PAT Advanced A1021 Deepest Root (25) [图的遍历,DFS,计算连通分量的个数,BFS,并查集]
题目
A graph which is connected and acyclic can be considered a tree. The height of the tree depends on the selected root. Now you are supposed to find the root that results in a highest tree. Such a root is called the deepest root.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=10000) which is the number of nodes, and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N. Then N-1 lines follow, each describes an edge by given the two adjacent nodes’ numbers.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print each of the deepest roots in a line. If such a root is not unique, print them in increasing order of their numbers. In case that the given graph is not a tree, print “Error: K components” where K is the number of connected components in the graph.
Sample Input 1:
5
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
Sample Output 1:
3
4
5
Sample Input 2:
5
1 3
1 4
2 5
3 4
Sample Output 2:
Error: 2 components
题目分析
已知图的顶点N和边N-1,判断所给图是否是一棵树,如果是,查找并打印最高树的所有根节点(从小到大)
- 判断图为树有两个条件:只有一个连通分量(否则为森林);无环(已知顶点数为N,边为N-1的连通图一定是树)
- 最高树的所有根节点,其含义可以从样例中推导得出(起始顶点不同,寻找出的最高树不同)
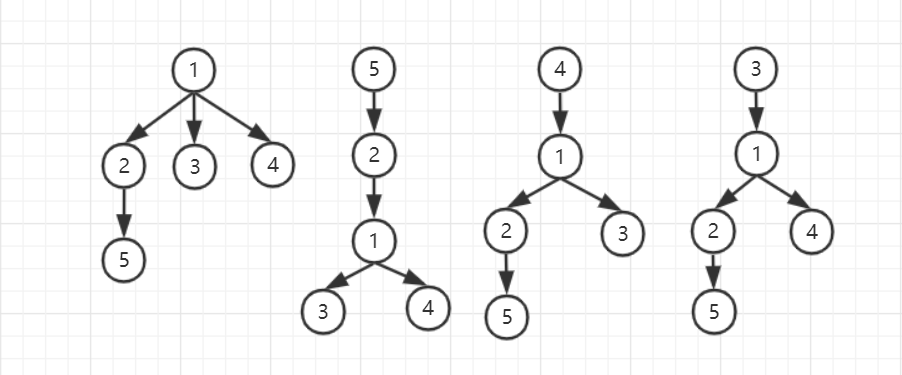
解题思路
1. 存储顶点和边
- 邻接表
- 邻接矩阵
2. 计算连通分量个数
连通分量等于1时,满足条件
- DFS
- BFS
- 并查集
3. 查找最大高度树的根节点
- 任意取一个顶点,求其能到达的最远的节点集合A,如测试样例1中:取1,可以得到5,3,4
- 任取取A集合中一个顶点,求其能到达的最远的节点集合B,如取A集合中3,可以得到4,5
- 集合A和集合B的并集去重排序,即为答案
Code
Code 01(邻接矩阵 并查集)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <set>using namespace std;const int maxn=10010;vector<int> g[maxn],temp; //邻接表 存储边set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest rootsint maxh,n,father[maxn],vis[maxn];/*并查集判断连通分量树两次dfs求the deepest root*/int init() { /* 并查集 初始化 */for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)father[i]=i;}int find(int x) { /* 并查集 查 */int a = x;while(x!=father[x]) {x=father[x];}while(a!=father[a]) { // 路径压缩int temp=a;a=father[a];father[a]=x;}return x;}void Union(int a,int b) { /* 并查集 并 */int fa=find(a);int fb=find(b);if(fa<fb)father[fb]=fa;else father[fa]=fb;}void dfs(int a, int h) { /* dfs */vis[a]=1;if(h>maxh) {temp.clear();temp.push_back(a); // the deepest rootmaxh=h;} else if(h==maxh)temp.push_back(a);for(int i=0; i<g[a].size(); i++) {if(vis[g[a][i]]==0)dfs(g[a][i],h+1);}}void pts() {for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)vs.insert(temp[i]);}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int a,b;scanf("%d",&n);init();for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);g[a].push_back(b);g[b].push_back(a);Union(a,b);}// 统计连通分量数for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {vs.insert(find(i));}if(vs.size()>1) {printf("Error: %d components",vs.size());return 0;}vs.clear(); //vs重置,方便下面使用dfs(1,1); // 第一次dfs,任意取一个顶点,获取最深根集合Apts(); //将集合A存入setfill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest rootdfs(temp[0],1);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合Bpts(); //将集合B存入setfor(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) { //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果printf("%d\n",*it);}return 0;}
Code 02(邻接矩阵 DFS)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <set>using namespace std;const int maxn=10010;vector<int> g[maxn],temp; //邻接表 存储边set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest rootsint n,maxh,vis[maxn];/*第一次dfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A第二次dfs 求the deepest root集合B集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案*/void dfs(int a, int h) { /* dfs */vis[a]=1;if(h>maxh) {temp.clear();temp.push_back(a); // the deepest rootmaxh=h;} else if(h==maxh)temp.push_back(a);for(int i=0; i<g[a].size(); i++) {if(vis[g[a][i]]==0)dfs(g[a][i],h+1);}}void pts() {for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)vs.insert(temp[i]);}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int a,b;scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);g[a].push_back(b);g[b].push_back(a);}// 统计连通分量数int cnt=0;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {if(vis[i]==0){dfs(i,0);pts(); //将集合A存入setcnt++;}}if(cnt>1) {printf("Error: %d components",cnt);return 0;}fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest rootdfs(temp[0],1);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合Bpts(); //将集合B存入setfor(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) { //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果printf("%d\n",*it);}return 0;}
