi */
unsigned int idx = perm[i];
unsigned char val = im[idx];
unsigned int r_idx; /* add the pixel to the forest as a root for now */
r[idx].parent = idx;
r[idx].shortcut = idx;
r[idx].area = ;
r[idx].height = ; r_idx = idx; /* convert the index IDX into the subscript SUBS; also initialize
* DSUBS to (-1,-1,...,-1) */
{
unsigned int temp = idx;
for (k = ndims - ; k >= ; --k)
{
dsubs[k] = -;
subs[k] = temp / strides[k];
temp = temp % strides[k];
}
} /* examine the neighbors of the current pixel */
while ()
{
unsigned int n_idx = ;
int good = ; /*
* Compute the neighbor subscript as NSUBS+SUB, the
* corresponding neighbor index NINDEX and check that the
* neighbor is within the image domain.
*/
for (k = ; k < ndims && good; ++k)
{
int temp = dsubs[k] + subs[k];
good &= ( <= temp) && (temp < dims[k]);
n_idx += temp * strides[k];
} /*
* The neighbor should be processed if the following conditions
* are met:
* 1. The neighbor is within image boundaries.
* 2. The neighbor is indeed different from the current node
* (the opposite happens when DSUB=(0,0,...,0)).
* 3. The neighbor is already in the forest, meaning that it has
* already been processed.
*/
if (good &&
n_idx != idx &&
r[n_idx].parent != MSER_VOID_NODE)
{
unsigned char nr_val = ;
unsigned int nr_idx = ;
int hgt = r[r_idx].height;
int n_hgt = r[nr_idx].height; /*
* Now we join the two subtrees rooted at
* R_IDX = ROOT( IDX)
* NR_IDX = ROOT(N_IDX).
* Note that R_IDX = ROOT(IDX) might change as we process more
* neighbors, so we need keep updating it.
*/ r_idx = climb(r, idx);
nr_idx = climb(r, n_idx); /*
* At this point we have three possibilities:
* (A) ROOT(IDX) == ROOT(NR_IDX). In this case the two trees
* have already been joined and we do not do anything.
* (B) I(ROOT(IDX)) == I(ROOT(NR_IDX)). In this case the pixel
* IDX is extending an extremal region with the same
* intensity value. Since ROOT(NR_IDX) will NOT be an
* extremal region of the full image, ROOT(IDX) can be
* safely added as children of ROOT(NR_IDX) if this
* reduces the height according to the union rank
* heuristic.
* (C) I(ROOT(IDX)) > I(ROOT(NR_IDX)). In this case the pixel
* IDX is starting a new extremal region. Thus ROOT(NR_IDX)
* WILL be an extremal region of the final image and the
* only possibility is to add ROOT(NR_IDX) as children of
* ROOT(IDX), which becomes parent.
*/ if (r_idx != nr_idx) /* skip if (A) */ {
nr_val = im[nr_idx]; if (nr_val == val && hgt < n_hgt)
{
/* ROOT(IDX) becomes the child */
r[r_idx].parent = nr_idx;
r[r_idx].shortcut = nr_idx;
r[nr_idx].area += r[r_idx].area;
r[nr_idx].height = MAX(n_hgt, hgt + ); joins[njoins++] = r_idx;
}
else {
/* cases ROOT(IDX) becomes the parent */
r[nr_idx].parent = r_idx;
r[nr_idx].shortcut = r_idx;
r[r_idx].area += r[nr_idx].area;
r[r_idx].height = MAX(hgt, n_hgt + ); joins[njoins++] = nr_idx; /* count if extremal */
if (nr_val != val)
++ner;
} /* check b vs c */
} /* check a vs b or c */
} /* neighbor done */ /* move to next neighbor */
k = ;
while (++dsubs[k] > )
{
dsubs[k++] = -;
if (k == ndims)
goto done_all_neighbors;
}
} /* next neighbor */
done_all_neighbors:;
} /* next pixel */ /* the last root is extremal too */
++ner; /* save back */
f->njoins = njoins; f->stats.num_extremal = ner; /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Extract extremal regions
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ /*
* Extremal regions are extracted and stored into the array ER. The
* structure R is also updated so that .SHORTCUT indexes the
* corresponding extremal region if any (otherwise it is set to
* VOID).
