How an Event Enters a Cocoa Application
How an Event Enters a Cocoa Application
An event is a low-level record of a user action that is usually routed to the application in which the action occurred. A typical event in OS X originates when the user manipulates an input device attached to a computer system, such as a keyboard, mouse, or tablet stylus. When the user presses a key or clicks a button or moves a stylus, the device detects the action and initiates a transfer of data to the device driver associated with it. Through the I/O Kit, the device driver creates a low-level event, puts it in the window server's event queue, and notifies the window server. The window server dispatches the event to the appropriate run-loop port of the target process. From there the event is forwarded to the event-handling mechanism appropriate to the application environment. Figure 1-1 depicts this event-delivery system.
Figure 1-1 The event stream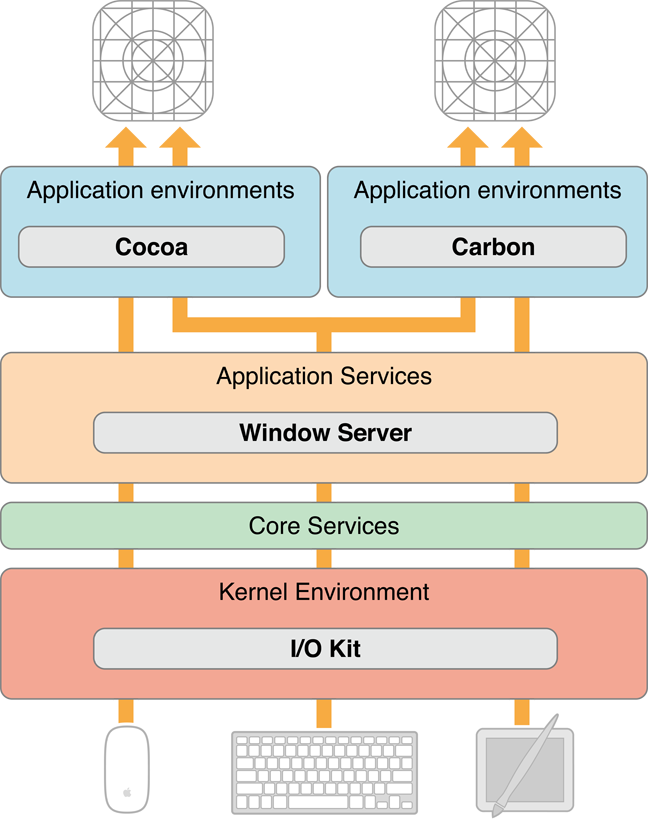
Note: Applications normally receive events from the keyboard and mouse only when they are in the foreground (that is, active). Although applications running in the background do not normally receive key and mouse events, low-level mechanisms called event taps make it possible for a background application to receive events and act upon them.
Before it dispatches an event to an application, the window server processes it in various ways; it time-stamps it, annotates it with the associated window and process port, and possibly performs other tasks as well. As an example, consider what happens when a user presses a key. The device driver translates the raw scan code into a virtual key code which it then passes off (along with other information about the key-press) to the window server in an event record. The window server has a translation facility that converts the virtual key code into a Unicode character.
In OS X, events are delivered as an asynchronous stream. This event stream proceeds “upward” (in an architectural sense) through the various levels of the system—the hardware to the window server to the Event Manager—until each event reaches its final destination: an application. As it passes through each subsystem, an event may change structure but it still identifies a specific user action.
Note: Lower levels of the system trap and handle some events early in the event stream. These events are never routed to a Cocoa application. These events are generated by reserved keys or key combinations, such as the power and media-eject keys.
Every application has a mechanism specific to its environment for receiving events from the window server. For a Cocoa application, that mechanism is called the main event loop. A run loop, which in Cocoa is an NSRunLoop object, enables a process to receive input from various sources. By default, every thread in OS X has its own run loop, and the run loop of the main thread of a Cocoa application is called the main event loop. What especially distinguishes the main event loop is an input source called the event source, which is constructed when the global NSApplication object (NSApp) is initialized. The event source consists of a port for receiving events from the window server and a FIFO queue—the event queue—for holding those events until the application can process them, as shown in Figure 1-2.