Code 03(邻接矩阵 BFS)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <set>#include <queue>using namespace std;const int maxn=10010;vector<int> g[maxn],temp; //邻接表 存储边set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest rootsint n,maxh,vis[maxn];struct node {int v;int h;};/*第一次bfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A第二次bfs 求the deepest root集合B集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案*/void bfs(int a) { /* dfs */vis[a]=1;queue<node> q;q.push({a,0});while(!q.empty()) {node now = q.front();q.pop();if(now.h>maxh) {temp.clear();temp.push_back(now.v); // the deepest rootmaxh=now.h;} else if(now.h==maxh)temp.push_back(now.v);for(int i=0; i<g[now.v].size(); i++)if(vis[g[now.v][i]]==0){q.push({g[now.v][i],now.h+1});vis[g[now.v][i]]=1;}}}void pts() {for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)vs.insert(temp[i]);}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int a,b;scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);g[a].push_back(b);g[b].push_back(a);}// 统计连通分量数int cnt=0;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {if(vis[i]==0) {bfs(i);pts(); //将集合A存入setcnt++;}}if(cnt>1) {printf("Error: %d components",cnt);return 0;}fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest rootbfs(temp[0]);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合Bpts(); //将集合B存入setfor(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果printf("%d\n",*it);return 0;}
Code 04(邻接表 DFS)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <set>using namespace std;const int maxn=10010;vector<int> temp; //邻接表 存储边set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest rootsint n,maxh,vis[maxn],g[maxn][maxn];/*第一次dfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A第二次dfs 求the deepest root集合B集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案*/void dfs(int a, int h) { /* dfs */vis[a]=1;if(h>maxh) {temp.clear();temp.push_back(a); // the deepest rootmaxh=h;} else if(h==maxh)temp.push_back(a);for(int i=1; i<maxn; i++)if(g[a][i]==1 && vis[i]==0)dfs(i,h+1);}void pts() {for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)vs.insert(temp[i]);}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int a,b;scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);g[a][b]=1;g[b][a]=1;}// 统计连通分量数int cnt=0;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {if(vis[i]==0) {dfs(i,0);pts(); //将集合A存入setcnt++;}}if(cnt>1) {printf("Error: %d components",cnt);return 0;}fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest rootdfs(temp[0],1);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合Bpts(); //将集合B存入setfor(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) { //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果printf("%d\n",*it);}return 0;}
Code 05(邻接表 BFS)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <set>#include <queue>using namespace std;const int maxn=10010;vector<int> temp; //邻接表 存储边set<int> vs; // 存储所有满足条件的 the deepest rootsint n,maxh,vis[maxn],g[maxn][maxn];struct node {int v;int h;};/*第一次bfs 求连通分量,求the deepest root集合A第二次bfs 求the deepest root集合B集合A+B,去重排序 即为答案*/void bfs(int a) { /* dfs */vis[a]=1;queue<node> q;q.push({a,0});while(!q.empty()) {node now = q.front();q.pop();if(now.h>maxh) {temp.clear();temp.push_back(now.v); // the deepest rootmaxh=now.h;} else if(now.h==maxh)temp.push_back(now.v);for(int i=1; i<maxn; i++)if(g[now.v][i]==1 && vis[i]==0){q.push({i,now.h+1});vis[i]=1;}}}void pts() {for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)vs.insert(temp[i]);}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int a,b;scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1; i<=n-1; i++) {scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);g[a][b]=1;g[b][a]=1;}// 统计连通分量数int cnt=0;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {if(vis[i]==0) {bfs(i);pts(); //将集合A存入setcnt++;}}if(cnt>1) {printf("Error: %d components",cnt);return 0;}fill(vis,vis+maxn,0); //重置vis访问标记数组//maxh=0; //无需重置maxh,因为第一轮得到的maxh即为最高树高度,第二轮中h==maxh时添加剩余的the deepest rootbfs(temp[0]);// 第二次dfs,从集合A中任取一个顶点,获取最深根集合Bpts(); //将集合B存入setfor(set<int>::iterator it=vs.begin(); it!=vs.end(); it++) //set默认从小到大,A+B去重即为结果printf("%d\n",*it);return 0;}
PAT Advanced A1021 Deepest Root (25) [图的遍历,DFS,计算连通分量的个数,BFS,并查集]的更多相关文章
- PAT Advanced 1013 Battle Over Cities (25) [图的遍历,统计连通分量的个数,DFS,BFS,并查集]
题目 It is vitally important to have all the cities connected by highways in a war. If a city is occup ...
