《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.33

代码:
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 7.33 \n\n'); banner();
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ws1 = 0.44*pi; wp1 = 0.49*pi; wp2 = 0.51*pi; ws2=0.56*pi; As = 30; Rp = 1.0;
[delta1, delta2] = db2delta(Rp, As) weights = [1 delta2/delta1 1]
deltaH = max([delta1,delta2]); deltaL = min([delta1,delta2]); %Dw = min((wp1-ws1), (ws2-wp2));
%M = ceil((-20*log10((delta1*delta2)^(1/2)) - 13) / (2.285*Dw) + 1) M = 51;
f = [ 0 ws1 wp1 wp2 ws2 pi]/pi;
m = [ 0 0 1 1 0 0]; h = firpm(M-1, f, m, weights);
[db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h, [1]);
delta_w = 2*pi/1000;
ws1i = floor(ws1/delta_w)+1; wp1i = floor(wp1/delta_w)+1;
wp2i = floor(wp2/delta_w)+1; ws2i = floor(ws2/delta_w)+1; Asd = -max(db(1:ws1i)) %[Hr, ww, a, L] = Hr_Type1(h);
[Hr,omega,P,L] = ampl_res(h);
l = 0:M-1; %% -------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ------------------------------------------------- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 Parks-McClellan Method')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); subplot(2,2,1); stem(l, h); axis([-1, M, -0.1, 0.1]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)'); title('Actual Impulse Response, M=51');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[0,M-1])
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-0.3:0.1:0.4]) subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0, 1, -80, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB ');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',f)
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-60,-30,0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['60';'30';' 0']); subplot(2,2,3); plot(omega/pi, Hr); axis([0, 1, -0.2, 1.2]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('Hr(w)'); title('Amplitude Response');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',f)
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[0,1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000; subplot(2,2,4); axis([0, 1, -deltaH, deltaH]);
sb1w = omega(1:1:ws1i)/pi; sb1e = (Hr(1:1:ws1i)-m(1)); %sb1e = (Hr(1:1:ws1i)-m(1))*weights(1);
pbw = omega(wp1i:wp2i)/pi; pbe = (Hr(wp1i:wp2i)-m(3)); %pbe = (Hr(wp1i:wp2i)-m(3))*weights(2);
sb2w = omega(ws2i:501)/pi; sb2e = (Hr(ws2i:501)-m(5)); %sb2e = (Hr(ws2i:501)-m(5))*weights(3);
plot(sb1w,sb1e,pbw,pbe,sb2w,sb2e); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Hr(w)'); title('Error Response'); %title('Weighted Error');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',f);
