【Computer Vision】角点检测和匹配——Harris算子
一、基本概念
角点corner:可以将角点看做两个边缘的交叉处,在两个方向上都有较大的变化。具体可由下图中分辨出来:
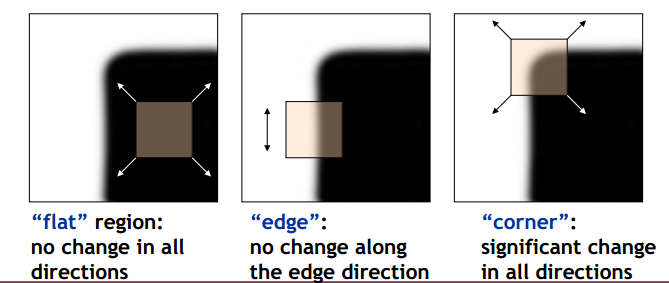
兴趣点interest point:兴趣点是图像中能够较鲁棒的检测出来的点,它不仅仅局限于角点. 也可以是灰度图像极大值或者极小值点等
二、Harris角点检测
Harris 算子是 Haris & Stephens 1988年在 "A Combined Corner and Edge Detector" 中提出的 提出的检测算法, 现在已经成为图像匹配中常用的算法.
对于一幅RGB图像我们很很容易得到corner 是各个方向梯度值较大的点, 定义 函数WSSD(Weighted Sum Squared Difference)为:
$$S(x,y) = \sum_{u} \sum_{v}w(u,v)(I((u+x,v+y)-I(u,v))^2 (1)$$
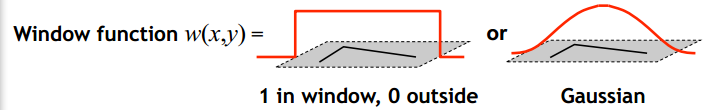
其中$w(u,v)$可以看作采样窗,可以选择矩形窗函数,也可以选择高斯窗函数:
$I(u+x,v+y)-I(u,v)$可以看作像素值变化量(梯度):
使用泰勒展开:$I(u+x,v+y) \approx I(u,v)+I_x(u,v)x+I_y(u,v)y (2)$
(1)代入(2) $S(x,y) \approx \sum_u \sum_v w(u,v) (I_x(u,v)x + I_y(u,v)y)^2$
写成$S(x,y) \approx (x,y) A (x,y)^T $
其中 A 为 二阶梯度矩阵(structure tensor/ second-moment matrix)
$$A = \sum_u \sum_v w(u,v) \begin{bmatrix} I_x^2& I_x I_y \\ I_x I_y & I_y^2 \end{bmatrix} $$
将A定义为Harris Matrix,A 的特征值有三种情况:
1. $\lambda_1 \approx 0, \lambda_2 \approx 0$,那么点$x$不是兴趣点
2. $\lambda_1 \approx 0, \lambda_2$为一个较大的正数, 那么点$x$为边缘点(edge)
3. $\lambda_1, \lambda_2$都为一个较大的正数, 那么点$x$为角点(corner)
由于特征值的计算是 computationally expensive,引入如下函数
$M_c = \lambda_1\lambda_2 - \kappa(\lambda_1+\lambda_2)^2 = det(A) - \kappa trace^2(A) $
为了去除加权常数$\kappa$ 直接计算
$M_{c}^{'} = \frac{det(A)}{trace(A)+\epsilon}$
三、角点匹配
Harris角点检测仅仅检测出兴趣点位置,然而往往我们进行角点检测的目的是为了进行图像间的兴趣点匹配,我们在每一个兴趣点加入descriptors描述子信息,给出比较描述子信息的方法. Harris角点的,描述子是由周围像素值块batch的灰度值,以及用于比较归一化的相关矩阵构成。
通常,两个大小相同的像素块I_1(x)和I_2(x) 的相关矩阵为:
$$c(I_1,I_2) = \sum_x f(I_1(x),I_2(x))$$
$f函数随着方法变化而变化,c(I_1,I_2)$值越大,像素块相似度越高.
对互相关矩阵进行归一化得到normalized cross correlation :
$$ncc(I_1,I_2) = \frac{1}{n-2} \sum_x \frac{(I_1(x)-\mu_1)}{\sigma_1} \cdot \frac{(I_2(x)-\mu_2)}{\sigma_2}$$
其中$\mu$为像素块的均值,\sigma为标准差. ncc对图像的亮度变化具有更好的稳健性.
四、python实现
python版本:2.7
依赖包: numpy,scipy,PIL, matplotlib
图片:
trees_002.jpg

trees003.jpg

from PIL import Image
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from numpy import *
from pylab import * def compute_harris_response(im,sigma=3):
"""Compute the Harris corner detector response function for each
pixel in a graylevel image.""" #derivative
imx = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im,(sigma,sigma),(0,1),imx) imy = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im,(sigma,sigma),(1,0),imy) #compute components of the Harris matrix Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imx,sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imy,sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy*imy,sigma) #determinant and trace Wdet = Wxx*Wyy-Wxy**2
Wtr = Wxx+Wyy
return Wdet/Wtr def get_harris_points(harrisim,min_dist=10,threshold=0.1):
"""Return corners from a Harris response image min_dist is the
minimum number of pixels separating corners and image boundary.""" #find top corner candidates above a threshold
corner_threshold = harrisim.max()*threshold
harrisim_t = 1*(harrisim>corner_threshold) #get coordiantes of candidate
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T #...and their valus
candicates_values = [harrisim[c[0],c[1]] for c in coords] #sort candicates
index = argsort(candicates_values) #sort allowed point loaction in array
allowed_location = zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_location[min_dist:-min_dist,min_dist:-min_dist] = 1 #select the best points taking min_distance into account
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_location[coords[i,0],coords[i,1]]==1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_location[(coords[i,0]-min_dist):(coords[i,0]+min_dist),
(coords[i,1]-min_dist):(coords[i,1]+min_dist)]=0
return filtered_coords def plot_harris_points(image,filtered_coords):
"""plots corners found in image."""
figure
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords],[p[0] for p in filtered_coords],'*')
axis('off')
show() def get_descriptors(image,filter_coords,wid=5):
"""For each point return pixel values around the point using a neihborhood
of 2*width+1."""
desc=[]
for coords in filter_coords:
patch = image[coords[0]-wid:coords[0]+wid+1,
coords[1]-wid:coords[1]+wid+1].flatten()
desc.append(patch) # use append to add new elements
return desc def match(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
"""For each corner point descriptor in the first image, select its match
to second image using normalized cross correlation.""" n = len(desc1[0]) #num of harris descriptors
#pair-wise distance
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i]-mean(desc1[i]))/std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j]-mean(desc2[j]))/std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1*d2)/(n-1)
if ncc_value>threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0] return matchscores def match_twosided(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
"""two sided symmetric version of match()."""
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2,threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1,threshold) ndx_12 = where(matches_12>=0)[0]
print ndx_12.dtype
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] !=n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12 def appendimages(im1,im2):
"""Return a new image that appends that two images side-by-side.""" #select the image with the fewest rows and fill in enough empty rows
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0] if rows1<rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1,zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0)
elif rows1<rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2,zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0)
return concatenate((im1,im2),axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True):
"""show a figure with lines joinging the accepted matches
Input:im1,im2(images as arrays),locs1,locs2,(feature locations),
metachscores(as output from 'match()'),
show_below(if images should be shown matches)."""
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3,im3)) imshow(im3) cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i,m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m>0:
plot([locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1]+cols1],[locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]],'c')
axis('off') """
im = array(Image.open('F:/images/lena.bmp').convert('1'))
harrisim = compute_harris_response(im)
filtered_coords = get_harris_points(harrisim,6)
plot_harris_points(im,filtered_coords)
""" im1 = array(Image.open('trees_002.jpg').convert('L'))
im2 = array(Image.open('trees_003.jpg').convert('L')) wid = 5 harrisim = compute_harris_response(im1,5)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisim,wid+1)
d1 = get_descriptors(im1,filtered_coords1,wid) harrisim = compute_harris_response(im2,5)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisim,wid+1)
d2 = get_descriptors(im2,filtered_coords2,wid) print 'starting matching'
matches = match_twosided(d1,d2) figure()
gray()
plot_matches(im1,im2,filtered_coords1,filtered_coords2,matches)
show()
运行结果:

【Computer Vision】角点检测和匹配——Harris算子的更多相关文章
- 角点检测和匹配——Harris算子
一.基本概念 角点corner:可以将角点看做两个边缘的交叉处,在两个方向上都有较大的变化.具体可由下图中分辨出来: 兴趣点interest point:兴趣点是图像中能够较鲁棒的检测出来的点,它不仅 ...
- 第十一节、Harris角点检测原理(附源码)
OpenCV可以检测图像的主要特征,然后提取这些特征.使其成为图像描述符,这类似于人的眼睛和大脑.这些图像特征可作为图像搜索的数据库.此外,人们可以利用这些关键点将图像拼接起来,组成一个更大的图像,比 ...
- opencv-角点检测之Harris角点检测
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/poem_qianmo/article/details/29356187 先看看程序运行截图: 一.引言:关于兴趣点(interest point ...
- OpenCV计算机视觉学习(13)——图像特征点检测(Harris角点检测,sift算法)
如果需要处理的原图及代码,请移步小编的GitHub地址 传送门:请点击我 如果点击有误:https://github.com/LeBron-Jian/ComputerVisionPractice 前言 ...
- OpenCV-Python:Harris角点检测与Shi-Tomasi角点检测
一.Harris角点检测 原理: 角点特性:向任何方向移动变换都很大. Chris_Harris 和 Mike_Stephens 早在 1988 年的文章<A CombinedCorner an ...
- [Computer Vision]Harris角点检测的详细推导
Harris角点检测 思想 为什么要检测角点呢?因为角点的特征比较明显.进行角点检测的朴素思想是利用图像梯度,也就是根据图像强度的变化来寻找角点.如图所示 这里举了个例子,给定一个小的区域(Patch ...
- Harris角点及Shi-Tomasi角点检测(转)
一.角点定义 有定义角点的几段话: 1.角点检测(Corner Detection)是计算机视觉系统中用来获得图像特征的一种方法,广泛应用于运动检测.图像匹配.视频跟踪.三维建模和目标识别等领域中.也 ...
- 【OpenCV】角点检测:Harris角点及Shi-Tomasi角点检测
角点 特征检测与匹配是Computer Vision 应用总重要的一部分,这需要寻找图像之间的特征建立对应关系.点,也就是图像中的特殊位置,是很常用的一类特征,点的局部特征也可以叫做“关键特征点”(k ...
- 角点检测:Harris角点及Shi-Tomasi角点检测
角点 特征检测与匹配是Computer Vision 应用总重要的一部分,这需要寻找图像之间的特征建立对应关系.点,也就是图像中的特殊位置,是很常用的一类特征,点的局部特征也可以叫做“关键特征点”(k ...
随机推荐
- MyEclipse如何设置自动提示?
MyEclipse --> Preferences --> Java --> Editor --> Content Assist --> Enable auto acti ...
- 实验楼—Mysql—查找最爱学的课程
转载:https://www.shiyanlou.com/challenges/2651 背景 从上节题目构建的课程数据库中提取每个用户最爱学的课程数据. 右边桌面是实验楼的服务器,服务器中的 MyS ...
- Android 7.0 Gallery图库源码分析4 - SlotView手势监听及页面跳转
上篇文章讲了初始化View时会实例化一个SlotView并监听其事件,至于它是怎么实现的,用的是Android自带的GestureDetector. GestureDetector是Android自带 ...
- rest-framework框架
rest-framework框架是Django里面非常重要的框架,但提到rest-framework框架就不得不说两种请求方式,那就是CBV和FBV. FBV(function base views) ...
- qt quick中qml编程语言
Qt QML 入门 — 使用C++定义QML类型 发表于 2013 年 3 月 11 日 注册C++类 注册可实例化的类型 注册不实例化的QML类型 附带属性 注册C++类 注册可实例化的类型 如 ...
- python_函数、局部变量与全局变量
#函数优点:代码重用.保持一致性.可扩展性import time def logger(): """时间年-月-日 分""" time_fo ...
- 洛谷P5238 整数校验器
看到没有边读入边处理的,我来水一发 我们要看一下有那些情况是格式不合法的 单独的负号 -0(后面可以有其他数字) 0 +(后面一些数字) 我们用快速读入的方法 读取字符进行处理 还有可能超出范围的 考 ...
- LeetCode104_MaximumDepthofBinaryTree Java题解
题目: Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth. The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the ...
- Scratch单机版下载
Scratch单机版下载 这两个地址速度比较快: Adobe Air:http://7dx.pc6.com/wwb5/AdobeAIR2800127.zip Scratch :http://7dx.p ...
- 博客迁移到reetsee.com
正如上一篇博客所言.眼下CSDN的博客已经基本完毕它的使命了.感谢CSDN带给我的全部美好回顾. 如今我想尝试一下自己维护一个博客,所以博客的全部内容都迁移到了reetsee.com. 以后博客更新会 ...
