SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter初始化
HandlerAdapter初始化时,主要是进行注解解析器初始化注册;返回值处理类初始化;全局注解@ControllerAdvice内容读取并缓存.
目录:
注解解析器初始化注册:@ModelAttribute(往model中添加属性)
注解解析器初始化注册:@InitBinder(用于注册校验器,参数编辑器等)
返回值处理returnValueHandlers初始化
全局的@ControllerAdvice注解使用类的@ModelAttribute 和 @InitBinder信息读取并缓存
注:具体解析器的分析还是看后续文章吧,要不文章跟裹脚布似的.
注解@ModelAttritue解析器初始化并注册
我们先看下@ModelAttribute注解的使用吧:
1. 在注解中定义属性名,方法返回值
2. 通过model直接设置
3. 暂时没搞定
// 在注解中定义属性名,方法返回值
@ModelAttribute("clazzName")
public String setModel() {
return this.getClass().getName();
}
// 通过model直接设置
@ModelAttribute
public void setModel1(Model model){
model.addAttribute("movie", "who");
}
// 暂时没搞定
@ModelAttribute()
public String setModel2(){
return "actor";
}
新建解析器时的逻辑:
1 如果没有配置,直接读取默认实现
这边默认实现多达24种+自定义实现,主要分为4类解析器:基于注解,基于类型,自定义,号称解析全部
2 通过Composite封装,并注册
解析策略实在太多,这边封装一个HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite,迭代解析器委托处理(有点责任链的味道)
先看初始化解析器,并注册的代码:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation;
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware,
InitializingBean {
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers();
this.argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
// ...
}
private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> getDefaultArgumentResolvers() {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = new ArrayList<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver>(); // Annotation-based argument resolution 基于注解的解析器
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory(), false));
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor(false));
resolvers.add(new RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor(getMessageConverters()));
resolvers.add(new RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver(getMessageConverters()));
resolvers.add(new RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory()));
resolvers.add(new RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory()));
resolvers.add(new ExpressionValueMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory())); // Type-based argument resolution 基于类型的解析器
resolvers.add(new ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new HttpEntityMethodProcessor(getMessageConverters()));
resolvers.add(new RedirectAttributesMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ModelMethodProcessor());
resolvers.add(new MapMethodProcessor());
resolvers.add(new ErrorsMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new SessionStatusMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new UriComponentsBuilderMethodArgumentResolver()); // Custom arguments 自定义解析器
if (getCustomArgumentResolvers() != null) {
resolvers.addAll(getCustomArgumentResolvers());
} // Catch-all 全能的解析器
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory(), true));
resolvers.add(new ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor(true)); return resolvers;
}
}
然后是HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite迭代具体解析器委托处理的代码:
GOF对责任链意图的定义是:
使多个对象都有机会iu处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接受者直接的耦合关系.将这些对象连成一条链,并沿这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止.