%set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-deltaH,0,deltaH]); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 AmpRes of h(n), Parks-McClellan Method')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); plot(omega/pi, Hr); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Hr'); title('Amplitude Response');
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-0.0334,0, 0.0334,1,1.057]);
%set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['90';'40';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[0,0.44,0.49,0.51,0.56,1]); %% -------------------------------------------------------
%% Input is given, and we want the Output
%% -------------------------------------------------------
num = 200; mean_val=0; variance=1;
x2 = mean_val + sqrt(variance)*randn(num,1);
n_x2 = 0:num-1;
x_axis = min(x2):0.02:max(x2); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 hist');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
%hist(x1,x_axis);
hist(x2,100);
title('Gaussian Distributed Random Numbers (using hist)');
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x2(n)'); grid on; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 bar');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
%[counts,binlocal] = hist(x1, x_axis);
[counts,binlocal] = hist(x2, 100);
counts = counts/num;
bar(binlocal, counts, 1); title('Gaussian Distributed Random Numbers (using bar)');
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x2(n)'); grid on; % Input
n_x3 = [0:1:num-1];
x3 = 2*cos(n_x3*pi/2);
[x,n_x] = sigadd (x2, n_x2, x3, n_x3); y = filter(h, 1, x);
n_y = n_x; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 Input[x(n)] and Output[y(n)]');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(n_x, x); axis([-1, 200, -5, 5]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); title('Input Response, Length=200');
subplot(2,1,2); stem(n_y, y); axis([-1, 200, -3, 3]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('y(n)'); title('Output Response'); % ---------------------------
% DTFT of x and y
% ---------------------------
MM = 500;
[X, w1] = dtft1(x, n_x, MM);
[Y, w1] = dtft1(y, n_y, MM); magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X);
magY = abs(Y); angY = angle(Y); realY = real(Y); imagY = imag(Y); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 DTFT of Input[x(n)]')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w1/pi,magX); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w1/pi, angX/pi); grid on; axis([0,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot(2,2,2); plot(w1/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w1/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 DTFT of Output[y(n)]')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w1/pi,magY); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |Y|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w1/pi, angY/pi); grid