终极CRUD-3-用Jackson解析json
- 1 jackson json基本介绍和使用
- 2 jackson 常用的注解
- 3 jackson 处理泛型转换
- 4 jackson 自定义序列化和反序列化规则
- 4.1 enable disable configure
- 4.2 SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT
- 4.3 SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS
- 4.4 SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS
- 4.5 DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES
- 4.6 DeserializationFeature.ACCEPT_EMPTY_STRING_AS_NULL_OBJECT
- 4.7 SerializationFeature.WRAP_ROOT_VALUE
- 5 踩坑心得
- 6 感悟
1 jackson json基本介绍和使用
网上有很多关于jackson和json的介绍和使用,我就不重复造轮子了,本篇博客主要介绍jackson的高级应用和博主我自己踩坑心得。
如果对json和jackson不熟悉的朋友,可以看下面两篇博客。
https://www.runoob.com/json/json-tutorial.html JSON教程
https://blog.csdn.net/u011054333/article/details/80504154#commentBox jackson快速入门
2 jackson 常用的注解
2.1@JsonProperty
这个注解非常有用,看下面代码:
public class Person {
@JsonProperty("username")
private String name;
private Integer age;
//省略getter setter
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Person person = new Person("adai",21);
System.out.println(mapper.writeValueAsString(person));
}
输出为 {"age":21,"username":"adai"}
可以看到,在序列化的json串中,username替代了name
2.2 @JsonIgnore
public class Person {
@JsonIgnore
private String name;
private Integer age;
//省略getter setter
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Person person = new Person("adai",21);
System.out.println(mapper.writeValueAsString(person));
}
输出为 {"age":21}
2.3 @JsonIgnoreProperties
①这个注解和@JsonIgnore有些类似,不过主要是作用在类上面
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"name","age"})
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
//省略getter setter
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Person person = new Person("adai", 21, 172D);
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(json);
}
输出为 {"height":172.0}
可以看出@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"name","age"}) 忽略了name和age属性,在序列化的时候,会忽略这两个属性
②@JsonIgnoreProperties注解还有一个ignoreUnknown属性,主要用在反序列化上
在正常情况下,如果我们json串中有一些key值和我们的POJO对象不匹配,那么将会抛出异常。
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
System.out.println(mapper.readValue(" {\"name\":\"adai\",\"age\":21,\"height222\":172.0}", Person.class));
// !!注意height222与我们的pojo对象不匹配
}
程序将会抛出异常
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.UnrecognizedPropertyException: Unrecognized field "height222" (class com.antiy.common.adai.demo.Person), not marked as ignorable (3 known properties: "name", "age", "height"])
at [Source: (String)"{"name":"adai","age":21,"height222":172.0}"; line: 1, column: 42] (through reference chain: com.antiy.common.adai.demo.Person["height222"])
此时如果我们在Person类上加上@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
@JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true)
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
//省略getter setter
}
输出为 Person(name=adai, age=21, height=null)
③使用 mapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES); 也可以达到同样的目的
④建议:ignoreUnknown和FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES尽量不要设置为true,如果反序列化的时候,json串中的相关key和POJO属性不匹配,就让程序抛出异常,即使发现错误,不过具体情况还需要参考具体业务,jackson默认该值为false
2.4 @JsonTypeName和@JsonTypeInfo
主要作用:在json串中又包装了一层
①正常情况下,序列化的字符串是 {"name":"adai","age":21,"height":172.0}
当我们在Person类上加上@@JsonTypeName和@JsonTypeInfo时
@JsonTypeName(value = "user222")
@JsonTypeInfo(include = JsonTypeInfo.As.WRAPPER_OBJECT, use = JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME)
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
//省略getter setter
}
输出为 {"user222":{"name":"adai","age":21,"height":172.0}}
②我们也可以使用@JsonRootName("user222")和mapper.enable(SerializationFeature.WRAP_ROOT_VALUE)来达到同样的效果
@JsonRootName("user222")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
//省略getter setter
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.enable(SerializationFeature.WRAP_ROOT_VALUE);