*/ /* make room */
if (f->rer < ner)
{
if (er)
free(er);
f->er = er = (MserExtrReg *)malloc(sizeof(MserExtrReg) * ner);
f->rer = ner;
}
; /* save back */
f->nmer = ner; /* count again */
ner = ; /* scan all regions Xi */
if (er != NULL)
{
for (i = ; i < (int)nel; ++i)
{
/* pop next node xi */
unsigned int idx = perm[i]; unsigned char val = im[idx];
unsigned int p_idx = r[idx].parent;
unsigned char p_val = im[p_idx]; /* is extremal ? */
int is_extr = (p_val > val) || idx == p_idx; if (is_extr)
{
/* if so, add it */
er[ner].index = idx;
er[ner].parent = ner;
er[ner].value = im[idx];
er[ner].area = r[idx].area; /* link this region to this extremal region */
r[idx].shortcut = ner; /* increase count */
++ner;
}
else {
/* link this region to void */
r[idx].shortcut = MSER_VOID_NODE;
}
}
} /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Link extremal regions in a tree
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ for (i = ; i < ner; ++i)
{
unsigned int idx = er[i].index; do
{
idx = r[idx].parent;
} while (r[idx].shortcut == MSER_VOID_NODE); er[i].parent = r[idx].shortcut;
er[i].shortcut = i;
} /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Compute variability of +DELTA branches
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ /* For each extremal region Xi of value VAL we look for the biggest
* parent that has value not greater than VAL+DELTA. This is dubbed
* `top parent'. */ for (i = ; i < ner; ++i)
{
/* Xj is the current region the region and Xj are the parents */
int top_val = er[i].value + delta;
int top = er[i].shortcut; /* examine all parents */
while ()
{
int next = er[top].parent;
int next_val = er[next].value; /* Break if:
* - there is no node above the top or
* - the next node is above the top value.
*/
if (next == top || next_val > top_val)
break; /* so next could be the top */
top = next;
} /* calculate branch variation */
{
int area = er[i].area;
int area_top = er[top].area;
er[i].variation = (float)(area_top - area) / area;
er[i].max_stable = ;
} /* Optimization: since extremal regions are processed by
* increasing intensity, all next extremal regions being processed
* have value at least equal to the one of Xi. If any of them has
* parent the parent of Xi (this comprises the parent itself), we
* can safely skip most intermediate node along the branch and
* skip directly to the top to start our search. */
{
int parent = er[i].parent;
int curr = er[parent].shortcut;
er[parent].shortcut = MAX(top, curr);
}
} /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Select maximally stable branches
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ nmer = ner;
for (i = ; i < ner; ++i)
{
unsigned int parent = er[i].parent;
unsigned char val = er[i].value;
float var = er[i].variation;
unsigned char p_val = er[parent].value;
float p_var = er[parent].variation;
unsigned int loser; /*
* Notice that R_parent = R_{l+1} only if p_val = val + 1. If not,
* this and the parent region coincide and there is nothing to do.
*/
if (p_val > val + )
continue; /* decide which one to keep and put that in loser */
if (var < p_var)
loser = parent;
else loser = i; /* make loser NON maximally stable */
if (er[loser].max_stable)
{
--nmer;
er[loser].max_stable = ;
}
} f->stats.num_unstable = ner - nmer; /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Further filtering
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ /* It is critical for correct duplicate detection to remove regions
* from the bottom (smallest one first). */
{
float max_area = (float)f->max_area * nel;
float min_area = (float)f->min_area * nel;
float max_var = (float)f->max_variation;
float min_div = (float)f->min_diversity; /* scan all extremal regions (intensity value order) */
for (i = ner - ; i >= 0L; --i)
{
/* process only maximally stable extremal regions */
if (!er[i].max_stable)
continue; if (er[i].variation >= max_var)
{
++nbad; goto remove;
}
if (er[i].area > max_area)
{
++nbig; goto remove;
}
if (er[i].area < min_area)
{
++nsmall; goto remove;
} /*
* Remove duplicates
*/
if (min_div < 1.0)
{
unsigned int parent = er[i].parent;
int area, p_area;
float div; /* check all but the root mser */
if ((int)parent != i)
{
/* search for the maximally stable parent region */
while (!er[parent].max_stable)
{
unsigned int next = er[parent].parent;
if (next == parent)
break;
parent = next;
} /* Compare with the parent region; if the current and parent
* regions are too similar, keep only the parent. */
area = er[i].area;
p_area = er[parent].area;
div = (float)(p_area - area) / (float)p_area; if (div < min_div)
{
++ndup; goto remove;
}
} /* remove dups end */
}
continue;
remove:
er[i].max_stable = ;
--nmer;
} /* check next region */ f->stats.num_abs_unstable = nbad;
f->stats.num_too_big = nbig;
f->stats.num_too_small = nsmall;
f->stats.num_duplicates = ndup;
} /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Save the result
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ /* make room */
if (f->rmer < nmer)
{
if (mer)
free(mer);
f->mer = mer = (unsigned int *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned int) * nmer);
f->rmer = nmer;
} /* save back */
f->nmer = nmer; j = ;
if (er != NULL && mer != NULL)
{
for (i = ; i < ner; ++i)
{
if (er[i].max_stable)
mer[j++] = er[i].index;