Figure 1-2 The main event loop, with event source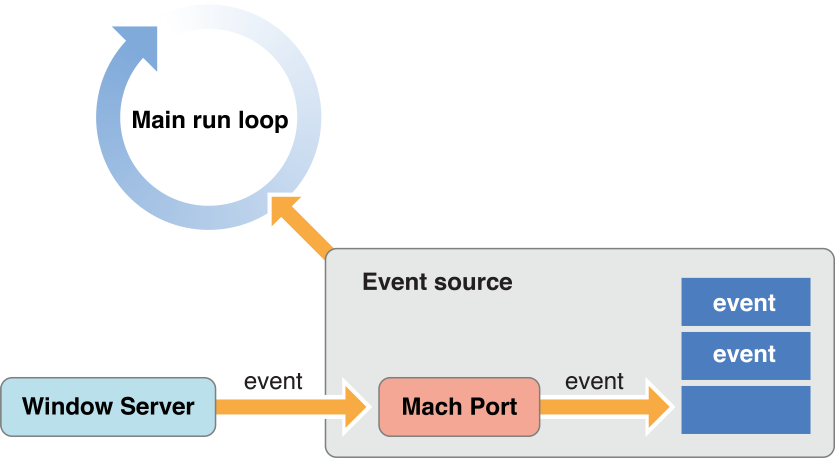
A Cocoa application is event driven: It fetches an event from the queue, dispatches it to an appropriate object, and, after the event is handled, fetches the next event. With some exceptions (such as modal event loops) an application continues in this pattern until the user quits it. The following section, Event Dispatch, describes how an application fetches and dispatches events.
Events delivered via the event source are not the only kinds of events that enter Cocoa applications. An application can also respond to Apple events, high-level interprocess events typically sent by other processes such as the Finder and Launch Services. For example, when users double-click an application icon to open the application or double-click a document to open the document, an Apple event is sent to the target application. An application also fetches Apple events from the queue but it does not convert them into NSEvent objects. Instead an Apple event is handled directly by an event handler. When an application launches, it automatically registers several event handlers for this purpose. For more on Apple events and event handlers, see Apple Events Programming Guide.
Event Dispatch
In the main event loop, the application object (NSApp) continuously gets the next (topmost) event in the event queue, converts it to an NSEvent object, and dispatches it toward its final destination. It performs this fetching of events by invoking the nextEventMatchingMask:untilDate:inMode:dequeue:method in a closed loop. When there are no events in the event queue, this method blocks, resuming only when there are more events to process.
After fetching and converting an event, NSApp performs the first stage of event dispatching in the sendEvent: method. In most cases NSApp merely forwards the event to the window in which the user action occurred by invoking the sendEvent: method of that NSWindow object. The window object then dispatches most events to the NSView object associated with the user action in an NSResponder message such as mouseDown: or keyDown:. An event message includes as its sole argument an NSEvent object describing the event.
The object receiving an event message differs slightly by type of event. For mouse and tablet events, the NSWindow object dispatches the event to the view over which the user pressed the mouse or stylus button. It dispatches most key events to the first responder of the key window. Figure 1-3 and Figure 1-4illustrate these different general delivery paths. The destination view may decide not to handle the event, instead passing it up the responder chain (see The Responder Chain).
