Mysql数据库下InnoDB数据引擎下的事务详解
一、什么是数据库事务?
数据库事务( transaction)是访问并可能操作各种数据项的一个数据库操作序列,这些操作要么全部执行,要么全部不执行,是一个不可分割的工作单位。事务由事务开始与事务结束之间执行的全部数据库操作组成。
简言之就是,更新、新增、删除的sql要么一起成功,要么一起失败(回滚)。
二、使用数据库的事务可能出现什么问题?
可能会出现脏读、幻读、不可重复读的问题。
1.什么是脏读?
比如说A事务修改了一条数据,B事务读取了该条事务,A事务回滚,B事务读取了错误的数据,这叫做脏读。
例子:数据库中张三的工资为5K,事务B读取成了8k的行为叫做脏读。
| 时间 | 事务A | 事务B |
| T1 | 开始事务 | |
| T2 | 开始事务 | |
| T3 | 张三的工资从5K改为8K(update操作) | |
| T4 | 读取到张三的工资为8k(select操作) | |
| T5 | 提交事务 | |
| T6 |
事务提交失败回滚,数据库中张三的数据变回5K |
2.什么是不可重复读?
例子:张三在一个事务中前后两次读取的工资的金额不同的情况叫做不可重复读。
| 时间 | 事务A | 事务B |
| T1 | 开始事务 | |
| T2 | 开始事务 | |
| T3 | 读取张三的工资为5K(select操作) | |
| T4 | 修改的张三的工资为8k(update操作) | |
| T5 | 提交事务 | |
| T6 |
读取张三的工资为8K(select操作) |
3.什么是幻读?
是指当事务不是独立执行时发生的一种现象,例如第一个事务对一个表中的数据进行了修改,这种修改涉及到表中的全部数据行。同时,第二个事务也修改这个表中的数据,这种修改是向表中插入\删除一行数据。那么,以后就会发生操作第一个事务的用户发现表中还有没有修改的数据行,就好象发生了幻觉一样。
例子:初始数据库中,有张三、李四工资为5K的数据
| 时间 | 事务A | 事务B |
| T1 | 开始事务 | |
| T2 | 开始事务 | |
| T3 |
读取张三李四的工资为5K |
|
| T4 |
添加王五的工资为5K的数据(add操作) /删除李四的工资为5K的数据(delete操作) |
|
| T5 | 提交事务 | |
| T6 |
修改工资为5k的员工工资改为6K(update操作) 操作影响了3条(添加操作)/1条(删除操作)数据 |
|
| T7 |
查询员工工资, (预期张三李四工资6K) 实际上张三李四王五工资为6K/张三工资为6K |
三、Spring是如何完成事务的,脏读幻读不可重复读是怎么解决的?
Spring中有一个@Transactional注解/* * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
//上面就是一些版权说明的内容
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition; /**
* Describes transaction attributes on a method or class.
*
* <p>This annotation type is generally directly comparable to Spring's
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RuleBasedTransactionAttribute}
* class, and in fact {@link AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource} will directly
* convert the data to the latter class, so that Spring's transaction support code
* does not have to know about annotations. If no rules are relevant to the exception,
* it will be treated like
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute}
* (rolling back on {@link RuntimeException} and {@link Error} but not on checked
* exceptions).
*
* <p>For specific information about the semantics of this annotation's attributes,
* consult the {@link org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition} and
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute} javadocs.
*
* @author Colin Sampaleanu
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 1.2
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RuleBasedTransactionAttribute
*/
//上面就是说,这个类的方法主要是处理事务的问题,具体使用到的注解去具体的注解类里面看
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Transactional { /**
* Alias for {@link #transactionManager}.
* @see #transactionManager
*/
//事务管理器的名字默认是空的,你可以自己赋值
@AliasFor("transactionManager")//这个注解主要是标签的作用,具体实现可以去看他专门的类
String value() default ""; /**
* A <em>qualifier</em> value for the specified transaction.
* <p>May be used to determine the target transaction manager,
* matching the qualifier value (or the bean name) of a specific
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager}
* bean definition.
* @since 4.2
* @see #value
*/
//去配置文件或者配置类里面找上面定义的那个名字的事务管理器的名字,找到匹配的事务管理器
@AliasFor("value")
String transactionManager() default ""; /**
* The transaction propagation type.
