How to Kill All Processes That Have Open Connection in a SQL Server Database[关闭数据库链接 最佳方法] -摘自网络
SQL Server database administrators may frequently need in especially development and test environments instead of the production environments to kill all the open connections to a specific database in order to process SQL Server maintenance task over the SQL Server database.
In such situations when you need to kill or close all the active or open connections to the SQL Server database, you may manage this task by using the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio or by running t-sql commands or codes. Actually, this task can be thought as a batch task to kill sql process running on a SQL Server.
If you open the SQL Server Management Studio and connect to a SQL Server instance you will see the Activity Monitor object in the Object Explorer screen of the related database instance. You can double click the Activity Monitor object or right click to view the context menu and then select a desired item to display the activities to be monitored on the Activity Monitor screen.
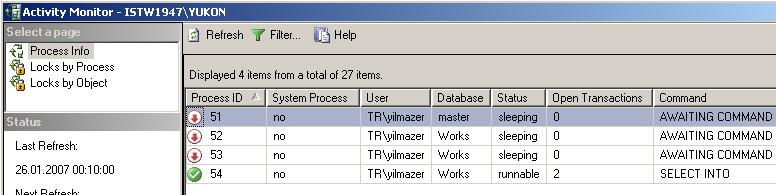
As seen on below you can monitor and view process id's and process details on the list of prcesses running on the database instance. If you want you can filter processes based on specific values like user, database or status.
Note that default view when displayed the screen is first opened is filtered only for non-system processes which means system processes which own the first 50 reserved processid's are not listed in the view by default. You can view system processes by removing the filter on "Show System Processes" criteria in the filter settings screen.
SQL Server 2005 SQL Server Management Studio Activity Monitor screen
You can kill a process by a right click on the process in the grid and selecting the Kill Process menu item. You will be asked for a confirmation to kill the related process and then will kill the open connection to the database over this process. This action is just like running to kill sql process t-sql command for a single process.
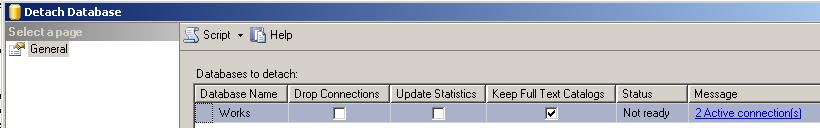
A second method which I do not recommend but can be used in some situations may be using the Detach Database screen to drop connections and detaching the database and then re-attaching the database. You can open the Detach Database screen from the context menu displayed by a right click on the related daabase for example for the below screen shot the name of the database is Works. On the menu, highlight menu item Tasks then select the Detach... menu item. This selection will open the detach database dialog screen. Note that if in the message column it is declared that active connections exists as for our case the number of active connections is 2, you will not be able to detach the database unless the Drop Connections checkbox is also selected.
The above configuration as the Drop Connections check box is cleared and active connections exist, the detach task will fail:
Detach database failed for Server '{DatabaseInstanceName}'. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo)
For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server& ProdVer=9.00.2047.00& EvtSrc=Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.ExceptionTemplates. FailedOperationExceptionText& EvtID=Detach+database+Server& LinkId=20476
An exception occurred while executing a Transact-SQL statement or batch. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
Cannot detach the database '{DatabaseName}' because it is currently in use. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 3703) But if the Drop Connections is selected you can successfully detach the database. Then you will have to re-attach the database by selecting the Attach command from the context menu item displayed on the Databases node of the SQL Server instance.
For SQL Server 2000 the default behaviour was different than the SQL Server 2005. Because in SQL Server 2000, when you run the detach command from the menu item, you are prompted if you want to drop all active connections. Then you can confirm closing of all open connections, but the nice thing is that you can cancel detach process after the open connections are dropped or closed. But for SQL Server 2005, this behaviour is not valid.