- PAT 甲级 1021 Deepest Root (25 分)(bfs求树高,又可能存在part数part>2的情况)
1021 Deepest Root (25 分) A graph which is connected and acyclic can be considered a tree. The heig ...
- PAT甲级——A1021 Deepest Root
A graph which is connected and acyclic can be considered a tree. The height of the tree depends on t ...
- PAT Advanced 1020 Tree Traversals (25) [⼆叉树的遍历,后序中序转层序]
题目 Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. Given the postorder an ...
- PAT Advanced 1138 Postorder Traversal (25) [树的遍历,前序中序转后序]
题目 Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. Given the preorder and ...
- [PAT] 1021 Deepest Root (25)(25 分)
1021 Deepest Root (25)(25 分)A graph which is connected and acyclic can be considered a tree. The hei ...
- PAT甲级1021. Deepest Root
PAT甲级1021. Deepest Root 题意: 连接和非循环的图可以被认为是一棵树.树的高度取决于所选的根.现在你应该找到导致最高树的根.这样的根称为最深根. 输入规格: 每个输入文件包含一个 ...
- PAT 甲级 1021 Deepest Root (并查集,树的遍历)
1021. Deepest Root (25) 时间限制 1500 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue A graph ...
- 图的遍历DFS
图的遍历DFS 与树的深度优先遍历之间的联系 树的深度优先遍历分为:先根,后根 //树的先根遍历 void PreOrder(TreeNode *R){ if(R!=NULL){ visit(R); ...
随机推荐
- JuJu团队1月7号工作汇报
JuJu团队1月7号工作汇报 JuJu 周六周日放假,所以空了两天~ Scrum 团队成员 今日工作 剩余任务 困难 飞飞 完成data process readme部分 实现三维Dense 无 ...
- windows环境批量更改文件名
1.打开命令提示符,进入需更新文件所在的目录下(不熟悉的参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012995964/article/details/53119516)2.批量命名 ...
- CodeForces - 869B The Eternal Immortality
题意:已知a,b,求的最后一位. 分析: 1.若b-a>=5,则尾数一定为0,因为连续5个数的尾数要么同时包括一个5和一个偶数,要么包括一个0. 2.若b-a<5,直接暴力求即可. #in ...
- MySQL 如何使用 PV 和 PVC?【转】
本节演示如何为 MySQL 数据库提供持久化存储,步骤为: 创建 PV 和 PVC. 部署 MySQL. 向 MySQL 添加数据. 模拟节点宕机故障,Kubernetes 将 MySQL 自动迁移到 ...
- centos 7安装nodejs
ps: {install_path} 安装目录路径 1.安装wget yum install wget 2. 下载对应文件 wget -c https://nodejs.org/dist/v8.9.1 ...
- R 对数变换 《回归分析与线性统计模型》page103
BG:在box-cox变换中,当λ = 0时即为对数变换. 当所分析变量的标准差相对于均值而言比较大时,这种变换特别有用.对数据作对数变换常常起到降低数据波动性和减少不对称性的作用..这一变换也能有效 ...
- Day4 - M - Roads in Berland CodeForces - 25C
There are n cities numbered from 1 to n in Berland. Some of them are connected by two-way roads. Eac ...
- 把自己的项目发布到maven仓库并在maven和gradle中开始使用
把自己的项目发布到maven仓库并在maven和gradle中开始使用 上一条博客中提到的日志打印项目总算是维护的差不多了, 不过现在使用它还是打成jar包放到其他项目内, 所以决定把项目传到mave ...
- 使用conda创建虚拟环境
conda创建python虚拟环境 前言 conda常用的命令: conda list 查看安装了哪些包. conda env list 或 conda info -e 查看当前存在哪些虚拟环境 co ...
- [题解] LuoguP2257 YY的GCD
传送门 给\(n,m\),让你求 \[ \sum\limits_{i=1}^n \sum\limits_{j=1}^m [\gcd(i,j) \in prime] \] 有\(T\)组询问\((T \ ...