从百度百科盗了个类图,来类比下:
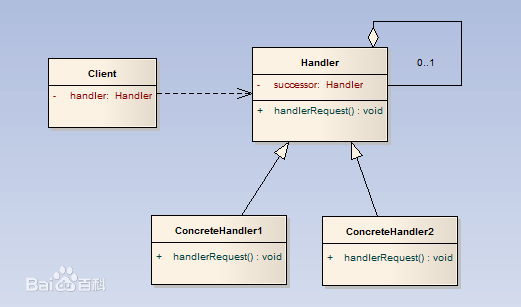
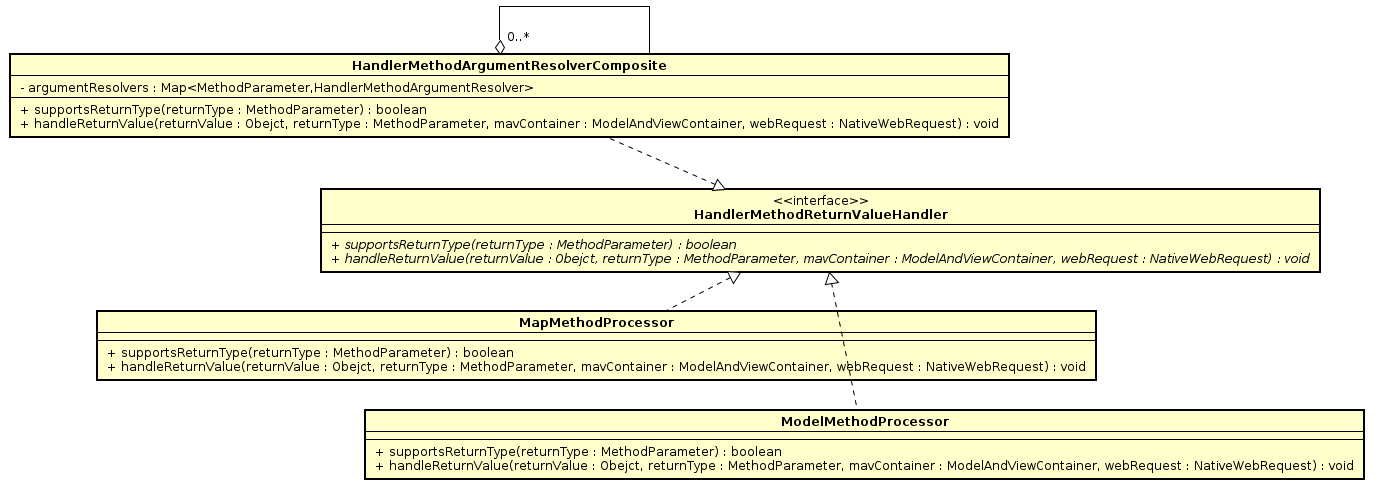
上面是标准的责任链,下面是HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler部分类图
package org.springframework.web.method.support;
public class HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
public Object resolveArgument(
MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory)
throws Exception { HandlerMethodArgumentResolver resolver = getArgumentResolver(parameter);
return resolver.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, webRequest, binderFactory);
}
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
return getArgumentResolver(parameter) != null;
}
private HandlerMethodArgumentResolver getArgumentResolver(MethodParameter parameter) {
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver result = this.argumentResolverCache.get(parameter);
if (result == null) {
for (HandlerMethodArgumentResolver methodArgumentResolver : this.argumentResolvers) {
if (methodArgumentResolver.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
result = methodArgumentResolver;
this.argumentResolverCache.put(parameter, result);
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
// ...
}
注解@InitBinder解析器初始化
先看@InitBinder注解的使用吧:
/**
* 使用WebDataBinder实现日期校验
* @param dataBinder
*/
@InitBinder
public void dateFormat(WebDataBinder dataBinder){
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
dateFormat.setLenient(false);
dataBinder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(dateFormat,false));
}
这边的代码逻辑其实跟@ModelAttribute解析器初始化的逻辑是一样的,就不具体分析,只是这边初始化使用的解析器是不一样的.至于差异的原因,暂时还不知道,哪位有兴趣可以帮忙科普科普.
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation;
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware,
InitializingBean {
private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers() {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = new ArrayList<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver>(); // Annotation-based argument resolution 基于注解的解析器
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory(), false));
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ExpressionValueMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory())); // Type-based argument resolution 基于类型的解析器
resolvers.add(new ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver()); // Custom arguments 自定义解析器
if (getCustomArgumentResolvers() != null) {
resolvers.addAll(getCustomArgumentResolvers());
} // Catch-all 全能的解析器
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory(), true)); return resolvers;
}
// ...
}
返回值处理returnValueHandlers初始化
用于将handler处理器的返回值封装成ModelAndView.