Person person = new Person("adai", 21, 172D);
System.out.println(mapper.writeValueAsString(person));
}
输出为 {"user222":{"name":"adai","age":21,"height":172.0}}
2.5 @JsonFormat
主要用在Date属性上
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
private Date date;
//省略getter setter
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Person person = new Person("adai", 21, 172D,new Date());
System.out.println(mapper.writeValueAsString(person));
}
输出为 {"name":"adai","age":21,"height":172.0,"date":1558842751645}
注意:jackson默认会将Date类型序列化成时间戳,这是因为SerializationFeature中的WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS(true),该值默认为true,当我们手动将改值设为false时。
mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
输出为 {"name":"adai","age":21,"height":172.0,"date":"2019-05-26T03:56:38.660+0000"}
这时候date就不再是时间戳了,但是和我们中国的时间格式有一些差别,这个时候就可以使用@JsonFormat
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
@JsonFormat(pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS",timezone="GMT+8")
private Date date;
//省略getter setter
}
输出为 {"name":"adai","age":21,"height":172.0,"date":"2019-05-26 11:58:07:296"}
2.6 @JsonAnyGetter
该注解主要用在序列化:
1.方法是非静态,没有参数的,方法名随意
2.方法返回值必须是Map类型
3.在一个实体类中仅仅用在一个方法上
4.序列化的时候json字段的key就是返回Map的key,value就是Map的value
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@JsonAnyGetter // 注意这个注解
public Map<String, Object> getOther(){
return map;
}
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("adai");
person.setAge(21);
Map<String, Object> other = person.getOther();
other.put("city", "chengdu");
System.out.println(mapper.writeValueAsString(person));
}
输出为 {"name":"adai","age":21,"city":"chengdu"}
当我们在public Map<String, Object> getOther()上去掉@JsonAnyGetter这个注解的时候
输出为 {"name":"adai","age":21,"other":{"city":"chengdu"}}
可以看出加上这个注解以后序列化的时候就会将Map里面的值也相当于实体类里面的字段给显示出来了。
2.7 @JsonAnySetter
主要作用于反序列化上
1.用在非静态方法上,注解的方法必须有两个参数,第一个是json字段中的key,第二个是value,方法名随意
2.反序列化的时候将对应不上的字段全部放到Map里面
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@JsonAnySetter //注意这个注解
public void setOther(String key, String value){
this.map.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", map=" + map +
'}';
}
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String json = "{\"name\":\"adai\",\"age\":21,\"color\":\"red\",\"city\":12}";
Person person = mapper.readValue(json, Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
输出为 Person{name='adai', age=21, map={color=red, city=12}}
可以看出,使用@JsonAnySetter注解,在json串中多余的属性会被自动放在map属性中,而不会抛出UnrecognizedPropertyException异常
注意:如果是Map<String,String> 那么即使是 {"name":"adai","age":21,"city":12,"weather":true}中的city对应数值 12 和weather对应布尔 true也会被封装进Map<String, String>中,但是Map<String, Integer> 无法封装String或其他类型,只能封装Integer
3 jackson 处理泛型转换
Java中 List和Map主要和泛型打交道,我们重点以这两个为例子,来学习jackson中如何在反序列中保留泛型信息的。
3.1 思考下面程序
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
//省略getter setter
}
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("adai",21));
list.add(new Student("apei",22));
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(list);
List<Student> student = mapper.readValue(json, List.class);
System.out.println(student.get(0).getName());
}
该程序在编译期不会报错,可以执行。那么在运行期的时候可以通过吗?
答案是:否定的。 即程序运行失败
java.lang.ClassCastException: java.util.LinkedHashMap cannot be cast to com.antiy.common.adai.demo.Student
原因①:因为在反序列化的时候,mapper.readValue(json, List.class)并没有告诉jackson,这个json数据可以封装成Student对象,所以jackson默认将[{"name":"adai","age":21},{"name":"apei","age":22}]封装成两个LinkedHashMap对象,然后放入到List集合中。
原因②:既然我们知道了List中保存的对象在运行期是LinkedHashMap,那么为什么在代码中还可以student.get(0).getName(),这就跟Java编译期的泛型擦除有关系了,我们可以看下反编译后的代码
List<Student> student = (List)mapper.readValue(json, List.class);
System.out.println(((Student)student.get(0)).getName());
student.get(0)实际上的对象是LinkedHashMap,然后强转成Student,自然就报错了!
