《机器学习Python实现_09_02_决策树_CART》
简介
CART树即分类回归树(classification and regression tree),顾名思义,它即能用作分类任务又能用作回归任务,它的应用比较广泛,通常会用作集成学习的基分类器,总得来说,它与ID3/C4.5有如下不同:
(1)它是一颗二叉树;
(2)特征选择的方法不一样,CART分类树利用基尼系数做特征选择,CART回归树利用平方误差做特征选择;
接下来,分别对CART分类树和回归树做介绍
CART分类树
首先介绍特征选择方法,基尼系数:
\]
所以,对于给定的样本集合\(D\),其基尼指数:
\]
这里,\(C_k\)是\(D\)中属于第\(k\)类的样本子集,\(K\)是类的个数,由于CART树是二叉树,所以对于某特征\(A\),判断其对分类标签的贡献时,只需要判断该特征是否等于某个取值\(a\)的情况,将当前数据集分割成\(D_1\)和\(D_2\)两部分:
\]
所以在特征\(A(x)=a\)的条件下,集合\(D\)的基尼指数可以定义为:
\]
代码实现
接下来进行CART分类树的代码实现,这里与ID3/C4.5最大的不同就是每次对当前结点仅进行二分处理
"""
定义计算gini系数相关的函数,代码封装到ml_models.utils
"""
import numpy as np
def gini(x, sample_weight=None):
"""
计算基尼系数 Gini(D)
:param x:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
x_num = len(x)
# 如果sample_weight为None设均设置一样
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * x_num)
x_counter = {}
weight_counter = {}
# 统计各x取值出现的次数以及其对应的sample_weight列表
for index in range(0, x_num):
x_value = x[index]
if x_counter.get(x_value) is None:
x_counter[x_value] = 0
weight_counter[x_value] = []
x_counter[x_value] += 1
weight_counter[x_value].append(sample_weight[index])
# 计算gini系数
gini_value = 1.0
for key, value in x_counter.items():
p_i = 1.0 * value * np.mean(weight_counter.get(key)) / x_num
gini_value -= p_i * p_i
return gini_value
def cond_gini(x, y, sample_weight=None):
"""
计算条件gini系数:Gini(y,x)
"""
x = np.asarray(x)
y = np.asarray(y)
# x中元素个数
x_num = len(x)
# 如果sample_weight为None设均设置一样
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * x_num)
# 计算
gini_value = .0
for x_value in set(x):
x_index = np.where(x == x_value)
new_x = x[x_index]
new_y = y[x_index]
new_sample_weight = sample_weight[x_index]
p_i = 1.0 * len(new_x) / x_num
gini_value += p_i * gini(new_y, new_sample_weight)
return gini_value
def gini_gain(x, y, sample_weight=None):
"""
gini值的增益
"""
x_num = len(x)
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * x_num)
return gini(y, sample_weight) - cond_gini(x, y, sample_weight)
import os
os.chdir('../')
from ml_models import utils
from ml_models.wrapper_models import DataBinWrapper
"""
CART分类树的实现,代码封装到ml_models.tree模块
"""
class CARTClassifier(object):
class Node(object):
"""
树节点,用于存储节点信息以及关联子节点
"""
def __init__(self, feature_index: int = None, feature_value=None, target_distribute: dict = None,
weight_distribute: dict = None,
left_child_node=None, right_child_node=None, num_sample: int = None):
"""
:param feature_index: 特征id
:param feature_value: 特征取值
:param target_distribute: 目标分布
:param weight_distribute:权重分布
:param left_child_node: 左孩子结点
:param right_child_node: 右孩子结点
:param num_sample:样本量
"""
self.feature_index = feature_index
self.feature_value = feature_value
self.target_distribute = target_distribute
self.weight_distribute = weight_distribute
self.left_child_node = left_child_node
self.right_child_node = right_child_node
self.num_sample = num_sample
def __init__(self, criterion='gini', max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1,
min_impurity_decrease=0, max_bins=10):
"""
:param criterion:划分标准,默认为gini,另外entropy表示用信息增益比
:param max_depth:树的最大深度
:param min_samples_split:当对一个内部结点划分时,要求该结点上的最小样本数,默认为2
:param min_samples_leaf:设置叶子结点上的最小样本数,默认为1
:param min_impurity_decrease:打算划分一个内部结点时,只有当划分后不纯度(可以用criterion参数指定的度量来描述)减少值不小于该参数指定的值,才会对该结点进行划分,默认值为0
"""
self.criterion = criterion
if criterion == 'gini':
self.criterion_func = utils.gini_gain
else:
self.criterion_func = utils.info_gain_rate
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leaf
self.min_impurity_decrease = min_impurity_decrease
self.root_node: self.Node = None
self.dbw = DataBinWrapper(max_bins=max_bins)
def _build_tree(self, current_depth, current_node: Node, x, y, sample_weight):
"""
递归进行特征选择,构建树
:param x:
:param y:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
rows, cols = x.shape
# 计算y分布以及其权重分布
target_distribute = {}
weight_distribute = {}
for index, tmp_value in enumerate(y):
if tmp_value not in target_distribute:
target_distribute[tmp_value] = 0.0
weight_distribute[tmp_value] = []
target_distribute[tmp_value] += 1.0
weight_distribute[tmp_value].append(sample_weight[index])
for key, value in target_distribute.items():
target_distribute[key] = value / rows
weight_distribute[key] = np.mean(weight_distribute[key])
current_node.target_distribute = target_distribute
current_node.weight_distribute = weight_distribute
current_node.num_sample = rows
# 判断停止切分的条件
if len(target_distribute) <= 1:
return
if rows < self.min_samples_split:
return
if self.max_depth is not None and current_depth > self.max_depth:
return
# 寻找最佳的特征以及取值
best_index = None
best_index_value = None
best_criterion_value = 0
for index in range(0, cols):
for index_value in set(x[:, index]):
criterion_value = self.criterion_func((x[:, index] == index_value).astype(int), y, sample_weight)
if criterion_value > best_criterion_value:
best_criterion_value = criterion_value
best_index = index
best_index_value = index_value
# 如果criterion_value减少不够则停止
if best_index is None:
return
if best_criterion_value <= self.min_impurity_decrease:
return
# 切分
current_node.feature_index = best_index
current_node.feature_value = best_index_value
selected_x = x[:, best_index]
# 创建左孩子结点
left_selected_index = np.where(selected_x == best_index_value)
# 如果切分后的点太少,以至于都不能做叶子节点,则停止分割
if len(left_selected_index[0]) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
left_child_node = self.Node()
current_node.left_child_node = left_child_node
self._build_tree(current_depth + 1, left_child_node, x[left_selected_index], y[left_selected_index],
sample_weight[left_selected_index])
# 创建右孩子结点
right_selected_index = np.where(selected_x != best_index_value)
# 如果切分后的点太少,以至于都不能做叶子节点,则停止分割
if len(right_selected_index[0]) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
right_child_node = self.Node()
current_node.right_child_node = right_child_node
self._build_tree(current_depth + 1, right_child_node, x[right_selected_index], y[right_selected_index],
sample_weight[right_selected_index])
def fit(self, x, y, sample_weight=None):
# check sample_weight
n_sample = x.shape[0]
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * n_sample)
# check sample_weight
if len(sample_weight) != n_sample:
raise Exception('sample_weight size error:', len(sample_weight))
# 构建空的根节点
self.root_node = self.Node()
# 对x分箱
self.dbw.fit(x)
# 递归构建树
self._build_tree(1, self.root_node, self.dbw.transform(x), y, sample_weight)
# 检索叶子节点的结果
def _search_node(self, current_node: Node, x, class_num):
if current_node.left_child_node is not None and x[current_node.feature_index] == current_node.feature_value:
return self._search_node(current_node.left_child_node, x, class_num)
elif current_node.right_child_node is not None and x[current_node.feature_index] != current_node.feature_value:
return self._search_node(current_node.right_child_node, x, class_num)
else:
result = []
total_value = 0.0
for index in range(0, class_num):
value = current_node.target_distribute.get(index, 0) * current_node.weight_distribute.get(index, 1.0)
result.append(value)
total_value += value
# 归一化
for index in range(0, class_num):
result[index] = result[index] / total_value
return result
def predict_proba(self, x):
# 计算结果概率分布
x = self.dbw.transform(x)
rows = x.shape[0]
results = []
class_num = len(self.root_node.target_distribute)
for row in range(0, rows):
results.append(self._search_node(self.root_node, x[row], class_num))
return np.asarray(results)
