redis学习笔记——Redis过期键的删除策略
Redis过期键的删除策略
对于过期键一般有三种删除策略
- 定时删除:在设置键的过期时间的同时,创建一个定时器(timer),让定时器在键的过期时间来临时,立即执行对键的删除操作;
- 惰性删除:放任键过期不管,但是每次从键空间中获取键时,都检查取得的键是否过期,如果过期的话,就删除该键;如果没有过期,那就返回该键;
- 定期删除:每隔一段时间,程序就对数据库进行一次检查,删除里面的过期键。至于删除多少过期键,以及要检查多少个数据库,则由算法决定。
下面我们来看看三种策略的优缺比较:
- 定时删除策略对内存是最友好的:通过使用定时器,定时删除策略可以保证过期键会尽可能快地被删除,并释放过期键所占用的内存;但另一方面,定时删除策略的缺点是,他对CPU是最不友好的:在过期键比较多的情况下,删除过期键这一行为可能会占用相当一部分CPU时间,在内存不紧张但是CPU时间非常紧张的情况下,将CPU时间用在删除和当前任务无关的过期键上,无疑会对服务器的响应时间和吞吐量造成影响;
- 惰性删除策略对CPU时间来说是最友好的:程序只会在取出键时才对键进行过期检查,这可以保证删除过期键的操作只会在非做不可的情况下进行;惰性删除策略的缺点是,它对内存是最不友好的:如果一个键已经过期,而这个键又仍然保留在数据库中,那么只要这个过期键不被删除,它所占用的内存就不会释放;
- 定时删除占用太多CPU时间,影响服务器的响应时间和吞吐量;惰性删除浪费太多内存,有内存泄漏的危险。定期删除策略是前两种策略的一种整合和折中:
- 定期删除策略每隔一段时间执行一次删除过期键操作,并通过限制删除操作执行的时长和频率来减少删除操作对CPU时间的影响;
- 通过定期删除过期键,定期删除策略有效地减少了因为过期键而带来的内存浪费;
- 定期删除策略的难点是确定删除操作执行的时长和频率。
Redis的过期键删除策略:Redis服务器实际使用的是惰性删除和定期删除两种策略。
下面我们就结合源码进行分析:
惰性删除策略的实现
过期键的惰性删除策略由db.c/expireIfNeeded函数实现,所有读写数据库的Redis命令在执行之前都会调用expireIfNeeded函数对输入键进行检查:
下面结合代码,用伪代码简要描述:/* * 检查 key 是否已经过期,如果是的话,将它从数据库中删除。 * * 返回 0 表示键没有过期时间,或者键未过期。 *
* 返回 表示键已经因为过期而被删除了。
*/
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
// getExpire(db,key)函数取出键key的过期时间,如果key没有设置过期时间那么返回-1
mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
mstime_t now; if (when < ) return ; /* No expire for this key key没有设置过期时间*/
/* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
// 如果服务器正在进行载入,那么过会儿再执行
if (server.loading) return ; /* If we are in the context of a Lua script, we claim that time is
* blocked to when the Lua script started. This way a key can expire
* only the first time it is accessed and not in the middle of the
* script execution, making propagation to slaves / AOF consistent.
* See issue #1525 on Github for more information. */
//如果我们是正在执行lua脚本,那么必须先将脚本进行阻塞。lua部分知识还没学,所以这里并不是很懂为什么????
now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime(); /* If we are running in the context of a slave, return ASAP:
* the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will
* send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.
