MongoDB 基础命令 (MongoDB Shell)
1、我们 mongodb 安装成功后,用上一篇的方法启动 mongodb服务 然后使用 mongodb shell 来做数据库的增删改查
2、创建数据库
语法:
- use 数据库名称
案例:
- > use juyou
- switched to db juyou
- > show dbs
- admin .000GB
- config .000GB
- local .000GB
这时创建完成过,使用命令查询数据库却没有我们刚创建的数据库,这时因为刚创建的数据库没有数据,下面我们在数据库中插入一条数据
- > db.juyou.insert({"name":"聚优福利"})
- WriteResult({ "nInserted" : })
- > show dbs
- admin .000GB
- config .000GB
- juyou .000GB
- local .000GB
这时就能看到刚刚创建的数据库了
3、删除数据库
语法:
- db.dropDatabase()
案例:
首先我们先查询一下所有的数据库
- > show dbs
- admin .000GB
- config .000GB
- juyou .000GB
- local .000GB
然后我们可以使用 db 来查看当前的数据库
- > db
- juyou
当前链接的数据库就是 juyou,如果不是可以使用 use juyou 命令切换到 juyou 数据库
- > use juyou
- switched to db juyou
执行删除命令
- > db.dropDatabase()
- { "dropped" : "juyou", "ok" : }
然后再我们再查询一下所有数据库
- > show dbs
- admin .000GB
- config .000GB
- local .000GB
已经成功删除了
4、创建集合
语法:
- db.createCollection(name, options)
- name:集合名称
- options: 可选参数
案例:
创建一个名为 userinfo 的集合
- > db.createCollection("userinfo")
- { "ok" : }
- > show collections
- userinfo
创建成功后可以使用 show collections 命令查询已有集合
5、插入文档
语法:
- db.集合名称.insert(document)
案例:
在 juyou 集合下的 userinfo 文档中插入一条数据
- > db.userinfo.insert({name:"郭大爷","sex":"男","age":"不详"})
- WriteResult({ "nInserted" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abaf679a3aadbe625070c4f"), "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
插入成功后,可以使用 find() 来查询刚刚插入的数据,下面会对查询做详细的讲解,这里不多做解释
可以看到插入数据后,多了一列 _id 的数据,在文档中 mongodb 会将 _id 字段自动设置为主键,如果不指定mongodb会自动生成
自动生成的 ObjectId 是由时间戳、MachineID(电脑的 mac 地址)、进程ID以及自增计数器组成的,基本上不会重复
- > db.userinfo.insert({"_id":,name:"郭少爷","sex":"男","age":"不详"})
- WriteResult({ "nInserted" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abaf679a3aadbe625070c4f"), "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
也可以在插入数据时指定 _id 值,在之前使用mongodb开发中会指定给 _id 值,使用GUID(全球唯一标识)代替
我们也可以先将要插入的数据定义成变量
- > var user = {name:"郭老师",sex:"男",age:""}
- > db.userinfo.insert(user)
- WriteResult({ "nInserted" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abaf679a3aadbe625070c4f"), "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abb05afa3aadbe625070c50"), "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
mongodb 在3.2版本后 提供了一次插入多条数据的方法 insertMany() ,我们下面把上面的三条数据删除,然后试一下一次插入多条数据
- > db.userinfo.remove({})
- WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- > var users = [
- {
- _id:,
- name:"郭大爷",
- sex:"男",
- age:""
- },
- {
- _id:,
- name:"郭老师",
- sex:"男",
- age:"不详"
- },
- {
- _id:,
- name:"郭少爷",
- sex:"男",
- age:""
- }
- ]
- > db.userinfo.insertMany(users)
- { "acknowledged" : true, "insertedIds" : [ , , ] }
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
这样我们可以直接插入一个数组
6、更新文档
更新文档有 update() 和 save() 两个方法,接下来分别介绍
update() 语法:
- db.collection.update(
- <query>,
- <update>,
- {
- upsert: <boolean>,
- multi: <boolean>,
- writeConcern: <document>
- }
- )
- query:条件,相当于sql update时where条件
- update: 要更新的内容,类似 sql 的 set 后面的内容
案例:
我们先查询一下,郭老师的年龄是不详,现在我们根据主键_id来把年龄更新成20岁
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > db.userinfo.update({"_id":},{$set:{"age":""}})
- WriteResult({ "nMatched" : , "nUpserted" : , "nModified" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
已经成功将郭老师的年龄改成20,然后我们看到在更新命令中又一个 $set 的关键词,这个是更新操作符,接下来我们介绍一下操作符
- $inc:将文档中的数字字段,增加值。比如个郭老师的年龄增加5岁就可以用这个操作符
- $set:将文档中的字段,更新为传入的字段。上面已经演示过了
- $unset:将文档中的某个字段删除
- $rename:给字段重命名
- (下面的操作符都是用来操作文档中类型是数组的字段)
- $push:将传入的参数追加到,文档中某个字段中,要追加的字段必须是数组类型
- $addToSet:在文档某个数组类型的字段中增加值,和上面两个操作符类似,不过这个操作符在增加值时,数组中不能存在要增加的值
- $pop:删除文档数组类型字段中第一个 {$pop:{name:1}} 或者最后一个值 {$pop:{name:-1}}
