Hibernate (二)
1 一级缓存的引入
- 示例:
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);//持久态对象
p.setName("呵呵");//持久态对象
tx.commit();
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
- 上述的代码中。Hibernate是如何控制是否向数据库发送update的SQL语句?请看下图分解。
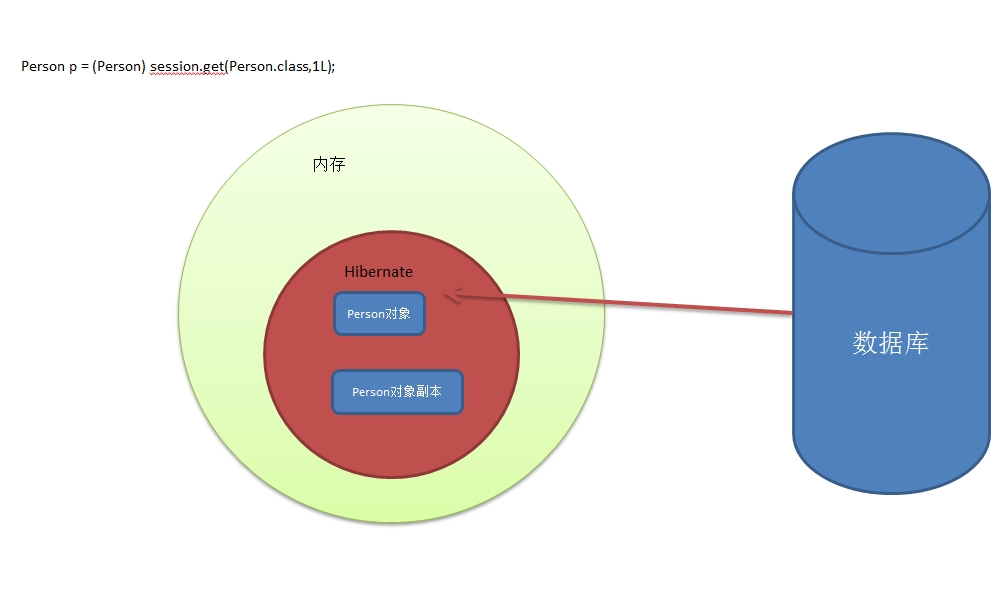
- 过程如下:
- ①当执行get方法的时候,Hibernate会从数据库查询数据,并将其封装到一个对象(持久化对象)之中,然后再内存中复制这个对象,我们称这个复制的对象为“副本”。
- ②当执行事务提交的时候,Hibernate会将此时的持久化对象和“副本”对象进行对比,如果不一致,那么说明持久化对象发生了修改,此时会将原来的“副本”对象覆盖掉,然后向数据库发送SQL语句。
- ③当执行事务提交的时候,Hibernate会将此时的持久化对象和“副本”对象进行对比,如果一致,那么说明持久化对象没有发生修改,那么就不需要向数据库发送SQL语句,也就意味着此时的“副本”对象和数据库中的数据是一致的。
2 Session的flush()方法
- 示例:
@Test
public void testFlush(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p1 = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
Person p2 = (Person) session.get(Person.class,2L);
p2.setName("林志玲");
Person p3 = new Person();
p3.setName("嘻嘻");
p3.setSex("女");
session.save(p3);
session.flush();
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
- 执行过程如下:
- ①当执行session.flush()方法的是偶,hibernate内部会检查所有的持久化对象。
- ②会判断该对象和数据库有没有对应的数据(标识符id),如果没有,就发出Insert语句。
- ③如果有,则再让该对象和副本进行对比,如果和副本一样,则什么也不做,否则,则发出update语句。
- ④session.flush()只不过向数据库发送SQL语句,但是值在数据库中并不存在。
3 缓存和缓存类型
- 缓存:
- 通过什么方法可以把对象或数据存到缓存中
- 通过什么方法可以把缓存中的对象或数据提取出来
- 把缓存中的一些数据或者一些对象释放出来
- 把缓存中的内容清空
- 把缓存中的数据同步到数据库中
- 把数据库中的数据同步到缓存中
- 缓存类型:
- 对象缓存:把对象的标识符(id)作为key值,对象本身作为value值。
- 数据缓存:把SQL语句作为key值,把结果作为value值。
4 常用方法
- get方法:会将查询到的对象放入到一级缓存中
@Test
public void testGet(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Person p1 = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);//发出SQL语句
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
p1 = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);//不发出SQL语句
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
session.close();
}
- save方法:会先要增加的对象放入到一级缓存中
@Test
public void testInsert(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("许威威");
p.setSex("男");
session.save(p);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
- update方法:
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
session.evict(p);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
session.update(p);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
- evict方法
@Test
public void testEvict(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
session.evict(p);//把对象从缓存中清空
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
- clear方法
@Test
public void testClear(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
Person p2 = (Person) session.get(Person.class,2L);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
session.clear();//把对象从缓存中清空
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
- close方法
@Test
public void testClose(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
tx.commit();
session.close();
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
System.out.println("hibernate一级缓存中对象的个数:"+session.getStatistics().getEntityCount());
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
- 【注意】
- ①一级缓存的生命周期和session的生命周期是一致的。
- ②当执行session.close()方法的时候,一级缓存就消失了。
5 对象的状态和一级缓存的关系
- 如果一个对象是持久化状态,那么该对象在一级缓存中。