* <p>Defaults to {@link Propagation#REQUIRED}.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getPropagationBehavior()
*/
//定义事务传播方式的方法,默认是Propagation.REQUIRED枚举
//REQUIRED 支持当前事务,如果不存在则创建一个新事务。 类似于同名的EJB事务属性,
就是说这个传播方式下,事务内是可以嵌套事务的,子事务以主事务管理,
网上说的事务里面不能嵌套事务操作是片面的,具体是要看事务的传播类型是怎么定义的
//SUPPORTS 如果上下文存在事物,则支持事物加入,如果没有事物,则使用非事物的方式执行。
//MANDATORY 该级别的事物要求上下文中必须要存在事物,否则就会抛出异常
//REQUIRES_NEW 每次都会新建事物,并且上下文的事物挂机,执行当前新建事物完成以后,上下文事物回复再执行。
//NOT_SUPPORTED 当前级别的特点就是上下文中存在事物,则挂起事物,执行当前逻辑,结束后回复上下文的事物。
//NEVER 上下文中不能存在事物,一旦有事物,就抛出runtime异常,强制停止执行
//NESTED 如果上下文中存在事物,则嵌套事物执行,如果不存在事物,则新建事物。
//具体详情见 org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition类
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;
/**
* The transaction isolation level.
* <p>Defaults to {@link Isolation#DEFAULT}.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getIsolationLevel()
*/
//事务的隔离级别
//TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT 使用基础数据存储的默认隔离级别。 所有其他级别对应于JDBC隔离级别。
//TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED 表示脏读,不可重复读和幻像读的常数可以发生,啥问题都没解决基本不用
//TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED 一个常量,指示防止脏读;不可重复读取和幻像读取可能会发生。此级别仅禁止事务,读取行中未提交的更改
//TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ 指示防止脏读和不可重复读的常量,可能会发生幻像读取
//TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 一个常数,指示防止脏读,不可重复读和幻像读
//具体详情见 org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition
Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT;
/**
* The timeout for this transaction.
* <p>Defaults to the default timeout of the underlying transaction system.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getTimeout()
*/
//事务超时时间,默认不设置,默认值为-1
int timeout() default TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT; /**
* {@code true} if the transaction is read-only.
* <p>Defaults to {@code false}.
* <p>This just serves as a hint for the actual transaction subsystem;
* it will <i>not necessarily</i> cause failure of write access attempts.
* A transaction manager which cannot interpret the read-only hint will
* <i>not</i> throw an exception when asked for a read-only transaction
* but rather silently ignore the hint.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#isReadOnly()
*/
//是否为只读事务,只读事务一般是通过共享锁,读写事务使用排他锁
boolean readOnly() default false; /**
* Defines zero (0) or more exception {@link Class classes}, which must be
* subclasses of {@link Throwable}, indicating which exception types must cause
* a transaction rollback.
* <p>By default, a transaction will be rolling back on {@link RuntimeException}
* and {@link Error} but not on checked exceptions (business exceptions). See
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)}
* for a detailed explanation.
* <p>This is the preferred way to construct a rollback rule (in contrast to
* {@link #rollbackForClassName}), matching the exception class and its subclasses.
* <p>Similar to {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RollbackRuleAttribute#RollbackRuleAttribute(Class clazz)}.
* @see #rollbackForClassName
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)
*/
//检查到指定异常后回滚
Class<? extends Throwable>[] rollbackFor() default {}; /**
* Defines zero (0) or more exception names (for exceptions which must be a
* subclass of {@link Throwable}), indicating which exception types must cause
* a transaction rollback.
* <p>This can be a substring of a fully qualified class name, with no wildcard
* support at present. For example, a value of {@code "ServletException"} would
* match {@code javax.servlet.ServletException} and its subclasses.
* <p><b>NB:</b> Consider carefully how specific the pattern is and whether
* to include package information (which isn't mandatory). For example,
* {@code "Exception"} will match nearly anything and will probably hide other
* rules. {@code "java.lang.Exception"} would be correct if {@code "Exception"}
* were meant to define a rule for all checked exceptions. With more unusual
* {@link Exception} names such as {@code "BaseBusinessException"} there is no
* need to use a FQN.
* <p>Similar to {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RollbackRuleAttribute#RollbackRuleAttribute(String exceptionName)}.
* @see #rollbackFor
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)
*/
//上一个方法中异常类的名字
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {}; /**
* Defines zero (0) or more exception {@link Class Classes}, which must be
* subclasses of {@link Throwable}, indicating which exception types must
* <b>not</b> cause a transaction rollback.
