P10009 [集训队互测 2022] 线段树 题解
题目链接:P10009 [集训队互测 2022] 线段树
神仙分块题,先给一下出题人的神仙官解:
官解链接
前面还看得懂。后面是啥?这不是 ds 题咋和 dp、轮廓线扯上关系了。看了半天,还是这个启发了我:


其手玩下,在 Excel 里写一下,可以理解到这里其实是想表达的一个核心意思是啥:对于一组序列而言,我们对操作 \(1\) 进行 \(2^k\) 次,很容易发现一个性质此时最终的数组和原数组有以下关系:
\]
证明可以参照 pdf 里面说的,转化为网格图,然后转变为路径数问题,考虑一个点是否计入最终点的贡献。因为异或两次就为 \(0\),所以只需要计算从这个点出发到查询点的路径数的数量再模 \(2\),而路径数:

这点还是很好理解的。而 \(diff_y\) 就是操作数,\(diff_x\) 则是步长。假如操作数为 \(2^k\)。温习下 Lucas 定理:

很显然的是由卢卡斯定理我们有:
\]
\]
\]
显然需要有每个 \(\lfloor \dfrac{diff_x}{2^i}\rfloor \mod 2==0\) 才能使结果为 \(1\)。容易知道 \(diff_x=2^t(t>k-1)\)。
接下来只需要证明 \(diff_x=2^t (t>k)\) 都是无贡献的。换句话来说,对于 \(a_i\) 来说,操作了 \(2^k\) 次方次以后,\(a_j(j \in [1,i-2^k)\ )\) 对 \(a_i\) 无贡献。非常简单,考虑 \(a_1\) ,第一次操作会影响 \(a_2\),第二次影响 \(a_3\),以此类推每次影响的对象往右平移一位。其实每次操作可以看做整体往右平移一位再异或。
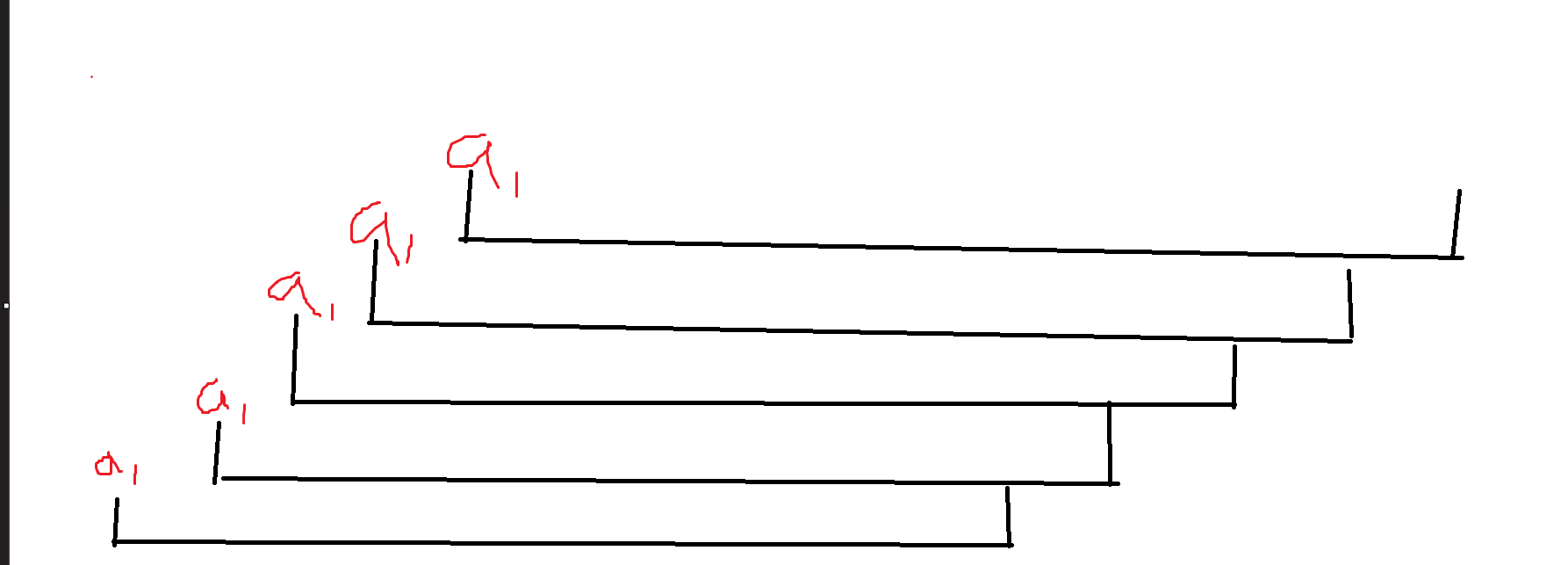
最初始的 \(a_1\) 会随着每轮操作而影响对象向右移动一位。所以此时此刻的最大的 \(a_j\) 在进行了 \(2^k\) 操作以后,最多只会 \(a_j 影响 a_{i-1} (j==2^k-1)\)。所以上式当且仅当 \(diff_x==2^k\) 时才为 \(1\),才有贡献。
非 \(2^k\) 次操作该如何解决。答案是倍增/二进制分解,把它分解为若干个 \(2^t\) 次操作累计就行了。这样一来我们就解决了“整块操作”。散块暴力即可。结束。
算法框架及其细节
首先,需要注意一点,既然都上分块了,那么显而易见的 \(new_i=a_i \oplus a_{i-step}\) 里的 \(step\) 最多为 \(\sqrt{n}\) 会跨个一整块。实际上是我们可以考虑每次两块两块地处理,这样写较为方便。而什么时候有可能达到这个数字,显然是当修改达到至少 \(\sqrt{n}\) 次时才有可能,所以我们可以考虑每出现 \(\sqrt{n}\) 次修改再处理查询。
其次,对于查询而言,我们可以遍历每个查询和每个块,记录整块操作数,遇到散块就直接处理完整块的就行了。这一部分外层遍历的复杂度为 \(O(\sqrt{n} 个查询 \times \sqrt{n} 块)=O(n)\),再套一个处理完整块的操作次数显然最坏应该为:
\]
\]
所以单次查询的最坏复杂度 \(O(\sqrt{n}\log{\sqrt{n}})\)
而又因为这 \(\sqrt{n}\) 个查询,全是最坏的散块处理,整块处理我们可以累计到下次 \(op==2\) 时进行统一处理。实际上摊还分析一下,一次处理 \(\sqrt{n}\) 个查询的复杂度单个是 \(\sqrt{n}\log{\sqrt{n}}\),总复杂度是就是 \(O(n\log{\sqrt{n}})\)