- $pull:删除和传入参数相等的第一个值
- $pullAll:和 $pull 一样删除值,$pullAll 可以传入数组,一次删除多个值
- 参考文档:https://blog.csdn.net/u014344668/article/details/52460682
save() 语法:
- db.collection.save(
- <document>,
- {
- writeConcern: <document>
- }
- )
- docment:文档
案例:
先查询一下所有的用户,然后把_id为2的用户年龄改为不详。save() 方法会根据主键_id为条件替换文档
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > var user = { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- > db.userinfo.save(user)
- WriteResult({ "nMatched" : , "nUpserted" : , "nModified" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
问题:
save() 方法是以主键_id作条件,来替换文档,如果在传入的文档中没有主键_id,会怎么样?下面我们试一下
- > var user = { "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- > db.userinfo.save(user)
- WriteResult({ "nInserted" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abb2f42a3aadbe625070c51"), "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
也可以执行成功,不过没有更新其中的一个文档,却新插入了一条数据
7、查询文档
语法:
- db.collection.find(query, projection)
- query:查询条件
案例:
可以在 find() 方法后面在 pertty() 方法以格式化的方式显示文档
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abb2f42a3aadbe625070c51"), "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- > db.userinfo.find().pretty()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- {
- "_id" : ObjectId("5abb2f42a3aadbe625070c51"),
- "name" : "郭老师",
- "sex" : "男",
- "age" : "不详"
- }
mongodb query 条件与 sql where 条件 对比
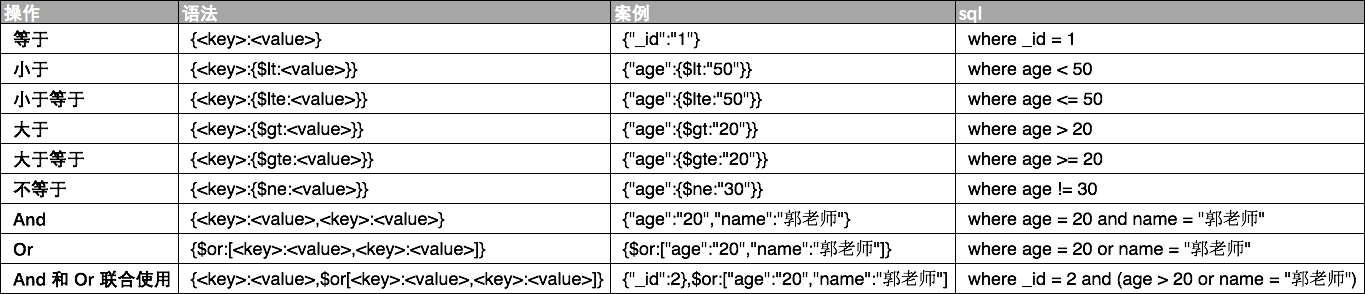
8、$type 操作符
匹配字段类型
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "age" : }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "age" : }
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abb2f42a3aadbe625070c51"), "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- > db.userinfo.find({"age":{$type:}})
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : ObjectId("5abb2f42a3aadbe625070c51"), "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
上面我们把字段 age 类型为 String 的文档查询出来,下面是 mongodb 中类型和数字的对照表
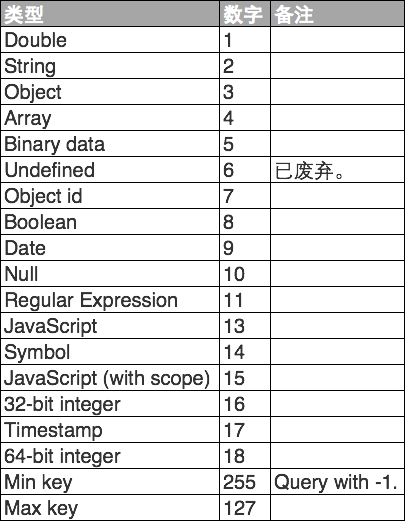
9、Limit() 方法与 Skip() 方法
Limit()
语法
- db.集合名称.find().limit(数量)
取集合中指定数量的数据
案例
- db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > db.userinfo.find().limit()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
Skip()
语法
- db.集合名称.find().skip(数量)
在集合中取数据时跳过指定量数据
案例
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > db.userinfo.find().skip()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
这两个方法配合使用,就可以达到分页的目的
10、排序
语法
- >db.collection.find().sort({key:})
key:指定排序列,1代表正序、-1代表倒序
案例
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > db.userinfo.find().sort({"age":})
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- > db.userinfo.find().sort({"age":-})
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- >
上面分别是不排序、根据age正序、根据age倒序查询
11、删除文档
语法
- db.collection.remove(
- <query>,
- <justOne>
- )
- query:删除的条件
- justOne:如果为 true 或者 1,只删除满足条件的第一个文档
案例
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭大爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > db.userinfo.remove({"sex":"男"},true)
- WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭老师", "sex" : "男", "age" : "不详" }
- { "_id" : , "name" : "郭少爷", "sex" : "男", "age" : "" }
- > db.userinfo.remove({"sex":"男"})
- WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : })
- > db.userinfo.find()
>
12、删除集合
语法
- db.collection.drop()
案例
- > show collections
- userinfo
- > db.userinfo.drop()
- true
- > show collections
- >
MongoDB 基础命令 (MongoDB Shell)的更多相关文章
- MongoDB基础命令笔记
一.创建数据库 use foobar 二.创建集合 db.persons.insert({name:"zhaomin",age:23}) 三.查找 db.persons.find( ...
