吴裕雄--天生自然 Tensorflow卷积神经网络:花朵图片识别
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image, ImageChops
from skimage import color,data,transform,io #获取所有数据文件夹名称
fileList = os.listdir("F:\\data\\flowers")
trainDataList = []
trianLabel = []
testDataList = []
testLabel = [] #读取每一种花的文件
for j in range(len(fileList)):
data = os.listdir("F:\\data\\flowers\\"+fileList[j])
#取每一种花四分之一的数据作为测试数据集
testNum = int(len(data)*0.25)
#把每种花的图片进行testNum次乱序处理
while(testNum>0):
np.random.shuffle(data)
testNum -= 1
#把每种花经过乱序后的四分之三当作训练集
trainData = np.array(data[:-(int(len(data)*0.25))])
#把每种花经过乱序后的四分之一当作测试集
testData = np.array(data[-(int(len(data)*0.25)):])
#从上面选出来的训练集中逐张读取出对应的图片
for i in range(len(trainData)):
#其中这些图片都要满足jpg格式的
if(trainData[i][-3:]=="jpg"):
#读取一张jpg图片
image = io.imread("F:\\data\\flowers\\"+fileList[j]+"\\"+trainData[i])
#把这张图片变成64*64大小的图片
image=transform.resize(image,(64,64))
#保存改变大小的图片到trainDataList列表
trainDataList.append(image)
#保存这张图片的标签到trianLabel列表
trianLabel.append(int(j))
#随机生成一个角度,这个角度的范围在顺时针90度和逆时针90度之间
angle = np.random.randint(-90,90)
#然后把上面那张64*64大小的图片随机旋转angle个角度
image =transform.rotate(image, angle)
#把旋转得到的新图片再变成64*64大小的,因为旋转会改变一张图片的大小
image=transform.resize(image,(64,64))
#把旋转后并且大小是64*64的图片保存到trainDataList列表
trainDataList.append(image)
#把旋转后并且大小是64*64的图片对应的标签保存到trianLabel列表
trianLabel.append(int(j))
#逐张读取每种花的测试图片
for i in range(len(testData)):
#选取的图片要满足jpg格式的
if(testData[i][-3:]=="jpg"):
#读取一张图片
image = io.imread("F:\\data\\flowers\\"+fileList[j]+"\\"+testData[i])
#改变这张图片的大小为64*64
image=transform.resize(image,(64,64))
#把改变后的图片保存到testDataList列表中
testDataList.append(image)
#把这张图片对应的标签保存到testLabel列表中
testLabel.append(int(j))
print("图片数据读取完了...")
#打印训练集和测试数据集以及它们对应标签的规模
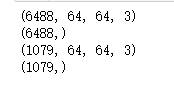
print(np.shape(trainDataList))
print(np.shape(trianLabel))
print(np.shape(testDataList))
print(np.shape(testLabel))
#保存训练集和测试数据集以及它们对应标签到磁盘
np.save("G:\\trainDataList",trainDataList)
np.save("G:\\trianLabel",trianLabel)
np.save("G:\\testDataList",testDataList)
np.save("G:\\testLabel",testLabel)
print("数据处理完了...")

import numpy as np
from keras.utils import to_categorical #将训练数据集和测试数据集对应的标签转变为one-hot编码
trainLabel = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
testLabel = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy")
trainLabel_encoded = to_categorical(trainLabel)
testLabel_encoded = to_categorical(testLabel)
np.save("G:\\trianLabel",trainLabel_encoded)
np.save("G:\\testLabel",testLabel_encoded)
print("转码类别写盘完了...")

import random
import numpy as np trainDataList = np.load("G:\\trainDataList.npy")
trianLabel = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
print("数据加载完了...") trainIndex = [i for i in range(len(trianLabel))]
random.shuffle(trainIndex)
trainData = []
trainClass = []
for i in range(len(trainIndex)):
trainData.append(trainDataList[trainIndex[i]])
trainClass.append(trianLabel[trainIndex[i]])
print("训练数据shuffle完了...") np.save("G:\\trainDataList",trainData)
np.save("G:\\trianLabel",trainClass)
print("训练数据写盘完毕...")

X = np.load("G:\\trainDataList.npy")
Y = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
print(np.shape(X))
print(np.shape(Y))

import random
import numpy as np testDataList = np.load("G:\\testDataList.npy")
testLabel = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy") testIndex = [i for i in range(len(testLabel))]
random.shuffle(testIndex)
testData = []
testClass = []
for i in range(len(testIndex)):
testData.append(testDataList[testIndex[i]])
testClass.append(testLabel[testIndex[i]])
print("测试数据shuffle完了...") np.save("G:\\testDataList",testData)
np.save("G:\\testLabel",testClass)
print("测试数据写盘完毕...")

