常见任务&基本工具 1 软件包管理
打包系统主要有两个阵营
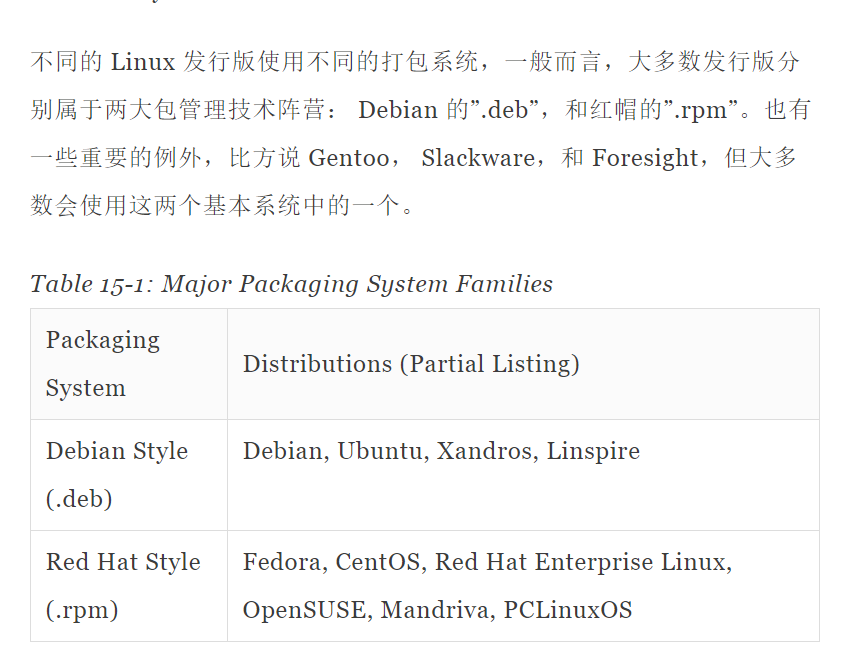
包文件的简介

Package files are created by a person known as a package maintainer, often (but not always) an employee of the distribution vendor. The package maintainer gets the software in source code form from the upstream provider (the author of the program), compiles it, and creates the package metadata and any necessary installation scripts. Often, the package maintainer will apply modifications to the original source code to improve the program’s integration with the other parts of the Linux distribution.
资源库
While some software projects choose to perform their own packaging and distribution, most packages today are created by the distribution vendors and interested third parties. Packages are made available to the users of a distribution in central repositories that may contain many thousands of packages, each specially built and maintained for the distribution.
测试资源库
A distribution may maintain several different repositories for different stages of the software development life cycle. For example, there will usually be a “testing” repository that contains packages that have just been built and are intended for use by brave souls who are looking for bugs before they are released for general distribution. A distribution will often have a “development” repository where work-in-progress packages destined for inclusion in the distribution’s next major release are kept.
第三方资源库(法律原因)
A distribution may also have related third-party repositories. These are often needed to supply software that, for legal reasons such as patents or DRM anti-circumvention issues, cannot be included with the distribution. Perhaps the best known case is that of encrypted DVD support, which is not legal in the United States. The third-party repositories operate in countries where software patents and anti-circumvention laws do not apply. These repositories are usually wholly independent of the distribution they support and to use them, one must know about them and manually include them in the configuration files for the package management system.
依赖性
Programs seldom “standalone;” rather they rely on the presence of other software components to get their work done. Common activities, such as input/output for example, are handled by routines shared by many programs. These routines are stored in what are called shared libraries, which provide essential services to more than one program. If a package requires a shared resource such as a shared library, it is said to have a dependency. Modern package management systems all provide some method of dependency resolution to ensure that when a package is installed, all of its dependencies are installed, too.
上层和底层软件包工具
Package management systems usually consist of two types of tools: low-level tools which handle tasks such as installing and removing package files, and high-level tools that perform metadata searching and dependency resolution. In this chapter, we will look at the tools supplied with Debian-style systems (such as Ubuntu and many others) and those used by recent Red Hat products. While all Red Hat-style distributions rely on the same low-level program (rpm), they use different high-level tools. For our discussion, we will cover the high-level program yum, used by Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and CentOS. Other Red Hat-style distributions provide high-level tools with comparable features.
Low level and high level

