Nginx 启动、停止、平滑重启和平滑升级 graceful shutdown of worker processes
Controlling nginx http://nginx.org/en/docs/control.html
nginx can be controlled with signals. The process ID of the master process is written to the file/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid by default. This name may be changed at configuration time, or innginx.conf using the pid directive. The master process supports the following signals:
TERM, INT fast shutdown QUIT graceful shutdown HUP changing configuration, keeping up with a changed time zone (only for FreeBSD and Linux), starting new worker processes with a new configuration, graceful shutdown of old worker processes USR1 re-opening log files USR2 upgrading an executable file WINCH graceful shutdown of worker processes
Individual worker processes can be controlled with signals as well, though it is not required. The supported signals are:
TERM, INT fast shutdown QUIT graceful shutdown USR1 re-opening log files WINCH abnormal termination for debugging (requires debug_points to be enabled)
Changing Configuration
In order for nginx to re-read the configuration file, a HUP signal should be sent to the master process. The master process first checks the syntax validity, then tries to apply new configuration, that is, to open log files and new listen sockets. If this fails, it rolls back changes and continues to work with old configuration. If this succeeds, it starts new worker processes, and sends messages to old worker processes requesting them to shut down gracefully. Old worker processes close listen sockets and continue to service old clients. After all clients are serviced, old worker processes are shut down.
Let’s illustrate this by example. Imagine that nginx is run on FreeBSD and the command
- ps axw -o pid,ppid,user,%cpu,vsz,wchan,command | egrep '(nginx|PID)'
produces the following output:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 33126 1 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 33127 33126 nobody 0.0 1380 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33128 33126 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33129 33126 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
If HUP is sent to the master process, the output becomes:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 33129 33126 nobody 0.0 1380 kqread nginx: worker process is shutting down (nginx)
- 33134 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33135 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33136 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
One of the old worker processes with PID 33129 still continues to work. After some time it exits:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 33134 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33135 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33136 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
Rotating Log-files
In order to rotate log files, they need to be renamed first. After that USR1 signal should be sent to the master process. The master process will then re-open all currently open log files and assign them an unprivileged user under which the worker processes are running, as an owner. After successful re-opening, the master process closes all open files and sends the message to worker process to ask them to re-open files. Worker processes also open new files and close old files right away. As a result, old files are almost immediately available for post processing, such as compression.
Upgrading Executable on the Fly
In order to upgrade the server executable, the new executable file should be put in place of an old file first. After that USR2 signal should be sent to the master process. The master process first renames its file with the process ID to a new file with the .oldbin suffix, e.g./usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin, then starts a new executable file that in turn starts new worker processes:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 33134 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33135 33126 nobody 0.0 1380 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 33136 33126 nobody 0.0 1368 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36264 33126 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
After that all worker processes (old and new ones) continue to accept requests. If the WINCH signal is sent to the first master process, it will send messages to its worker processes, requesting them to shut down gracefully, and they will start to exit:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 33135 33126 nobody 0.0 1380 kqread nginx: worker process is shutting down (nginx)
- 36264 33126 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
After some time, only the new worker processes will process requests:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 33126 1 root 0.0 1164 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 36264 33126 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
It should be noted that the old master process does not close its listen sockets, and it can be managed to start its worker processes again if needed. If for some reason the new executable file works unacceptably, one of the following can be done:
Send the HUP signal to the old master process. The old master process will start new worker processes without re-reading the configuration. After that, all new processes can be shut down gracefully, by sending the QUIT signal to the new master process.
Send the TERM signal to the new master process. It will then send a message to its worker processes requesting them to exit immediately, and they will all exit almost immediately. (If new processes do not exit for some reason, the KILL signal should be sent to them to force them to exit.) When the new master process exits, the old master process will start new worker processes automatically.
If the new master process exits then the old master process discards the .oldbin suffix from the file name with the process ID.