- 如果一个对象是脱管态,那么该对象已经从一级缓存中清除了。
6 Session
- ①CRUD操作都是通过Session完成的。
- ②和数据库的连接也是通过Session来完成的。
- ③对象的状态以及一级缓存也是和Session紧密关联的。
- ④数据安全性的问题
- 示例:openSession
@Test
public void testGet(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Person p1 = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);//发出SQL语句
System.out.println(p1.getPid()+":"+p1.getName()+":"+p1.getSex());
//可以通过session拿到缓存中的数据
Set set = session.getStatistics().getEntityKeys();
for(Iterator iterator = set.iterator();iterator.hasNext();){
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
session.close();
}
- openSession方式的弊端:
- ①只要调用openSession就会打开一个连接,效率太低,就算使用了连接池也没起什么作用。
- ②利用这种方式可以操作session中的缓存。
- getCurrentSession源码分析:
- SessionFactory.java
public interface SessionFactory extends Referenceable, Serializable{
Session getCurrentSession() throws HibernateException;
}
- SessionFactoryImpl.java
public final class SessionFactoryImpl implements SessionFactory, SessionFactoryImplementor{
public Session getCurrentSession() throws HibernateException {
if (this.currentSessionContext == null) {
//从这边我们知道如果你要使用getCurrentSession(),你必须配置,
//在hibernate.cfg.xml中配置<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
//否则会抛出异常
throw new HibernateException("No CurrentSessionContext configured!");
} else {
return this.currentSessionContext.currentSession();
}
}
}
- CurrentSessionContext.java
public interface CurrentSessionContext extends Serializable {
Session currentSession() throws HibernateException;
}
- ThreadLocalSessionContext.java
public class ThreadLocalSessionContext implements CurrentSessionContext {
//ThreadLocal中的值是Map<SessionFactory,Sessoin>
//因为SessionFactory是单例的,这样可以保证Map中的数据也是唯一的,当然Session也是唯一的,这样将Map放入到ThreadLocal中,就能保证在线程中,可以共享Session
//获取当前ThreadLocal中的Map的Session
public final Session currentSession() throws HibernateException {
//获取当前线程中的Session
Session current = existingSession(this.factory);
if (current == null) {
//如果current是null
current = this.buildOrObtainSession();
current.getTransaction().registerSynchronization(this.buildCleanupSynch());
if (this.needsWrapping(current)) {
current = this.wrap(current);
}
doBind(current, this.factory);
}
//返回当前线程中的Session
return current;
}
//判断ThreadLocal中是否存在Session
private static Session existingSession(SessionFactory factory) {
//从ThreadLocal中取得值
Map sessionMap = sessionMap();
//如果sessionMap是null,就返回null
//如果sessionMap不是null,那么就根据sessionFactory从map根据SessionFactory获取Session
return sessionMap == null ? null : (Session)sessionMap.get(factory);
}
//将Map<SessionFactory,Session>放入到ThreadLocal中
private static void doBind(org.hibernate.Session session, SessionFactory factory) {
Map sessionMap = sessionMap();
if (sessionMap == null) {
sessionMap = new HashMap();
context.set(sessionMap);
}
((Map)sessionMap).put(factory, session);
}
//从ThreadLocal中取值
protected static Map sessionMap() {
return (Map)context.get();
}
}
- 示例:使用getCurrentSession
- ①在hibernate.cfg.xml中配置current_session_context_class
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
- ②使用getCurrentSession()方法
/**
* 获取当前线程的session
*/
@Test