}
}
} /** -------------------------------------------------------------------
** @brief Fit ellipsoids
**
** @param f MSER filter.
**
** @sa @ref mser-ell
**/ void
mser_ell_fit(MserFilt* f)
{
/* shortcuts */
int nel = f->nel;
int dof = f->dof;
int *dims = f->dims;
int ndims = f->ndims;
int *subs = f->subs;
int njoins = f->njoins;
unsigned int *joins = f->joins;
MserReg *r = f->r;
unsigned int *mer = f->mer;
int nmer = f->nmer;
mser_acc *acc = f->acc;
mser_acc *ell = f->ell; int d, index, i, j; /* already fit ? */
if (f->nell == f->nmer)
return; /* make room */
if (f->rell < f->nmer)
{
if (f->ell)
free(f->ell);
f->ell = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * f->nmer * f->dof);
f->rell = f->nmer;
} if (f->acc == )
{
f->acc = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * f->nel);
} acc = f->acc;
ell = f->ell; /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Integrate moments
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ /* for each dof */
for (d = ; d < f->dof; ++d)
{
/* start from the upper-left pixel (0,0,...,0) */
memset(subs, , sizeof(int) * ndims); /* step 1: fill acc pretending that each region has only one pixel */
if (d < ndims)
{
/* 1-order ................................................... */ for (index = ; index < nel; ++index)
{
acc[index] = (float)subs[d];
adv(ndims, dims, subs);
}
}
else {
/* 2-order ................................................... */ /* map the dof d to a second order moment E[x_i x_j] */
i = d - ndims;
j = ;
while (i > j)
{
i -= j + ;
j++;
}
/* initialize acc with x_i * x_j */
for (index = ; index < nel; ++index)
{
acc[index] = (float)(subs[i] * subs[j]);
adv(ndims, dims, subs);
}
} /* step 2: integrate */
for (i = ; i < njoins; ++i)
{
unsigned int index = joins[i];
unsigned int parent = r[index].parent;
acc[parent] += acc[index];
} /* step 3: save back to ellpises */
for (i = ; i < nmer; ++i)
{
unsigned int idx = mer[i];
ell[d + dof * i] = acc[idx];
}
} /* next dof */ /* -----------------------------------------------------------------
* Compute central moments
* -------------------------------------------------------------- */ for (index = ; index < nmer; ++index)
{
float *pt = ell + index * dof;
unsigned int idx = mer[index];
float area = (float)r[idx].area; for (d = ; d < dof; ++d)
{
pt[d] /= area; if (d >= ndims)
{
/* remove squared mean from moment to get variance */
i = d - ndims;
j = ;
while (i > j)
{
i -= j + ;
j++;
}
pt[d] -= pt[i] * pt[j];
}
}
} /* save back */
f->nell = nmer;
} void drawEllipse(const float * region, int width, int height, int depth, unsigned char* bits, const uint8_t * color)
{
/* Centroid (mean) */
const float x = region[];
const float y = region[]; /* Covariance matrix [a b; b c] */
const float a = region[];
const float b = region[];
const float c = region[]; /* Eigenvalues of the covariance matrix */
const float d = a + c;
const float e = a - c;
const float f = sqrtf(4.0f * b * b + e * e);