3.1 JavaType
我们可以使用JavaType来保存泛型信息
List:
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
JavaType javaType = mapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, Student.class);
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("adai",21));
list.add(new Student("apei",22));
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(list);
List<Student> student2 = mapper.readValue(json, javaType);
System.out.println(student2.get(0).getName());
}
输出为 adai
Map:
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
JavaType javaType = mapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(Map.class, String.class, Student.class); // 第二个参数是Map的key,第三个参数是Map的value
Map<String, Student> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("first",new Student("adai",21));
map.put("second",new Student("apei",22));
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(map);
Map<String, Student> result = mapper.readValue(json, javaType);
System.out.println(result.get("first").getName());
}
输出为 adai
3.2 TypeReference
TypeReference比javaType模式更加方便,代码也更加简洁
List:
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("adai",21));
list.add(new Student("apei",22));
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(list);
List<Student> student2 = mapper.readValue(json, new TypeReference<List<Student>>(){});
System.out.println(student2.get(0).getName());
}
输出为 adai
Map:
@Test
public void test7() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Map<String, Student> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("first",new Student("adai",21));
map.put("second",new Student("apei",22));
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(map);
Map<String, Student> result = mapper.readValue(json, new TypeReference<Map<String,Student>>(){});
System.out.println(result.get("first").getName());
}
输出为 adai
可以看到,使用TypeReference,只需要在mapper.readValue后面增加一个 new TypeReference匿名内部类,写上自己想要封装的泛型对象,比javaType少了一行mapper.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType声明
4 jackson 自定义序列化和反序列化规则
jackson可以通过SerializationFeature和DeserializationFeature来自定义,序列化和反序列化规则,这也是jackson非常强大的地方。
4.1 enable disable configure
请看下面一个例子:
mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT,true);
mapper.enable(SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT);
mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT);
这里有三个方法,configure方法接受配置名和要设置的值,Jackson 2.5版本新加的enable和disable方法则直接启用和禁用相应属性,我推荐使用后面两个方法。
4.2 SerializationFeature.INDENT_OUTPUT
默认为false,该属性主要是美化json输出
普通序列化的json串:
{"name":"adai","age":21}
开启该属性后的json串:
{
"name" : "adai",
"age" : 21
}
4.3 SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS
默认为true,该属性的意思是,如果一个对象中没有任何的属性,那么在序列化的时候就会报错
public class Teacher {}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
System.out.println(mapper.writeValueAsString(teacher));
}
程序运行将会报错:
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException: No serializer found for class com.antiy.common.adai.entity.Teacher and no properties discovered to create BeanSerializer (to avoid exception, disable SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS)
当我们进行设置: mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS)
输出为 {}
4.4 SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS
默认为true,该属性的意思是,jackson默认会将Date类型的数据序列化成时间戳
详情可以参考 2.5 @JsonFormat
4.5 DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES
默认为true,该属性的意思是,在反序列的时候,如果json串中存在一些key,但是在POJO中没有,那么程序将会抛出异常