def predict(self, x):
return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x), axis=1)
def _prune_node(self, current_node: Node, alpha):
# 如果有子结点,先对子结点部分剪枝
if current_node.left_child_node is not None:
self._prune_node(current_node.left_child_node, alpha)
if current_node.right_child_node is not None:
self._prune_node(current_node.right_child_node, alpha)
# 再尝试对当前结点剪枝
if current_node.left_child_node is not None or current_node.right_child_node is not None:
# 避免跳层剪枝
for child_node in [current_node.left_child_node, current_node.right_child_node]:
# 当前剪枝的层必须是叶子结点的层
if child_node.left_child_node is not None or child_node.right_child_node is not None:
return
# 计算剪枝的前的损失值
pre_prune_value = alpha * 2
for child_node in [current_node.left_child_node, current_node.right_child_node]:
for key, value in child_node.target_distribute.items():
pre_prune_value += -1 * child_node.num_sample * value * np.log(
value) * child_node.weight_distribute.get(key, 1.0)
# 计算剪枝后的损失值
after_prune_value = alpha
for key, value in current_node.target_distribute.items():
after_prune_value += -1 * current_node.num_sample * value * np.log(
value) * current_node.weight_distribute.get(key, 1.0)
if after_prune_value <= pre_prune_value:
# 剪枝操作
current_node.left_child_node = None
current_node.right_child_node = None
current_node.feature_index = None
current_node.feature_value = None
def prune(self, alpha=0.01):
"""
决策树剪枝 C(T)+alpha*|T|
:param alpha:
:return:
"""
# 递归剪枝
self._prune_node(self.root_node, alpha)
#造伪数据
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
data, target = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1, n_redundant=0,
n_repeated=0, n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=.5,random_state=21)
#训练并查看效果
tree = CARTClassifier()
tree.fit(data, target)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, tree)
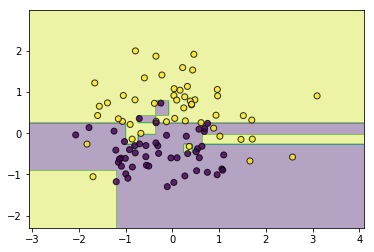
一样的,如果不加以限制,同样会存在过拟合现象,所以可以剪枝...
#剪枝
tree.prune(5)
utils.plot_decision_function(data, target, tree)
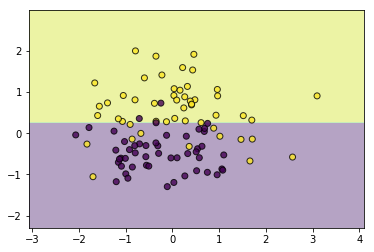
CART回归树
回归树的特征选择是使用的平方误差,即选择一个特征\(j\)和一个取值\(s\),将训练集按\(X^j\leq s\)和\(X^j>s\)分为两部分,寻找使这两部分的误差平方之和下降最多的\(j,s\),这个过程可以描述如下:
\]
这里\(R_1(j,s)=\{x\mid x^j\leq s\},R_2(j,s)=\{x\mid x^j> s\},c_1=ave(y_i\mid x_i\in R_1(j,s)),c_2=ave(y_i\mid x_i\in R_2(j,s))\)
代码实现:
"""
平方误差相关函数,封装到ml_models.utils
"""
def square_error(x, sample_weight=None):
"""
平方误差
:param x:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
x = np.asarray(x)
x_mean = np.mean(x)
x_num = len(x)
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * x_num)
error = 0.0
for index in range(0, x_num):
error += (x[index] - x_mean) * (x[index] - x_mean) * sample_weight[index]
return error
def cond_square_error(x, y, sample_weight=None):
"""
计算按x分组的y的误差值
:param x:
:param y:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
x = np.asarray(x)
y = np.asarray(y)
# x中元素个数
x_num = len(x)
# 如果sample_weight为None设均设置一样
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * x_num)
# 计算
error = .0
for x_value in set(x):
x_index = np.where(x == x_value)
new_y = y[x_index]
new_sample_weight = sample_weight[x_index]
error += square_error(new_y, new_sample_weight)
return error
def square_error_gain(x, y, sample_weight=None):
"""
平方误差带来的增益值
:param x:
:param y:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
x_num = len(x)
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * x_num)
return square_error(y, sample_weight) - cond_square_error(x, y, sample_weight)
"""
CART回归树实现,封装到ml_models.tree
"""
class CARTRegressor(object):
class Node(object):
"""
树节点,用于存储节点信息以及关联子节点
"""
def __init__(self, feature_index: int = None, feature_value=None, y_hat=None, square_error=None,