- MongoDB 基础命令行
本文专门介绍MongoDB的命令行操作.其实,这些操作在MongoDB官网提供的Quick Reference上都有,但是英文的,为了方便,这里将其稍微整理下,方便查阅. 登录和退出 mongo命令直 ...
- MongoDB基础命令
MongoDB 入门命令 查看当前数据库 > show dbs admin 0.000GB config 0.000GB local 0.000GB > -- use databaseNa ...
- MongoDB基础命令及操作
MongoDB:NoSQL数据库 MongoDB中的重要指示点 MongoDB中的三要素 数据库 集合 文档 MongoDB中的数据存储是以Bson的形式存储的,Bson是二进制的json,所以看上去 ...
- 2、链接数据库+mongodb基础命令行+小demo
链接数据库并且打印出数据的流程:1.在CMD里面输入 mongod 2.在CMD里面输入 mongo 3.在输入mongodb命令行里面进行操作,首先输入 show dbs 来查看是否能够链接得上库4 ...
- MongoDB 基础命令——数据库表的增删改查——遍历操作表中的记录
分组排序查询最大记录 //对 "catagory" 不等于 null 的数据进行分组查询,且查询结果倒序 db.getCollection('userAccount').aggre ...
- MongoDB 基础命令使用学习记录
1. 启动 mongod 几个常用命令说明:--dbpath : 指定数据库相关文件的存储目录 --logpath: 指定日志文件的存储目录 --port: 指定数据库的端口,默认是 27017 -- ...
- Mongodb基础知识----Mongodb权威指南阅读
文档是Mongodb中数据的基本单元,类型关系型数据库中的行,每个文档都有一个键值唯一的键_id.集合可以看做拥有动态模式的表. Mongodb一个实例可以拥有多个相互独立的数据库. Mongodb区 ...
- Linux 基础命令3 shell
echo 显示一行文本 各种展开的实例 波浪线展开 算术表达式展开 支持的运算 奇怪的花括号展开 花括号的..用法 花括号(任选一个)的嵌套 参数展开$符很重要哦(一种展开做另一种的参数) 命令的替换 ...
随机推荐
- T型知识实践结构的力量(转载)
最近在做的一些新的事情,这其中获得的一些新的思考. T型的知识积累,深度的挖掘可以通过"举一反三"的应用在广度上,广度可以通过"交叉验证"加强我们的认识,可以说 ...
- C和指针之学习笔记(4)
第9章 字符串 字符串的输入与输出 int ch; char strings[80]; FILE *input; (1)scanf(“%c”,&ch); printf(“%c \n” ...
- nginx+php-fpm 配置和错误总结
<strong>空白页面:</strong>需要这个参数: fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_scrip ...
- hihocoder1489 Legendary Items (微软2017年预科生计划在线编程笔试)
http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1489 笔试题第一道,虽然说第一道都很水,但是我感觉这题不算特别水把..这道题我就卡住了我记得,tle,最后只有30分 ...
- PHP自动加载下——PSR4
1.先来介绍一下PSR规范 PHP-FIG,它的网站是:www.php-fig.org.就是这个联盟组织发明和创造了PSR规范,其中自动加载涉及其中两个规范,一个是PSR0,一个是PSR4, PSR0 ...
- 用C++/CLI搭建C++和C#之间的桥梁(一)—— 简介
C#和C++是非常相似的两种语言,然而我们却常常将其用于两种不同的地方,C#得益于其简洁的语法和丰富的类库,常用来构建业务系统.C++则具有底层API的访问能力和拔尖的执行效率,往往用于访问底层模块和 ...
- ADC In An FPGA
http://davidkessner.wordpress.com/2011/05/01/adc-in-an-fpga/ Geek Alert! What follows is very techn ...
- LINQ中的动态排序
使用Linq动态属性排序 使用反射: public static Func<T,Tkey> DynamicLambda<T, Tkey>(string propertyName ...
- SQLiteOpenHelper 操作不成功
SDK和ADT为22.6.2版本号 project为4.4.2 今天在练习SQLiteOpenHelper里,使用的是三个JAVA文件操作.DatabaseHelper.java,Const.java ...
- 要使用C#实现一个ActiveX控件
要使用C#实现一个ActiveX控件,需要解决三个问题: 1.使.NET组件能够被COM调用 2.在客户机上注册后,ActiveX控件能通过IE的安全认证 3.未在客户机上注册时,安装包能通过IE的签 ...