*
* Still we try to return the right information to the caller,
* that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if
* we think the key is expired at this time. */
// 附属节点并不主动删除 key,它只返回一个逻辑上正确的返回值
// 真正的删除操作要等待主节点发来删除命令时才执行,从而保证数据的同步
//这部分知识可以查看redis的主从同步
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return now > when; // 运行到这里,表示键带有过期时间,并且服务器为主节点 /* Return when this key has not expired */
// 如果未过期,返回 0
if (now <= when) return ;
/* 已过期的键的数量 */
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
// 向 AOF 文件和附属节点传播过期信息.当key过期时,DEL 操作也会传递给所有的AOF文件和附属节点
propagateExpire(db,key);
// 发送事件通知,关于redis的键事件通知和键空间通知,可以查询资料后面学习硬挨也会讲到
notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
"expired",key,db->id);
// 调用dbDelete(db,keu)将过期键从数据库中删除
return dbDelete(db,key);
}
流程图:
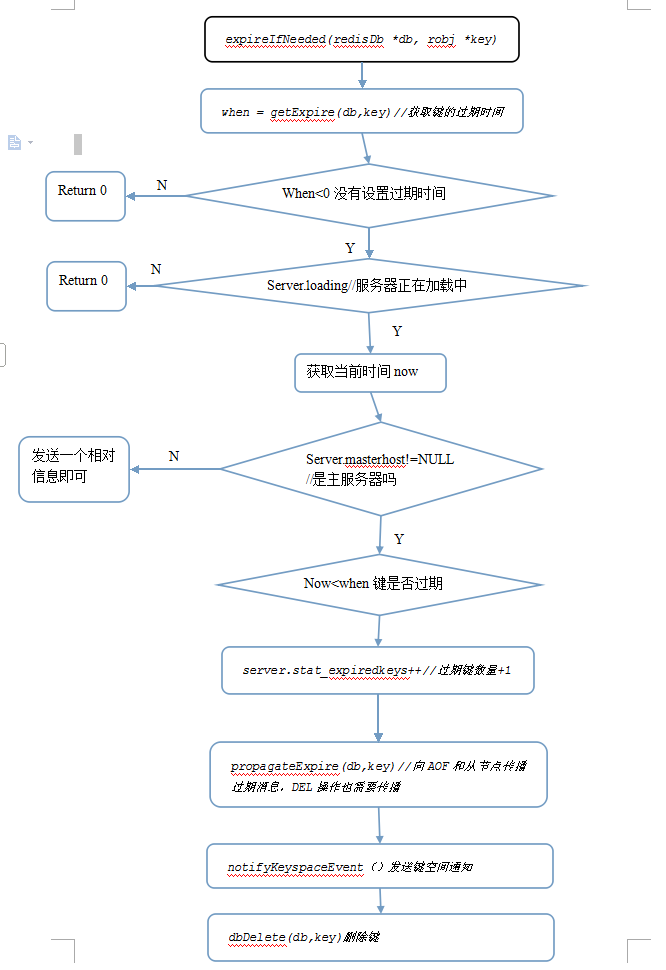
定期删除策略的实现
过期键的定期删除策略由redis.c/activeExpireCycle函数实现,每当Redis的服务器周期性操作redis.c/serverCron函数执行时,activeExpireCycle函数就会被调用,它在规定的时间内,分多次遍历服务器中的各个数据库,从数据库的expires字典中随机检查一部分键的过期时间,并删除其中的过期键。
源码分析如下:
/* Try to expire a few timed out keys. The algorithm used is adaptive and
* will use few CPU cycles if there are few expiring keys, otherwise
* it will get more aggressive to avoid that too much memory is used by
* keys that can be removed from the keyspace.
*
* 函数尝试删除数据库中已经过期的键。
* 当带有过期时间的键比较少时,函数运行得比较保守,
* 如果带有过期时间的键比较多,那么函数会以更积极的方式来删除过期键,
* 从而可能地释放被过期键占用的内存。
*
* No more than REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL databases are tested at every
* iteration.
*
* 每次循环中被测试的数据库数目不会超过 REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL 。
*
* This kind of call is used when Redis detects that timelimit_exit is
* true, so there is more work to do, and we do it more incrementally from
* the beforeSleep() function of the event loop.
*
* 如果 timelimit_exit 为真,那么说明还有更多删除工作要做,(在我看来timelimit_exit如果为真的话那表示上一次删除过期键时是因为删除时间过长超时了才退出的,所以这次将删除方法更加积极)
* 那么在 beforeSleep() 函数调用时,程序会再次执行这个函数。
*
* Expire cycle type:
*
* 过期循环的类型:
*
* If type is ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST the function will try to run a
* "fast" expire cycle that takes no longer than EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION
* microseconds, and is not repeated again before the same amount of time.
*
* 如果循环的类型为 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST ,
* 那么函数会以“快速过期”模式执行,
* 执行的时间不会长过 EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION 毫秒,
* 并且在 EXPIRE_FAST_CYCLE_DURATION 毫秒之内不会再重新执行。
*
* If type is ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW, that normal expire cycle is
* executed, where the time limit is a percentage of the REDIS_HZ period
* as specified by the REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_TIME_PERC define.
*
* 如果循环的类型为 ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW ,
* 那么函数会以“正常过期”模式执行,
* 函数的执行时限为 REDIS_HS 常量的一个百分比,
* 这个百分比由 REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_TIME_PERC 定义。
*/ void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
/* This function has some global state in order to continue the work
* incrementally across calls. */
// 共享变量,用来累积函数连续执行时的数据
static unsigned int current_db = ; /* Last DB tested. 正在测试的数据库*/
static int timelimit_exit = ; /* Time limit hit in previous call 上一次执行是否时间超时的提示 */
static long long last_fast_cycle = ; /* When last fast cycle ran. 上次快速模式执行的时间*/ unsigned int j, iteration = ;
// 默认每次处理的数据库数量
unsigned int dbs_per_call = REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL; //默认REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL=16
// 函数开始的时间
long long start = ustime(), timelimit; // 快速模式
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
/* Don't start a fast cycle if the previous cycle did not exited
* for time limt. Also don't repeat a fast cycle for the same period
* as the fast cycle total duration itself. */
// 如果上次函数没有触发 timelimit_exit ,那么不执行处理
if (!timelimit_exit) return;
// 如果距离上次执行未够一定时间,那么不执行处理
if (start < last_fast_cycle + ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION*) return;
// 运行到这里,说明执行快速处理,记录当前时间
last_fast_cycle = start;
} /* We usually should test REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL per iteration, with
* two exceptions:
*
* 一般情况下,每次迭代(也就是每次调用这个函数)函数只处理 REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL 个数据库,
* 除非:
*
* 1) Don't test more DBs than we have.