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Student student = new Student("adai",21);
String json = "{\"name\":\"adai\",\"age222\":21}"; //Student中没有age222
mapper.readValue(json,Student.class);
}
程序将会报错:UnrecognizedPropertyException: Unrecognized field "age222"
此时我们将FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES设置为false
public void test2() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);
Student student = new Student("adai",21);
String json = "{\"name\":\"adai\",\"age222\":21}";
System.out.println(mapper.readValue(json, Student.class));
}
输出为 Student(name=adai, age=null)
4.6 DeserializationFeature.ACCEPT_EMPTY_STRING_AS_NULL_OBJECT
该值默认为false,该属性的意思是,允许JSON空字符串值(“”)作为null绑定到POJO的属性上,看代码可能比较好理解一点。
public class Teacher {
private Student student;
// 省略 getter setter constructor
}
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String json = "{\"student\":\"\"}";
System.out.println(mapper.readValue(json, Teacher.class));
}
程序将会报错,MismatchedInputException,因为json串中key值student对应的value为 ""
此时我们可以设置DeserializationFeature.ACCEPT_EMPTY_STRING_AS_NULL_OBJECT为true
输出为 Teacher(student=null)
"" 空串 被转换成null值 封装到Teacher对象的student属性中
4.7 SerializationFeature.WRAP_ROOT_VALUE
默认为false,该属性的意思是,将内容包裹为一个JSON属性,属性名由@JsonRootName注解指定。
详情请见 2.4 @JsonTypeName和@JsonTypeInfo
5 踩坑心得
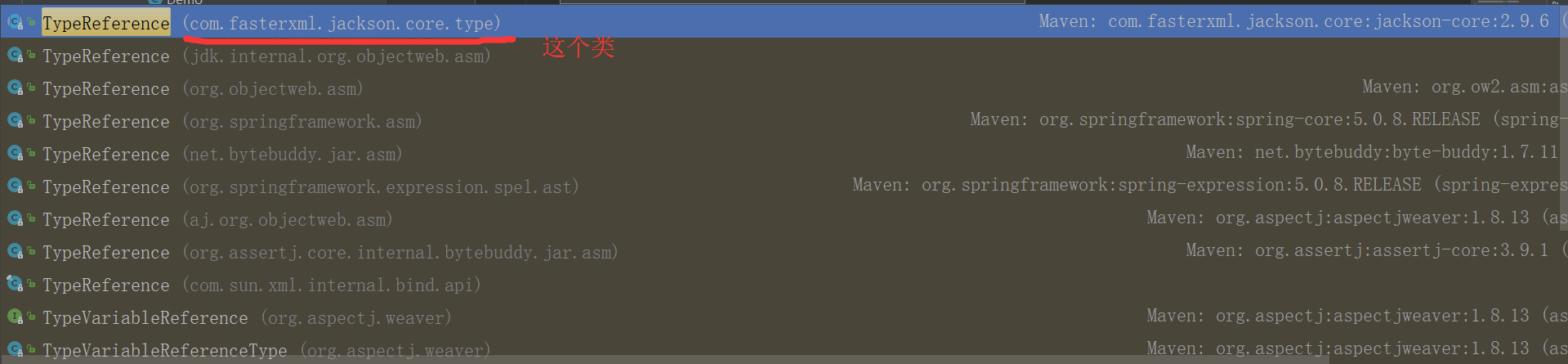
5.1 TypeReference
一定要导入正确的TypeReference类
5.2 DeserializationFeature.ACCEPT_EMPTY_STRING_AS_NULL_OBJECT
注意,该属性只接受POJO的 “” 空字符串转换成 null,在json中,String非常特殊。
请先看4.6章节的内容。
此时我将Teacher中的student类型,换成String
public class Teacher {
private String student;
}
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String json = "{\"student\":\"\"}";
System.out.println(mapper.readValue(json, Teacher.class));
}
输出为 Teacher(student=)
原来以为,如果是String属性,那么""也会转换成null,结果恰恰相反,只有POJO对象,“”才会转换成null
参考 stackoverflow:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22688713/jackson-objectmapper-deserializationconfig-feature-accept-empty-string-as-null-o
6 感悟
6.1 以Json的角度理解Map和List
在对象序列化和反序列化的过程中,自己对Map和List又有了新的理解。
Map可以当做是一个任意对象,保存字段属性。
在 3.1中,如果jackson不知道反序列化的对象,那么jackson将会以LinkedHashMap来进行处理,这正是因为Map的 Key-Value 特性。
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(2);
map.put("name","adai");
map.put("age",21);
System.out.println("map序列化: " + mapper.writeValueAsString(map));
Student student = new Student("adai",21);
System.out.println("student序列化: " + mapper.writeValueAsString(student));
}
输出为 map序列化: {"name":"adai","age":21}
student序列化: {"name":"adai","age":21}
可以看到Map和Student序列化的结果都是一样的,那么在反序列化的时候,可以用Student对象接受的数据,自然而然也可以用Map接收,这就是为什么在关于泛型反序列化的时候,如果jackson不知道具体的对象,全部都会用LinkHashMap接收
List就当做是一个数组
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/u011054333/article/details/80504154#commentBox
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/jackson-advanced-application/index.html
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/AdaiCoffee/
本文以学习、研究和分享为主,欢迎转载。如果文中有不妥或者错误的地方还望指出,以免误人子弟。如果你有更好的想法和意见,可以留言讨论,谢谢!
终极CRUD-3-用Jackson解析json的更多相关文章
- JackSon解析json字符串
JackSon解析json字符串 原文:http://blog.csdn.net/java_huashan/article/details/9353903 概述 jackson解析json例子 准备工 ...
- 记一次FastJSON和Jackson解析json时遇到的中括号问题
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/jadyer/article/details/24395015 完整版见https://jadyer. ...
- 使用 jackson 解析 json 演示样例
首先须要下载3个包,下载地址在Github FasterXML,这三个核心模块各自是: Streaming ("jackson-core") defines low-level s ...
