RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化流程!
之前的文章里,介绍了DispatcherSerlvet处理请求的流程。
其中一个核心的步骤是:请求地址映射,即根据request获取对应的HandlerExcecutionChain。
为了后续的请求地址映射,在项目初始化时,需要先将request-handler映射关系缓存起来。
HandlerMapping有很多实现类,比如RequestMappingHandlerMapping、BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和RouterFunctionMapping,它们分别对应不同的Controller接口定义规则。
这篇文章要介绍的是RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化流程。
大家看到RequestMappingHandlerMapping可能会感到陌生。
实际上,它是我们日常打交道最多的HandlerMapping实现类:它是@Controller和@RequestMapping的底层实现。
在RequestMappingHanlderMapping初始化时,会根据@Controller和@RequestMapping创建RequestMappingInfo,将request-handler映射关系缓存起来。
首先,我们简单来看一下RequestMappingHandlerMapping的类图:
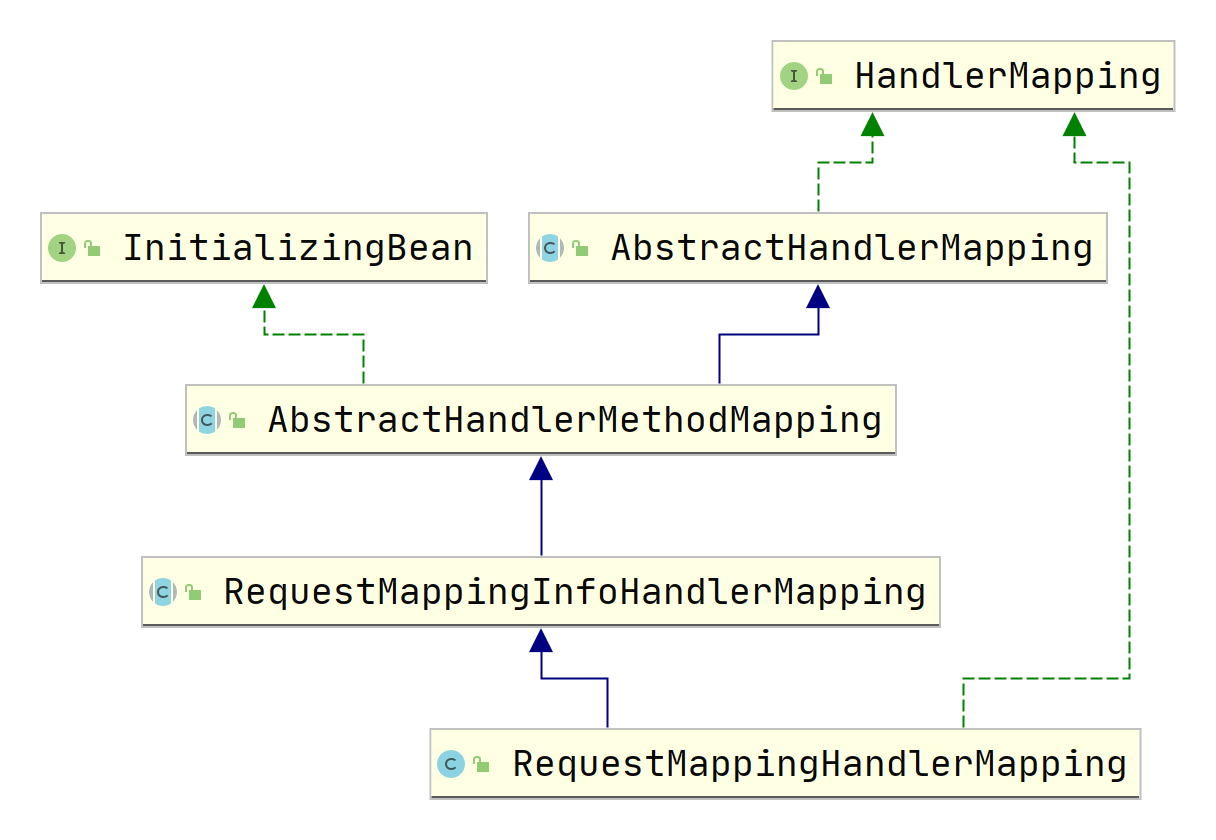
RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean接口。
在Spring容器设置完所有bean的属性,以及执行完XxxAware接口的setXxx()方法后,会触发InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()方法。
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet()方法中,会完成请求地址映射的初始化流程:
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods方法中,会遍历容器中所有bean进行处理:
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
// 1、遍历所有bean的名称
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
// 2、解析bean
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的processCandidateBean方法中,会对bean进行筛选。如果该bean的类对象中包含@Controller或RequestMapping注解,会进一步遍历该类对象的各个方法:
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// 1、判断bean的类对象是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
// 2、构造request-handler映射信息
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的isHandler()方法中,会判断当前类对象是否包含@Controller或@RequestMapping注解:
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的detectHandlerMethods方法中,会构造并缓存request-handler信息:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 1、遍历类对象的各个方法,返回Method-RequestMappingInfo映射
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
// 2、构造request-handler请求地址映射
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
else if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
// 3、缓存request-handler请求地址映射
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
在MethodIntrospector的selectMethods()方法中,会遍历类对象各个方法,调用RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getMappingForMethod()方法,构造request地址信息:
- 如果该方法满足书写规则,即含有
@RequestMapping,会返回RequestMappingInfo对象 - 如果该方法不满足书写规则,会返回
null。
MethodIntrospector的selectMethods()方法会将所有request地址信息不为null的Method-RequestMappingInfo映射返回。
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getMappingForMethod()方法中,会构造完整的request地址信息。主要包括以下步骤:
- 构造方法级别的
request地址信息 - 构造类级别的
request地址信息 - 整合两个级别的
request地址信息,构造出完整的request地址信息
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getMappingForMethod()方法源码如下:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