public void testCurrentSession(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Person p = (Person) session.get(Person.class,1L);
tx.commit();
}
- 【注意】
- ①CRUD都必须在事务的条件下进行
- ②当事务提交的时候,session自动关闭
- 【注意】
7 一对多单向关联
- 以学生和班级为例
- Student.java
package com.xuweiwei.vo;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* 学生
*/
public class Student implements Serializable{
private Long sid;//学生的ib
private String name;//学生的名称
private String description;//学生的描述
public Long getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(Long sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
- Classes.java
package com.xuweiwei.vo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 班级
*/
public class Classes implements Serializable {
private Long cid;//班级的编号
private String name;//班级的名称
private String description;//班级的描述
private Set<Student> students = new HashSet<>();//一个班级有多个学生
public Long getCid() {
return cid;
}
public void setCid(Long cid) {
this.cid = cid;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public Set<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public void setStudents(Set<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
}
- Student.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.xuweiwei.vo.Student">
<id name="sid">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="name"/>
<property name="description"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- Classes.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.xuweiwei.vo.Classes">
<id name="cid">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name"/>
<property name="description"/>
<!--
set元素描述了集合
name就是属性的名称
-->
<set name="students">
<!--
key代表外键
-->
<key>
<column name="cid"/>
</key>
<!--
建立了对象和对象之间的关联
-->
<one-to-many class="com.xuweiwei.vo.Student"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<!--
一个sessionFactory就代表一个数据库的描述
-->
<session-factory>
<!-- 链接数据库的用户名 -->
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<!-- 链接数据库的密码 -->
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<!-- 链接数据库的驱动 -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
</property>
<!-- 链接数据库的url -->
<property name="connection.url">
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate
</property>
<!--
方言
告诉hibernate用什么样的数据库,将来会生成什么样的sql语句
-->
<property name="dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</property>
<!--
hibernate对表的策略
validate 在hibernate容器启动的时候,根据映射文件和持久化类校验表
create 每次当hibernate启动的时候,都会根据持久化类和映射文件创建表
create-drop 每次当hibernate启动的时候,都会根据持久化类和映射文件创建表,销毁的时候删除表
update 检查,如果和映射文件不一致,则更新表的结构,如果没有表,则会创建表
-->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!-- -->
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<mapping resource="com/xuweiwei/vo/Classes.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="com/xuweiwei/vo/Student.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
- 保存学生
/**
* 保存班级
*/
@Test
public void testClasses(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes = new Classes();
classes.setName("Linux班级");
classes.setDescription("牛逼");
session.save(classes);
tx.commit();
}
- 保存班级
/**
* 保存学生
*/
@Test
