Python turtle库学习笔记
1.简介
Python的turtle库的易操作,对初学者十分友好。对于初学者来说,刚学编程没多久可以写出许多有趣的可视化东西,这是对学习编程极大的鼓舞,可以树立对编程学习的信心。当然turtle本身也十分有趣,可以用它画出很多奇妙的图案。
2.绘图的基本知识
(1)画布(canvas)
画布就是turtle为我们展开用于绘图区域,我们可以设置它的大小和初始位置。
设置画布大小
turtle.screensize(canvwidth=None,canvheight=None,bg=None),参数分别为画布的宽(单位像素),高,背景颜色。
如:
turtle.screensize(800,600,"green")
turtle.screensize()#返回默认大小(400,300)
turtle.setup(width=0.5,height=0.75,startx=None,starty=None) 参数:width,height:输入宽和高为整数时,表示像素;为小数时,表示占据 电脑屏幕的比例,(startx,starty):这一坐标表示矩形窗口左上角顶点的位置,如果为空,则 窗口位于屏幕中心。
如:
turtle.setup(width=0.6,height=0.6)
turtle.setup(width=800,height=800,startx=100,starty=100)
(2)画笔
i)画笔的状态
在画布上,默认有一个坐标原点为画布中心的坐标轴,坐标原点上有一只面朝x轴正方向小乌龟。这里我们描述小乌龟时使用了两个词语:坐标原点(位置),面朝x轴正方向(方向),turtle绘图中,就是使用位置方向描述小乌龟(画笔)的状态。
ii)画笔的属性
画笔(画笔的属性,颜色、画线的宽度等)
turtle.pensize(): 设置画笔的宽度;
turtle.pencolor(): 没有参数传入,返回当前画笔颜色,传入参数设置画笔颜色,可以是字符串如"green","red",也可以是RGB3元组。
turtle.speed(speed): 设置画笔移动速度,画笔绘制的速度范围[0,10]整数,数字越大越快。
(3)绘图窗口的原点(0,0)在正中间。默认情况下,海龟向正右方移动。
(4)操纵海龟绘图有着许多的命令,这些命令可以划分为两种: 一种为运动命令,一种为画笔控制命令
i)运动命令:
forward(d) 向前移动距离d代表距离
backward(d) 向后移动距离d代表距离
right(degree) 向右转动多少度
left(degree) 向左转动多少度
goto(x,y) 将画笔移动到坐标为(x,y)的位置
stamp() 绘制当前图形
speed(speed) 画笔绘制的速度范围[0,10]整数
ii)画笔控制命令:
down() 画笔落下,移动时绘制图形
up() 画笔抬起,移动时不绘制图形
setheading(degree) 海龟(turtle)朝向,degree代表角度
reset() 恢复所有设置
