【赵渝强老师】Flink的DataSet算子
Flink为了能够处理有边界的数据集和无边界的数据集,提供了对应的DataSet API和DataStream API。我们可以开发对应的Java程序或者Scala程序来完成相应的功能。下面举例了一些DataSet API中的基本的算子。
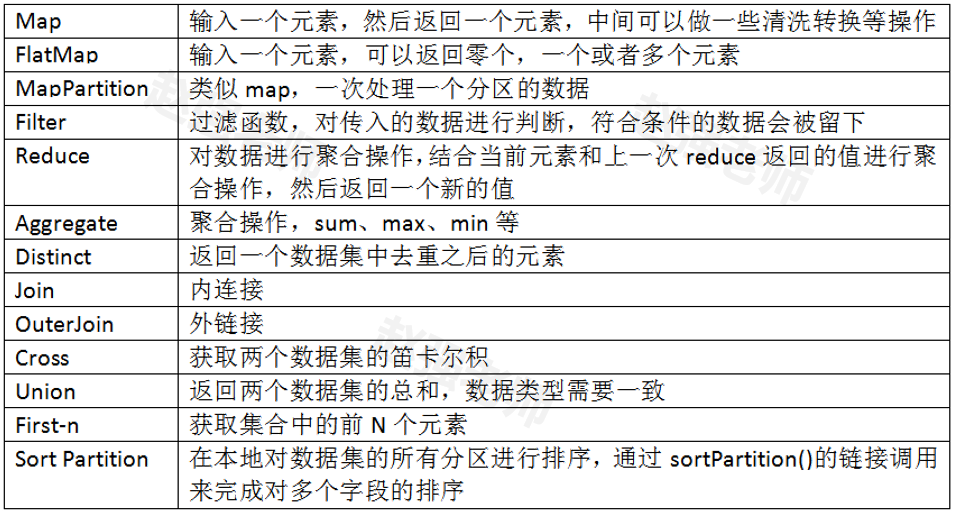
下面我们通过具体的代码来为大家演示每个算子的作用。
1、Map、FlatMap与MapPartition
//获取运行环境
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); ArrayList<String> data = new ArrayList<String>();
data.add("I love Beijing");
data.add("I love China");
data.add("Beijing is the capital of China");
DataSource<String> text = env.fromCollection(data); DataSet<List<String>> mapData = text.map(new MapFunction<String, List<String>>() { public List<String> map(String data) throws Exception {
String[] words = data.split(" "); //创建一个List
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
for(String w:words){
result.add(w);
}
return result;
}
});
mapData.print();
System.out.println("*****************************************"); DataSet<String> flatMapData = text.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() { public void flatMap(String data, Collector<String> collection) throws Exception {
String[] words = data.split(" ");
for(String w:words){
collection.collect(w);
}
}
});
flatMapData.print(); System.out.println("*****************************************");
/* new MapPartitionFunction<String, String>
第一个String:表示分区中的数据元素类型
第二个String:表示处理后的数据元素类型*/
DataSet<String> mapPartitionData = text.mapPartition(new MapPartitionFunction<String, String>() { public void mapPartition(Iterable<String> values, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//针对分区进行操作的好处是:比如要进行数据库的操作,一个分区只需要创建一个Connection
//values中保存了一个分区的数据
Iterator<String> it = values.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String next = it.next();
String[] split = next.split(" ");
for (String word : split) {
out.collect(word);
}
}
//关闭链接
}
});
mapPartitionData.print();
2、Filter与Distinct
//获取运行环境
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); ArrayList<String> data = new ArrayList<String>();
data.add("I love Beijing");
data.add("I love China");
data.add("Beijing is the capital of China");
DataSource<String> text = env.fromCollection(data); DataSet<String> flatMapData = text.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() { public void flatMap(String data, Collector<String> collection) throws Exception {
String[] words = data.split(" ");
for(String w:words){
collection.collect(w);
}
}
}); //去掉重复的单词
flatMapData.distinct().print();
System.out.println("*********************"); //选出长度大于3的单词
flatMapData.filter(new FilterFunction<String>() { public boolean filter(String word) throws Exception {
int length = word.length();
return length>3?true:false;
}
}).print();
3、Join操作
//获取运行的环境
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); //创建第一张表:用户ID 姓名
ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>> data1 = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer,String>>();
data1.add(new Tuple2(1,"Tom"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(2,"Mike"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(3,"Mary"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(4,"Jone"));
//创建第二张表:用户ID 所在的城市
ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>> data2 = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer,String>>();
data2.add(new Tuple2(1,"北京"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(2,"上海"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(3,"广州"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(4,"重庆")); //实现join的多表查询:用户ID 姓名 所在的程序
DataSet<Tuple2<Integer, String>> table1 = env.fromCollection(data1);
DataSet<Tuple2<Integer, String>> table2 = env.fromCollection(data2); table1.join(table2).where(0).equalTo(0)
/*第一个Tuple2<Integer,String>:表示第一张表
* 第二个Tuple2<Integer,String>:表示第二张表
* Tuple3<Integer,String, String>:多表join连接查询后的返回结果 */
.with(new JoinFunction<Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple3<Integer,String, String>>() {
public Tuple3<Integer, String, String> join(Tuple2<Integer, String> table1,
Tuple2<Integer, String> table2) throws Exception {
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table1.f0,table1.f1,table2.f1);
} }).print();
4、笛卡尔积
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); //创建第一张表:用户ID 姓名
ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>> data1 = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer,String>>();
data1.add(new Tuple2(1,"Tom"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(2,"Mike"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(3,"Mary"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(4,"Jone")); //创建第二张表:用户ID 所在的城市
ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>> data2 = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer,String>>();
data2.add(new Tuple2(1,"北京"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(2,"上海"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(3,"广州"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(4,"重庆")); //实现join的多表查询:用户ID 姓名 所在的程序
DataSet<Tuple2<Integer, String>> table1 = env.fromCollection(data1);
DataSet<Tuple2<Integer, String>> table2 = env.fromCollection(data2); //生成笛卡尔积
table1.cross(table2).print();
5、First-N
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); //这里的数据是:员工姓名、薪水、部门号
DataSet<Tuple3<String, Integer,Integer>> grade =
env.fromElements(new Tuple3<String, Integer,Integer>("Tom",1000,10),
new Tuple3<String, Integer,Integer>("Mary",1500,20),
new Tuple3<String, Integer,Integer>("Mike",1200,30),
new Tuple3<String, Integer,Integer>("Jerry",2000,10)); //按照插入顺序取前三条记录
grade.first(3).print();
System.out.println("**********************"); //先按照部门号排序,在按照薪水排序
grade.sortPartition(2, Order.ASCENDING).sortPartition(1, Order.ASCENDING).print();
System.out.println("**********************"); //按照部门号分组,求每组的第一条记录
grade.groupBy(2).first(1).print();
6、外链接操作
ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); //创建第一张表:用户ID 姓名
ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>> data1 = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer,String>>();
data1.add(new Tuple2(1,"Tom"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(3,"Mary"));
data1.add(new Tuple2(4,"Jone")); //创建第二张表:用户ID 所在的城市
ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer, String>> data2 = new ArrayList<Tuple2<Integer,String>>();
data2.add(new Tuple2(1,"北京"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(2,"上海"));
data2.add(new Tuple2(4,"重庆")); //实现join的多表查询:用户ID 姓名 所在的程序
DataSet<Tuple2<Integer, String>> table1 = env.fromCollection(data1);
DataSet<Tuple2<Integer, String>> table2 = env.fromCollection(data2); //左外连接
table1.leftOuterJoin(table2).where(0).equalTo(0)
.with(new JoinFunction<Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple3<Integer,String,String>>() { public Tuple3<Integer, String, String> join(Tuple2<Integer, String> table1,
Tuple2<Integer, String> table2) throws Exception {
// 左外连接表示等号左边的信息会被包含
if(table2 == null){
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table1.f0,table1.f1,null);
}else{
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table1.f0,table1.f1,table2.f1);
}
}
}).print(); System.out.println("***********************************");
//右外连接
table1.rightOuterJoin(table2).where(0).equalTo(0)
.with(new JoinFunction<Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple3<Integer,String,String>>() { public Tuple3<Integer, String, String> join(Tuple2<Integer, String> table1,
Tuple2<Integer, String> table2) throws Exception {
//右外链接表示等号右边的表的信息会被包含
if(table1 == null){
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table2.f0,null,table2.f1);
}else{
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table2.f0,table1.f1,table2.f1);
}
}
}).print(); System.out.println("***********************************"); //全外连接
table1.fullOuterJoin(table2).where(0).equalTo(0)
.with(new JoinFunction<Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple2<Integer,String>, Tuple3<Integer,String,String>>() { public Tuple3<Integer, String, String> join(Tuple2<Integer, String> table1, Tuple2<Integer, String> table2)
throws Exception {
if(table1 == null){
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table2.f0,null,table2.f1);
}else if(table2 == null){
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table1.f0,table1.f1,null);
}else{
return new Tuple3<Integer, String, String>(table1.f0,table1.f1,table2.f1);
}
} }).print();
【赵渝强老师】Flink的DataSet算子的更多相关文章
- 201871010136—赵艳强《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
201871010136—赵艳强<面向对象程序设计(java)>第十三周学习总结 博文正文开头格式:(2分) 项目 内容 <面向对象程序设计(java)> https:// ...