* <p>This is the preferred way to construct a rollback rule (in contrast
* to {@link #noRollbackForClassName}), matching the exception class and
* its subclasses.
* <p>Similar to {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.NoRollbackRuleAttribute#NoRollbackRuleAttribute(Class clazz)}.
* @see #noRollbackForClassName
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)
*/
//如果你在声明异常类中发生的异常,不回滚
Class<? extends Throwable>[] noRollbackFor() default {}; /**
* Defines zero (0) or more exception names (for exceptions which must be a
* subclass of {@link Throwable}) indicating which exception types must <b>not</b>
* cause a transaction rollback.
* <p>See the description of {@link #rollbackForClassName} for further
* information on how the specified names are treated.
* <p>Similar to {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.NoRollbackRuleAttribute#NoRollbackRuleAttribute(String exceptionName)}.
* @see #noRollbackFor
* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)
*/
//上一个异常类中的类名
String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {}; }
上述主要为Spring中Transactional中的方法使用介绍,现在具体来介绍一下错误读的问题是怎么解决的。
此处要引入三个概念,分别是记录锁,临建锁,间隙锁
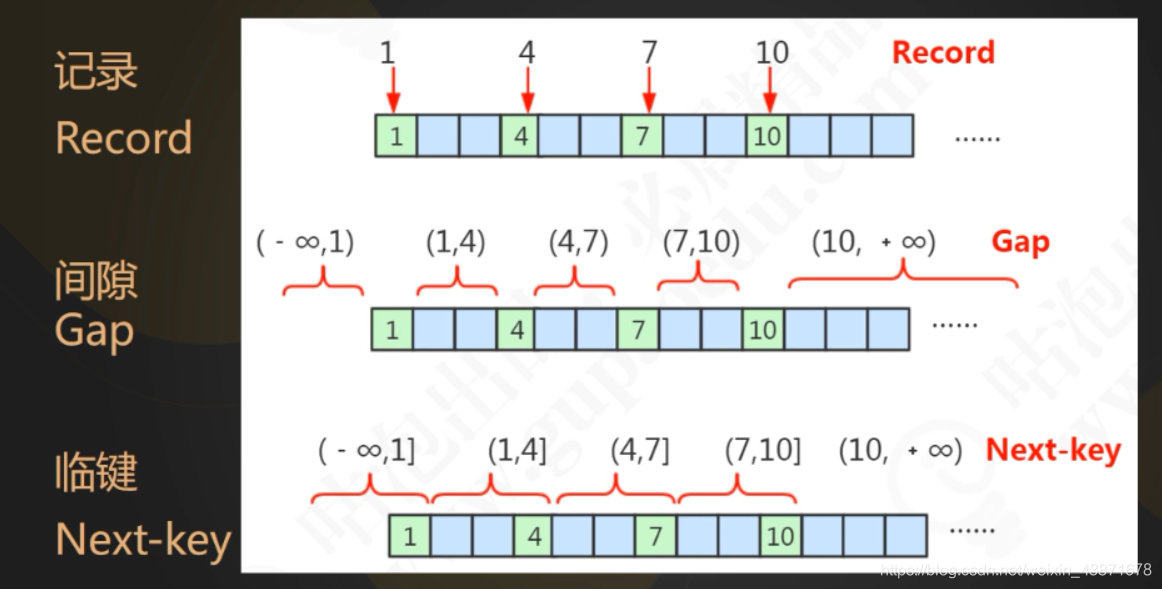
记录锁:记录锁就是为某行记录加锁,列必须为唯一索引列或主键列,否则加的锁就会变成临键锁,
查询语句必须为精准匹配 = ,不能为 >、<、like等,否则也会退化成临键锁。
如

间隙锁:间隙锁基于非唯一索引,它锁定一段范围内的索引记录。比如查询字段区间为4-7,即1-5内的记录行都会被锁住,5、6 的数据行的会被阻塞,但是 4 和 7 两条记录行并不会被锁住。
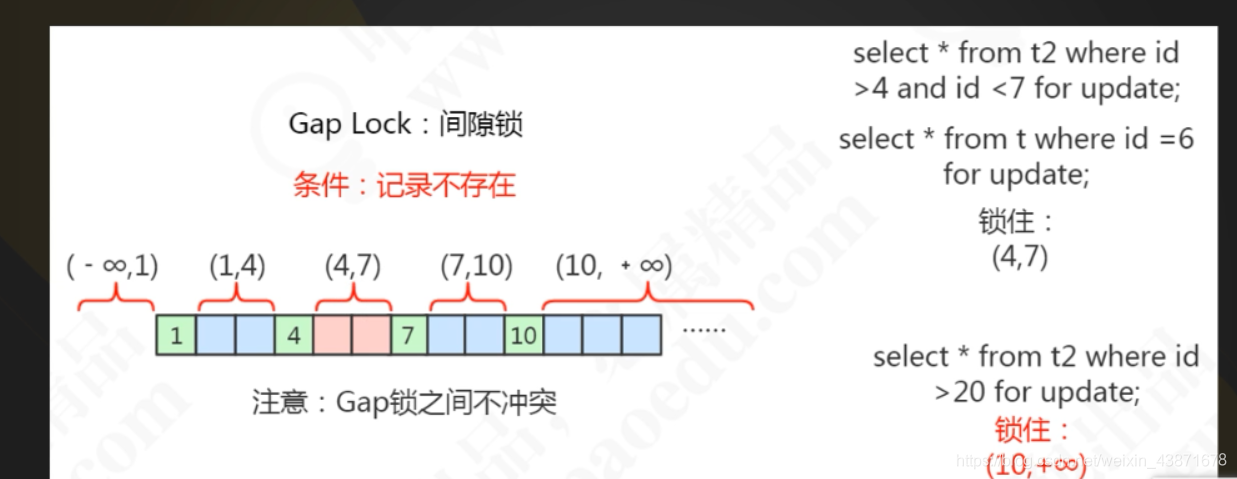
临建锁:临键锁可以理解为一种特殊的间隙锁,上面说过了通过临建锁可以解决幻读的问题。 每个数据行上的非唯一索引列上都会存在一把临键锁,当某个事务持有该数据行的临键锁时,会锁住一段左开右闭区间的数据。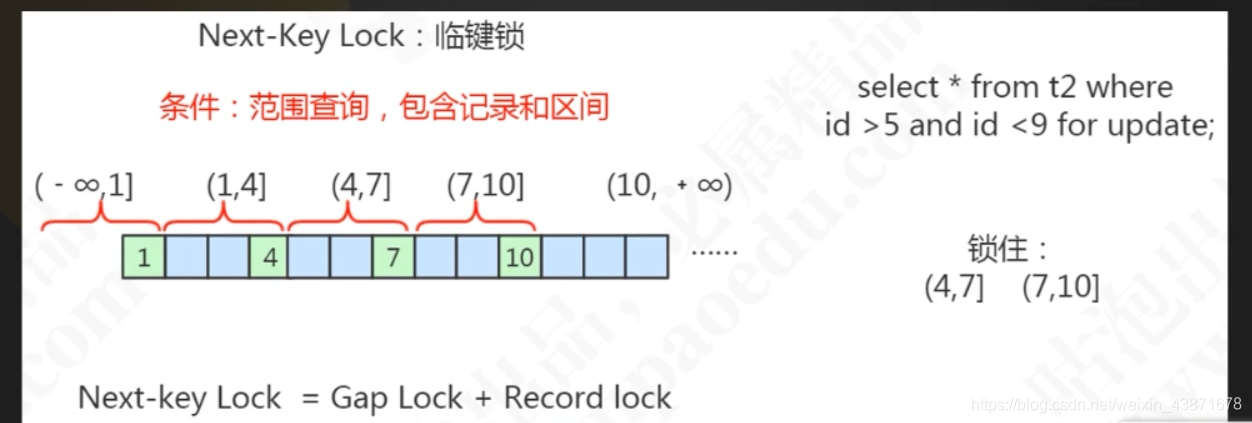
Mysql数据库下InnoDB数据引擎下的事务详解的更多相关文章
- MySQL数据库和InnoDB存储引擎文件
参数文件 当MySQL示例启动时,数据库会先去读一个配置参数文件,用来寻找数据库的各种文件所在位置以及指定某些初始化参数,这些参数通常定义了某种内存结构有多大等.在默认情况下,MySQL实例会按照一定 ...
- MySql中启用InnoDB数据引擎的方法
1.存储引擎是什么? Mysql中的数据用各种不同的技术存储在文件(或者内存)中.这些技术中的每一种技术都使用不同的存储机制.索引技巧.锁定水平并且最终提供广泛的不同的功能和能力.通过选择不同的技术, ...
- MySQL内核:InnoDB存储引擎 卷1
MySQL内核:InnoDB存储引擎卷1(MySQL领域Oracle ACE专家力作,众多MySQL Oracle ACE力捧,深入MySQL数据库内核源码分析,InnoDB内核开发与优化必备宝典) ...