pensize(width) 画笔的宽度
pencolor(colorstring) 画笔的颜色
fillcolor(colorstring) 绘制图形的填充颜色
circle(radius,extent) 绘制一个圆形,其中radius为半径,extent为度数,例如若extent为120,则画一个三分之一圆;
3.turtle绘图案例
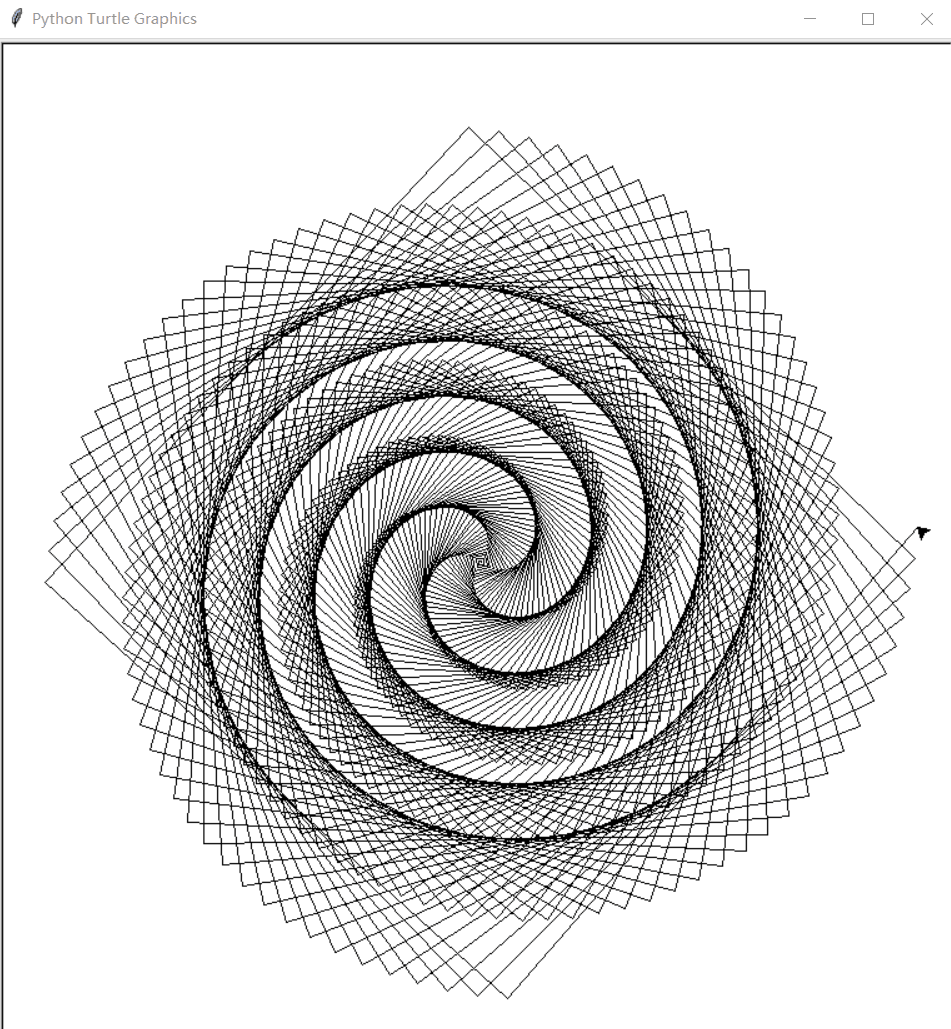
(1)方形螺旋图像:
from turtle import *
for i in range(500):
forward(i)
left(91)
运行效果:

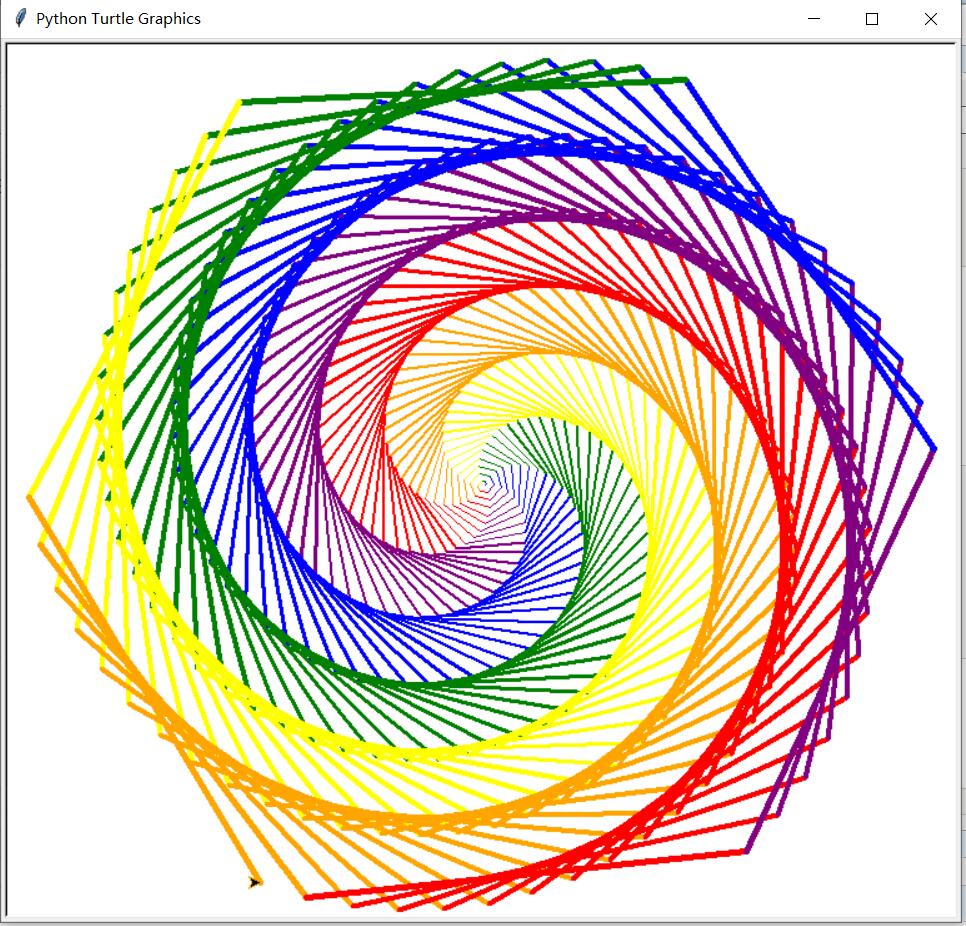
(2)彩色螺旋图
from turtle import *
colors = ['red', 'purple', 'blue', 'green', 'yellow', 'orange']
for x in range(360):
pencolor(colors[x % 6])
width(x / 100 + 1)
forward(x)
left(59)
运行效果:
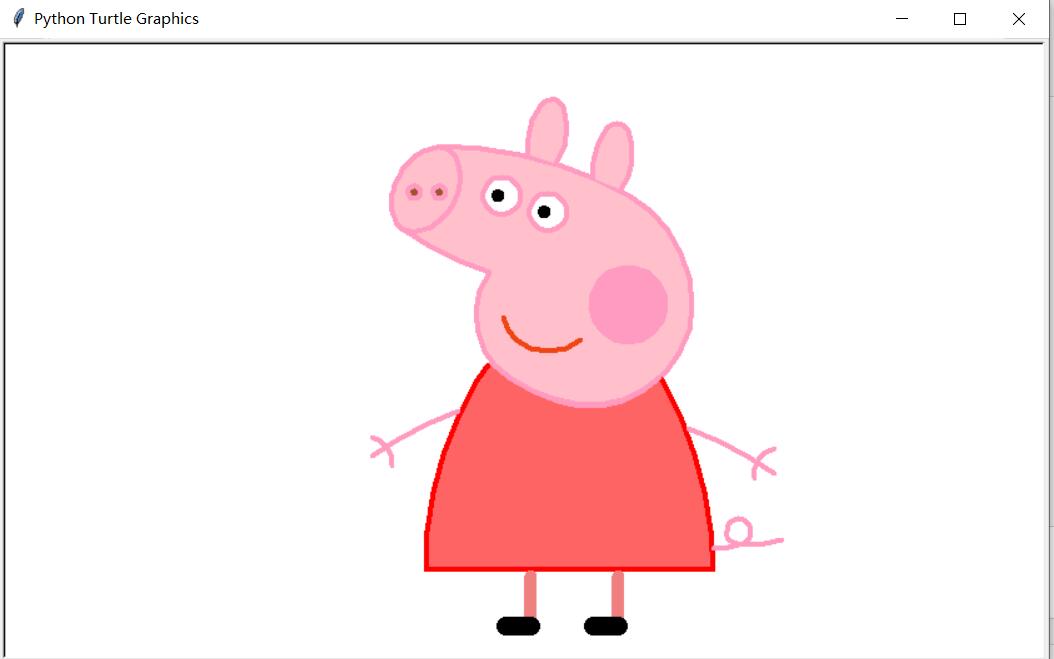
(3)小猪佩奇
# coding:utf-8
from turtle import* def nose(x,y):#鼻子
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
seth(-30)
begin_fill()
a=0.4
for i in range(120):
if 0<=i<30 or 60<=i<90:
a=a+0.08
lt(3) #向左转3度
fd(a) #向前走a的步长
else:
a=a-0.08
lt(3)
fd(a)
end_fill() pu()
seth(90)
fd(25)
seth(0)
fd(10)
pd()
pencolor(255,155,192)
seth(10)
begin_fill()
circle(5)
color(160,82,45)
end_fill() pu()
seth(0)
fd(20)
pd()
pencolor(255,155,192)
seth(10)
begin_fill()
circle(5)
color(160,82,45)
end_fill() def head(x,y):#头
color((255,155,192),"pink")
pu()
goto(x,y)
seth(0)
pd()
begin_fill()
seth(180)
circle(300,-30)
circle(100,-60)
circle(80,-100)
circle(150,-20)
circle(60,-95)
seth(161)
circle(-300,15)
pu()
goto(-100,100)
pd()
seth(-30)
a=0.4
for i in range(60):