又因为最多有 $\lceil \frac{q}{\sqrt{n}} \rceil $ 个这种查询,所以理想复杂度是近似于 \(O(n\sqrt{n}\log{\sqrt{n}})\)? \(n\) 和 \(q\) 差不多是一个数量级,把它俩当相等。
参考代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
#define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 2.5e5 + 10;
constexpr int SIZE = sqrt(N);
constexpr int CNT = (N + SIZE - 1) / SIZE + 1;
int pos[N];
int s[CNT], e[CNT];
int pre[N]; //上一轮序列
int nxt[N]; //下一轮序列
int tmp[N]; //临时序列
int ans[N]; //答案
int n, q;
int siz, cnt; //块大小,块数量
struct Query
{
int op, l, r, id;
} qu[N];
//整块更新,2^i次方就直接tmp[x]^=tmp[x-2^i],否则二进制拆分倍增
inline void allUpdate(const int id, int updateCnt)
{
while (updateCnt)
{
int t = log2(updateCnt);
int step = 1 << t; //步长
//两块两块处理,因为updateCnt最多为sqrt(n)
forv(i, e[id], s[id-1]+step)tmp[i] ^= tmp[i - step];
updateCnt -= step;
}
}
//处理操作
inline void update(const int queryCnt)
{
//遍历每个块进行贡献更新
forn(idx, 1, cnt)
{
int blockCnt = 0; //整块操作次数
//两块两块进行处理,对于当前块,同时拿到它之前的块进行一并处理方便a[i]^=a[i-step],step=sqrt(n)。
forn(i, s[idx-1], e[idx])tmp[i] = pre[i];
forn(curr, 1, queryCnt)
{
if (auto [op,l,r,id] = qu[curr]; op == 1)
{
const int L1 = s[idx - 1]; //前一块边界
const int R2 = e[idx]; //当前块边界
//完全包括
if (l <= L1 and R2 <= r)
{
++blockCnt;
continue;
}
//部分包括,有交集,暴力
if (l <= R2 and r >= L1)
{
//先把之前的整块更新改了
allUpdate(idx, blockCnt);
blockCnt = 0;
//起点需要+1
forv(i, min(r,R2), max(l+1,L1+1))tmp[i] ^= tmp[i - 1];
}
}
else
{
//计算当前块的贡献
if (s[idx] <= l and l <= e[idx])
{
allUpdate(idx, blockCnt);
blockCnt = 0;
ans[id] = tmp[l];
}
}
}
allUpdate(idx, blockCnt); //处理还未处理的整块更新
forn(i, s[idx], e[idx])nxt[i] = tmp[i]; //下一轮的序列
}
forn(i, 1, n)pre[i] = nxt[i];
forn(i, 1, queryCnt)if (qu[i].op == 2)cout << ans[qu[i].id] << endl;