// 1、构造方法级别的request-handler信息
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
// 2、构造类级别的request-handler信息
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
// 3、整合两个级别的request-handler信息,构造出完整的request-handler信息
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
构造request地址信息很简单,只是从@RequestMapping注解中获取各个属性,创建RequestMappingInfo(在实际请求地址映射时,会对所有属性进行校验):
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
在整合request地址信息过程中,会分别调用各个属性的整合规则进行整合:
public RequestMappingInfo combine(RequestMappingInfo other) {
String name = combineNames(other);
PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatterns =
(this.pathPatternsCondition != null && other.pathPatternsCondition != null ?
this.pathPatternsCondition.combine(other.pathPatternsCondition) : null);
PatternsRequestCondition patterns =
(this.patternsCondition != null && other.patternsCondition != null ?
this.patternsCondition.combine(other.patternsCondition) : null);
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.combine(other.methodsCondition);
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.combine(other.paramsCondition);
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.combine(other.headersCondition);
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.combine(other.consumesCondition);
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.combine(other.producesCondition);
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.combine(other.customConditionHolder);
return new RequestMappingInfo(name, pathPatterns, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom, this.options);
}
不同的属性有不同的整合规则,比如对于methods、params和headers会取并集,而对于consumes和produces方法级别优先。
介绍完request地址信息的构造过程,我们回到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的detectHandlerMethods方法中。此时,我们得到了Method-RequestMappingInfo映射信息。
接下来,会遍历这个映射,筛选出实际可执行的方法(即非私有的、非静态的和非超类的)。
最终,将可执行的方法对应的request-handler信息缓存起来。核心代码位于AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry内部类的register()方法:
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 1、创建HandlerMethod对象,即handler
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
// 2、校验该request地址信息是否已经存在
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
// 3、缓存path-RequestMappingInfo映射
Set<String> directPaths = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getDirectPaths(mapping);
for (String path : directPaths) {
this.pathLookup.add(path, mapping);
}
// 4、缓存name-RequestMappingInfo映射
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
// 5、缓存CORS配置信息
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
corsConfig.validateAllowCredentials();
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
// 6、缓存RequestMappingInfo-MappingRegistration信息
this.registry.put(mapping,