if 0<=i<30 or 60<=i<90:
a=a+0.08
lt(3) #向左转3度
fd(a) #向前走a的步长
else:
a=a-0.08
lt(3)
fd(a)
end_fill() def ears(x,y): #耳朵
color((255,155,192),"pink")
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
begin_fill()
seth(100)
circle(-50,50)
circle(-10,120)
circle(-50,54)
end_fill() pu()
seth(90)
fd(-12)
seth(0)
fd(30)
pd()
begin_fill()
seth(100)
circle(-50,50)
circle(-10,120)
circle(-50,56)
end_fill() def eyes(x,y):#眼睛
color((255,155,192),"white")
pu()
seth(90)
fd(-20)
seth(0)
fd(-95)
pd()
begin_fill()
circle(15)
end_fill() color("black")
pu()
seth(90)
fd(12)
seth(0)
fd(-3)
pd()
begin_fill()
circle(3)
end_fill() color((255,155,192),"white")
pu()
seth(90)
fd(-25)
seth(0)
fd(40)
pd()
begin_fill()
circle(15)
end_fill() color("black")
pu()
seth(90)
fd(12)
seth(0)
fd(-3)
pd()
begin_fill()
circle(3)
end_fill() def cheek(x,y):#腮
color((255,155,192))
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
seth(0)
begin_fill()
circle(30)
end_fill() def mouth(x,y): #嘴
color(239,69,19)
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
seth(-80)
circle(30,40)
circle(40,80) def body(x,y):#身体
color("red",(255,99,71))
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
begin_fill()
seth(-130)
circle(100,10)
circle(300,30)
seth(0)
fd(230)
seth(90)
circle(300,30)
circle(100,3)
color((255,155,192),(255,100,100))