left_child_node=None, right_child_node=None, num_sample: int = None):
"""
:param feature_index: 特征id
:param feature_value: 特征取值
:param y_hat: 预测值
:param square_error: 当前结点的平方误差
:param left_child_node: 左孩子结点
:param right_child_node: 右孩子结点
:param num_sample:样本量
"""
self.feature_index = feature_index
self.feature_value = feature_value
self.y_hat = y_hat
self.square_error = square_error
self.left_child_node = left_child_node
self.right_child_node = right_child_node
self.num_sample = num_sample
def __init__(self, criterion='mse', max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, min_std=1e-3,
min_impurity_decrease=0, max_bins=10):
"""
:param criterion:划分标准,目前仅有平方误差
:param max_depth:树的最大深度
:param min_samples_split:当对一个内部结点划分时,要求该结点上的最小样本数,默认为2
:param min_std:最小的标准差
:param min_samples_leaf:设置叶子结点上的最小样本数,默认为1
:param min_impurity_decrease:打算划分一个内部结点时,只有当划分后不纯度(可以用criterion参数指定的度量来描述)减少值不小于该参数指定的值,才会对该结点进行划分,默认值为0
"""
self.criterion = criterion
if criterion == 'mse':
self.criterion_func = utils.square_error_gain
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leaf
self.min_std = min_std
self.min_impurity_decrease = min_impurity_decrease
self.root_node: self.Node = None
self.dbw = DataBinWrapper(max_bins=max_bins)
def _build_tree(self, current_depth, current_node: Node, x, y, sample_weight):
"""
递归进行特征选择,构建树
:param x:
:param y:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
rows, cols = x.shape
# 计算当前y的加权平均值
current_node.y_hat = np.dot(sample_weight / np.sum(sample_weight), y)
current_node.num_sample = rows
# 判断停止切分的条件
current_node.square_error = np.dot(y - np.mean(y), y - np.mean(y))
if np.sqrt(current_node.square_error / rows) <= self.min_std:
return
if rows < self.min_samples_split:
return
if self.max_depth is not None and current_depth > self.max_depth:
return
# 寻找最佳的特征以及取值
best_index = None
best_index_value = None
best_criterion_value = 0
for index in range(0, cols):
for index_value in sorted(set(x[:, index])):
criterion_value = self.criterion_func((x[:, index] <= index_value).astype(int), y, sample_weight)
if criterion_value > best_criterion_value:
best_criterion_value = criterion_value
best_index = index
best_index_value = index_value
# 如果criterion_value减少不够则停止
if best_index is None:
return
if best_criterion_value <= self.min_impurity_decrease:
return
# 切分
current_node.feature_index = best_index
current_node.feature_value = best_index_value
selected_x = x[:, best_index]
# 创建左孩子结点
left_selected_index = np.where(selected_x <= best_index_value)
# 如果切分后的点太少,以至于都不能做叶子节点,则停止分割
if len(left_selected_index[0]) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
left_child_node = self.Node()
current_node.left_child_node = left_child_node
self._build_tree(current_depth + 1, left_child_node, x[left_selected_index], y[left_selected_index],
sample_weight[left_selected_index])
# 创建右孩子结点
right_selected_index = np.where(selected_x > best_index_value)
# 如果切分后的点太少,以至于都不能做叶子节点,则停止分割
if len(right_selected_index[0]) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
right_child_node = self.Node()
current_node.right_child_node = right_child_node
self._build_tree(current_depth + 1, right_child_node, x[right_selected_index], y[right_selected_index],
sample_weight[right_selected_index])
def fit(self, x, y, sample_weight=None):
# check sample_weight
n_sample = x.shape[0]
if sample_weight is None:
sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * n_sample)
# check sample_weight
if len(sample_weight) != n_sample:
raise Exception('sample_weight size error:', len(sample_weight))
# 构建空的根节点
self.root_node = self.Node()
# 对x分箱
self.dbw.fit(x)
# 递归构建树
self._build_tree(1, self.root_node, self.dbw.transform(x), y, sample_weight)
# 检索叶子节点的结果
def _search_node(self, current_node: Node, x):