Figure 1-3 Path of a mouse event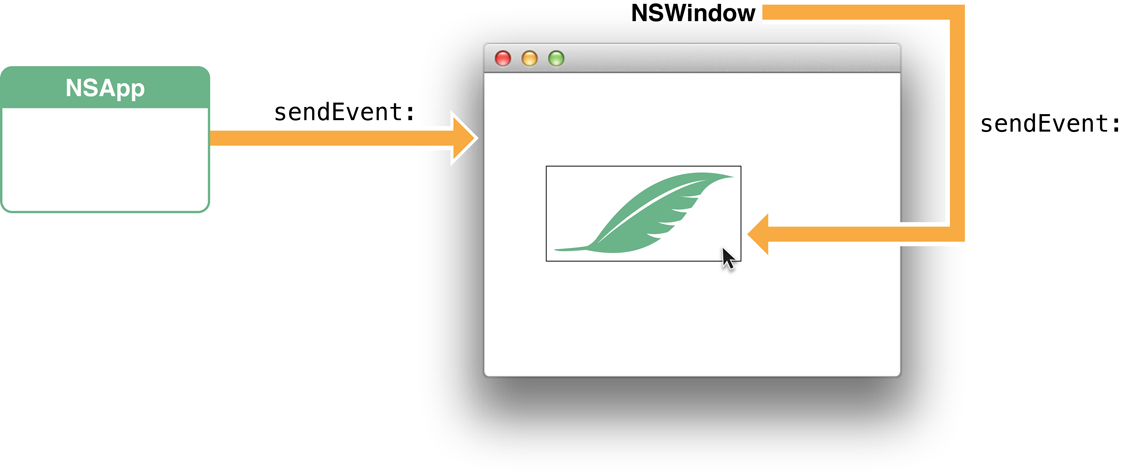 Figure 1-4 Path of a key event (character to insert)
Figure 1-4 Path of a key event (character to insert)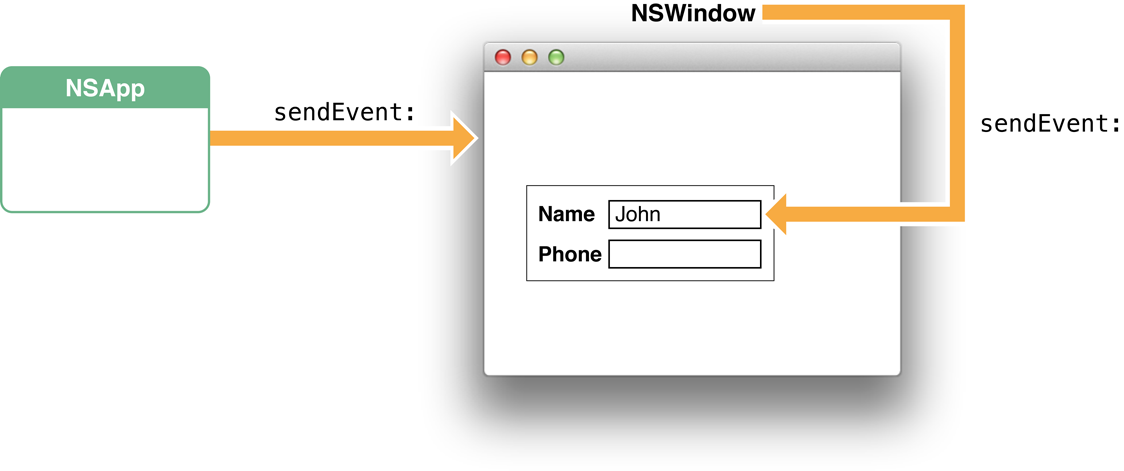
In the preceding paragraph you might have noticed the use of qualifiers such as “in most cases” and “usually.“ The delivery of an event (and especially a key event) in Cocoa can take many different paths depending on the particular kind of event. Some events, many of which are defined by the Application Kit (type NSAppKitDefined), have to do with actions controlled by a window or the application object itself. Examples of these events are those related to activating, deactivating, hiding, and showing the application. NSApp filters out these events early in its dispatch routine and handles them itself.
The following sections describe the different paths of the events that can reach your view objects. For detailed information on these event types, read Event Objects and Types.
https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/Cocoa/Conceptual/EventOverview/EventArchitecture/EventArchitecture.html
How an Event Enters a Cocoa Application的更多相关文章
- 深入浅出 Cocoa 之 Core Data(3)- 使用绑定
深入浅出 Cocoa 之 Core Data(3)- 使用绑定 罗朝辉(http://blog.csdn.net/kesalin) CC 许可,转载请注明出处 前面讲解了 Core Data 的框架, ...
- Main event loop
https://developer.apple.com/library/archive/documentation/General/Conceptual/Devpedia-CocoaApp/MainE ...