seth(-135)
circle(-80,63)
circle(-150,24)
end_fill() def hands(x,y):#手
color((255,155,192))
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
seth(-160)
circle(300,15)
pu()
seth(90)
fd(15)
seth(0)
fd(0)
pd()
seth(-10)
circle(-20,90) pu()
seth(90)
fd(30)
seth(0)
fd(237)
pd()
seth(-20)
circle(-300,15)
pu()
seth(90)
fd(20)
seth(0)
fd(0)
pd()
seth(-170)
circle(20,90) def foot(x,y):#脚
pensize(10)
color((240,128,128))
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
seth(-90)
fd(40)
seth(-180)
color("black")
pensize(15)
fd(20) pensize(10)
color((240,128,128))
pu()
seth(90)
fd(40)
seth(0)
fd(90)
pd()
seth(-90)
fd(40)
seth(-180)
color("black")
pensize(15)
fd(20) def tail(x,y):#尾巴
pensize(4)
color((255,155,192))
pu()
goto(x,y)
pd()
seth(0)
circle(70,20)
circle(10,330)
circle(70,30) def setting(): #参数设置
pensize(4)
hideturtle()
colormode(255)
color((255,155,192),"pink")
setup(840,500)
speed(10) def main():
setting() #画布、画笔设置
nose(-100,100) #鼻子
head(-69,167) #头
ears(0,160) #耳朵
eyes(0,140) #眼睛
cheek(80,10) #腮
mouth(-20,30) #嘴
body(-32,-8) #身体
hands(-56,-45) #手
foot(2,-177) #脚
tail(148,-155) #尾巴
done() #结束 main() main()
运行效果:
Python turtle库学习笔记的更多相关文章
- 对于Python turtle的学习笔记
进一步地,我尝试学习了Python 的其中一个非常重要的函数库——turtle库 这是一个用于python绘图的函数库,方便又好用! 对于它的安装,现在我们所用的python 3的系统运用到的指令是: ...