这边的处理逻辑跟@ModelAttribute注解解析器的初始化高度雷同,我们还是看看使用的HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler接口
接口的定义方式也是高度雷同,一个api问是否支持,一个api进行具体处理.
package org.springframework.web.method.support;
public interface HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType);
void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue,
MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception; }
分类貌似也有一定的相似.
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation;
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware,
InitializingBean {
private List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> getDefaultReturnValueHandlers() {
List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = new ArrayList<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler>(); // Single-purpose return value types 单一目的
handlers.add(new ModelAndViewMethodReturnValueHandler());
handlers.add(new ModelMethodProcessor());
handlers.add(new ViewMethodReturnValueHandler());
handlers.add(new HttpEntityMethodProcessor(getMessageConverters(), this.contentNegotiationManager));
handlers.add(new CallableMethodReturnValueHandler());
handlers.add(new DeferredResultMethodReturnValueHandler());
handlers.add(new AsyncTaskMethodReturnValueHandler(this.beanFactory)); // Annotation-based return value types 基于注解
handlers.add(new ModelAttributeMethodProcessor(false));
handlers.add(new RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor(getMessageConverters(), this.contentNegotiationManager)); // Multi-purpose return value types 多目的
handlers.add(new ViewNameMethodReturnValueHandler());
handlers.add(new MapMethodProcessor()); // Custom return value types 自定义
if (getCustomReturnValueHandlers() != null) {
handlers.addAll(getCustomReturnValueHandlers());
} // Catch-all 又是全能
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(getModelAndViewResolvers())) {
handlers.add(new ModelAndViewResolverMethodReturnValueHandler(getModelAndViewResolvers()));
}
else {
handlers.add(new ModelAttributeMethodProcessor(true));
} return handlers;
}
}
全局的@ControllerAdvice注解使用类的@ModelAttribute 和 @InitBinder信息读取并缓存
@ControllerAdvice注解主要是为了解决以下的场景问题:
如果@ModelAttribute或@InitBinder注解如果需要在很多地方使用,怎么办?
使用集成的话,由于java的单继承会限制父类,不够灵活.
使用时只需要如下添加注解就可以
@ControllerAdvice()
public class AdviceController {
// ...
}
源码解析时,是通过InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet调用initControllerAdviceCache初始化的解析器.
查找使用注解@ControllerAdivce的类时,通过spring迭代容器过滤容器中全部的类,找到使用ControllerAdvice.class的类并注册.
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation;
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter implements BeanFactoryAware,
InitializingBean {
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// ...
initControllerAdviceCache();
}
private void initControllerAdviceCache() {
// ...
// 扫描方式找到使用@ControllerAdvice的类
List<ControllerAdviceBean> beans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
Collections.sort(beans, new OrderComparator()); for (ControllerAdviceBean bean : beans) {
Set<Method> attrMethods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(bean.getBeanType(), MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
if (!attrMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.put(bean, attrMethods);
}
Set<Method> binderMethods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(bean.getBeanType(), INIT_BINDER_METHODS);
if (!binderMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.initBinderAdviceCache.put(bean, binderMethods);
}
}
}
}
这边扫描获取类的方式跟之前的有所不同,我们可以细看下.
1 package org.springframework.web.method;
2 public class ControllerAdviceBean implements Ordered {
3 /**
4 * Find the names of beans annotated with
5 * {@linkplain ControllerAdvice @ControllerAdvice} in the given
6 * ApplicationContext and wrap them as {@code ControllerAdviceBean} instances.
7 */
8 public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
9 List<ControllerAdviceBean> beans = new ArrayList<ControllerAdviceBean>();
10 for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
11 if (applicationContext.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class) != null) {
12 beans.add(new ControllerAdviceBean(name, applicationContext));
13 }
14 }
15 return beans;
16 }
17 }
看下两个api在接口中定义:
1. getBeanDefinitionNames 返回容器中定义的全部bean 的 name
2. findAnnotationOnBean 查找类上定义的注解,包括父类与接口
1 package org.springframework.beans.factory;
2 public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
3 // ...