- Cocoa深入学习:NSOperationQueue、NSRunLoop和线程安全 (转)
目前在 iOS 和 OS X 中有两套先进的同步 API 可供我们使用:NSOperation 和 GCD .其中 GCD 是基于 C 的底层的 API ,而 NSOperation 则是 GCD 实 ...
- Event List 2
The list of events can be found in src/switch_event.c in a char array called EVENT_NAMES and is summ ...
- Event List
Created by John Boteler on 2015.01.16 Go to start of metadata About The current up-to-date list of ...
- [BTS] Faulting application name: BTSNTSvc.exe, version: 3.9.469.0, time stamp: 0x4c547e09
Log Name: ApplicationSource: Application ErrorDate: 8/22/2013 1:28:35 AMEvent ID: 1000Task Category: ...
- 《苹果开发之Cocoa编程》挑战1 创建委托 练习
<苹果开发之Cocoa编程>第4版 P87 新建一个单窗口应用程序,设置某对象为窗口的委托,当用户调整窗口尺寸时,确保窗口高度为宽度的2倍. 需要实现的委托方法为:-(NSSize)win ...
- Cocoa深入学习:NSOperationQueue、NSRunLoop和线程安全
http://blog.cnbluebox.com/blog/2014/07/01/cocoashen-ru-xue-xi-nsoperationqueuehe-nsoperationyuan-li- ...
- Cocoa包管理器之Carthage详解及CocoaPods中心化+Carthage的二进制化
上篇博客详细的聊了CocoaPods的相关内容,今天我们就来介绍另一个Cocoa的包管理器Carthage.在上家公司用Swift开发工程时,用的就是Carthage.Carthage诞生于14年11 ...
随机推荐
- Java中数组遍历
就是将数组中的每个元素分别获取出来,就是遍历.遍历也是数组操作中的基石. 数组的索引是 0 到 lenght-1 ,可以作为循环的条件出现 public class ArrayDemo4 { publ ...
- day05_20190127_python之路——常用模块
什么是模块? 常见的场景:一个模块就是一个包含了python定义和声明的文件,文件名就是模块名字加上.py的后缀.模块的本质:就是封装了很多很多函数.功能的一个文件 但其实import加载的模块分为四 ...
- 【转】【Oracle 集群】ORACLE DATABASE 11G RAC 知识图文详细教程之RAC 工作原理和相关组件(三)
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/baiboy/p/orc3.html 阅读目录 目录 RAC 工作原理和相关组件 ClusterWare 架构 RAC 软件结构 集群注册(OC ...
- shell中的交互模式:expect
在shell开发中,我们连接FTP或者passwd或sudo等操作时,需要手动输入密码.对于自动化而言,这显然是不合适的.而expect的强交互模式解决了这个问题.工作中偶有涉及到这个,个人也是简单的 ...
- String、Stringbuffer、StringBuffer回顾
前言: 久了没用到,一下子就忘了..,参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/su-feng/p/6659064.html.https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s ...
- git 教程2 (git常用命令解说)
<1>$ git -- help (调出git的帮助文档) <2>$ git +命令 --help (查看某个具体命令的帮助文档) <3>$ git --versi ...
- mysql新建用户,修改权限
(1)登录:mysql -u root -p (2)查看现有用户(mysql8.0.1) mysql> select host,user,authentication_string from m ...
- 喵哈哈村的魔法考试 Round #3 (Div.2)
菜的抠脚 A 题解:判断能否构成一个三角形. #include "iostream" #include "algorithm" #include "c ...
- SpProcPool阅读笔记--1
公司产品用了一个开源的框架,最近出了点问题,细看了这个框架. SpProcPool: https://github.com/spsoft/spprocpool.git 我们的线程池用的是传递文件描述 ...
- Linux设备驱动--块设备(一)之概念和框架(转)
基本概念 块设备(blockdevice) --- 是一种具有一定结构的随机存取设备,对这种设备的读写是按块进行的,他使用缓冲区来存放暂时的数据,待条件成熟后,从缓存一次性写入设备或者从设备一次性 ...