- python requests库学习笔记(上)
尊重博客园原创精神,请勿转载! requests库官方使用手册地址:http://www.python-requests.org/en/master/:中文使用手册地址:http://cn.pytho ...
- Turtle库学习笔记
一.Turtle库是Python语言中一个很流行的绘制图像的函数库,想象一个小乌龟,在一个横轴为x.纵轴为y的坐标系原点,(0,0)位置开始,它根据一组函数指令的控制,在这个平面坐标系中移动,从而在它 ...
- python requests库学习笔记(下)
1.请求异常处理 请求异常类型: 请求超时处理(timeout): 实现代码: import requestsfrom requests import exceptions #引入exc ...
- Python PIL库学习笔记
1.PIL简介 Python Imaging Library(缩写为PIL)(在新的版本中被称为Pillow)是Python编程语言的开源库,它增加了对打开,操作和保存许多不同图像文件格式的支持.它适 ...
- python os库学习笔记
os.getcwd(): 获取当前目录 os.name: 获取当前使用的操作系统 eg: print os.name os.remove(): 删除指定文件 eg: os.remove('test.t ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然Python Matplotlib库学习笔记:matplotlib绘图(1)
Matplotlib 可能是 Python 2D-绘图领域使用最广泛的套件.它能让使用者很轻松地将数据图形化,并且提供多样化的输出格式. from pylab import * size = 128, ...
- Python Requests 库学习笔记
概览 实例引入 import requests response = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com/') print(type(response)) prin ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然Python Matplotlib库学习笔记:matplotlib绘图(2)
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure() fig.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.0 ...
随机推荐
- android安装前期遇到的问题
1.安装的eclipse与对应的java版本位数要一致,要么32位,要么64位. 2.关于新版ADT创建项目时出现appcompat_v7的问题 更新ADT至22.6.0版本之后,创建新的安装项目,会 ...
- nginx 集群介绍
nginx 集群介绍 完成一次请求的步骤 1)用户发起请求 2)服务器接受请求 3)服务器处理请求(压力最大) 4)服务器响应请求 缺点:单点故障 单台服务器资源有限 单台服务器处理耗时长 ·1)部署 ...
- Oracle学习笔记(五)
七.查询 1.基本查询语句 select 列名字,列名字 from 表名字 例如 select user_a_id from userinfo; 2.在SQL*PLUS中设置格式 (1)设置新的字段名 ...
- db_autopwn
nmap -Pn -sV -oX dmz 192.168.1.0/24 db_import /root/dmz db_hosts db_hosts -d ip db_services db_hosts ...
- java并发编程实战:第十三章----显示锁
一.Lock与ReentrantLock Lock接口中定义了一种无条件.可轮询的.定时的以及可中断的锁获取操作,所有加锁和解锁的方法都是显式的. 1 public interfece Lock 2 ...
- 8.使用Exists监控ZNode的三大Change事件
一. zookeeper是一个分布式的协调程序(所有程序都是通过订阅它来相互感知) 1. tcp(长链接) + watcher server ->client client ->ser ...
- ASP.NET Core2调用Azure云上的PowerBI报表展示
在开发企业应用中,报表功能是当之无愧的重头戏,如何将数据通过合适的报表呈现出来成为每个项目人员必需面临的问题.而找到一款合适的报表往往都需要考率价格.开发.风格.支撑等因素.那么,我在这里给大家介绍一 ...
- vue实现随机验证码功能
效果图: 1.html代码 <div class="form-group" style="display: flex;"> <div> ...
- PHP全栈学习笔记19
thinkphp框架是一个免费的,开源,快速,简单的面向对象的轻量级PHP开发框架. 了解什么是thinkphp概述,thinkphp项目目录结构,thinkphp的控制器,视图,thinkphp项目 ...
- 更改JupyterNotebook默认文件路径 行之有效!
在安装了Anaconda以后浏览器默认打开的是C盘用户目录,平时不想把一些文件.代码放在C盘尤其是用户目录下,所以考虑将默认路径改掉,尝试了网上的几种方法,终于找到了一种可行有效的. 1.找到jupy ...