- Jackson 解析json数据之忽略解析字段注解@JsonIgnoreProperties
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/ngl272/article/details/70217104 以前解析json用的惯的就是Google的gson了,用惯了基本就用它了,一直也没发现什 ...
- [转]Jackson 解析json数据之忽略解析字段注解@JsonIgnoreProperties
以前解析json用的惯的就是Google的gson了,用惯了基本就用它了,一直也没发现什么大问题,因为都是解析简单的json数据.但是最近学习springboot,要解析一个比较复杂的json数据.就 ...
- Jackson 解析 JSON 详细教程
点赞再看,动力无限. 微信搜「程序猿阿朗 」. 本文 Github.com/niumoo/JavaNotes 和 未读代码博客 已经收录,有很多知识点和系列文章. JSON 对于开发者并不陌生,如今的 ...
- 使用Jackson解析Json示例
原文http://blog.csdn.net/gebitan505/article/details/17005735 custom.json: { "country":&q ...
- 使用jackson解析JSON数据
本文介绍使用jackson来对json数据进行解析操作 首先,需要去官网下载jackson,本文使用的是(jackson-all-1.9.11.jar) 主要通过ObjectMapper对json进行 ...
- 使用jackson解析json串得到树模型,然后遍历树模型获得需要的数据
Problem:从网址 http://quotes.money.163.com/hs/service/marketradar_ajax.php?host=http%3A%2F%2Fquotes.mon ...
- jackson 解析json问题
1.json串中有key为A,但指定转换的mybean中未定义属性A,会抛异常.处理:mapper.configure(Feature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, fals ...
随机推荐
- Linux命令之---cp/scp
命令简介 cp命令用来复制文件或者目录,是Linux系统中最常用的命令之一.一般情况下,shell会设置一个别名,在命令行下复制文件时,如果目标文件已经存在,就会询问是否覆盖,不管你是否使用-i参数. ...
- Redis实现之压缩列表
压缩列表 压缩列表(ziplist)是列表键和哈希键的底层实现之一,当一个列表键只包含少量列表项,并且每个列表项要嘛是整数值,要嘛是比较短的字符串,那么Redis就会使用压缩列表来做列表键的底层实现. ...
- 通过js date对象获取各种开始结束日期的示例
有时候做一些任务计划的功能时候,需要提供一个开始时间或者结束时间,比如本周结束,本月结束,今天结束等等,因此,我参考网上的资料把相关的实现为一个项目: gitee: https://gitee.com ...
- cf984c Finite or not?
一个十进制分数 \(p/q\) 在 \(b\) 进制下是有限小数的充要条件是 \(q\) 的所有质因子都是 \(b\) 的质因子. First, if \(p\) and \(q\) are not ...
- 安装 Windows Server 2012 Active Directory 只读域控制器 (RODC)(级别 200)
安装 Windows Server 2012 Active Directory 只读域控制器 (RODC)(级别 200) 适用对象:Windows Server 2012 本主题介绍如何创建分步的 ...
- 浅谈我所见的CSS组织风格
1.简单组织(见习级) projectName ├─css | └style.css 优点:简单,单一文件,适合一些简单项目. 缺点:过度集中,没有模块化,无法适应大型项目. 2.公共组织(见习级) ...
- c4d 帮助 prime r16 usage
c4d 帮助 prime cinema 4d prime c4d 基础 前言 usage 开始 双击程序图标 双击一个场景文件 用开始菜单 windows 二选一 从 ...
- Struts2请求流程
1. 一个请求在Struts2框架中的处理步骤: a) 客户端初始化一个指向Servlet容器的请求: b) 根据Web.xml配置,请求首先经过ActionContextCleanUp过滤器,其为可 ...
- BZOJ 1864:[Zjoi2006]三色二叉树(树DP)
三色二叉树 问题描述 输入 仅有一行,不超过500000个字符,表示一个二叉树序列. 输出 输出文件也只有一行,包含两个数,依次表示最多和最少有多少个点能够被染成绿色. 样例输入 1122002010 ...
- 【bzoj2427】[HAOI2010]软件安装 Tarjan+树形背包dp
题目描述 现在我们的手头有N个软件,对于一个软件i,它要占用Wi的磁盘空间,它的价值为Vi.我们希望从中选择一些软件安装到一台磁盘容量为M计算机上,使得这些软件的价值尽可能大(即Vi的和最大).但是现 ...