If upgrade was successful, then the QUIT signal should be sent to the old master process, and only new processes will stay:
- PID PPID USER %CPU VSZ WCHAN COMMAND
- 36264 1 root 0.0 1148 pause nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 36265 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36266 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
- 36267 36264 nobody 0.0 1364 kqread nginx: worker process (nginx)
Nginx 启动、停止、平滑重启和平滑升级 - 综合编程类其他综合 - 红黑联盟 https://www.2cto.com/kf/201701/586973.html
启动操作
# nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
-c参数指定了要加载的nginx配置文件路径
停止操作
停止操作是通过向nginx进程发送信号(什么是信号请参阅Linux文章)来进行的
步骤1:查询nginx主进程号
# ps -ef | grep nginx
在进程列表里面找master进程,它的编号就是主进程号了。
步骤2:发送信号
从容停止Nginx:
# kill-QUIT主进程号 快速停止Nginx:
# kill-TERM主进程号 强制停止Nginx:
# pkill-9主进程号 另外,若在nginx.conf配置了pid文件存放路径则该文件存放的就是Nginx主进程号,如果没指定则放在nginx的logs目录下。有了pid文件,我们就不用先查询Nginx的主进程号,而直接向Nginx发送信号了,命令如下:
# kill-信号类型'/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid'
平滑重启
如果更改了配置就要重启Nginx,要先关闭Nginx再打开?不是的,可以向Nginx发送信号,平滑重启。
平滑重启命令:
# kill-HUP住进称号或进程号文件路径
或者使用
# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx-sreload
注意,修改了配置文件后最好先检查一下修改过的配置文件是否正确,以免重启后Nginx出现错误影响服务器稳定运行。判断Nginx配置是否正确命令如下:
# nginx-t-c/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
或者
# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx-t
当nginx接收到HUP信号时,它会尝试先解析配置文件(如果指定文件,就使用指定的,否则使用默认的),如果成功,就应用新的配置文件(例如:重新打开日志文件或监听的套接字),之后,nginx运行新的工作进程并从容关闭旧的工作进程,通知工作进程关闭监听套接字,但是继续为当前连接的客户提供服务,所有客户端的服务完成后,旧的工作进程就关闭,如果新的配置文件应用失败,nginx再继续使用早的配置进行工作。
补充内容:nginx的几种信号
TERM,INT 快速关闭
QUIT 从容关闭
HUP 平滑重启,重新加载配置文件
USR1 重新打开日志文件,在切割日志时用途较大
USR2 平滑升级可执行程序
WINCH 从容关闭工作进程
平滑升级
Nginx方便地帮助我们实现了平滑升级。其原理简单概括,就是:
(1)在不停掉老进程的情况下,启动新进程。
(2)老进程负责处理仍然没有处理完的请求,但不再接受处理请求。
(3)新进程接受新请求。
(4)老进程处理完所有请求,关闭所有连接后,停止。
这样就很方便地实现了平滑升级。一般有两种情况下需要升级Nginx,一种是确实要升级Nginx的版本,另一种是要为Nginx添加新的模块。
平滑升级命令:
cd /mnt
下载nginx升级包
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.10.2.tar.gz
解压升级包
tar zxvf nginx-1.10.2.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.10.2/
查看当前版本得到编译参数
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
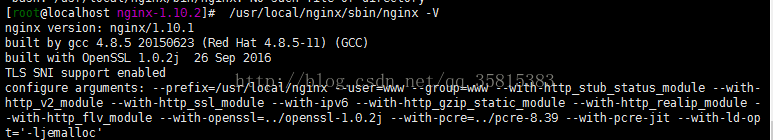
用上面编译参数
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=www --group=www --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-ipv6 --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_flv_module --with-openssl=../openssl-1.0.2j --with-pcre=../pcre-8.39 --with-pcre-jit --with-ld-opt='-ljemalloc'
然后make,千万别make install
make完了 在objs目录下就多了个nginx,这个就是新版本的程序了
备份原nginx文件
mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx-2017110
将新生成nginx执行文件复制到nginx/sbin下
cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
检测配置文件是否正确
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
执行升级
make upgrade
执行完后
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V
到此就完成平滑升级。
Nginx的启动、停止、平滑启动、平滑升级_服务器应用_Linux公社-Linux系统门户网站 https://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2015-08/121856.htm
Nginx的启动
启动nginx,可以执行一下命令(默认安装位置):
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
参数“-c”指定了配置文件的路径,如果不加,则Nginx会默认加载其安装目录的conf子目录中的ngin.conf
Nginx的停止
nginx的停止方法有很多种,一般是发送系统信号给nginx主进程来停止nginx。
我们通过ps命令来查找nginx的主进程号
ps -ef |grep nginx
我们可以看到备注信息为“master process”它表示主进程。为“worker”的是子进程。
如果在nginx.conf中指定了pid文件存放路径,则该文件存放的就是nginx的主进程号。如果没有指定,则默认存放在Nginx安装目录的log目录下。所以我们还可以这样做:
kill -信号类型 '/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid'
nginx支持以下几种信号:
TERM,INT :快速关闭
QUIT:从容关闭
HUP:平滑启动
USR1:重新打开日志文件
USR2:平滑升级可执行程序
EINCH:从容关闭工作进程
(1)从容停止nginx
kill -QUIT Nginx 主进程号
(2)快速停止Nginx
kill -TERM Nginx主进程号
(3)强制停止所有nginx进程
pkill -9 nginx
Nginx的平滑启动
kill -HUP nginx主进程号
nginx平滑升级
当需要将正在运行的nginx升级、添加/删除服务器模块时,可以在不中断的情况下使用新版本、重编译的nginx可执行程序替换旧版本的可执行程序。步骤如下:
(1)备份旧的可执行程序
(2)发送以下指令
kill -USR2 旧的版本nginx主进程号
(3)旧版本的nginx的主进程将重命名他的pid文件为.oldbin。然后执行新版本的nginx可执行程序。依次启动新的主进程和新的工作进程。
(4)此时新旧版本的nginx会同时运行,共同处理输入请求。要逐步停止旧版本的nginx实例,需要发送WINCH信号给旧的主进程,然后他的工作进程就从容关闭:
kill -WINCH 旧版本的主进程号
(5)一段时间后,旧的工作进程处理完所有的已连接请求后退出,仅有新的工作进程来处理输入请求。
(6)这时候我们可以决定是使用新的版本还是恢复到旧版本。
Nginx 启动、停止、平滑重启和平滑升级 graceful shutdown of worker processes的更多相关文章
- nginx平滑重启与平滑升级的方法
如何实现nginx平滑重启与平滑升级? 平滑重启 kill -HUP `cat /usr/local/www/nginx/logs/nginx.pid` 平滑升级nginx: cd /yujialin ...