const float e0 = (d + f) / 2.0f; /* First eigenvalue */
const float e1 = (d - f) / 2.0f; /* Second eigenvalue */ /* Desired norm of the eigenvectors */
const float e0sq = sqrtf(e0);
const float e1sq = sqrtf(e1); /* Eigenvectors */
float v0x = e0sq;
float v0y = 0.0f;
float v1x = 0.0f;
float v1y = e1sq; if (b)
{
v0x = e0 - c;
v0y = b;
v1x = e1 - c;
v1y = b; /* Normalize the eigenvectors */
const float n0 = e0sq / sqrtf(v0x * v0x + v0y * v0y);
v0x *= n0;
v0y *= n0; const float n1 = e1sq / sqrtf(v1x * v1x + v1y * v1y);
v1x *= n1;
v1y *= n1;
} for (float t = 0.0f; t < 2.0f * M_PI; t += 0.001f)
{
int x2 = (int)(x + (cosf(t) * v0x + sinf(t) * v1x) * 2.0f + 0.5f);
int y2 = (int)(y + (cosf(t) * v0y + sinf(t) * v1y) * 2.0f + 0.5f); if ((x2 >= ) && (x2 < width) && (y2 >= ) && (y2 < height))
for (int i = ; i < min(depth, ); ++i)
bits[(y2 * width + x2) * depth + i] = color[i];
}
} /** @brief MSER driver entry point
**/
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/* algorithm parameters */
float delta = ;
float max_area = 0.5f;
float min_area = 0.0001f;
float max_variation = 0.5f;
float min_diversity = 0.33f;
int dark_on_bright = ; bool err = false;
char err_msg[];
int exit_code = ;
MserFilt *filt = ;
MserFilt *filtinv = ; unsigned int const *regions;
unsigned int const *regionsinv;
float const *frames;
float const *framesinv;
enum { ndims = };
int dims[ndims];
int nregions = , nregionsinv = , nframes = , nframesinv = ;
int i, dof; if (argc != )
{
fprintf
(stderr,
"Usage: %s input.jpg output.jpg\n",
argv[]);
return(-);
}
char * inputfile = argv[];
char * outputfile = argv[]; int width;
int height;
int depth;
unsigned char * data = loadImage(inputfile, &width, &height, &depth); unsigned char *datainv = NULL;
if (!data)
{
err = false;
snprintf(err_msg, sizeof(err_msg),
"Could not allocate enough memory.");
goto done;
}
dims[] = width;
dims[] = height; filt = mser_new(ndims, dims);
filtinv = mser_new(ndims, dims); if (!filt || !filtinv)
{
snprintf(err_msg, sizeof(err_msg),
"Could not create an MSER filter.");
goto done;
} if (delta >= )
mser_set_delta(filt, (unsigned char)delta);
if (max_area >= )
mser_set_max_area(filt, max_area);
if (min_area >= )
mser_set_min_area(filt, min_area);
if (max_variation >= )
mser_set_max_variation(filt, max_variation);
if (min_diversity >= )
mser_set_min_diversity(filt, min_diversity);
if (delta >= )
mser_set_delta(filtinv, (unsigned char)delta);
if (max_area >= )
mser_set_max_area(filtinv, max_area);
if (min_area >= )
mser_set_min_area(filtinv, min_area);
if (max_variation >= )
mser_set_max_variation(filtinv, max_variation);
if (min_diversity >= )
mser_set_min_diversity(filtinv, min_diversity); printf("mser: parameters:\n");
printf("mser: delta = %d\n", mser_get_delta(filt));
printf("mser: max_area = %g\n", mser_get_max_area(filt));
printf("mser: min_area = %g\n", mser_get_min_area(filt));
printf("mser: max_variation = %g\n", mser_get_max_variation(filt));