* 当前数据库的数量小于 REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL
* 2) If last time we hit the time limit, we want to scan all DBs
* in this iteration, as there is work to do in some DB and we don't want
* expired keys to use memory for too much time.
* 如果上次处理遇到了时间上限,那么这次需要对所有数据库进行扫描,
* 这可以避免过多的过期键占用空间
*/
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)//以服务器的数据库数量为准
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum; /* We can use at max ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC percentage of CPU time
* per iteration. Since this function gets called with a frequency of
* server.hz times per second, the following is the max amount of
* microseconds we can spend in this function. */
// 函数处理的微秒时间上限
// ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 默认为 25 ,也即是 25 % 的 CPU 时间
timelimit = *ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/;
timelimit_exit = ;
if (timelimit <= ) timelimit = ; // 如果是运行在快速模式之下
// 那么最多只能运行 FAST_DURATION 微秒
// 默认值为 1000 (微秒)
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION; /* in microseconds. */ // 遍历数据库
for (j = ; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
int expired;
// 指向要处理的数据库
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum); /* Increment the DB now so we are sure if we run out of time
* in the current DB we'll restart from the next. This allows to
* distribute the time evenly across DBs. */
// 为 currrnt_DB 计数器加一,如果进入 do 循环之后因为超时而跳出
// 那么下次会直接从下个 currrnt_DB 开始处理。这样使得分配在每个数据库上处理时间比较平均
current_db++; /* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle more than 25%
* of the keys were expired. */
//如果每次循环清理的过期键是过期键的25%以上,那么就继续清理
do {
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples; /* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */
// 获取数据库中带过期时间的键的数量
// 如果该数量为 0 ,直接跳过这个数据库
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == ) {
db->avg_ttl = ;
break;
}
// 获取数据库中键值对的数量
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
// 当前时间
now = mstime(); /* When there are less than 1% filled slots getting random
* keys is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times...
* The dictionary will be resized asap. */
// 这个数据库的使用率低于 1% ,扫描起来太费力了(大部分都会 MISS)
// 跳过,等待字典收缩程序运行
if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*/slots < )) break; /* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys
* with an expire set, checking for expired ones.
*
* 样本计数器
*/
// 已处理过期键计数器
expired = ;
// 键的总 TTL 计数器
ttl_sum = ;
// 总共处理的键计数器
ttl_samples = ; // 每次最多只能检查 LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP 个键,默认是20
if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP; // 开始遍历数据库
while (num--) {
dictEntry *de;
long long ttl; // 从 expires 中随机取出一个带过期时间的键
if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
// 计算 TTL
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now;
// 如果键已经过期,那么删除它,并将 expired 计数器增一
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
if (ttl < ) ttl = ;
// 累积键的 TTL
ttl_sum += ttl;
// 累积处理键的个数
ttl_samples++;
} /* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */
// 为这个数据库更新平均 TTL 统计数据
if (ttl_samples) {
// 计算当前平均值
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples; // 如果这是第一次设置数据库平均 TTL ,那么进行初始化
if (db->avg_ttl == ) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
/* Smooth the value averaging with the previous one. */
// 否则取数据库的上次平均 TTL 和今次平均 TTL 的平均值
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl+avg_ttl)/;
} /* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to
* expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the
* caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. */
// 如果过期键太多的话,我们不能用太长时间处理,所以这个函数执行一定时间之后就要返回,等待下一次循环
// 更新遍历次数
iteration++; // 每遍历 16 次执行一次
if ((iteration & 0xf) == && /* check once every 16 iterations. */
(ustime()-start) > timelimit)
{
// 如果遍历次数正好是 16 的倍数
// 并且遍历的时间超过了 timelimit,超时了
// 那么将timelimit_exit赋值为1,下一个if返回吧
timelimit_exit = ;
} // 已经超时了,返回
if (timelimit_exit) return; /* We don't repeat the cycle if there are less than 25% of keys
* found expired in the current DB. */
// 如果删除的过期键少于当前数据库中过期键数量的 25 %,那么不再遍历。当然如果超过了25%,那说明过期键还很多,继续清理
} while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/);
}
}
上面代码注释比较详细,所以这里就不给流程图了。
redis学习笔记——Redis过期键的删除策略的更多相关文章
- redis中关于过期键的删除策略
我们已经了解到了Redis是一种内存数据库,Redis中数据都是以key-value的形式存储在内存中.由Redisserver来维护和管理这部分内存,内存是何足珍贵,不须要的数据或者是已经使用过的无 ...