How to Kill All Processes using T-SQL Code
By using t-sql commands or sql codes, similarly closing connections can be implemented by a few methods. One of the methods is using a cursor which loops for all the active connections of the related database and kill these processes. This method was also mention on SQL Server article named How to Alter a SQL Server Database as Single User Mode and as Multi User Mode
The below code block can be used to kill all processes which are connected to the sql database named @DatabaseName except the process that the code block is running in the scope of. You can also set the SQL Server database name by the DB_NAME() property.
The base of the below t-sql script is sql Kill SPId command. Within the sql cursor which loops through each process in sysProcesses view, each time a tsql Kill process command is called passing the SPId as an argument. And after Kill SPId sql statement is executed for each process, all database connections are dropped.
SQL Server database administrators can use below t-sql script in order to drop connections SQL Server 2008, or SQL Server 2005 and also drop connections to sql server 2000 database.
DECLARE @DatabaseName nvarchar(50) DECLARE @SPId int DECLARE @SQL nvarchar(100)
--SET @DatabaseName = N'AdventureWorks2008' SET @DatabaseName = DB_NAME() DECLARE my_cursor CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR SELECT SPId FROM MASTER..SysProcesses WHERE DBId = DB_ID(@DatabaseName) AND SPId <> @@SPId
OPEN my_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM my_cursor INTO @SPId
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN SET @SQL = 'KILL ' + CAST(@SPId as nvarchar(10)) print @SQL EXEC sp_executeSQL @SQL --KILL @SPId -- Causing Incorrect syntax near '@spid'.
FETCH NEXT FROM my_cursor INTO @SPId END
CLOSE my_cursor DEALLOCATE my_cursor UPDATE : Please note that I altered above t-sql script and removed KILL @SPId sql statement. It was causing the below error. Msg 102, Level 15, State 1, Line 19 Incorrect syntax near '@SPId'. This is because the sql processid can not be used using a variable with sql KILL command. The solution is using dynamic t-sql statement as shown in the above sql cursor code.
A second way to drop all active connections of a database can be implemented by generating dynamic sql commands that runs a list of "Kill @spId" commands.
DECLARE @DatabaseName nvarchar(50) SET @DatabaseName = N'Works' --SET @DatabaseName = DB_NAME()
DECLARE @SQL varchar(max) SET @SQL = ''
SELECT @SQL = @SQL + 'Kill ' + Convert(varchar, SPId) + ';' FROM MASTER..SysProcesses WHERE DBId = DB_ID(@DatabaseName) AND SPId <> @@SPId
-- SELECT @SQL EXEC(@SQL) A very similar to the sql code above, an other code block can be used by using the COALESCE as shown below
DECLARE @DatabaseName nvarchar(50) SET @DatabaseName = N'Works'
DECLARE @SQL varchar(max)
SELECT @SQL = COALESCE(@SQL,'') + 'Kill ' + Convert(varchar, SPId) + ';' FROM MASTER..SysProcesses WHERE DBId = DB_ID(@DatabaseName) AND SPId <> @@SPId
--SELECT @SQL EXEC(@SQL) The above sql queries can be modified further for specific needs. For example you may create a sql stored procedure that drops all existing active connections. You may pass SQL database name or database id as parameter or use the current database information to kill processes except its own process, etc.
How to Kill All Processes That Have Open Connection in a SQL Server Database[关闭数据库链接 最佳方法] -摘自网络的更多相关文章
- (转)How To Kill runaway processes After Terminating Concurrent Request
终止EBS并发请求后,解锁相关的进程. 还有种方法可以在PLSQL->tools->session 中找到并且kill Every concurrent Request uses some ...
- SQL Server会话KILL不掉,一直处于KILLED /ROLLBACK状态情形浅析
今天遇到一个很奇怪的情况,发现一个会话异常,这个会话只是在执行一个简单的存储过程,里面使用了链接服务器(Linked Server)查询另外一台服务器数据(存储过程里面没有任何显性事务.UPDATE. ...