public void testStudent(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("许威威");
s1.setDescription("java开发");
session.save(s1);
tx.commit();
}
- 级联保存:保存班级的同时保存学生
<!--
set元素描述了集合
name就是属性的名称
cascade:save-update保存或更新的时候对Student进行操作
-->
<set name="students" cascade="save-update">
<!--
key代表外键
-->
<key>
<column name="cid"/>
</key>
<!--
建立了对象和对象之间的关联
-->
<one-to-many class="com.xuweiwei.vo.Student"/>
</set>
/**
* 保存班级的同时保存学生
*/
@Test
public void testOneToMany(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes = new Classes();
classes.setName("java班级");
classes.setDescription("必须牛逼");
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("许威威");
s1.setDescription("java开发1");
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("王伟");
s2.setDescription("java开发2");
classes.getStudents().add(s1);
classes.getStudents().add(s2);
session.save(classes);
tx.commit();
}
- 如果在级联保存的同时,在*.hbm.xml中没有配置cascade属性的话,会出现错误。
<!--
set元素描述了集合
name就是属性的名称
cascade:save-update保存或更新的时候对Student进行操作
-->
<set name="students" cascade="save-update">
<!--
key代表外键
-->
<key>
<column name="cid"/>
</key>
<!--
建立了对象和对象之间的关联
-->
<one-to-many class="com.xuweiwei.vo.Student"/>
</set>
/**
* 保存班级的同时保存学生
*/
@Test
public void testOneToMany(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes = new Classes();
classes.setName("java班级");
classes.setDescription("必须牛逼");
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("许威威");
s1.setDescription("java开发1");
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("王伟");
s2.setDescription("java开发2");
classes.getStudents().add(s1);
classes.getStudents().add(s2);
session.save(classes);
tx.commit();
}
- 出现的异常如下:
org.hibernate.TransientObjectException: object references an unsaved transient instance - save the transient instance before flushing: com.xuweiwei.vo.Student
- 错误分析:
- 当去掉cascade的时候,我们会发现此时的Classes和Student对象都是瞬时态对象,那么此时,当我们保存班级的时候,班级对象是没有问题的,反正是将班级对象的瞬时态变为持久态,但是这时比较尴尬的是,此时学生对象也是瞬时态对象,而我们却在此时将班级对象的瞬时态和学生对象的瞬时态进行了关联,此时Hibernate会感到疑惑。
- 所以,在级联保存的同时,需要在*.hbm.xml上需要配置cascade属性。
- 错误分析:
- 在保存班级的同时级联更新学生信息
@Test
public void testInsertClassesCascadeUpdateStudent(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes = new Classes();
classes.setName("php2");
classes.setDescription("呵呵");
Student student = (Student) session.get(Student.class,3L);
student.setDescription("java学习");
classes.getStudents().add(student);
session.save(classes);
tx.commit();
}
- 更新班级的时候级联更新学生
/**
* 更新班级的同时更新学生
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateClassesCascadeUpdateStudent(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes1 = (Classes) session.get(Classes.class,1L);
Set<Student> students = classes1.getStudents();
classes1.setDescription("Linux操作系统很牛逼");
for(Student s: students){
s.setDescription("学Linux的很牛逼");
}
tx.commit();
}
- 删除一个班级的指定的学生
/**
* 删除某个班级中的某个学生
*/
@Test
public void testDelete(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes1 = (Classes) session.get(Classes.class,1L);
Set<Student> students = classes1.getStudents();
for(Student student:students){
if(student.getSid().longValue() == 2){