new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name, corsConfig != null));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
需要注意的是,在这个过程中还会缓存跨域配置信息,主要是@CrossOrigin注解方式的跨域配置信息。
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping的initCorsConfiguration()方法中,会获取类级别和方法级别的@CrossOrigin信息,构造出完整的跨域配置信息:
protected CorsConfiguration initCorsConfiguration(Object handler, Method method, RequestMappingInfo mappingInfo) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
Class<?> beanType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
// 1、获取类级别的@CrossOrigin信息
CrossOrigin typeAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(beanType, CrossOrigin.class);
// 2、获取方法级别的@CrossOrigin信息
CrossOrigin methodAnnotation = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, CrossOrigin.class);
if (typeAnnotation == null && methodAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// 3、整合两个级别的@CrossOrigin信息
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
updateCorsConfig(config, typeAnnotation);
updateCorsConfig(config, methodAnnotation);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(config.getAllowedMethods())) {
for (RequestMethod allowedMethod : mappingInfo.getMethodsCondition().getMethods()) {
config.addAllowedMethod(allowedMethod.name());
}
}
return config.applyPermitDefaultValues();
}
在整合@CrossOrigin信息过程中,有三种情况:
- 对于
origins、originPatterns、allowedHeaders、exposedHeaders和methods等列表属性,会获取全部。 - 对于
allowCredentials,会优先获取方法级别的配置。 - 对于
maxAge,会获取最大值。
至此,我们走完了RequestMappingHandlerMapping中请求地址映射的初始化流程。最后总结一下流程如下:
- 遍历容器中所有
bean对象 - 如果
bean的类对象含有@Controller或@RequestMapping注解,进行下一步 - 遍历
bean的类对象的所有方法,根据方法的@RequestMapping注解,构造RequestMappingInfo对象 - 遍历
Method-RequestMappingInfo映射,过滤出可执行方法 - 缓存各种
request-handler映射信息,同时会缓存@CrossOrigin的跨域配置信息
此时,我们可以充分理解到,request-handler请求地址映射信息中request和handler的含义:
request:主要是@RequestMapping中含有的各个属性的信息handler:标注@RequestMapping的方法
RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化流程!的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC源码剖析(三)- DispatcherServlet的初始化流程
在我们第一次学Servlet编程,学Java Web的时候,还没有那么多框架.我们开发一个简单的功能要做的事情很简单,就是继承HttpServlet,根据需要重写一下doGet,doPost方法,跳转 ...
- ASP.NET初始化流程分析2
上一篇讲了从创建应用程序域到创建ISAPIRuntime实例的过程,本篇继续讲Asp.net处理第一次请求的必要的初始化过程. ISAPIRuntime分析 ISAPIRuntime在System.W ...
- Shiro权限管理框架(三):Shiro中权限过滤器的初始化流程和实现原理
本篇是Shiro系列第三篇,Shiro中的过滤器初始化流程和实现原理.Shiro基于URL的权限控制是通过Filter实现的,本篇从我们注入的ShiroFilterFactoryBean开始入手,翻看 ...
- 痞子衡嵌入式:深入i.MXRT1050系列ROM中串行NOR Flash启动初始化流程
大家好,我是痞子衡,是正经搞技术的痞子.今天痞子衡给大家分享的是深入i.MXRT1050系列ROM中串行NOR Flash启动初始化流程. 从外部串行NOR Flash启动问题是i.MXRT系列开发最 ...
- 【技术博客】Flutter—使用网络请求的页面搭建流程、State生命周期、一些组件的应用
Flutter-使用网络请求的页面搭建流程.State生命周期.一些组件的应用 使用网络请求的页面搭建流程 在开发APP时,我们常常会遇到如下场景:进入一个页面后,要先进行网络调用,然后使用调用返 ...