- MySQL技术内幕InnoDB存储引擎(三)——文件相关
构成MySQL数据库和InnoDB存储引擎表的文件类型有: 参数文件:MySQL实例运行时需要的参数就是存储在这里. 日志文件:用来记录MySQL实例对某种条件做出响应时写入的文件. socket文件 ...
- 设置mysql InnoDB存储引擎下取消自动提交事务
mysql 存储引擎中最长用的有两种,MyISAM 存储引擎和InnoDB存储引擎. 1.MyISAM 存储引擎 不支持事务,不支持外键,优势是访问速度快: 2.InnoDB存储引擎 支持事务,一般项 ...
- MySQL数据表修复, 如何修复MySQL数据库(MyISAM / InnoDB)
常用的Mysql数据库修复方法有下面3种: 1. mysql原生SQL命令: repair 即执行REPAIR TABLE SQL语句 语法:REPAIR TABLE tablename[,table ...
- [转帖]一文看懂mysql数据库本质及存储引擎innodb+myisam
一文看懂mysql数据库本质及存储引擎innodb+myisam https://www.toutiao.com/i6740201316745740807/ 原创 波波说运维 2019-09-29 0 ...
- MySQL数据库在WINDOWS系统CMD下的编码问题
MySQL数据库在WINDOWS系统CMD下的编码问题 1. 查看MySQL数据库编码 * SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'char%'; 2. 编码解释 * character_set_c ...
- MySQL数据库的各种存储引擎详解
原文来自:MySQL数据库的各种存储引擎详解 MySQL有多种存储引擎,每种存储引擎有各自的优缺点,大家可以择优选择使用: MyISAM.InnoDB.MERGE.MEMORY(HEAP).BDB ...
随机推荐
- 类818tu.c微信小说分销系统设计之定时模板消息源码
近期将出个系列讲解开发过程,同时作为此系统的开发记录吧,万能的博客园,本边讲解如何发送模板消息,并且能够定时发送,下一篇讲解如何处理多个公众号的网页授权登录问题 [后台]http://xiaoshuo ...
- [UWP] - 修改应用程序在任务栏上的显示Logo
用VS2015在windows 10上开发一个UWP的应用,由于windows 10对store应用进行了窗口化,因此可以看到在任务栏上看到应用程序的图标,但是看起来会感觉应用Logo会被嵌在另一个容 ...
- [UWP] - 用Json格式来发送一个Post请求到WCF服务
测试实体类:(需要在客户端和服务端建了有相同字段名称的实体) public class CompositeType { public CompositeType() { SubCompositeTyp ...
- 7.mysql8.0版本MGR搭建
搭建MGR 1.配置文件 loose-group_replication_ip_whitelist = 192.168.124.0/24 loose-group_replication_start_o ...
- 2021韩顺平图解Linux课程(全面升级)基础篇
第1章 Linux 开山篇-内容介绍 本套 Linux 课程内容 Linux 主要应用领域:服务器 第2章 Linux 基础篇-Linux 入门 Linux 之父 Linus Torvalds Git ...
- 其实吧,LRU也就那么回事。
这是why哥的第 81 篇原创文章 你面试的时候遇见过LRU吗? LRU 算法,全称是Least Recently Used. 翻译过来就是最近最少使用算法. 这个算法的思想就是:如果一个数据在最近一 ...
- Vue项目如何打包问题总结
当我们将 vue 项目完成后,面临的就是如何将项目进行打包上线,放到服务器中.我使用的是 vue-cli(simple) 脚手架,所以就讲一下如何将项目进行打包,并放到 tomcat 上. 先来描述一 ...
- 每日一个linux命令6 -- mv
mv test.log test1.txt 文件改名 mv test1.log test3 文件移动 mv test1.log test2.log test3.log test4 将1,2,3.log ...
- [每日一题]面试官问:for in和for of 的区别和原理?
关注「松宝写代码」,精选好文,每日一题 时间永远是自己的 每分每秒也都是为自己的将来铺垫和增值 作者:saucxs | songEagle 一.前言 2020.12.23 日刚立的 flag,每日一 ...
- 紧急预警】关于爆发的 incaseformat 病毒事件亲身体验
相关报道 incaseformat病毒 360安全卫士服务号 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/KM6esd1eUlBt-YHtEwnfuw 广东省网络安全应急响应平台 https ...