session.delete(student);
}
}
tx.commit();
}
- 出现如下异常:
org.hibernate.ObjectDeletedException: deleted object would be re-saved by cascade (remove deleted object from associations): [com.xuweiwei.vo.Student#2]
- 异常分析:
- 异常的意思是:要删除的对象是从一个对象中关联提取出来的。
- 异常分析:
<!--
set元素描述了集合
name就是属性的名称
cascade:save-update保存或更新的时候对Student进行操作
-->
<set name="students" cascade="save-update" >
<!--
key代表外键
-->
<key>
<column name="cid"/>
</key>
<!--
建立了对象和对象之间的关联
-->
<one-to-many class="com.xuweiwei.vo.Student"/>
</set>
- 但是,我们在映射文件中,却设置了classes和student之间的关系。
Classes classes1 = (Classes) session.get(Classes.class,1L);
Set<Student> students = classes1.getStudents();
for(Student student:students){
if(student.getSid().longValue() == 2){
session.delete(student);
}
}
- 而上面的代码,却是让classes和student没有关系,所以会报错。
- 解决方案:有弊端,解除关系后,其它的学生就不属于这个班级了
/**
* 删除某个班级中的某个学生
*/
@Test
public void testDelete(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes1 = (Classes) session.get(Classes.class,1L);
Set<Student> students = classes1.getStudents();
classes1.setStudents(null);//将关系解除
for(Student s:students){
if(s.getSid().longValue() == 2){
session.delete(s);
}
}
tx.commit();
}
8 级联说明
- 对象与对象之间的操作,在保存班级的同时保存学生,指的是保存班级的一般属性和学生的一般属性,和外键没有关系。
9 inverse 属性
- classes.xml
<!--
set元素描述了集合
name就是属性的名称
cascade:save-update保存或更新的时候对Student进行操作
inverse 是否维护关系:Classes是否维护和Student之间的关系
true 不维护关系
false 维护关系
default=false
-->
<set name="students" cascade="save-update" inverse="false" >
<!--
key代表外键
-->
<key>
<column name="cid"/>
</key>
<!--
建立了对象和对象之间的关联
-->
<one-to-many class="com.xuweiwei.vo.Student"/>
</set>
- 示例:给一个已经存在的班级增加一个学生
@Test
public void testUpdateClassesCascadeAddStudentBuildRelationship(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Classes classes1 = (Classes) session.get(Classes.class,1L);
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("许威威");
stu.setDescription("java开发");
classes1.getStudents().add(stu);
tx.commit();
}
10 cascade属性和inverse属性的区别
- cascade属性:
- 如果值是save-update,如果以上面的例子,班级和学生来说,就是增加班级或修改班级,会级别改变学生。
- 默认是false,inverse是反转的意思,默认的情况就是不反转,不反转,那就是维护关系啦,那么就是会管理外键。
- 如果是true,就是反转的意思,既然是反转,那么就是我不管理了,不就是不维护关系,那就是不管理外键。
inverse属性:就是维护关系(数据库是通过外键来维护关系的)
11 一级缓存的意义

- 一级缓存的意义就在于:
- 将所有的持久化对象放到一级缓存中,然后当执行session.flush()方法的时候,才去和数据库交互(hibernate内部会决定到底是发送insert语句还是update语句)。
- 或者,可以换个场景,如果一个班级有50个学生,我第一次查询了班级和学生的信息,然后修改了学生的信息,当执行session.flush()方法的时候,hibernate才会和数据库交互,而不是原来的,我们用JDBC的时候,只要修改一次学生信息,我就要和数据库交互一次。
- 当然,如果你的理解是,hibernate的一级缓存就是当执行get方法的时候,会与数据库交互一次,发出select语句,当再执行get方法的时候,就从缓存中查询,而不再和数据库交互,这样理解有点肤浅了。
12 一级缓存、二级缓存和副本的区别
- 一级缓存和二级缓存是用来存放数据并提取数据的
- 副本是和数据库同步的,当从一级缓存中提取出来的数据,如果调用了session.flush(),就是说,要和数据库中的数据同步的时候,副本决定了是不是要发出update语句。
Hibernate (二)的更多相关文章
- Hibernate二次学习一----------Hibernate简单搭建
因为博客园自带的markdown不太好用,因此所有markdown笔记都使用cmd_markdown发布 Hibernate二次学习一----------Hibernate简单搭建: https:// ...
- hibernate(二)一级缓存和三种状态解析
序言 前一篇文章知道了什么是hibernate,并且创建了第一个hibernate工程,今天就来先谈谈hibernate的一级缓存和它的三种状态,先要对着两个有一个深刻的了解,才能对后面我要讲解的一对 ...
- Hibernate(二)——POJO对象的操作
POJO对象其实就是我们的实体,这篇博客总结一下框架对POJO对象对应数据库主键的生成策略,和一些对POJO对象的简单增删改查的操作. 一,Hibernate框架中主键的生成策略有三种方式: 1,数 ...