4 /**
5 * Return the names of all beans defined in this factory.
6 * <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,
7 * and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by
8 * other means than bean definitions.
9 * @return the names of all beans defined in this factory,
10 * or an empty array if none defined
11 */
12 String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
13 /**
14 * Find a {@link Annotation} of {@code annotationType} on the specified
15 * bean, traversing its interfaces and super classes if no annotation can be
16 * found on the given class itself.
17 * @param beanName the name of the bean to look for annotations on
18 * @param annotationType the annotation class to look for
19 * @return the annotation of the given type found, or {@code null}
20 */
21 <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType);
22
23 }
顺便关心下@ControllerAdvice信息是如何保存的,就是对应的pojo ControllerAdviceBean:
这边只是记录bean,还没有添加添加根据类,包进行过滤匹配类的功能.
这边值得说的有3个:
1. 根据类是否实现Ordered接口,设置排序顺序
2. 扫描应用下使用ControllerAdvice注解的类就是上面说的api
3. 实现getBeanType获取类的类型 和resolveBean获取类实例 ,这个算是advice的行为吧.作为容器的行为吧.
1 package org.springframework.web.method;
2
3 public class ControllerAdviceBean implements Ordered {
4 // 使用注解的类
5 private final Object bean;
6 private final int order;
7 private final BeanFactory beanFactory;
8
9 public ControllerAdviceBean(String beanName, BeanFactory beanFactory) {
10 // ...
11 }
12
13 public ControllerAdviceBean(Object bean) {
14 // ...
15 }
16
17 // 如果类实现Ordered,根据order的值设置排序
18 private static int initOrderFromBeanType(Class<?> beanType) {
19 Order annot = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Order.class);
20 return (annot != null) ? annot.value() : Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
21 }
22
23 private static int initOrderFromBean(Object bean) {
24 return (bean instanceof Ordered) ? ((Ordered) bean).getOrder() : initOrderFromBeanType(bean.getClass());
25 }
26
27 /**
28 * 扫描应用下使用ControllerAdvice注解的类
29 */
30 public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
31 List<ControllerAdviceBean> beans = new ArrayList<ControllerAdviceBean>();
32 for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
33 if (applicationContext.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class) != null) {
34 beans.add(new ControllerAdviceBean(name, applicationContext));
35 }
36 }
37 return beans;
38 }
39
40 public Class<?> getBeanType() {
41 Class<?> clazz = (this.bean instanceof String)
42 ? this.beanFactory.getType((String) this.bean) : this.bean.getClass();
43
44 return ClassUtils.getUserClass(clazz);
45 }
46
47 public Object resolveBean() {
48 return (this.bean instanceof String) ? this.beanFactory.getBean((String) this.bean) : this.bean;
49 }
50 // ...
51 }
SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter初始化的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter - ModelFactory(转)
ModelFactory主要是两个职责: 1. 初始化model 2. 处理器执行后将modle中相应参数设置到SessionAttributes中 我们来看看具体的处理逻辑(直接充当分析目录): 1 ...
- SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter - ModelFactory
ModelFactory主要是两个职责: 1. 初始化model 2. 处理器执行后将modle中相应参数设置到SessionAttributes中 我们来看看具体的处理逻辑(直接充当分析目录): 1 ...
- SpringMVC源码解析 - HandlerAdapter - @SessionAttributes注解处理
使用SpringMVC开发时,可以使用@SessionAttributes注解缓存信息.这样业务开发时,就不需要一次次手动操作session保存,读数据. @Controller @RequestMa ...
- SpringMVC源码解析 - HandlerAdapter - HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver主要负责执行handler前参数准备工作. 看个例子,红色部分的id初始化,填充值就是它干的活: @RequestMapping(value ...
- SpringMVC源码分析--容器初始化(五)DispatcherServlet
上一篇博客SpringMVC源码分析--容器初始化(四)FrameworkServlet我们已经了解到了SpringMVC容器的初始化,SpringMVC对容器初始化后会进行一系列的其他属性的初始化操 ...