X = np.load("G:\\testDataList.npy")
Y = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy")
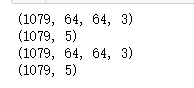
print(np.shape(X))
print(np.shape(Y))
print(np.shape(testData))
print(np.shape(testLabel))
import tensorflow as tf
from random import shuffle INPUT_NODE = 64*64
OUT_NODE = 5
IMAGE_SIZE = 64
NUM_CHANNELS = 3
NUM_LABELS = 5 #第一层卷积层的尺寸和深度
CONV1_DEEP = 16
CONV1_SIZE = 5
#第二层卷积层的尺寸和深度
CONV2_DEEP = 32
CONV2_SIZE = 5
#全连接层的节点数
FC_SIZE = 512 def inference(input_tensor, train, regularizer):
#卷积
with tf.variable_scope('layer1-conv1'):
conv1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV1_SIZE,CONV1_SIZE,NUM_CHANNELS,CONV1_DEEP],stddev=0.1),name='weight')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer1/weights1', conv1_weights)
conv1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV1_DEEP])),name="bias")
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer1/bias1', conv1_biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_tensor,conv1_weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer1/conv1', conv1)
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1,conv1_biases))
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer1/relu1', relu1)
#池化
with tf.variable_scope('layer2-pool1'):
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer1/pool1', pool1)
#卷积
with tf.variable_scope('layer3-conv2'):
conv2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV2_SIZE,CONV2_SIZE,CONV1_DEEP,CONV2_DEEP],stddev=0.1),name='weight')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer2/weights2', conv2_weights)
conv2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV2_DEEP]),name="bias")
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer2/bias2', conv2_biases)
#卷积向前学习
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,conv2_weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer2/conv2', conv2)
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2,conv2_biases))
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer2/relu2', relu2)
#池化
with tf.variable_scope('layer4-pool2'):
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer2/pool2', pool2)
#变型
pool_shape = pool2.get_shape().as_list()
#计算最后一次池化后对象的体积(数据个数\节点数\像素个数)
nodes = pool_shape[1]*pool_shape[2]*pool_shape[3]
#根据上面的nodes再次把最后池化的结果pool2变为batch行nodes列的数据
reshaped = tf.reshape(pool2,[-1,nodes]) #全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('layer5-fc1'):
fc1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([nodes,FC_SIZE],stddev=0.1),name='weight')
if(regularizer != None):
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.03)(fc1_weights))
fc1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([FC_SIZE]),name="bias")
#预测
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshaped,fc1_weights)+fc1_biases)
if(train):
fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1,0.5)
#全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('layer6-fc2'):
fc2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([FC_SIZE,64],stddev=0.1),name="weight")
if(regularizer != None):
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.03)(fc2_weights))
fc2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64]),name="bias")
#预测
fc2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(fc1,fc2_weights)+fc2_biases)
if(train):
fc2 = tf.nn.dropout(fc2,0.5)
#全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('layer7-fc3'):
fc3_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64,NUM_LABELS],stddev=0.1),name="weight")
if(regularizer != None):
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.03)(fc3_weights))
fc3_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([NUM_LABELS]),name="bias")
#预测
logit = tf.matmul(fc2,fc3_weights)+fc3_biases
return logit
import time
import keras
import numpy as np
from keras.utils import np_utils X = np.load("G:\\trainDataList.npy")
Y = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
print(np.shape(X))
print(np.shape(Y))
print(np.shape(testData))
print(np.shape(testLabel)) batch_size = 10
n_classes=5
epochs=16#循环次数
learning_rate=1e-4
batch_num=int(np.shape(X)[0]/batch_size)
dropout=0.75 x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,64,64,3])
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_classes])
# keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
#加载测试数据集
test_X = np.load("G:\\testDataList.npy")
test_Y = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy")
back = 64
ro = int(len(test_X)/back) #调用神经网络方法
pred=inference(x,1,"regularizer")
cost=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred,labels=y)) # 三种优化方法选择一个就可以
optimizer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cost)
# train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
# train_step = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(0.001,0.9).minimize(cost) #将预测label与真实比较
correct_pred=tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
#计算准确率
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32))
merged=tf.summary.merge_all()
#将tensorflow变量实例化
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
start_time = time.time() with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
#保存tensorflow参数可视化文件
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('F:/Flower_graph', sess.graph)
for i in range(epochs):
for j in range(batch_num):
offset = (j * batch_size) % (Y.shape[0] - batch_size)
# 准备数据
batch_data = X[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = Y[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x:batch_data,y:batch_labels})
result=sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x:batch_data,y:batch_labels})
writer.add_summary(result, i)
loss,acc = sess.run([cost,accuracy],feed_dict={x:batch_data,y:batch_labels})
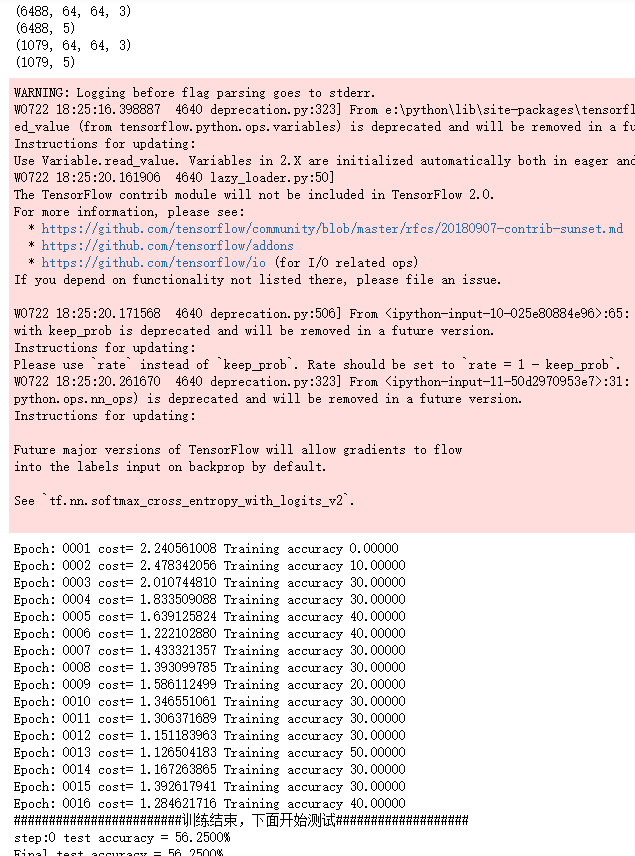
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (i+1),"cost=", "{:.9f}".format(loss),"Training accuracy","{:.5f}".format(acc*100))
writer.close()
print("########################训练结束,下面开始测试###################")
for i in range(ro):
s = i*back
e = s+back
test_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:test_X[s:e],y:test_Y[s:e]})
print("step:%d test accuracy = %.4f%%" % (i,test_accuracy*100))
print("Final test accuracy = %.4f%%" % (test_accuracy*100)) end_time = time.time()
print('Times:',(end_time-start_time))
print('Optimization Completed')

