rocketmq刷盘过程
- public enum FlushDiskType {
- // 同步刷盘
- SYNC_FLUSH,
- // 异步刷盘
- ASYNC_FLUSH
- }
| 线程服务 | 场景 | 写消息性能 |
| CommitRealTimeService | 异步刷盘 && 开启内存字节缓冲区 | 第一 |
| FlushRealTimeService | 异步刷盘 | 第二 |
| GroupCommitService | 同步刷盘 | 第三 |
其中CommitRealTimeService是老一些版本中没有的,它为开启内存字节缓存的刷盘服务。
介绍各个线程工作之前,先需要重点了解一下waitForRunning方法,因为在三个刷盘服务线程中都频繁使用该方法:
- protected void waitForRunning(long interval) {
- if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
- this.onWaitEnd();
- return;
- }
- //entry to wait
- waitPoint.reset();
- try {
- waitPoint.await(interval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- log.error("Interrupted", e);
- } finally {
- hasNotified.set(false);
- this.onWaitEnd();
- }
- }
- shutdown()
- stop()
- wakeup()
这里我们关心的是wakeup()方法,调用wakeup方法的几处如下
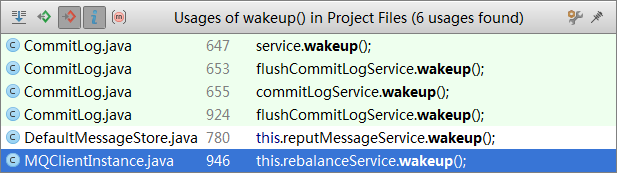
- public void run() {
- CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
- while (!this.isStopped()) {
- try {
- this.waitForRunning(10);
- this.doCommit();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
- }
- }
- // Under normal circumstances shutdown, wait for the arrival of the
- // request, and then flush
- try {
- Thread.sleep(10);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- CommitLog.log.warn("GroupCommitService Exception, ", e);
- }
- synchronized (this) {
- this.swapRequests();
- }
- this.doCommit();
- CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
- }
- if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
- final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
- if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
- GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes());
- service.putRequest(request);
- boolean flushOK = request.waitForFlush(this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
- if (!flushOK) {
- log.error("do groupcommit, wait for flush failed, topic: " + messageExt.getTopic() + " tags: " + messageExt.getTags()
- + " client address: " + messageExt.getBornHostString());
- putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
- }
- } else {
- service.wakeup();
- }
- }
这条消息是否已经刷盘成功进行汇报的逻辑 -- waitForFlush方法:
- public static class GroupCommitRequest {
- private final long nextOffset;
- private final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
- private volatile boolean flushOK = false;
- public GroupCommitRequest(long nextOffset) {
- this.nextOffset = nextOffset;
- }
- public long getNextOffset() {
- return nextOffset;
- }
- public void wakeupCustomer(final boolean flushOK) {
- this.flushOK = flushOK;
- this.countDownLatch.countDown();
- }
- public boolean waitForFlush(long timeout) {
- try {
- // 阻塞当前工作线程,等待时间5s后或者countDownLatch记数为0时,停止阻塞,执行下一条语句
- this.countDownLatch.await(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- return this.flushOK;
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- log.error("Interrupted", e);
- return false;
- }
- }
- }
- private void swapRequests() {
- List<GroupCommitRequest> tmp = this.requestsWrite;
- this.requestsWrite = this.requestsRead;
- this.requestsRead = tmp;
- }
- private void doCommit() {
- //
- synchronized (this.requestsRead) {
- if (!this.requestsRead.isEmpty()) {
- for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) {
- // There may be a message in the next file, so a maximum of
- // two times the flush
- boolean flushOK = false;
- for (int i = 0; i < 2 && !flushOK; i++) {
- flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
- if (!flushOK) {
- CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
- }
- }
- req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK);
- }
- long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();
- if (storeTimestamp > 0) {
- CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
- }
- this.requestsRead.clear();
- } else {
- // Because of individual messages is set to not sync flush, it
- // will come to this process
- CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
- }
- }
- }
- public boolean flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
- boolean result = true;
- MappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.flushedWhere, false);
- if (mappedFile != null) {
- long tmpTimeStamp = mappedFile.getStoreTimestamp();
- int offset = mappedFile.flush(flushLeastPages);
- long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;
- result = where == this.flushedWhere;
- this.flushedWhere = where;
- if (0 == flushLeastPages) {
- this.storeTimestamp = tmpTimeStamp;
- }
- }
- return result;
- }
commit
- public boolean commit(final int commitLeastPages) {
- boolean result = true;
- MappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.committedWhere, false);
- if (mappedFile != null) {
- int offset = mappedFile.commit(commitLeastPages);
- long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;
- result = where == this.committedWhere;
- this.committedWhere = where;
- }
- return result;
- }
rocketmq刷盘过程的更多相关文章
- RocketMQ消息丢失解决方案:同步刷盘+手动提交
前言 之前我们一起了解了使用RocketMQ事务消息解决生产者发送消息时消息丢失的问题,但使用了事务消息后消息就一定不会丢失了吗,肯定是不能保证的. 因为虽然我们解决了生产者发送消息时候的消息丢失问题 ...