- Nginx的平滑重启和平滑升级
一,Nginx的平滑重启如果改变了Nginx的配置文件(nginx.conf),想重启Nginx,可以发送系统信号给Nginx主进程的方式来进行.在重启之前,要确认Nginx配置文件的语法是正确的. ...
- nginx 启动/停止/重启
启动: -c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf) [root@LinuxServer sbin]# /usr/ ...
- nginx 启动/停止/重启 BAT
cls @ECHO OFF SET NGINX_PATH=D: SET NGINX_DIR=D:\Hack\nginx\color 0a TITLE Nginx 管理程序 Power By AntsG ...
- Nginx启动停止命令
操作环境是Windows 一.nginx命令:启动nginx 在Windows上安装好nginx后,我们需要启动nginx服务,启动nginx服务的命令行操作主要有两种方式,即 cd D:\opens ...
- ubuntu14.04上 nginx启动停止
sudo service nginx stop 停止 sudo nginx 启动
- Nginx启动关闭和重启、文档直接下载不阅览
nginx启动相关 启动:sbin/nginx -c conf/nginx.conf 关闭:sbin/nginx -s stop 重启(重新加载配置文件):sbin/nginx -s reload 检 ...
- nginx启动停止
nginx -s reload :修改配置后重新加载生效 nginx -s reopen :重新打开日志文件 nginx -t -c /path/to/nginx.conf 测试nginx配置文件是否 ...
- Nginx学习——Nginx启动、停止、重启和信号控制以及平滑升级
1.Nginx 启动与停止 (1)启动方式 启动格式:Nginx可执行文件地址 -c Nginx配置文件地址 /etc/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /root/dufy/ngi ...
随机推荐
- 神奇的canvas——巧用 canvas 为图片添加水印
代码地址如下:http://www.demodashi.com/demo/11637.html 很久之前写过一篇关于 canvas 的文章,是通过 canvas 来实现一个绚丽的动画效果,不管看过没看 ...
- 在 .NET 4.0 下编写扩展代码以支持 async 异步编程
微软在C# 5中引入了async.await这两个异步编程的关键字,要使用这两个关键字需要你的IDE支持C#5.0语法,也就意味着你需要使用VS 2012版本以上IDE,或者在Vs2010卸载其编译器 ...
- Android Volley框架的几种post提交请求方式
首先简单描述一下Google的Android开发团队在2013年推出的一个网络通信框架Volley.它的设计目标是进行数据量不大,但通信频繁的网络操作,而对于大数据量的网络操作,比如下载文件等,Vol ...
- 简体字丶冯|服务网关kong-docker安装
tags: kong ,服务网关,docker安装教程 grammar_cjkRuby: true --- 作为一名技术探索者,想了解一个未知系统的最有效方法就是去用.然而搭建一个陌生系统的最快捷方法 ...
- Codeforces Round #240 (Div. 1)B---Mashmokh and ACM(水dp)
Mashmokh's boss, Bimokh, didn't like Mashmokh. So he fired him. Mashmokh decided to go to university ...
- protobuf 在win10系统如何编译jar包
最近在搞java服务器项目,前段要求用protobuf进行数据传输,以前没搞过,查了很多资料,走了一些弯路! 先把一些需要下载的链接放上来: protobuf下载地址:https://github.c ...
- Triangulation by Ear Clipping(耳切法处理多边形三角划分)
使用EarClipping三角化多边形(翻译) ---Triangulation by Ear Clipping(http://www.geometrictools.com/Documentation ...
- bonjour的使用
os中,bonjour是一个零配置的网络服务分发服务器与客户端. 在使用bonour之前你应该明白的是,bonjour并不负责数据传输,只负责发布服务与检索服务,并在客户端获取服务端的信息. ...
- Yarn源码分析之如何确定作业运行方式Uber or Non-Uber?
在MRAppMaster中,当MapReduce作业初始化时,它会通过作业状态机JobImpl中InitTransition的transition()方法,进行MapReduce作业初始化相关操作,而 ...
- FD_CLOEXEC用法及原因_转
转自:使用FD_CLOEXEC实现close-on-exec,关闭子进程无用文件描述符 我们经常会碰到需要fork子进程的情况,而且子进程很可能会继续exec新的程序.这就不得不提到子进程中无用文件描 ...