- Apache Flink - Batch(DataSet API)
Flink DataSet API编程指南: Flink中的DataSet程序是实现数据集转换的常规程序(例如,过滤,映射,连接,分组).数据集最初是从某些来源创建的(例如,通过读取文件或从本地集合创 ...
- Flink中的算子操作
一.Connect DataStream,DataStream -> ConnectedStream,连接两个保持他们类型的数据流,两个数据流被Connect之后,只是被放在了同一个流中,内部 ...
- Flink的异步算子的原理及使用
1.简介 Flink的特点是高吞吐低延迟.但是Flink中的某环节的数据处理逻辑需要和外部系统交互,调用耗时不可控会显著降低集群性能.这时候就可能需要使用异步算子让耗时操作不需要等待结果返回就可以继续 ...
- 201871010136 -赵艳强《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
201871010136-赵艳强<面向对象程序设计(java)>第十六周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 <任课教师博客主页链接>https://www.cnbl ...
- flink dataset api使用及原理
随着大数据技术在各行各业的广泛应用,要求能对海量数据进行实时处理的需求越来越多,同时数据处理的业务逻辑也越来越复杂,传统的批处理方式和早期的流式处理框架也越来越难以在延迟性.吞吐量.容错能力以及使用便 ...
- 入门大数据---Flink学习总括
第一节 初识 Flink 在数据激增的时代,催生出了一批计算框架.最早期比较流行的有MapReduce,然后有Spark,直到现在越来越多的公司采用Flink处理.Flink相对前两个框架真正做到了高 ...
- Flink及主流流框架spark,storm比较
干货 | Flink及主流流框架比较 IT刊 百家号17-05-2220:16 引言 随着大数据时代的来临,大数据产品层出不穷.我们最近也对一款业内非常火的大数据产品 - Apache Flink做了 ...
- Flink 灵魂两百问,这谁顶得住?
Flink 学习 https://github.com/zhisheng17/flink-learning 麻烦路过的各位亲给这个项目点个 star,太不易了,写了这么多,算是对我坚持下来的一种鼓励吧 ...
- Flink及Storm、Spark主流流框架比较
转自:http://www.sohu.com/a/142553677_804130 引言 随着大数据时代的来临,大数据产品层出不穷.我们最近也对一款业内非常火的大数据产品 - Apache Flink ...
随机推荐
- RHCA cl210 013 制作镜像 轮转key rabbitmq追踪 写时复制 keystone多域登录图形界面
undercloud 部署 overcloud overcloud控制节点上的组建rabbitmq 排错需要rabbitmq,开启追踪则会更详细,会消耗性能 环境问题 登录一下classroom os ...
- layui下拉框的数据如何直接从数据库提取(动态赋值)
代码说明部分 第一步:先把layui官方给的模板粘到自己的前端注:下面的代码是我直接从layui官网粘过来的 <div class="layui-form-item"> ...
- Jmeter二次开发函数 - 将指定时间转换为时间戳
1.达到效果:在jmeter的函数助手增加一个"timeStamp"函数,调用"timeStamp"函数可以将用户传入的时间转换为时间戳. 2.eclipse项 ...
- 【vue3】详解单向数据流,大家千万不用为了某某而某某了。
总览 Vue3 的单向数据流 尽信官网,不如那啥. vue的版本一直在不断更新,内部实现方式也是不断的优化,官网也在不断更新. 既然一切皆在不停地发展,那么我们呢?等着官网更新还是有自己的思考? 我觉 ...
- 【WSDL】02 四种客户端调用方式
WSDL概念和一些语法内容: https://www.w3school.com.cn/wsdl/index.asp SOAP概念: https://www.runoob.com/soap/soap-t ...
- 【MongoDB】Re01 安装与基础操作
Linux安装 官网下载红帽安装版 #下载三个rpm包 wget https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/mongodb/yum/el7-4.2/RPMS/mongo ...
- 【转载】 Makefile的静态模式%.o : %.c
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「猪哥-嵌入式」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明.原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u012351051 ...
- java获取包下所有的类
1.背景 给一个Java的包名,获取包名下的所有类.. 根据类上的注解,可以展开很多统一操作的业务 2.直接看代码-spring环境下 package com.qxnw.digit.scm.commo ...
- 三台服务器上离线安装redis哨兵集群,一主二从三哨兵
三台服务器上离线安装redis哨兵集群,一主二从三哨兵 系统安装好gcc环境,(不然编译redis会报错).依旧不知道怎么离线安装gcc环境的可查看CentOS下离线安装gcc环境,图文详细 下载 点 ...
- Git-HEAD 的含义
在 Git 中,"HEAD" 是一个特殊的引用,它指向当前所处的分支或提交. 当你进行一些操作时,比如提交代码.切换分支等,HEAD 的指向会随之改变.下面是 HEAD 在不同情况 ...
