433B.Kuriyama Mirai's Stones
Kuriyama Mirai has killed many monsters and got many (namely n) stones. She numbers the stones from 1 to n. The cost of the i-th stone is vi. Kuriyama Mirai wants to know something about these stones so she will ask you two kinds of questions:
- She will tell you two numbers, l and r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), and you should tell her
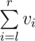 .
. - Let ui be the cost of the i-th cheapest stone (the cost that will be on the i-th place if we arrange all the stone costs in non-decreasing order). This time she will tell you two numbers, l and r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), and you should tell her
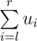 .
.
For every question you should give the correct answer, or Kuriyama Mirai will say "fuyukai desu" and then become unhappy.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers: v1, v2, ..., vn (1 ≤ vi ≤ 109) — costs of the stones.
The third line contains an integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 105) — the number of Kuriyama Mirai's questions. Then follow m lines, each line contains three integers type, l and r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ type ≤ 2), describing a question. If type equal to 1, then you should output the answer for the first question, else you should output the answer for the second one.
Print m lines. Each line must contain an integer — the answer to Kuriyama Mirai's question. Print the answers to the questions in the order of input.
6
6 4 2 7 2 7
3
2 3 6
1 3 4
1 1 6
24
9
28
4
5 5 2 3
10
1 2 4
2 1 4
1 1 1
2 1 4
2 1 2
1 1 1
1 3 3
1 1 3
1 4 4
1 2 2
10
15
5
15
5
5
2
12
3
5
Please note that the answers to the questions may overflow 32-bit integer type.
刚开始没有注意下面的Note,用int类型的数组WA了。后来改用long long型。我之前也没去算过OJ可以接受多大的数组,就这道AC的代码来看4W的long long是没有问题的。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <numeric>
#include <cmath>
#include<unordered_set>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int dir[][] = { {,},{-,},{,},{,-} }; int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<ll> v(n),a(n);
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
v[i] = t;
a[i] = t;
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
v[i] += v[i - ];
a[i] += a[i - ];
} int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--)
{
int q, l, r;
cin >> q >> l >> r;
if (q == )
{
if (l == )
cout << v[r - ] << endl;
else
cout << v[r - ] - v[l - ] << endl;
}
else
{
if (l == )
cout << a[r - ] << endl;
else
cout << a[r - ] - a[l - ] << endl;
}
}
//system("pause");
return ;
}
433B.Kuriyama Mirai's Stones的更多相关文章
- 动态规划,而已! CodeForces 433B - Kuriyama Mirai's Stones
Kuriyama Mirai has killed many monsters and got many (namely n) stones. She numbers the stones from ...
- Codeforces Round #248 (Div. 2) B. Kuriyama Mirai's Stones
题目简单描述就是求数组中[l,r]区间的和 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #inc ...
- CF433B Kuriyama Mirai's Stones 题解
Content 有一个长度为 \(n\) 的数组 \(a_1,a_2,a_3,...,a_n\).有 \(m\) 次询问,询问有以下两种: \(1~l~r\),求 \(\sum\limits_{i=l ...
- codeforces433B
Kuriyama Mirai's Stones CodeForces - 433B 有n颗宝石,每个宝石都有自己的价值. 然后m次询问.问区间[i,j]的宝石的总值,或者问排序后的区间[i,j]的总值 ...
- Codeforces Round #248 (Div. 2) (ABCD解决问题的方法)
比赛链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/433 A. Kitahara Haruki's Gift time limit per test:1 second memory ...
- Anna-senpai帖子翻译与Mirai源代码使用
Anna-senpai这个人太好玩了,整件事就像没有黄段子的无聊世界那样. 无聊翻译了一下,顺便实验了效果. --------------------------------------------- ...
- HDU 5973 Game of Taking Stones 威佐夫博弈+大数
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5973 Game of Taking Stones Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS ...
- HDU 4573 Throw the Stones(动态三维凸包)(2013 ACM-ICPC长沙赛区全国邀请赛)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4573 Problem Description Remember our childhood? A fe ...
- codechef Jewels and Stones 题解
Soma is a fashionable girl. She absolutely loves shiny stones that she can put on as jewellery acces ...
随机推荐
- [ZJOI2008] 骑士 - 基环树dp
一类基环树dp都是这个套路吧 随便拆掉环上的一条边 然后跑树形dp,设\(f[i][0/1]\)表示以第\(i\)个人为根的子树,第\(i\)个人选或不选,能收获的最大值 以断点\(u,v\)为根分别 ...
- BZOJ3680 JSOI2004 平衡点 - 随机/近似算法
迭代乱搞了下就过了…… #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ],y[],w[]; double xm,ym,wt,k,lambda= ...
- nice-validator判断表单是否验证通过
$("#formSurvery").isValid(function(is){ if(is){ alert("通过!") } } 如果is为false则表示不通 ...
- Python环境搭建(win)——Pycharm(破解+汉化)
Pycharm搭建方法(破解+汉化): 本文以pycharm2019.2为例 写在前面:有能力的朋友,希望大家支持正版. IDE是集成开发环境 “Integrated Development Envi ...
- promise的连缀写法
promise的连缀写法 以上写法相当于写了两个实例 promise.all() 1. promise.all() all这个方法是 promise 构造函数的成员不是实例对象成员,这个方法接受一个参 ...
- ECMAScript基本语法——④变量
简介 变量:一小块存储数据的内存空间先申请了一块内存空间,规定空间的存储类型,给空间赋值3, 想找到这个3可以通过内存空间的地址值,但是通过地址值太麻烦了,给这个空间起了一个名字a 通过这个a可以找到 ...
- 理解Login函数
_LoginPartial.cshtml文件 其中 <li>@Html.ActionLink("Log in", "Login", "Ac ...
- Flatmap 和map 区别
map将函数作用到数据集的每一个元素上,生成一个新的分布式的数据集(RDD)返回 map函数的源码: def map(self, f, preservesPartitioning=False): ...
- JAVA 注解教程(三)注解的属性
简介 注解的属性也叫做成员变量,注解只有成员变量,没有方法.注解的成员变量在注解的定义中以“无形参的方法”形式来声明,其方法名定义了该成员变量的名字,其返回值定义了该成员变量的类型 实例 @Targe ...
- JAVA 注解教程(二)元注解
简介 元注解是可以注解到注解上的注解,或者说元注解是一种基本注解,但是它能够应用到其它的注解上面 元注解有 @Retention.@Documented.@Target.@Inherited.@Rep ...