if current_node.left_child_node is not None and x[current_node.feature_index] <= current_node.feature_value:
return self._search_node(current_node.left_child_node, x)
elif current_node.right_child_node is not None and x[current_node.feature_index] > current_node.feature_value:
return self._search_node(current_node.right_child_node, x)
else:
return current_node.y_hat
def predict(self, x):
# 计算结果概率分布
x = self.dbw.transform(x)
rows = x.shape[0]
results = []
for row in range(0, rows):
results.append(self._search_node(self.root_node, x[row]))
return np.asarray(results)
def _prune_node(self, current_node: Node, alpha):
# 如果有子结点,先对子结点部分剪枝
if current_node.left_child_node is not None:
self._prune_node(current_node.left_child_node, alpha)
if current_node.right_child_node is not None:
self._prune_node(current_node.right_child_node, alpha)
# 再尝试对当前结点剪枝
if current_node.left_child_node is not None or current_node.right_child_node is not None:
# 避免跳层剪枝
for child_node in [current_node.left_child_node, current_node.right_child_node]:
# 当前剪枝的层必须是叶子结点的层
if child_node.left_child_node is not None or child_node.right_child_node is not None:
return
# 计算剪枝的前的损失值
pre_prune_value = alpha * 2 + \
(0.0 if current_node.left_child_node.square_error is None else current_node.left_child_node.square_error) + \
(0.0 if current_node.right_child_node.square_error is None else current_node.right_child_node.square_error)
# 计算剪枝后的损失值
after_prune_value = alpha + current_node.square_error
if after_prune_value <= pre_prune_value:
# 剪枝操作
current_node.left_child_node = None
current_node.right_child_node = None
current_node.feature_index = None
current_node.feature_value = None
current_node.square_error = None
def prune(self, alpha=0.01):
"""
决策树剪枝 C(T)+alpha*|T|
:param alpha:
:return:
"""
# 递归剪枝
self._prune_node(self.root_node, alpha)
#构造数据
data = np.linspace(1, 10, num=100)
target = np.sin(data) + np.random.random(size=100)#添加噪声
data = data.reshape((-1, 1))
tree = CARTRegressor(max_bins=50)
tree.fit(data, target)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, tree.predict(data), color='r')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x221783ed9b0>]
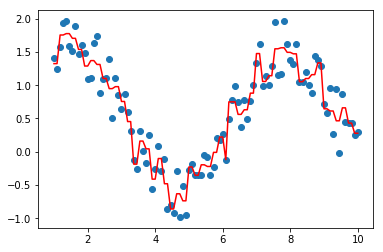
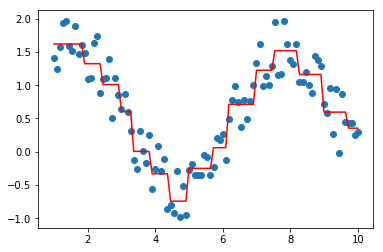
#剪枝
tree.prune(1)
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, tree.predict(data), color='r')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x221783fcb70>]
《机器学习Python实现_09_02_决策树_CART》的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- .html文件转换成.txt
@ 思路 @-@ 简要 根据尖括号将文件分隔成字符串,建立一套判断字符串是否为标签的标准,若不为标签则为文本内容,存入结果文件中: @-@ 详述 0. 建立两个哈希表: 哈希表1 unordere ...
- Apache2.4 根目录修改
需要修改两个地方: 1.httpd.conf 中的 DocumentRoot 项 和 Directory 项 2.httpd-vhosts.conf 中的 DocumentRoot 项 网上找到的大部 ...
- 一文揭秘测试平台中是如何将测试用例一键转化Jmeter压测脚本
接上篇,一键转化将接口测试平台测试用例转化成Jmeter压测脚本思路,这里我首先在java 上面做了一个简单的实验,看看 转化的中间遇到的问题,这里呢,我只是给了一个简单的demo 版本, ...
- lintcode 826电脑维修
826,一个n * m矩阵代表一个电脑的阵列,给你一个list< Point >代表坏掉的电脑坐标.现在我们从(0,0)出发修电脑,要求: 1.必须修完当前行所有坏掉的电脑才能走向下一 ...
- Java——Java集合那些事
集合概述: 集合和数组都可以保存多个对象,但是数组的长度不可变,集合可以保存数量变化的数据.java中的集合类主要由两个接口派生出,Collection和Map Collection接口和Iterat ...
- 猫狗大战("简单的二维背包")
题面:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1489 看上去是一道简单的二维费用背包,但是要特别小心循环顺序. Ⅰ先循环物品,再循环限制条件. Ⅱ每一个限制条件都必须从后 ...
- Oracle条件判断
一. if/else 语法:if 条件表达式 then语句块:if 条件表达式 then 语句块end if;elsif 条件表达式 then语句块:...else语句块:end if;举例:输入一个 ...
- react中redux的理解
定义 redux可以看作是flux的进阶版,主要用于react中公共状态(数据)的管理 redux底层原理 redux有一个createStore方法,这个方法用户创建公共存储空间,createSto ...
- 一文教你快速搞懂 FOC ramp function 斜坡函数的作用和实现
文章目录 定义 程序的实现 matlab 程序 C语言程序 定义 x(t)={0,t<0At,t≥0 x(t) = \begin{cases} 0,t<0\\ At,t \ge 0\\ \ ...
- Android将库导入到build.gradle
如图