}
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n >> q;
siz = sqrt(n);
cnt = (n + siz - 1) / siz;
forn(i, 1, n)cin >> pre[i], pos[i] = (i - 1) / siz + 1;
s[0] = 1;
forn(i, 1, cnt)s[i] = (i - 1) * siz + 1, e[i] = i * siz;
e[cnt] = n;
int updateCnt = 0; //修改次数
int queryCnt = 0; //待处理的操作次数
forn(i, 1, q)
{
cin >> qu[++queryCnt].op;
qu[queryCnt].id = i;
if (qu[queryCnt].op == 1)
{
cin >> qu[queryCnt].l >> qu[queryCnt].r;
if (++updateCnt == siz)update(queryCnt), updateCnt = 0, queryCnt = 0;
}
else cin >> qu[queryCnt].l;
}
update(queryCnt);
forn(i, 1, n)cout << pre[i] << endl;
}
signed int main()
{
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
int test = 1;
// read(test);
cin >> test;
test = 1;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
}
附一张手玩时,打表确认规律

PS:复杂度部分可能最终分析的有点乱,但实测下来确实跑得非快。官解剩余的神仙dp确实晦涩,后续如果看懂也会补充做法。文章证明如果有瑕疵或者不正确的地方,欢迎指出。
P10009 [集训队互测 2022] 线段树 题解的更多相关文章
- 【loj2461】【2018集训队互测Day 1】完美的队列
#2461. 「2018 集训队互测 Day 1」完美的队列 传送门: https://loj.ac/problem/2461 题解: 直接做可能一次操作加入队列同时会弹出很多数字,无法维护:一个操作 ...
- 【2018集训队互测】【XSY3372】取石子
题目来源:2018集训队互测 Round17 T2 题意: 题解: 显然我是不可能想出来的……但是觉得这题题解太神了就来搬(chao)一下……Orzpyz! 显然不会无解…… 为了方便计算石子个数,在 ...
- BZOJ3938 & UOJ88:[集训队互测2015]Robot——题解
https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3938 http://uoj.ac/problem/88 小q有n只机器人,一开始他把机器人放在了一 ...
- 【集训队互测2015】Robot
题目描述 http://uoj.ac/problem/88 题解 维护两颗线段树,维护最大值和最小值,因为每次只有单点查询,所以可以直接在区间插入线段就可以了. 注意卡常,不要写STL,用链表把同类修 ...
- [JZOJ2865]【集训队互测 2012】Attack
题目 题目大意 平面上有一堆带权值的点.两种操作:交换两个点的权值,查找一个矩形的第\(k\)小 \(N<=60000\) \(M<=10000\) \(10000ms\) 思考历程&am ...