- RocketMQ中Broker的刷盘源码分析
上一篇博客的最后简单提了下CommitLog的刷盘 [RocketMQ中Broker的消息存储源码分析] (这篇博客和上一篇有很大的联系) Broker的CommitLog刷盘会启动一个线程,不停地 ...
- 【RocketMQ】消息的刷盘机制
刷盘策略 CommitLog的asyncPutMessage方法中可以看到在写入消息之后,调用了submitFlushRequest方法执行刷盘策略: public class CommitLog { ...
- HTC A510C电信手机刷机过程
HTC A510C电信手机刷机过程记录 Writed by Peter Hu(2014.6.7) ON WIN7_64 刷机需要的步骤: 1) 将S-ON加密保护式去掉,改成S-OFF模式,这样才能 ...
- mq刷盘方式
Broker 在收到Producer发送过来的消息后,会存入CommitLog对应的内存映射区中,见CommitLog类的putMessage方法.该方法执行OK后,会判断存储配置中刷盘模式:同步or ...
- Rocket重试机制,消息模式,刷盘方式
一.Consumer 批量消费(推模式) 可以通过 consumer.setConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize(10);//每次拉取10条 这里需要分为2种情况 Consumer端先 ...
- MySQL InnoDB 日志管理机制中的MTR和日志刷盘
1.MTR(mini-transaction) 在MySQL的 InnoDB日志管理机制中,有一个很重要的概念就是MTR.MTR是InnoDB存储擎中一个很重要的用来保证物理写的完整性和持久性的机制. ...
- 【软件安装与环境配置】TX2刷机过程
前言 使用TX2板子之前需要进行刷机,一般都是按照官网教程的步骤刷机,无奈买不起的宝宝只有TX2核心板,其他外设自己搭建,所以只能重新制作镜像,使用该镜像进行刷机. 系统需求 1.Host Platf ...
- 从CM刷机过程和原理分析Android系统结构
前面101篇文章都是分析Android系统源代码,似乎不够接地气. 假设能让Android系统源代码在真实设备上跑跑看效果,那该多好.这不就是传说中的刷ROM吗?刷ROM这个话题是老罗曾经一直避免谈的 ...
随机推荐
- SpringMVC传递数据的流线图
流程含义解释:(1)HTTP请求到达web服务器,web服务器将其封装成一个httpServletRequest对象(2)springMVC框架截获这个httpServletRequest对象(3)s ...
- Android Activity活动状态及生存周期
1.活动状态 每个活动在其生命周期中最多可能会有4中状态. (1)运行状态 当一个活动位于返回栈的栈顶时,此时活动就处于运行状态.系统不会回收处于运行状态的活动. (2)暂停状态 当一个活动不再处于栈 ...
- Snippet取表字段说明和详细信息
IF OBJECT_ID (N'dbo.GetDetails', N'IF') IS NOT NULL DROP FUNCTION dbo.GetDetails; GO create function ...
- vss和vs2008组合搭建源代码管理器
用源代码管理项目,是为了方便开发和管理组内项目,一个组做的是同一套项目,彼此知道各个模块的进度和开发情况,这也是开发项目所需要的.今天整理了VSS的安装.创建.连接及添加项目等操作. 一.安装VSS( ...
- Top Android App使用的组件
唱吧_462 smack:de.measite.smack:??? ???:org.apache:??? smack:org.jivesoftware.smack:XMPP客户端类库 dnsjava: ...
- AngularJS.js: 杂项
ylbtech-AngularJS.js: 杂项 AngularJS诞生于2009年,由Misko Hevery 等人创建,后为Google所收购.是一款优秀的前端JS框架,已经被用于Google的多 ...
- Django缓存,信号,序列化
缓存 1.缓存的简介 在动态网站中,用户所有的请求,服务器都会去数据库中进行相应的增,删,查,改,渲染模板,执行业务逻辑,最后生成用户看到的页面. 当一个网站的用户访问量很大的时候,每一次的的后台操作 ...
- kubernetes 学习 pod相关
1 pod的状态: Pending, Running, Succeeded, Failed, Unknown 2 pod重启策略: Always(自动重启,是默认的) . OnFailure(容 ...
- 如何用xMind打开.mmap文件
首先右键单击mmap格式文档,选择“属性” > “更改了打开方式” > 选择使用Xmind软件打开.然后双击mmap格式文档,就可以用Xmind打开了!
- RefWorks
RefWorks公司简介/RefWorks 编辑 RefWorks是美国剑桥信息集团的子公司,是ProQuest 的姊妹公司.该公司于2001年由参考文献管理领域的一些专家组建而成,并致力于为学术机构 ...