- Sentinel-Go 源码系列(二)|初始化流程和责任链设计模式
上节中我们知道了 Sentinel-Go 大概能做什么事情,最简单的例子如何跑起来 其实我早就写好了本系列的第二篇,但迟迟没有发布,感觉光初始化流程显得有些单一,于是又补充了责任链模式,二合一,内容显 ...
- Spring框架系列(7) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC初始化流程
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:紧接着这篇,我们可以看下源码的实现了:Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的. ...
- spring自动扫描、DispatcherServlet初始化流程、spring控制器Controller 过程剖析
spring自动扫描1.自动扫描解析器ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser,从doScan开始扫描解析指定包路径下的类注解信息并注册到工厂容器中. 2.进入后findCa ...
- 【开源】OSharp3.3框架解说系列(7.1):初始化流程概述
OSharp是什么? OSharp是个快速开发框架,但不是一个大而全的包罗万象的框架,严格的说,OSharp中什么都没有实现.与其他大而全的框架最大的不同点,就是OSharp只做抽象封装,不做实现.依 ...
- u-boot中nandflash初始化流程分析(转)
u-boot中nandflash初始化流程分析(转) 原文地址http://zhuairlunjj.blog.163.com/blog/static/80050945201092011249136/ ...
随机推荐
- CSS基础-关于CSS注释的添加
在 CSS 中增加注释很简单,所有被放在/*和*/分隔符之间的文本信息都被称为注释. CSS 只有一种注释,不管是多行注释还是单行注释,都必须以/*开始.以*/结束,中间加入注释内容. 1.注释放在样 ...
- 一篇文章带你掌握MyBatis简化框架——MyBatisPlus
一篇文章带你掌握MyBatis简化框架--MyBatisPlus 我们在前面的文章中已经学习了目前开发所需的主流框架 类似于我们所学习的SpringBoot框架用于简化Spring开发,我们的国人大大 ...
- 【多线程那些事儿】如何使用C++写一个线程安全的单例模式?
如何写一个线程安全的单例模式? 单例模式的简单实现 单例模式大概是流传最为广泛的设计模式之一了.一份简单的实现代码大概是下面这个样子的: class singleton { public: stati ...
- 后端框架的学习----mybatis框架(6、日志)
六.日志 如果一个数据库操作,出现了异常,我们需要排错,日志就是最好的帮手 setting设置 <settings> <setting name="logImpl" ...
- __g is not defined
新手小白学习小程序开发遇到的问题以及解决方法 文章目录 1.出现的问题 2.解决的方法 1.出现的问题 2.解决的方法 删除app.json中的 "lazyCodeLoading" ...
- 使用NEON指令加速RGB888和RGB565的相互转换
最近在做一个项目需要将RGB888转换为RGB565,用C语言转换的代码很简单,这是从ffmpeg中摘抄的代码 static inline void rgb24to16_c(const uint8_t ...
- day09-Tomcat01
Tomcat01 1.WEB开发介绍 WEB,在英文中WEB表示网/网络资源,它用于表示WEB服务器(主机)供浏览器访问的资源 WEB服务器(主机)上供外界访问的Web资源为: 静态web资源(如ht ...
- 关于ASP.NET Core WebSocket实现集群的思考
前言 提到WebSocket相信大家都听说过,它的初衷是为了解决客户端浏览器与服务端进行双向通信,是在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通讯的协议.在没有WebSocket之前只能通过浏览器到服务端的请求应答 ...
- 2022极端高温!机器学习如何预测森林火灾?⛵ 万物AI
作者:ShowMeAI编辑部 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处 收藏ShowMeAI查看更多精彩内容 今年夏天,重庆北碚区山火一路向国家级自然保护区缙云山方向蔓延.为守护家园,数万名重庆 ...
- C#字典出错“集合已经修改,可能无法执行枚举操作”
出现这个现象的原因是由于线程安全考虑,如果你边对字典循环,又同时移除字典中的某个键值对, 那么将会出现这种错误,解决这种问题的方法是你没次remove某个键值对后需要break结束对字典的循环.