printf("mser: min_diversity = %g\n", mser_get_min_diversity(filt)); if (dark_on_bright)
{
double startTime = now();
mser_process(filt, (unsigned char *)data);
double nProcessTime = calcElapsed(startTime, now());
printf("Elapsed: %d ms \n ", (int)(nProcessTime * ));
/* Save result ----------------------------------------------- */
nregions = mser_get_regions_num(filt);
regions = mser_get_regions(filt); printf("nregions: %d \t", nregions); /*
* for (i = 0; i < nregions; ++i) {
* printf(" %d \t", regions[i]);
* }
*/
mser_ell_fit(filt); nframes = mser_get_ell_num(filt);
dof = mser_get_ell_dof(filt); printf("dof: %d \t", dof);
printf("nframes: %d \t", nframes);
/* Draw ellipses in the original image */
const uint8_t colors[] = { , , };
for (int x = ; x < ; ++x)
{
frames = mser_get_ell(filt);
for (i = ; i < nframes; ++i)
{
drawEllipse(frames, width, height, depth, data, colors);
frames += dof;
}
}
saveJpeg(outputfile, width, height, depth, data);
}
else {
/* allocate buffer */
datainv = (unsigned char *)malloc(width * height * depth);
for (i = ; i < width * height * depth; i++)
{
datainv[i] = ~data[i]; /* 255 - data[i] */
} if (!datainv)
{
err = false;
snprintf(err_msg, sizeof(err_msg),
"Could not allocate enough memory.");
goto done;
}
double startTime = now();
mser_process(filtinv, (unsigned char *)datainv);
double nProcessTime = calcElapsed(startTime, now());
printf("Elapsed: %d ms \n ", (int)(nProcessTime * ));
/* Save result ----------------------------------------------- */
nregionsinv = mser_get_regions_num(filtinv);
regionsinv = mser_get_regions(filtinv); /*
* for (i = 0; i < nregionsinv; ++i) {
* printf("%d \t ", -regionsinv[i]);
* }
*/ mser_ell_fit(filtinv); nframesinv = mser_get_ell_num(filtinv);
dof = mser_get_ell_dof(filtinv); const uint8_t colors[] = { , , }; framesinv = mser_get_ell(filtinv);
for (i = ; i < nframesinv; ++i)
{
drawEllipse(framesinv, width, height, depth, data, colors);
framesinv += dof;
}
saveJpeg(outputfile, width, height, depth, data);
} /* Next guy ----------------------------------------------- */
done:
/* release filter */
if (filt)
{
mser_delete(filt);
filt = ;
}
if (filtinv)
{
mser_delete(filtinv);
filtinv = ;
} /* release image data */
if (data)
{
free(data);
data = ;
}
if (datainv)
{
free(datainv);
datainv = ;
} /* if bad print error message */
if (err)
{
fprintf
(stderr,
"mser: err: %s (%d)\n",
err_msg,
err);
exit_code = ;
}
/* quit */
return(exit_code);
}
算法有两种模式,白底黑字,白字黑底,可根据具体需求进行开关。
可参照《图片文档倾斜矫正算法 附完整c代码》中判断是否为文本图片的方式进行算法思路的改进。
效果图例:


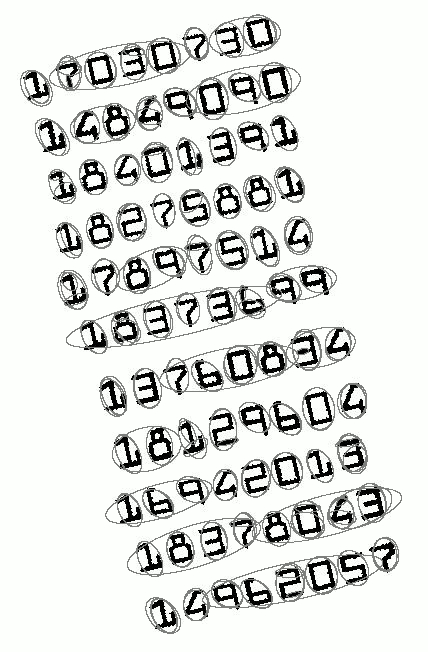
以上,再一次抛砖引玉。
若有其他相关问题或者需求也可以邮件联系俺探讨。
邮箱地址是:
gaozhihan@vip.qq.com
mser 最大稳定极值区域(文字区域定位)算法 附完整C代码的更多相关文章
- MSER最稳定极值区域源码分析
最稳定极值区域介绍 如把灰度图看成高低起伏的地形图,其中灰度值看成海平面高度的话,MSER的作用就是在灰度图中找到符合条件的坑洼.条件为坑的最小高度,坑的大小,坑的倾斜程度,坑中如果已有小坑时大坑与小 ...
- matlab实现MSER(最大极值稳定区域)来进行文本定位
一.自然场景文本定位综述 场景图像中文本占据的范围一般都较小,图像中存在着大范围的非文本区域.因此,场景图像文本定位作为一个独立步骤越来越受到重视.这包括从最先的CD和杂志封面文本定位到智能交通系 ...