- Redis学习笔记--Redis数据过期策略详解
本文对Redis的过期机制简单的讲解一下 讲解之前我们先抛出一个问题,我们知道很多时候服务器经常会用到redis作为缓存,有很多数据都是临时缓存一下,可能用过之后很久都不会再用到了(比如暂存sessi ...
- Redis学习笔记--Redis数据过期策略详解==转
本文对Redis的过期机制简单的讲解一下 讲解之前我们先抛出一个问题,我们知道很多时候服务器经常会用到redis作为缓存,有很多数据都是临时缓存一下,可能用过之后很久都不会再用到了(比如暂存sessi ...
- redis 过期键的删除策略?
1.定时删除:在设置键的过期时间的同时,创建一个定时器 timer). 让定时器在键 的过期时间来临时,立即执行对键的删除操作. 2.惰性删除:放任键过期不管,但是每次从键空间中获取键时,都检查取得的 ...
- Redis学习笔记--Redis配置文件redis.conf参数配置详解
########################################## 常规 ########################################## daemonize n ...
- redis学习笔记-redis的安装
Window 下安装 下载地址:https://github.com/MSOpenTech/redis/releases Redis 支持 32 位和 64 位.这个需要根据你系统平台的实际情况选择, ...
- Redis学习笔记~Redis主从服务器,读写分离
回到目录 Redis这个Nosql的存储系统一般会被部署到linux系统中,我们可以把它当成是一个数据服务器,对于并发理大时,我们会使用多台服务器充当Redis服务器,这时,各个Redis之间也是分布 ...
- Redis学习笔记-Redis内部数据结构
Redis内部数据结构 Redis和其他key-value数据库的很大区别是它支持非字符串类型的value值.它支持的value值的类型如下: sds (simple dynamic string) ...
- Redis学习笔记——Redis的基本操作
之前介绍过如何在ubuntu安装Redis服务器:https://www.cnblogs.com/zifeiy/p/9062738.html 接下来,我们在Redis上进行一些基本的操作. 所县使用命 ...
随机推荐
- SQL按多个字段排序时的实现规则
1.在使用SQL中的ORDER BY按照表中的多个列对表做排序是,会按照第一个列的排序条件作为排序基准,当第一个列的值都相同时,才会按照后面的列的排序条件作为排序基准: 案例如下: 图一和图二展示的是 ...
- 【C++】类的特殊成员变量+初始化列表
参考资料: 1.黄邦勇帅 2.http://blog.163.com/sunshine_linting/blog/static/448933232011810101848652/ 3.http://w ...
- mysql的expain(zz)
两张表,T1和T2,都只有一个字段,id int.各插入1000条记录,运行如下语句: explain SELECT t1.id,t2.id FROM t1 INNER JOIN t2 ON t1.i ...
- qt资源下载网站
1. 所有Qt版本下载地址: http://download.qt.io/archive/qt/ 2. 所有Qt Creator下载地址: http://download.qt.io/archive/ ...
- hdu6166
hdu6166 题意 给出一个有向图,选择 \(k\) 个点,问这 \(k\) 个点任意两点距离的最小值. 分析 按结点编号的二进制位,每次可以把所有点分到两个集合,那么求两个集合的点间的最短路即可( ...
- 模板-网络流-Dinic
//Dinic struct Edge{ int from,to,cap,flow; Edge(){ } Edge(int a,int b,int c,int d){ from=a; to=b; ca ...
- Jenkins使用SSH远程发布
远程发布需要安装Publish Over SSH插件 比如我们的应用服务器都是通过tomcat用户启动程序,因此,在jenkin服务器上配置免密登录远程服务器tomcat用户 //生成密钥对 ssh- ...
- Codeforces 914 C Travelling Salesman and Special Numbers
Discription The Travelling Salesman spends a lot of time travelling so he tends to get bored. To pas ...
- 【状压DP】旅行商问题
给定一张带权有向图,要求从顶点0出发,经过每个结点恰好一次后再返回0,求边权和的最小值. 2<=n<=15 0<=d(i,j)<=1000 样例 5 80 1 30 3 41 ...
- 【最小瓶颈生成树】【最小生成树】【kruscal】bzoj1083 [SCOI2005]繁忙的都市
本意是求最小瓶颈生成树,但是我们可以证明:最小生成树也是最小瓶颈生成树(其实我不会).数据范围很小,暴力kruscal即可. #include<cstdio> #include<al ...