Packge Search Commands

如果下载了没有安装

注意这种方法没有解析依赖

上层工具卸载软件

一步更新所需的文件


软件包升级软件实现更新


显示现在有的软件

显示该软件的状态

获取软件包的信息

那个软件对该文件负责

常见任务&基本工具 1 软件包管理的更多相关文章
- Debian的软件包管理工具命令 (dpkg,apt-get)详解
本文转载于:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-20769502-id-106056.html 1.dpkg包管理工具 dpkg --info "软件包名&quo ...
- Mac OSX上的软件包管理工具,brew 即 Homebrew
brew 即 Homebrew,是Mac OSX上的软件包管理工具,能在Mac中方便的安装软件或者卸载软件, 只需要一个命令, 非常方便. brew类似ubuntu系统下的apt-get的功能. 安装 ...
- Mac Pro 安装 Homebrew 软件包管理工具
Linux系统有个让人蛋疼的通病,软件包依赖,好在当前主流的两大发行版本都自带了解决方案,Red hat有 yum,Ubuntu有 apt-get. Mac os 中没有类似的东东,不过有第三方库支持 ...
- brew mac osx 上软件包管理工具
今天推荐 Mac OSX 下,方便高效的包管理工具 brew brew 的全名叫做 Homebrew 它的功能类似于 ubuntu 下同下 apt-get ,或者 Cent OS 下的 yum 等包管 ...
- RPM是RedHat Package Manager(RedHat软件包管理工具)
RPM是RedHat Package Manager(RedHat软件包管理工具)类似Windows里面的“添加/删除程序” rpm 执行安装包二进制包(Binary)以及源代码包(Source)两种 ...
- mac os x 10.9.1 安装 Homebrew软件包管理工具及brew安装maven3.1.1
Mac OSX上的软件包管理工具,安装软件或者卸载软件. 打开终端输入(如不行,可参考homebrew官网): ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githu ...
- 【one day one linux】linux下的软件包管理工具
Linux 下的软件包管理工具 linux下的软件安装可以通过两种方式,一种是直接使用自带的软件包管理工具安装,另外一种通过编译源码安装. 1.软件包的种类 Red Hat和Fedora:redhat ...
- Mac安装软件包管理工具Homebrew
PS:最近开始学习groovy,打算去官网下载SDK Bundle,可是官网半天加载不出来,而且莫名其妙就是下载不下来,Folx一直提示 "无效的HTTP相应:禁止",可能是插件和 ...
- linux的Yum软件包管理工具
Yum(全称为 Yellow dog Updater, Modified)是一个在Fedora和RedHat以及CentOS中的Shell前端软件包管理器.基于RPM包管理,能够从指定的服务器自动下载 ...
随机推荐
- Element-ui之修改样式
修改样式的方法 官网上面介绍了几种方法: 当然还有其他的方法,比如: 直接在标签上面采用行内式: 在组件中的style里面添加样式: 引入.scss文件(注意:如果是公用样式最好在index.scss ...
- 重磅榜单!互联网金融Top100总估值超1.1万亿,27家独角兽上榜!
时隔4个月,爱分析的“中国互联网金融企业估值排行榜”更新了! 在这4个月当中,我们调研了数十位企业创始人.专业投资人以及资深行业专家,尤其针对金服集团.消费金融.财富管理.征信等领域进行了深入研究.因 ...
- 深入浅出 Java Concurrency (35): 线程池 part 8 线程池的实现及原理 (3)[转]
线程池任务执行结果 这一节来探讨下线程池中任务执行的结果以及如何阻塞线程.取消任务等等. 1 package info.imxylz.study.concurrency.future;2 3 publ ...
- kafka集群搭建文档
kafka集群搭建文档 一. 下载解压 从官网下载Kafka,下载地址http://kafka.apache.org/downloads.html 注意这里最好下载scala2.10版本的kafka, ...
- Bitcoin 的基本原理
昨天读到了 Bitcoin 的中文介绍,觉得非常有意思.不过上面这篇文章解释的非常不靠谱,我花了一晚上去Bitcoin的官方网站 仔细研究了一下,总算理解了其原理.感觉非常有启发,尤其是对虚拟货币的流 ...
- Cesium官方教程12--材质(Fabric)
原文地址:https://github.com/AnalyticalGraphicsInc/cesium/wiki/Fabric 介绍 Fabric 是Cesium中基于JSON格式来描述materi ...
- AppScan的基础使用
AppScan是用于Web项目的安全测试工具,扫描网站所有url,自动测试是否存在各种类型的漏洞.AppScan安装在Windows环境上,版本越高,规则库越安全,扫描越全面. 1. 打开AppS ...
- HDU--2191 汶川地震购米(多重背包)
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2191 分析:有资金n元,而市场有m种大米,每种大米价格不等,重量不等,数量不等, 并且只能整袋购买.如何用 ...
- 使用ResponseEntity进行返回json数据
在最近的项目中,与上位机进行数据传输时,上位机需要服务器的响应得知服务器是否正常运行,数据是否正常发送 在最近的调试中我使用ResponseEntity<Map<String,Object ...
- OpenGL学习笔记2017/8/29
OpenGL学习日志: 感谢doing5552 的OpenGL入门学习:http://www.cppblog.com/doing5552/archive/2009/01/08/71532.html 相 ...
