Characterization of Dynkin diagrams
Nowadays, I am reading D.J.Benson's nice book, volume I of Representations and cohomology. I found it has a nice description on Dynkin diagrams. So I want to make a note on it and on it here. If the application is successful, I will have more time on Mathematiques intersting me. If the time permits, I will make anther note about the relationship of root system and Dynkin diagrams.
Contents
- Dynkin diagrams and Euclidean diagrams
- Cartan matrix and characterization of Dynkin diagrams using subadditve functions
- Characterization using positive definity of Cartan's matrix
Dynkin diagrams and Euclidean diagrams
The following labeled graphs are called Dynkin diagrams
- $A_n$($n\geq1$)

- $B_n$($n\geq 2$)

- $C_n$($n\geq 2$)
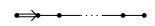
- $D_n$($n\geq 4$)

- $E_6$
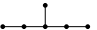 ; $E_7$
; $E_7$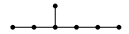 ; $E_8$
; $E_8$
$F_4$

$G_2$

The foot index illustrates the number of nodes. And  ,
,  and
and  stands a edge labelled by $(1,1)$, $(2,1)$ and $(3,1)$ respectively.
stands a edge labelled by $(1,1)$, $(2,1)$ and $(3,1)$ respectively.
The following labeled graphs are called Euclidean diagrams
- $\tilde{A}_n$($n\geq 1$)
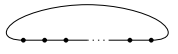 ; $\tilde{A}_{11}$
; $\tilde{A}_{11}$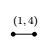 ; $\tilde{A}_{12}$
; $\tilde{A}_{12}$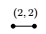 .
. - $\tilde{B}_n$($n\geq 3$)
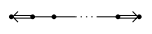
- $\tilde{C}_n$($n\geq 3$)
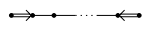
- $\tilde{D}_n$($n\geq 5$)

- $\widetilde{BC}_n$($n\geq 3$)

- $\widetilde{BD}_n$($n\geq 4$)

- $\widetilde{CD}_n$($n\geq 4$)