- SpringMVC源码分析--容器初始化(四)FrameworkServlet
在上一篇博客SpringMVC源码分析--容器初始化(三)HttpServletBean我们介绍了HttpServletBean的init函数,其主要作用是初始化了一下SpringMVC配置文件的地址 ...
- springMVC源码解析--ViewResolver视图解析器执行(三)
之前两篇博客springMVC源码分析--ViewResolver视图解析器(一)和springMVC源码解析--ViewResolverComposite视图解析器集合(二)中我们已经简单介绍了一些 ...
- SpringMVC源码分析--容器初始化(三)HttpServletBean
在上一篇博客springMVC源码分析--容器初始化(二)DispatcherServlet中,我们队SpringMVC整体生命周期有一个简单的说明,并没有进行详细的源码分析,接下来我们会根据博客中提 ...
- springMVC源码分析--容器初始化(二)DispatcherServlet
在上一篇博客springMVC源码分析--容器初始化(一)中我们介绍了spring web初始化IOC容器的过程,springMVC作为spring项目中的子项目,其可以和spring web容器很好 ...
随机推荐
- baby用品
新生嬰兒用品清單 1.哺育用品: 大奶瓶:6支,240ml左右.選擇PC材質耐高溫120度,可消毒:玻璃材質建議選用印刷安全無鉛材料,可消毒. 小奶瓶:2-3支,120ml左右.寬口徑/一般口徑(喝水 ...
- .NET泛型解析(下)
上一篇对.NET中的泛型进行了详细的介绍以及使用泛型的好处是什么,这篇将更加深入的去了解泛型的其他的知识点,重头戏. [1]泛型方法 上一篇我们也说过了,泛型可以是类,结构,接口,在这些泛型类型中定义 ...
- 大型发布会现场的 Wi-Fi 应该如何搭建(密集人群部署wifi抗干扰)?
原文连接: http://www.zhihu.com/question/20890194 WiFi网络的部署要远远比一般人想象的复杂,不是说放上几十个AP带宽就自动增加几十倍,恰恰相反,简单放几十个A ...
- web常用测试点记录
输入框 1.字符型输入框: 单行文本输入框:英文全角.英文半角.数字.空或者空格.特殊字符“~!@#¥%……&*?[]{}”,特别要注意单引号和&符号.如果禁止直接输入特殊字符时,使用 ...
- 1、hadoop HA分布式集群搭建
概述 hadoop2中NameNode可以有多个(目前只支持2个).每一个都有相同的职能.一个是active状态的,一个是standby状态的.当集群运行时,只有active状态的NameNode是正 ...
- [Java.web]简单计算器
项目的 WebRoot 目录下的 calculator.jsp <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" ...
- Java之解压流(ZipInputStream)
一.ZipInputStream相对于ZipOutputStream而言,使用上面简单的多了,相对的,既然存在压缩流,就会存在,解压的方式. 二.解压文件,流的使用过程中也是很常用的,在读取文件,根据 ...
- C# CS1591 缺少对公共可见类型或成员的 XML 注释 问题解决
最近在写web api的项目,用到微软的Web api help page组件,用于自动对生成API文档,见博文: https://www.cnblogs.com/lenmom/p/9081363.h ...
- python数据库连接池基于DBUtils
DBUtils模块的使用的两种方式 DBUtils是Python的一个用于实现数据库连接池的模块 安装 pip install DBUtils 1.使用姿势一(不建议此方法) 为每个线程 (资源占用过 ...
- Python 使用 Postfix 发送邮件
最近在做一个监控程序,需要用邮件发送告警.以前是使用注册的免费邮来发送,但是这样不免有很多限制,而且有时还会当作恶意登录,帐号异常等,还不让登录邮箱了.利用Postfix提供邮件SMTP服务,可以很自 ...