- 洛谷 P4463 - [集训队互测 2012] calc(多项式)
题面传送门 & 加强版题面传送门 竟然能独立做出 jxd 互测的题(及其加强版),震撼震撼(((故写题解以祭之 首先由于 \(a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_n\) 互不相同,故可以考虑求出 ...
- 「洛谷 P3834」「模板」可持久化线段树 题解报告
题目描述 给定n个整数构成的序列,将对于指定的闭区间查询其区间内的第k小值. 输入输出格式 输入格式 第一行包含两个正整数n,m,分别表示序列的长度和查询的个数. 第二行包含n个整数,表示这个序列各项 ...
- 集训队互测2016Unknown(UOJ191)
题目链接 前面部分和lzz的题解是一样的. 首先将输入点(x,y)变为(-y,x)然后,只需找一个向量与(-y,x)的点积最大,即找一个向量在(-y,x)上的投影最长.此时所有的点都是在x轴上方的,容 ...
- UOJ#191. 【集训队互测2016】Unknown
题意:维护一个数列,每个元素是个二维向量,每次可以在后面加一个元素或者删除一个元素.给定P(x,y),询问对于[l,r]区间内的元素$S_i$,$S_i \times P$的最大值是多少. 首先简单地 ...
- HDU 1556 Color the Ball 线段树 题解
本题使用线段树自然能够,由于区间的问题. 这里比較难想的就是: 1 最后更新须要查询全部叶子节点的值,故此须要使用O(nlgn)时间效率更新全部点. 2 截取区间不能有半点差错.否则答案错误. 这两点 ...
随机推荐
- spring中的核心类有那些,各有什么作用?
BeanFactory:产生一个新的实例,可以实现单例模式BeanWrapper:提供统一的get及set方法ApplicationContext:提供框架的实现,包括BeanFactory的所有功能 ...
- vue+spingboot 实现服务器端文件下载功能
vue3 和springboot配合如何实现服务器端文件的下载. 先看springboot的后台代码: @PostMapping("/download") @ResponseBod ...
- vue tabBar导航栏设计实现3-进一步抽取tab-item
系列导航 一.vue tabBar导航栏设计实现1-初步设计 二.vue tabBar导航栏设计实现2-抽取tab-bar 三.vue tabBar导航栏设计实现3-进一步抽取tab-item 四.v ...
- JavaScript合并多个数组
工作中经常会对数组进行合并,稍微总结一下常用的方法: concat JavaScript原生自带的函数,用法如下: let arr1 = [3, 5, 7]; let arr2 = [4, 78, 7 ...
- 【C/C++】 开发必备知识总结
>from: C/C++ 开发必备知识总结 (qq.com) const 作用 修饰变量,说明该变量不可以被改变: 修饰指针,分为指向常量的指针和指针常量: 常量引用,经常用于形参类型,即避免了 ...
- python环境 anaconda安装
官网: https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/#macos 国内镜像: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda ...
- SpringBoot利用自定义注解实现多数据源
自定义多数据源 SpringBoot利用自定义注解实现多数据源,前置知识:注解.Aop.SpringBoot整合Mybaits 1.搭建工程 创建一个SpringBoot工程,并引入依赖 <de ...
- MySQL复习——20211027
MYSQL MySQL创建数据库 我们可以在登录MySQL服务后,使用create命令创建数据库,语法如下: CREATE DATABASE 数据库名; 使用root用户登录,root用户拥有最高权限 ...
- [转帖]美国出口管制法律制度及中国企业风险防范——EAR核心内容解读
http://bzy.scjg.jl.gov.cn/wto/zszc/myxgzs/202202/t20220221_636006.html 发布时间:2022-01-18 一.<美国出口管理条 ...
- [转帖]oracle查询表变化量
根据变化量,可确定表的繁忙度,以及作为判断可能数据增长的对象. select obj.owner, obj.object_name, to_char(sn.BEGIN_INTERVAL_TIME,'y ...