on; axis([0,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot(2,2,2); plot(w1/pi, realY); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w1/pi, imagY); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.33 Magnitude Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(1,2,1); plot(w1/pi,magX); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part of Input');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(1,2,2); plot(w1/pi,magY); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part of Output');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |Y|');
运行结果:
设计一个50阶(即长度M=51)的线性相位FIR,通带宽度不超过0.02π,阻带衰减达到30dB,
最后要把输入中的高斯噪声过滤掉。
As=33dB,满足设计要求。
用P-M方法设计的脉冲响应幅度谱,

振幅谱

输入信号
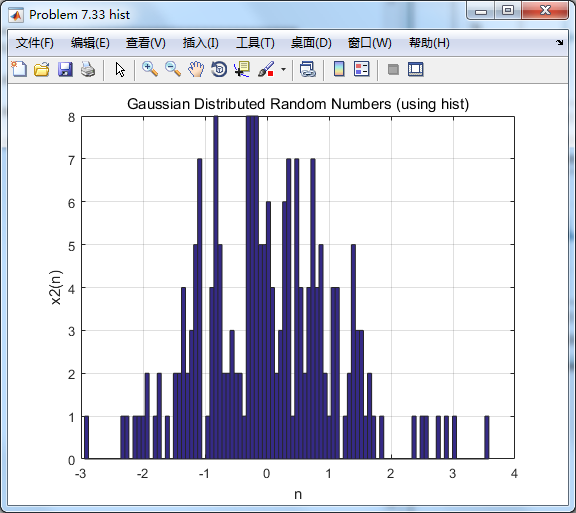

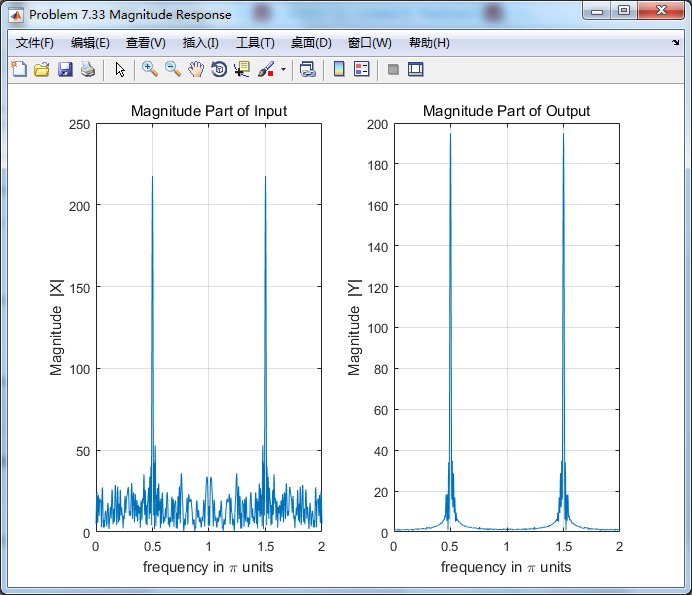
滤波前后,输入数出对比
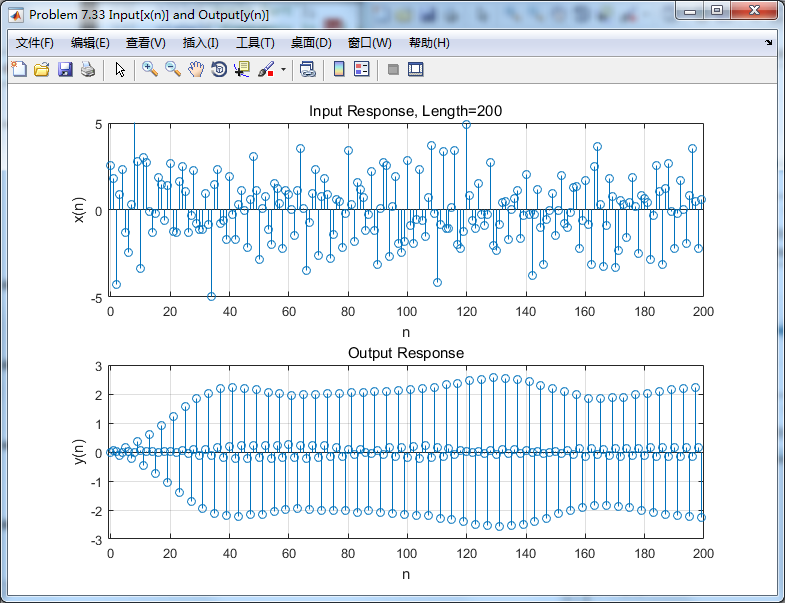
输入输出的谱:
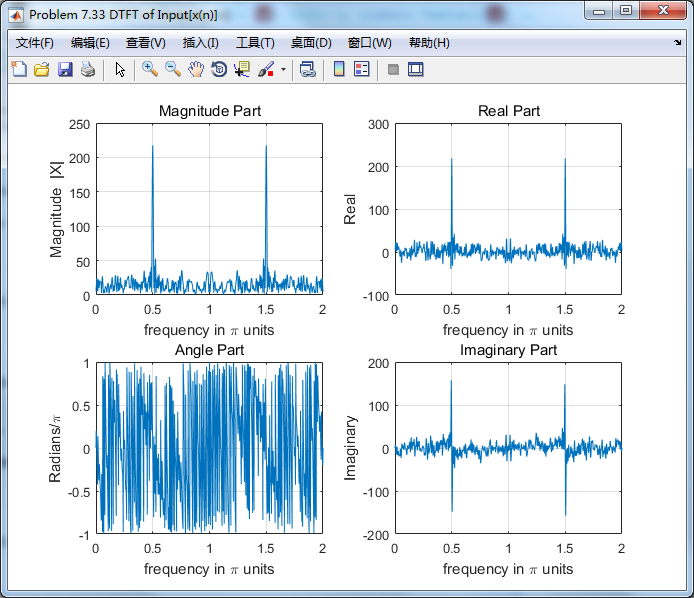
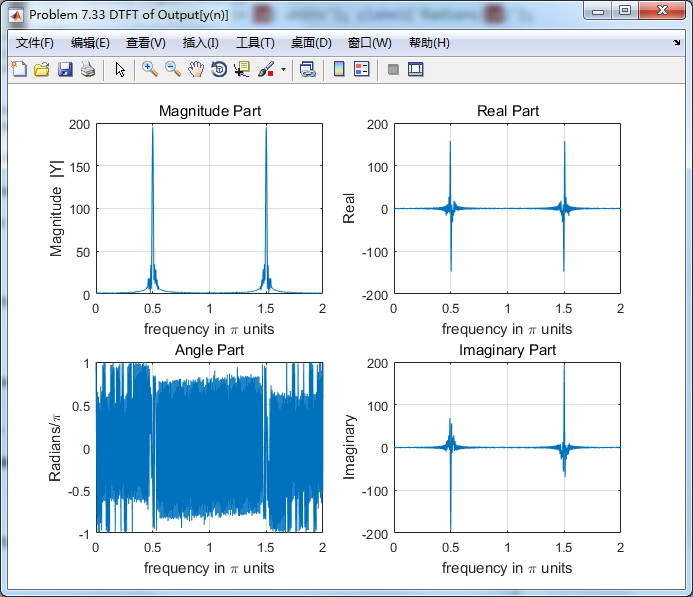
右下图可见,随即噪声分量已滤除,仅留0.5π频率分量,效果良好。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.33的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.33
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.36
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.29
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.23
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info a ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
随机推荐
- 第四周——重新clone项目后maven问题
重新clone项目后,一直报错,"类重复..." clean后install也无效果. 原因是idea在重启项目时会更改maven为默认的idea自带的maven配置,要重新设置
- 高性能代理缓存服务器—Squid
Squid是什么? Squid是一款比较知名的开源代理缓存软件,它不仅可以跑在linux上还可以跑在windows以及Unix上,它的技术已经非常成熟.目前使用Squid的用户也是十分广泛的. Squ ...
- 第二周课堂笔记1th
1. 三元运算 + 2. for循环 for为有限循环,while为无限循环 可迭代对象:是字符串,数字不可以 数字不可以迭代但是可以用range函数 for i in range(1 ...
- 属性面板:tabcontroller
Tabcontroller 布局 Anchor 设置控件距离选定方向固定: Dock 定义要绑定到容器的控件边框 Location 设置控件对于容器左上角的坐标 Margin 指定此控件与另一控件边距 ...
- C++ 系列:C++ 内存布局
1 前言 了解你所使用的编程语言究竟是如何实现的,对于C++程序员可能特别有意义.首先,它可以去除我们对于所使用语言的神秘感,使我们不至于对于编译器干的活感到完全不可思议:尤其重要的是,它使我们在De ...
- 位运算 - 左移右移运算符 >>, <<, >>>
1-左移运算符m<<n,表示把m左移n位.左移n位的时候,最左边的n位数将被丢弃,同时在最右边补上n个0.例如: 00001010<<2 = 00101000 10001010 ...
- css之height: 100%的有效场景
在css的日常应用中,经常会遇到想要通过 height: 100%来达到使子盒子与父盒子高度一样的目的,但是偶尔明明设置了height: 100%,但是却没有达到想要的结果,这次我们就一起探索一下,什 ...
- 前端基础之BOM与DOM操作
目录 BOM操作 navigator对象 screen对象 history对象 localtion对象 弹出框 计时 setTimeout() clearTimeout() setInterval() ...
- 转:进程上下文VS中断上下文
源地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zzx1045917067/archive/2012/12/19/2824552.html 内核空间和用户空间是现代操作系统的两种工作模式,内核模 ...
- PAT甲级——A1004 Counting Leaves
A family hierarchy is usually presented by a pedigree tree. Your job is to count those family member ...