吴裕雄--天生自然 Tensorflow卷积神经网络:花朵图片识别的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:使用TFLearn处理MNIST数据集实现LeNet-5模型
# 1. 通过TFLearn的API定义卷机神经网络. import tflearn import tflearn.datasets.mnist as mnist from tflearn.layer ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:使用TensorFlow-Slim处理MNIST数据集实现LeNet-5模型
# 1. 通过TensorFlow-Slim定义卷机神经网络 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.contrib. ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Estimator-自定义模型
# 1. 自定义模型并训练. import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist i ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Estimator-DNNClassifier
# 1. 模型定义. import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist impor ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-TensorFlow API
# 1. 模型定义. import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist_ ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-RNN
# 1. 数据预处理. from keras.layers import LSTM from keras.datasets import imdb from keras.models import S ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-CNN
# 1. 数据预处理 import keras from keras import backend as K from keras.datasets import mnist from keras.m ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow 卷积神经网络水果图片识别
#-*- coding:utf- -*- import time import keras import skimage import numpy as np import tensorflow as ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-多输入输出
# 1. 数据预处理. import keras from keras.models import Model from keras.datasets import mnist from keras. ...
随机推荐
- latex学习笔记----基本知识、文档排版
1.空格和制表符等空白字符视为相同的空白距离,多个连续的空白字符等同为一个字符. 2.# $ % ^ _ { } ~ 在这些字符前面加上反斜线,就可以在文本中得到它们. 反斜线\不 ...
- 关于Linux下Oracle安装后启动的问题
1.首先,切换成oracle用户,启动监听服务.(中间的横杠必须加上,不然会出现command not found 的错误) 命令1:su - oralce 命令2:lsnrctl start 参 ...
- 网站的ssl证书即将过期,需要续费证书并更新
SSL这个证书的续费也挺奇怪,续费跟新购买一样. 证书这个东西,申请成功之后,每次都要重新下载,需要处理好格式之后,放在服务器的指定目录里. 大致操作如下: 首先,申请/续费证书,证书下来后,下载下来 ...
- JS - ES5与ES6面向对象编程
1.面向对象 1.1 两大编程思想 1.2 面向过程编程 POP(Process-oriented programming) 1.3 面向对象编程 OOP (Object Oriented Progr ...
- Python 生成requirements文件以及使用requirements.txt部署项目
生成requirements.txt 当你的项目不再你的本地时,为了方便在新环境中配置好环境变量,你的项目需要一个记录其所有依赖包以及它们版本号的文件夹requirements.txt 文件. pip ...
- angular 父子组件传值 用get set 访问器设置默认值
private _PLACEHOLDER: string; @Input() public set placeholder(v: string) { this._PLACEHOLDER = v; } ...
- Java之异常的处理(try-catch)
import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java. ...
- iOS之input file调用相册控制器消失跳转到登陆页
最近在做一个app要用到H5,其中有一个需求是要点击H5的的控件弹出系统相册,通过在H5的input file 中定义<input type="file" class=&qu ...
- javaScript 面向对象 触发夫级构造函数
class Person{ constructor(name,age){ //直接写属性 this.name=name; this.age=age; console.log('a'); } showN ...
- VSTO开发中级教程 配套资源下载
项目实例源代码: 编程过程中用到的工具.软件: 教学视频:
