设计模式学习笔记(十六)迭代器模式及其在Java 容器中的应用
迭代器(Iterator)模式,也叫做游标(Cursor)模式。我们知道,在Java 容器中,为了提高容器遍历的方便性,我们利用迭代器把遍历逻辑从不同类型的集合类中抽取出来,从而避免向外部暴露集合容器的内部结构。这就是迭代器模式的
一、迭代器模式介绍
迭代器模式也就是提供一个对象来顺序访问聚合对象中的一系列数据,而不暴露聚合对象的内部表示。它是一种行为型模式,下面就来看看迭代器模式的结构:
1.1 迭代器模式的结构
迭代器模式的结构很简单,就是将聚合对象中的遍历行为分离,并抽象成迭代器类来实现:
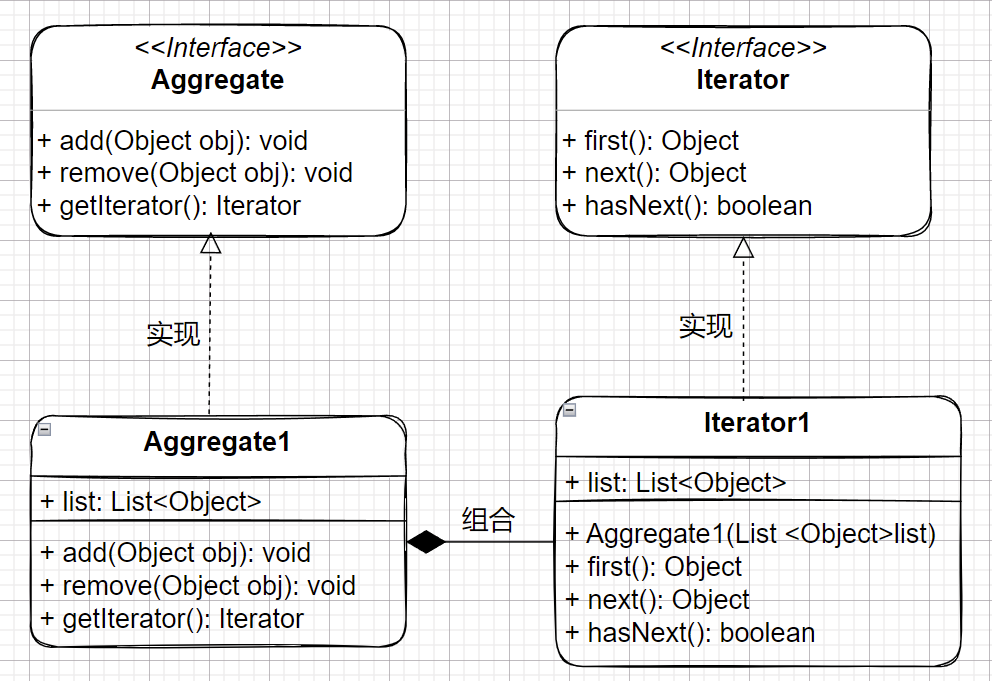
Aggregate:抽象聚合接口,定义对聚合对象的一些操作和创建迭代器对象的接口Iterator:抽象迭代器接口,定义访问和遍历聚合元素的接口Aggregate1:具体聚合实现,实现抽象聚合接口,返回一个具体迭代器实例对象Iterator1:具体迭代器实现,实现抽象迭代器接口中所定义的方法
1.2 迭代器模式的实现
根据上面的类图,可以实现如下代码:
/**
* @description: 抽象聚合接口
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public interface Aggregate {
/**
* 增加对象
* @param obj 对象
*/
void add(Object obj);
/**
* 移除对象
* @param obj 对象
*/
void remove(Object obj);
/**
* 调用迭代器
* @return 迭代器
*/
Iterator getIterator();
}
/**
* @description: 具体迭代器类
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class Aggregate1 implements Aggregate{
private List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void add(Object obj) {
list.add(obj);
}
@Override
public void remove(Object obj) {
list.remove(obj);
}
@Override
public Iterator getIterator() {
return new Iterator1(list);
}
}
/**
* @description: 抽象迭代器
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public interface Iterator {
/**
* 调用第一个对象
* @return 对象
*/
Object first();
/**
* 调用下一个对象
* @return 对象
*/
Object next();
/**
* 迭代器中是否还有下一个对象
* @return
*/
boolean hasNext();
}
/**
* @description: 具体迭代器类
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class Iterator1 implements Iterator{
private List<Object> list = null;
private int index = -1;
public Iterator1(List<Object> list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public Object first() {
index = 0;
Object obj = list.get(index);
return obj;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Object obj = null;
if (this.hasNext()) {
obj = list.get(++index);
}
return obj;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (index < list.size() - 1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 客户端类
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Aggregate1 aggregate1 = new Aggregate1();
aggregate1.add("A");
aggregate1.add("B");
aggregate1.add("C");
System.out.println("聚合对象有:");
Iterator iterator = aggregate1.getIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj.toString());
}
Object first = iterator.first();
System.out.println("第一个聚合对象是:" + first.toString());
}
}
客户端测试场结果为:
聚合对象有:
A
B
C
第一个聚合对象是:A
二、迭代器模式的应用场景
2.1 Java 集合容器
Java 集合容器中的使用就是容器中的迭代器了,以ArrayList为例,ArrayList是继承Collection的:
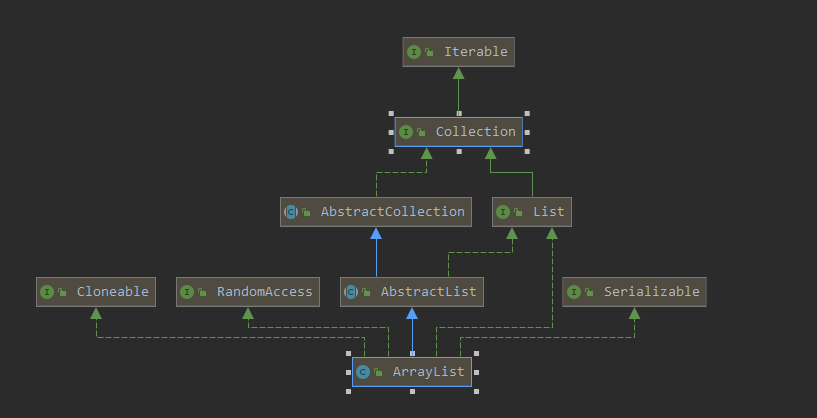
我们发现ArrayList类里面实现迭代器接口的内部类:
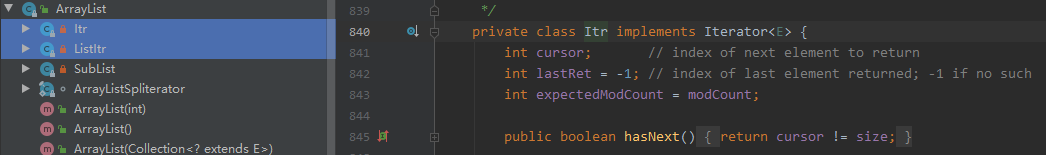
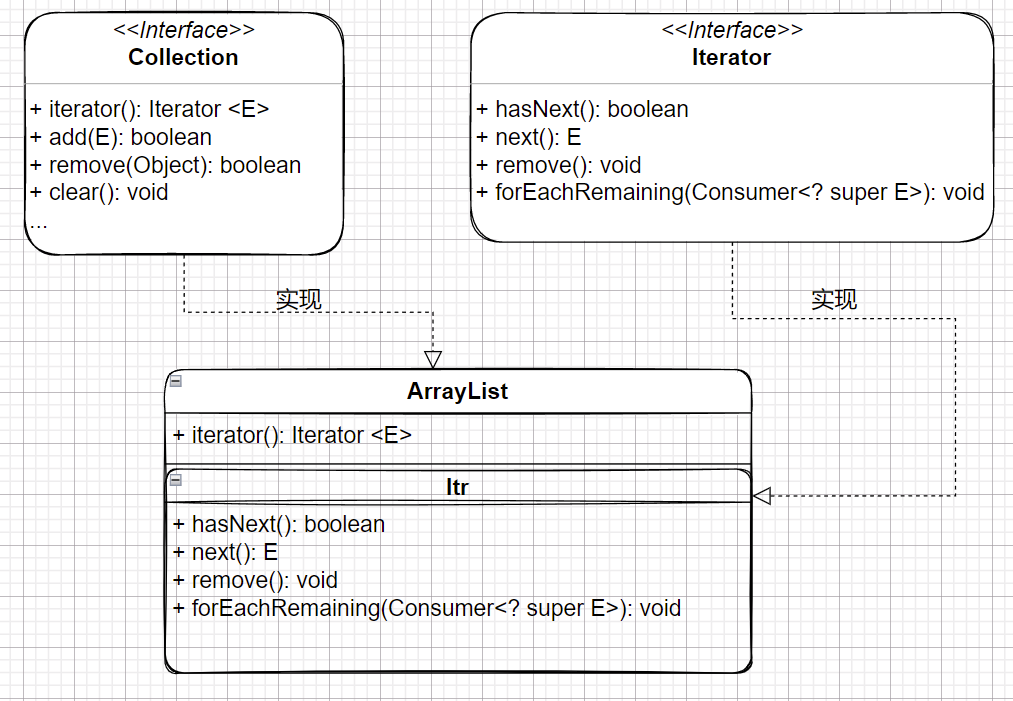
其中Itr实现Iterator,ListItr继承Itr并实现ListIterator,ListIterator是Iterator功能的扩展。所以实际上ArrayList是抽象聚合和抽象迭代器两者的具体实现,可以画出大致结构图如下:
举个使用ArrayList的例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("A");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator();
System.out.println("ArrayList中的聚合对象为:");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
输出结果:
ArrayList中的聚合对象为:
A
B
C
在日常业务的开发中,迭代器模式使用的场景并不多,下面就来看看关于迭代器的实战
三、迭代器模式实战
在本案例中模拟迭代遍历输出公司中树形结构的组织结构关系中雇员列表:
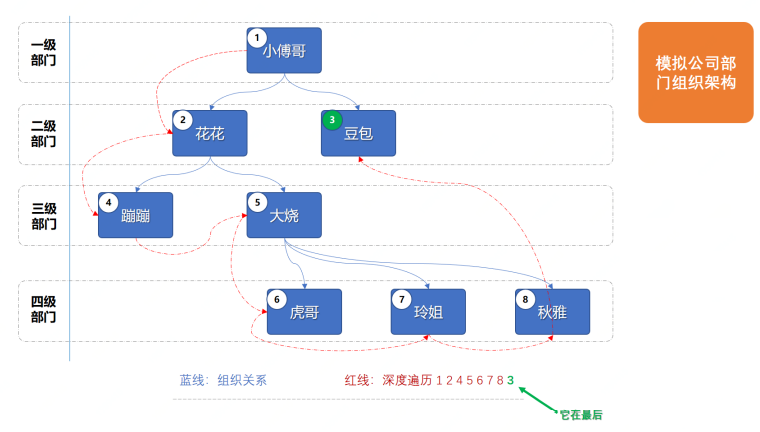
利用迭代器模式实现的结构如下:
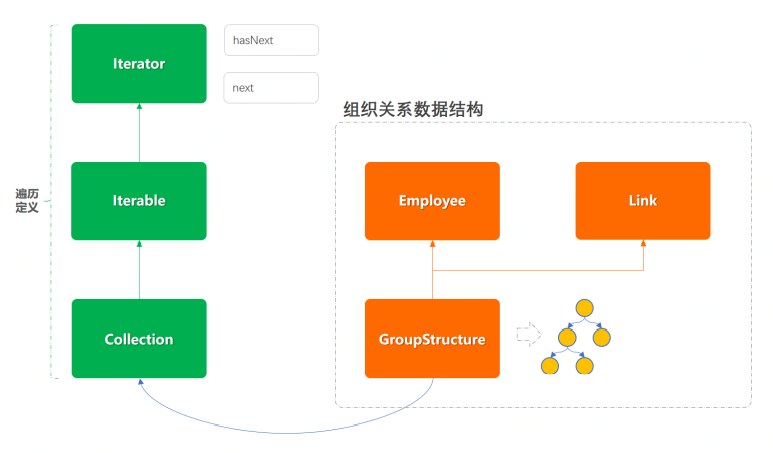
上面结构是以Java容器中迭代器模式基础构建的,左边是迭代器的定义,右边是实现的迭代器功能。具体代码结构图如下:
├─src
│ ├─main
│ │ ├─java
│ │ │ ├─group
│ │ │ │ Employee.java
│ │ │ │ GroupStructure.java
│ │ │ │ Link.java
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ └─lang
│ │ │ Collection.java
│ │ │ Iterable.java
│ │ │ Iterator.java
│ │ │
│ │ └─resources
│ └─test
│ └─java
│ ApiTest.java
对于lang包下是迭代器实现部分,具体代码如下:
/**
* @description: 可迭代接口定义
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
}
/**
* @description:
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public interface Iterable<E> {
Iterator<E> iterator();
}
/**
* @description: 集合功能接口
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public interface Collection<E, L> extends Iterable<E> {
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(E e);
boolean addLink(String key, L l);
boolean removeLink(String key);
/**
* 继承Iterable接口的方法
* @return Iterator
*/
@Override
Iterator<E> iterator();
}
group包下是组织结构以及聚类对象及其实现,具体代码如下所示:
/**
* @description: 雇员类
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class Employee {
private String uId;
private String name;
private String desc;
public Employee(String uId, String name, String desc) {
this.uId = uId;
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getuId() {
return uId;
}
public void setuId(String uId) {
this.uId = uId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
}
/**
* @description: 树节点链路
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class Link {
private String fromId;
private String toId;
public Link(String fromId, String toId) {
this.fromId = fromId;
this.toId = toId;
}
public String getFromId() {
return fromId;
}
public void setFromId(String fromId) {
this.fromId = fromId;
}
public String getToId() {
return toId;
}
public void setToId(String toId) {
this.toId = toId;
}
}
/**
* @description: 迭代器功能实现
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class GroupStructure implements Collection<Employee, Link> {
/**组织ID*/
private String groupId;
/**组织名称*/
private String groupName;
/**雇员列表*/
private Map<String, Employee> employeeMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**组织架构关系*/
private Map<String, List<Link>> linkMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**反向关系链*/
private Map<String, String> invertedMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public GroupStructure(String groupId, String groupName) {
this.groupId = groupId;
this.groupName = groupName;
}
@Override
public boolean add(Employee employee) {
return null != employeeMap.put(employee.getuId(), employee);
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Employee employee) {
return null != employeeMap.remove(employee.getuId());
}
@Override
public boolean addLink(String key, Link link) {
invertedMap.put(link.getToId(), link.getFromId());
if (linkMap.containsKey(key)) {
return linkMap.get(key).add(link);
} else {
List<Link> links = new LinkedList<>();
links.add(link);
linkMap.put(key, links);
return true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean removeLink(String key) {
return null != linkMap.remove(key);
}
@Override
public Iterator<Employee> iterator() {
return new Iterator<Employee>() {
HashMap<String, Integer> keyMap = new HashMap<>();
int totalIdx = 0;
//雇员ID,From
private String fromId = groupId;
//雇员ID,To
private String toId = groupId;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return totalIdx < employeeMap.size();
}
@Override
public Employee next() {
List<Link> links = linkMap.get(toId);
int cursorIdx = getCursorIdx(toId);
//同级扫描
if (null == links) {
cursorIdx = getCursorIdx(fromId);
links = linkMap.get(fromId);
}
//上级节点扫描
while (cursorIdx > links.size() - 1) {
fromId = invertedMap.get(fromId);
cursorIdx = getCursorIdx(fromId);
links = linkMap.get(fromId);
}
//获取节点
Link link = links.get(cursorIdx);
toId = link.getToId();
fromId = link.getFromId();
totalIdx++;
//返回最终结果
return employeeMap.get(link.getToId());
}
//给每个层级定义宽度遍历进度
public int getCursorIdx(String key) {
int idx = 0;
if (keyMap.containsKey(key)) {
idx = keyMap.get(key);
keyMap.put(key, ++idx);
} else {
keyMap.put(key, idx);
}
return idx;
}
};
}
}
最后是测试类及其结果:
/**
* @description: 单元测试类
* @author: wjw
* @date: 2022/4/6
*/
public class ApiTest {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ApiTest.class);
@Test
public void test_iterator() {
GroupStructure groupStructure = new GroupStructure("1", "ethan");
groupStructure.add(new Employee("2", "花花", "二级部门"));
groupStructure.add(new Employee("3", "豆包", "二级部门"));
groupStructure.add(new Employee("4", "蹦蹦", "三级部门"));
groupStructure.add(new Employee("5", "大烧", "三级部门"));
groupStructure.add(new Employee("6", "虎哥", "四级部门"));
groupStructure.add(new Employee("7", "玲姐", "四级部门"));
groupStructure.add(new Employee("8", "秋雅", "四级部门"));
//添加节点链接
groupStructure.addLink("1", new Link("1", "2"));
groupStructure.addLink("1", new Link("1", "3"));
groupStructure.addLink("2", new Link("2", "4"));
groupStructure.addLink("2", new Link("2", "5"));
groupStructure.addLink("5", new Link("5", "6"));
groupStructure.addLink("5", new Link("5", "7"));
groupStructure.addLink("5", new Link("5", "8"));
Iterator<Employee> iterator = groupStructure.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Employee employee = iterator.next();
logger.info("{},雇员 Id: {} Name: {}", employee.getDesc(), employee.getuId(), employee.getName());
}
}
}
21:50:11.087 [main] INFO ApiTest - 二级部门,雇员 Id: 2 Name: 花花
21:50:11.089 [main] INFO ApiTest - 三级部门,雇员 Id: 4 Name: 蹦蹦
21:50:11.089 [main] INFO ApiTest - 三级部门,雇员 Id: 5 Name: 大烧
21:50:11.089 [main] INFO ApiTest - 四级部门,雇员 Id: 6 Name: 虎哥
21:50:11.089 [main] INFO ApiTest - 四级部门,雇员 Id: 7 Name: 玲姐
21:50:11.089 [main] INFO ApiTest - 四级部门,雇员 Id: 8 Name: 秋雅
21:50:11.089 [main] INFO ApiTest - 二级部门,雇员 Id: 3 Name: 豆包
参考资料
《重学Java设计模式》
http://c.biancheng.net/view/1395.html
设计模式学习笔记(十六)迭代器模式及其在Java 容器中的应用的更多相关文章
- C#设计模式学习笔记:(15)迭代器模式
本笔记摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/PatrickLiu/p/7903617.html,记录一下学习过程以备后续查用. 一.引言 今天我们要讲行为型设计模式的第三个模式--迭 ...
- javascript设计模式学习之十六——状态模式
一.状态模式的定义 状态模式的关键是区分事务内部和外部的状态,事务内部状态改变往往会带来事务的行为改变. 状态模式中有意思的一点是,一般我们谈到封装,都是优先封装对象的行为,而非对象的状态.但在状态模 ...
- python3.4学习笔记(十六) windows下面安装easy_install和pip教程
python3.4学习笔记(十六) windows下面安装easy_install和pip教程 easy_install和pip都是用来下载安装Python一个公共资源库PyPI的相关资源包的 首先安 ...
- Java设计模式学习笔记(二) 简单工厂模式
前言 本篇是设计模式学习笔记的其中一篇文章,如对其他模式有兴趣,可从该地址查找设计模式学习笔记汇总地址 正文开始... 1. 简介 简单工厂模式不属于GoF23中设计模式之一,但在软件开发中应用也较为 ...
- Java设计模式学习笔记(三) 工厂方法模式
前言 本篇是设计模式学习笔记的其中一篇文章,如对其他模式有兴趣,可从该地址查找设计模式学习笔记汇总地址 1. 简介 上一篇博客介绍了简单工厂模式,简单工厂模式存在一个很严重的问题: 就是当系统需要引入 ...
- Java设计模式学习笔记(四) 抽象工厂模式
前言 本篇是设计模式学习笔记的其中一篇文章,如对其他模式有兴趣,可从该地址查找设计模式学习笔记汇总地址 1. 抽象工厂模式概述 工厂方法模式通过引入工厂等级结构,解决了简单工厂模式中工厂类职责太重的问 ...
- C#设计模式之十六迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)【行为型】
一.引言 今天我们开始讲"行为型"设计模式的第三个模式,该模式是[迭代器模式],英文名称是:Iterator Pattern.还是老套路,先从名字上来看看."迭代器模 ...
- C#设计模式学习笔记:(23)解释器模式
本笔记摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/PatrickLiu/p/8242238.html,记录一下学习过程以备后续查用. 一.引言 今天我们要讲行为型设计模式的第十一个模式-- ...
- C#设计模式学习笔记:(18)状态模式
本笔记摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/PatrickLiu/p/8032683.html,记录一下学习过程以备后续查用. 一.引言 今天我们要讲行为型设计模式的第六个模式--状 ...
随机推荐
- LGP6667题解
既然看到了这道"板子",那还是来写一下题解吧... 如果有机会希望能推一下 载谈binominial sum 的做法. \[\sum_{k=0}^nf(k)\binom n kx^ ...
- 翻译 | Kubernetes 将改变数据库的管理方式
作者:Álvaro Hernández 当技术决策人考虑在 Kubernetes 上部署数据库时,面临的第一个问题就是:"Kubernetes 有应对有状态服务的能力吗?"多年来的 ...
- 移动APP开发框架盘点2:Web移动前端框架大全
前言 自上次发布了<移动APP开发框架盘点>后,时间已经过去了三年, 为什么突然又写一篇续集呢?是因为有一个非常有意思的发现. 开源项目其实有一个成熟周期,这个周期大概是三年左右,自Rea ...
- WPF 布局之综合实例
WPF 布局之综合实例 <Window x:Class="UniFormGridDemo.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.mic ...
- 基于EMR离线数据分析-反馈有礼
"云上漫步"第三期-反馈有礼 参与体验产品,提交反馈,就有机会获得定制背包,T恤,超萌虎年鼠标垫,以及5到100元阿里云通用代金券~ 反馈地址: https://developer ...
- Nebula Graph 在网易游戏业务中的实践
本文首发于 Nebula Graph Community 公众号 当游戏上知识图谱,网易游戏是如何应对大规模图数据的管理问题,Nebula Graph 又是如何帮助网易游戏落地游戏内复杂的图的业务呢? ...
- 西门子S210驱动器接线
参考:SINAMICS S210 操作说明 1.系统概述 P28 节2.2 单相版驱动器的系统组件和附件 2.电源接线 P56 节3.2 单相 230 V 版驱动器的连接示例 单相版驱动器在 IT 电 ...
- Spring cloud config 客户端连接RabbitMQ 报 socket closed
java.net.SocketException: socket closed at java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead0(Native Method) ...
- Where和having都是条件筛选关键字,它们有什么分别?
WHERE是在数据分组前进行条件过滤, HAVING子句是在数据分组后进行条件过滤,WHERE子句中不能使用聚合函数,HAVING子句可以使用聚合函数. 需要注意说明:当同时含有where子句.gro ...
- 阐述 final、finally、finalize 的区别?
final:修饰符(关键字)有三种用法:如果一个类被声明为 final,意味 着它不能再派生出新的子类,即不能被继承,因此它和 abstract 是反义词.将 变量声明为 final,可以保证它们在使 ...