- sql server block如何查询并kill
本帖提供两种做法,可避免在 SQL Server 事务锁定时产生的不正常或长时间阻塞,让用户和程序也无限期等待,甚至引起 connection pooling 连接数超过容量. 所谓的「阻塞」,是指当 ...
- SQL Server会话KILL不掉,一直处于KILLED /ROLLBACK状态情形浅析[转]
本文将为您描述SQL Server会话KILL不掉,一直处于KILLED /ROLLBACK状态情形浅析,教程操作方法: 今天遇到一个很奇怪的情况,发现一个会话异常,这个会话只是在执行一个简单的存储过 ...
- sql server 查看表的死锁和Kill 死锁进程
查询出来 select request_session_id spid, OBJECT_NAME(resource_associated_entity_id) tableNa ...
- sql server 查询和Kill死锁进程
查询死锁进程语句 select request_session_id spid, OBJECT_NAME(resource_associated_entity_id) tab ...
- SQL Server查询死锁并KILL
杀掉死锁的sqlserver进程 SELECT request_session_id spid,OBJECT_NAME (resource_associated_entity_id)tableNa ...
- Sql server 查看锁和Kill 死锁进程
死锁的概念 死锁就是两个或多个会话(SPID)相互请求对方持有的锁资源,导致循环等待的情况.下面两种方法都是用来粗暴的解决死锁的. # 已知阻塞进程ID KILL ID SELECT blocking ...
- SHUTDOWN: Active processes prevent shutdown operation
在使用shutdown immediate关闭数据库时hang住,查看alert 日志,遭遇了SHUTDOWN: Active processes prevent shutdown operation ...
随机推荐
- listview滚动时背景闪烁,背景黑或白问题解决
android在使用listview时出现滚动时背景闪烁,变成背景黑或白的问题这样处理: 1:在布局文件中listview标签中加入: android:cacheColorHint="#00 ...
- Mongodb使用总结
学习Mongodb已经有半年多了,为啥学习它,工作需要啊.好了,废话不说,总结在实际项目应用中的几点问题. 学习总结 首先,mongodb基本上既照顾到了sql某些语法,又有nosql的许多优点.入门 ...
- POJ 2942 Knights of the Round Table(双连通分量)
http://poj.org/problem?id=2942 题意 :n个骑士举行圆桌会议,每次会议应至少3个骑士参加,且相互憎恨的骑士不能坐在圆桌旁的相邻位置.如果意见发生分歧,则需要举手表决,因此 ...
- Using FireMonkey Layouts
FireMonkey has many layout controls to choose from. Come learn the differences and how to use them t ...
- 对TCP/IP网络协议的深入浅出归纳(转)
前段时间做了一个开发,涉及到网络编程,开发过程比较顺利,但任务完成后始终觉得有一些疑惑.主要是因为对网络协议不太熟悉,对一些概念也没弄清楚.后来 我花了一些时间去了解这些网络协议,现在对TCP/IP网 ...
- Linux网络地址转换分析
Linux网络地址转换分析 地址转换用来改变源/目的端口,是netfilter的一部分,也是通过hook点上注册相应的结构来工作. Nat注册的hook点和conntrack相同,只是优先级不同,数据 ...
- ActionBar官方教程(3)更改标题处的图片
Using a logo instead of an icon By default, the system uses your application icon in the action bar, ...
- 【HDOJ】3505 Writing Robot
挺好的一道题目,我的做法是kmp+Dinic网络流.kmp求子串在P中出现的次数,从而计算love值.网络流主要用来处理最优解.case2中p1的love值是8,p2的love值是7,最终T包含p1和 ...
- Fedora 17下交叉编译vlc-2.0.6-win32小记
关于编译windows下的vlc网上的教程除了翻译N年前wiki官网的那些蚂蚁文之外,可以说基本没啥参考意义和价值.因为那些都是非常老的版本,0.8.x或者1.x.x,而我这个人有喜欢新鲜事儿,所以就 ...
- JSP个人总结
应用JSP技术开发动态网站 JSP基本语法 默认JSP: <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; char ...