- OpenCV入门笔记(七) 文字区域的提取
https://blog.csdn.net/huobanjishijian/article/details/63685503 前面我们已经学了一些OpenCV中基本的图片处理的知识,可以拿来做一些小应 ...
- ocr 文字区域检测及识别
ocr 文字区域检测及识别 # coding=utf- from PIL import Image, ImageFilter, ImageEnhance from skimage.filters im ...
- OpenCV:二值图像连通区域分析与标记算法实现
http://blog.csdn.net/cooelf/article/details/26581539?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral Open ...
- Trilateration三边测量定位算法
转载自Jiaxing / 2014年2月22日 基本原理 Trilateration(三边测量)是一种常用的定位算法: 已知三点位置 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (x3, y3) 已知未知 ...
- [CLPR] 定位算法探幽 - 边缘和形态学
一. 引言 如何从一副图片中找到车牌? 这是机器视觉的一个应用. 理所当然地, 思考的角度是从车牌本身的信息入手, 为了讨论方便, 下面均以长窄型蓝白车牌为例. 下图就是这样一张车牌的基本信息. 一眼 ...
- 关于APIT定位算法的讨论
关于APIT定位算法的讨论 [摘要] 无线传感器网络节点定位机制的研究中,基于距离无关的定位技术得到快速发展,其中基于重叠区域的APIT定位技术在实际环境中的定位精度高,被广泛研究和应用. [关键 ...
- php文字水印和php图片水印实现代码
本文章向码农们介绍php文字水印和php图片水印实现代码,需要的码农可以参考一下. php 文字水印 文字水印就是在图片上加上文字,主要使用gd库的imagefttext方法,并且需要字体文件. 实现 ...
随机推荐
- 客户端(winform)更新
winform更新有两种情况,一种是在线更新在线使用:直接右击项目发布出去就可以更新在线使用了.还有一种更新是不用一直连接网络的模式. 1:C#Winform程序如何发布并自动升级--------ht ...
- 解决flask的端口占用
问题:socket.error: [Errno 48] Address already in use 在编辑flask代码时,如果没有关闭flask的程序,默认的5000端口一直被占用. 再次运行fl ...
- 团队作业2:需求分析&原型设计
Deadline: 2017-11-5 22:00PM,以博客发表日期为准. 评分基准: 按时交 - 有分,检查的项目包括后文的三个方面 需求分析 原型设计 编码规范 晚交 - 0分 迟交两周以 ...
- 北亚关于HP EVA4400/6400/8400/P6000的数据恢复解决方案
[引言]本文档建立在针对HP EVA的大量测试性研究基础上,所有的细节几乎均为对EVA的破译型研究,目前全球范围内尚未发现类似资料,故可能表述方式和结论并不精确,仅为参考之用.我们公司为研究HP EV ...
- plsql启动提示监听服务无法连接
话说现在用的oracle少了,本人菜鸟一个,但是我真心的没有感觉到它用的少了,今天入了一个新项目,数据库使用的还是oracle,经理二话不说的给了一些东西,说了让一句你把环境啥地 配置一下,然后走人了 ...
- istio入门(03)istio的helloworld-场景说明
一.原生应用 四个微服务: python微服务:一个deployment(deployment含有一个pod,pod内含有一个容器) java微服务:三个deployment(deployment含有 ...
- Spark入门(1-2)Spark的特点、生态系统和技术架构
一.Spark的特点 Spark特性 Spark通过在数据处理过程中成本更低的洗牌(Shuffle)方式,将MapReduce提升到一个更高的层次.利用内存数据存储和接近实时的处理能力,Spark比其 ...
- SQL执行计划分析
explain执行计划中的字段以及含义在下面的博客中有详细讲述: https://blog.csdn.net/da_guo_li/article/details/79008016 执行计划能告诉我们什 ...
- 错误解决:HibernateSystemException-HHH000142: Javassist Enhancement failed
今天做项目报了一个错误 错误的原因是: 有级联查询的时候,一对多,多对一配置时要考虑默认延迟加载的问题,需要把延迟加载关闭. 然后就能正确查询出结果了 补充知识: 延迟加载表现在:比如:我们要查询 ...
- python基础——抽象类
python基础--抽象类 1 什么是抽象类 与java一样,python也有抽象类的概念但是同样需要借助模块实现,抽象类是一个特殊的类,它的特殊之处在于只能被继承,不能被实例化 2 为什么要有抽象 ...