$\tilde{E}_6$
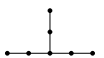 ; $\tilde{E}_7$
; $\tilde{E}_7$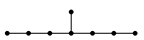 ; $\tilde{E}_8$
; $\tilde{E}_8$ 
$\tilde{F}_{41}$
 ; $\tilde{F}_{42}$
; $\tilde{F}_{42}$
$\tilde{G}_{21}$
 ; $\tilde{G}_{22}$
; $\tilde{G}_{22}$
The sum of foot index illustrates the number of nodes.
Cartan matrix and characterization of Dynkin diagrams using subadditve functions
Definition. For a labelled graph $G=(V,E)$, defined its Cartan matrix $(c_{xy})_{x,y\in V}$ where $$c_{xy}=2\delta_{xy}-\sum_{\textrm{all edges }x\stackrel{(a,b)}\longrightarrow y} a$$where $\delta_{xy}=1$ if $x=y$ and vanishes if $x\neq y$. A function $n: V\to \mathbb{Z}_{>0}$ is called subadditive if $$\forall y\in V, \qquad \sum_{x\in V} n_xc_{xy}\geq 0$$ And is called additive if $$\forall y\in V, \qquad \sum_{x\in V} n_xc_{xy}= 0$$ Clearly, subadditivity implies additivity.
We will show that Dynkin diagram and Euclidean diagrams are the only finite connected diagrams admitting a subadditive function, and Euclidean diagrams are the only ones admitting an addtive function.
We need three lemmas.
Lemma 1. Any finite connected labelled graph $T$, either $T$ is a Dynkin diagram or there is a Euclidean diagram smaller than $T$. Where "smaller" means both "subgraph" and "smaller" in the numbers of the label. Note that in the definition of labelled graph, all the number in labels are taken to be positive integers.
Proof is just exclude the possibilities of not being Dynkin diagram.
Lemma 2. Suppose $T$ and $T'$ are connected labelled graphs and $T$ is strickly smaller than $T'$, if $n$ is a subadditve function on $T'$, then the restriction of $n$ over $T$ is subadditve but not additive.
Proof. For any vertex $y$ of $T$, we have $$0\leq \sum_x n_xc'_{xy}=2n_y-\sum_{\textrm{all edges } x\stackrel{(a,b)}\longrightarrow y\textrm{ in $T'$}}n_x a\geq 2n_y-\sum_{\textrm{all edges } x\stackrel{(a,b)}\longrightarrow y\textrm{ in $T$}}n_x a=\sum_x n_xc_{xy}$$Since $T$ is strictly smaller, the inequality can not achieve for some $y$. The proof is complete. $\square$
Lemma 3. Any finite connected labelled graph $T$, if $T^{\mathsf{op}}$ admits an additive function, then any subadditve function over $T$ is additive.
Proof. Assume $T^{\mathsf{op}}$ admits an additive function $n$, then $\sum c_{yx}n_x=0$. Then for any subadditive function $m$ over $T$, we have$$0=\sum_ym_y\bigg(\sum_{x} c_{yx}n_x\bigg)=\sum_{x}n_x \bigg(\sum_{y}m_yc_{yx}\bigg)$$The sum is a series of non-negetive integer, so we have $\sum_{y}m_yc_{yx}=0$. $\square$
And it suffices to prove there exists an additive function on each Euclidean diagrams. As following
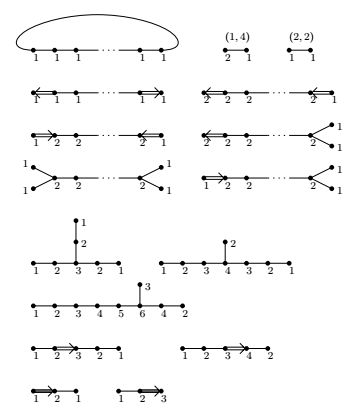
(To check the additivity, just check that the sum of number "come in" equals to 2 times of the number of point. )
Now, we can conclude the discription of Euclidean diagrams and Dynkin diagrams
Theroem. If a finite connected labelled graph $T$ admits a subaddtive function iff $T$ is either a Dynkin diagram or a Euclidean diagram. If furthermore, $T$ admits an additive function iff$T$ is a Euclidean diagram.
Proof. By the above lemmas.
Characterization using positive definity of Cartan's matrix
Using the characterization above, one can easily deriver the following characerization
Theroem. Given a finite connected labelled graph $T$, let $C$ be its Cartan matrix. $C$ is semidefinite iff $T$ is either a Dynkin diagram or a Euclidean diagram. Furthermore, $C$ is positive definite iff $T$ is a Dynkin diagram.