- Spring整合Hibernate 二 - 声明式的事务管理
Spring大战Hibernate之声明式的事务管理 Spring配置文件: 添加事务管理类的bean: <bean id="txManager" class="o ...
- Hibernate(二)
性能分析 抓取策略 研究对象 研究怎么样提取集合的,该策略应该作用与set元素上 研究从一的一方加载多的一方 案例 查询cid为1的班级的所有的学生 明:通过一条sql语句:左外链接,把classes ...
- Hibernate(二)__简单实例入门
首先我们进一步理解什么是对象关系映射模型? 它将对数据库中数据的处理转化为对对象的处理.如下图所示: 入门简单实例: hiberante 可以用在 j2se 项目,也可以用在 j2ee (web项目中 ...
- Hibernate二 映射 注解 一级缓存
Hibernate映射1.@Entity 被该注解修饰的POJO类是一个实体,可以用name属性指定该实体类的名称,系统默认以该类的类名作为实体类的名称.2.@Table 指定持久化类所映射的表,它的 ...
- Hibernate 二(一级缓存,多表设计之一对多)
1 对象状态与一级缓存 1.1 状态介绍 l hibernate 规定三种状态:瞬时态.持久态.脱管态 l 状态 瞬时态:transient,session没有缓存对象,数据库也没 ...
- ssh架构之hibernate(二)进阶学习
1.JPA入门 JPA的认识:JPA全称Java Persistence API.JPA通过JDK 5.0注解或XML描述对象-关系表的映射关系,并将运行期的实体对象持久化到数据库中Java持久层AP ...
- Hibernate(二)持久化对象的状态
简介 以前学习Hibernate的笔记,整理一下便发出来了,防止弄丢.有错误的话麻烦各位留言评论,感激不尽. 持久化类 Hibernate完成了从面向对象模型表示的对象至关系模型表示的数据结构的映射, ...
随机推荐
- 【转载】LINUX上MYSQL优化三板斧
现在MySQL运行的大部分环境都是在Linux上的,如何在Linux操作系统上根据MySQL进行优化,我们这里给出一些通用简单的策略.这些方法都有助于改进MySQL的性能. 闲话少说,进入正题. 一. ...
- 关于获得当前的index的方法
每日一句English(start from today): In the previous section we just displayed a list of string entered st ...
- request拿各种东西
例如 : http://localhost:8080/projectName/aaa/bbb?name=zhangsan获取项目名(目录) /projectNameString uri = reque ...
- 破解附近寝室的Wifi密码
[系统]运行在VMware虚拟机中的Kali Linux系统.(实测Kali运行在virtualbox中兼容性很差,VMware支持的很好.我认为这正是一个不要迷信开源的例子,多数情况下,大公司的商业 ...
- burpsuite截断绕过前端限制上传一句话
设置代理,这里就不说了 打开上传界面 burpsuite开启拦截,上传lurp.hpg 在burp找到上传文件的格式改回原来一句话的格式 上传= =
- js面向对象学习笔记(四):对象的混合写法
//对象的混合写法//1.构造函数function 构造函数() { this.属性}构造函数.原型.方法 = function () {};//调用var 对象1 = new 构造函数();对象1. ...
- codechef [snackdown2017 Onsite Final] Fusing Weapons
传送门 题目描述 大厨最近迷上了一款勇者斗恶龙的游戏. 游戏每局开始前,会有 N 件武器摆成一圈.每件武器有一个整数的等级.大厨可以选择两件 相邻的等级相同(不妨设同为 A 级)的武器,将它们合成.这 ...
- NowCoder牛客练习赛7-A.骰子的游戏 B.购物-优先队列
A.骰⼦的游戏 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒空间限制:C/C++ 32768K,其他语言65536K64bit IO Format: %lld 题目描述 在Alice和Bob面前的是两个骰 ...
- ACM中常见错误对应表
因为经常写错题,找了个这个看看... 传送门:http://www.cnblogs.com/ZouCharming/p/3868844.html 我太垃圾了... 我出现过的错误: Wrong Ans ...
- hdu_1370Biorhythms(互素的中国剩余定理)
Biorhythms Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