Proof. For an Euclidean diagram, let $n$ be an additive function, note that the condition of additivity implies for any fixed $x$, $\sum_{y\neq x}\frac{n_y c_{yx}}{n_x}=-2$, then$$\begin{array}{rl}\sum_{x,y\in V}a_xa_yc_{xy} & =2\sum_{x\in V}a_x^2+\sum_{x\neq y} a_xa_yc_{xy} \\ & =-\sum_{x\in V}\frac{a_x^2n_yc_{yx}}{n_x}+\sum_{x\neq y} a_xa_yc_{xy} \\& = -\frac{1}{2}\sum_{x\neq y}\big(\frac{a_x^2n_yc_{yx}}{n_x}+\frac{a_y^2n_xc_{xy}}{n_y}\big)+\sum_{x\neq y} a_xa_yc_{xy} \\ & =-\frac{1}{2}\sum_{x\neq y} n_xn_yc_{xy}\big(\frac{a_x}{n_x}-\frac{a_y}{n_y}\big)^2\geq 0\end{array}$$ Then, it is not difficult to see that the Cartan matrix is positive definite for Dynkin diagram, merely because Dynkin diagrams are exactly the graph strictly smaller than Euclidean diagrams. To prove when $T$ is neither a Dynkin diagram nor a Euclidean diagram. By the lemma above, there are some Euclidean diagram $T'$ strictly smaller than $T$. If $T$ contains all points of $T'$, then $(n_x)$ such that $\sum n_xn_yc_{xy}<0$, otherwise, pick a point, say $v$, in $T$ but not in $T'$, then $n'_x=\begin{cases}n_x & \textrm{$x$ in $T$} \\ \epsilon & x=v \\ 0 & \textrm{otherwise}\end{cases}$, then $$\begin{array}{rl}\sum n'_xn'_y c_{xy} & =\sum n_xn_yc_{xy}+2\epsilon^2+\underbrace{\bigg(\sum_{x\in V}c_{xv}\bigg)}_{<0}\epsilon \\ & \leq 0+ 2\epsilon^2+\underbrace{\bigg(\sum_{x\in V}c_{xv}\bigg)}_{<0}\epsilon\end{array}$$Take $\epsilon$ sufficient small, the above is strictly negetive. $\square$
Characterization of Dynkin diagrams的更多相关文章
- EF:split your EDMX file into multiple diagrams
我们可以把一个EDMX文件划分为多个类图: 1.在VS中打开EDMX设计器: 2.切换到“模型浏览器”属性设置窗口: 3.在diagrams上右键菜单中选择“添加新的关系图”: 4.在原来的关系图上可 ...
- How to generate UML Diagrams from Java code in Eclipse
UML diagrams compliment inline documentation ( javadoc ) and allow to better explore / understand a ...
- codeforces Diagrams & Tableaux1 (状压DP)
http://codeforces.com/gym/100405 D题 题在pdf里 codeforces.com/gym/100405/attachments/download/2331/20132 ...
- (转) Deep learning architecture diagrams
FastML Machine learning made easy RSS Home Contents Popular Links Backgrounds About Deep learning ar ...
- Class diagrams
So far we have seen stack diagrams, which show the state of a program, and object diagrams, which sh ...
- [RxJS] Marble diagrams in ASCII form
There are many operators available, and in order to understand them we need to have a simple way of ...
- 条形图(diagrams)
条形图(diagrams) 题目描述 小 虎刚上了幼儿园,老师让他做一个家庭作业:首先画3行格子,第一行有3个格子,第二行有2个格子,第三行有3个格子.每行的格子从左到右可以放棋子,但要 求除第一行外 ...
- Generating Sankey Diagrams from rCharts
A couple of weeks or so ago, I picked up an inlink from an OCLC blog post about Visualizing Network ...
- Reliability diagrams
Reliability diagrams (Hartmann et al. 2002) are simply graphs of the Observed frequency of an event ...
随机推荐
- Tomcat 对 HTTP 协议的实现(上)
协议,直白的说就是存在一堆字节,按照协议指定的规则解析就能得出这堆字节的意义.HTTP 解析分为两个部分:解析请求头和请求体. 请求头解析的难点在于它没有固定长度的头部,也不像其他协议那样提供数据包长 ...
- Java将数据按列写入Excel并设置格式(字体、背景色、自动列宽、对齐方式等)
本文使用jxl.jar工具类库将数据按列写入Excel并设置格式(字体.背景色.自动列宽.对齐方式等). /** * 按列写入Excel并设置格式 * * @param outputUrl * 输出路 ...
- 痞子衡嵌入式:飞思卡尔i.MX RT系列MCU开发那些事 - 索引
大家好,我是痞子衡,是正经搞技术的痞子.本系列痞子衡给大家介绍的是飞思卡尔i.MX RT系列微控制器相关知识. 飞思卡尔半导体(现恩智浦半导体)于2017年开始推出的i.MX RT系列开启了高性能MC ...
- c#进阶一:使用ILDASM来查看c#中间语言
平时工作的时候总是使用ctrl c+ctrl v去快速开发实现业务功能,但是在工作之余,我们也应该要注意静下心来去学习和提高自己.进阶的文章随性来写,不定时更新.希望可以和大家共同学习,共同进步.今天 ...
- c#下载文件选择路径控件
<input id="file1" style="width: 240px; height: 20px; display:none;" type=&quo ...
- Java开发笔记(八十一)如何使用系统自带的注解
之前介绍继承的时候,提到对于子类而言,父类的普通方法可以重写也可以不重写,但是父类的抽象方法是必须重写的,如果不重写,编译器就直接在子类名称那里显示红叉报错.例如,以前演示抽象类用法之时,曾经把Chi ...
- 【Redis】LRU算法和Redis的LRU实现
LRU原理 在一般标准的操作系统教材里,会用下面的方式来演示 LRU 原理,假设内存只能容纳3个页大小,按照 7 0 1 2 0 3 0 4 的次序访问页.假设内存按照栈的方式来描述访问时间,在上面的 ...
- MYSQL SQL语句优化
1.EXPLAIN 做MySQL优化,我们要善用EXPLAIN查看SQL执行计划. 下面来个简单的示例,标注(1.2.3.4.5)我们要重点关注的数据: type列,连接类型.一个好的SQL语句至少要 ...
- 学习day02
day021.结构标记 ***** 做布局 1.<header>元素 <header></header> ==> <div id="heade ...
- webpack4.x笔记-配置基本的前端开发环境(一)
webpack的基本使用 webpack 本质上是一个打包工具,它会根据代码的内容解析模块依赖,帮助我们把多个模块的代码打包.借用 webpack 官网的图片: 虽然webpack4.x的版本可以零配 ...
