STL的使用和背后数据结构
STL(Standard Template Library即,模板库)包括六个部分:容器(containers)、迭代器(iterators)、空间配置器(allocator)、配接器(adapters)、算法(algorithms)、仿函数(functors)
vector
1、vector:连续存储
(1)头文件,#include<vector>
(2)创建vector对象,vector<int> vec;
(3)尾部插入元素,vec.push_back(a);
(4)使用下标访问元素,cout<<vec[0]<<endl;
(5)使用迭代访问元素
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(it=vec.begin();it!=vec.end();it++)
3 cout<<(*it)<<endl;
(6)插入元素,vec.insert(vec.begin()+i,a);在第i+1个元素前面插入a
(7)删除元素,vec.erase(vec.begin()+2);删除第3个元素
vec.erase(vec.begin()+i,vec.end()+j);删除区间[i,j-1];区间从0开始
(8)向量大小,vec.size();
(9)清空,vec.clear();
vector的元素不仅仅只限于int型,int、double、string、全局结构体等都可以。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std; struct Student
{
int num;
double score;
double operator< (const Student &stu) const
{
if(stu.score>score)
return stu.score;
else
return score;
}
}; int main()
{
vector<Student> stu;
//student 1
Student stu_temp;
stu_temp.num = ;
stu_temp.score =9.9;
stu.push_back(stu_temp);
//student 2
Student stu_temp1;
stu_temp1.num = ;
stu_temp1.score =8.8;
stu.push_back(stu_temp1);
//student 3
Student stu_temp2;
stu_temp2.num = ;
stu_temp2.score =7.7;
stu.push_back(stu_temp2);
//print all the students
cout<<"the number of student:"<<stu.size()<<endl;
vector<Student>::iterator it;
for(it=stu.begin();it!=stu.end();it++)
cout<<"number:"<<(*it).num<<" score:"<<(*it).score<<endl;
//delete one student
stu.erase(stu.begin()+);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"the number of student:"<<stu.size()<<endl;
for(it=stu.begin();it!=stu.end();it++)
cout<<"number:"<<(*it).num<<" score:"<<(*it).score<<endl;
//print the better score
double _result = stu_temp<stu_temp1;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"the better score:"<<_result<<endl; return ;
}
vector_sample
string
2、string
平时最常用的一个,这里就不做过多说明了
map
3、map:关联容器,提供一对一的数据映射(关键字,值);数据结构为红黑树(RB-Tree)
关键字只能在map中出现一次;另外,map内部自建一颗红黑树(一种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的;
(1)头文件,#include<map>;
(2)创建map对象,map<int,string> mapStudent;
(3)插入数据,
第一种:用insert函数插入pair数据
mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(,"Christal"));
mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(,"Carl"));
第二种:用insert函数插入value_type数据
mapStudent.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (,"Christal"));
mapStudent.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (,"Carl"));
第三种:用数组方式插入数据
1 mapStudent[] = "Christal";
2 mapStudent[] = "Carl";
输出均为:

如果用前两种方法插入数据,因为关键字是唯一的,所以当关键字已经存在的时候,再插入相同关键字的map是不成功的;而第三种用数组插入的方法是仍然可以的,会将原来的关键字所对应的值进行更改,相当于被覆盖掉了。
所以要想知道前两种方法的插入是否成功,应该用一个返回值来检验。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int,string> mapStudent;
pair<map<int,string>::iterator,bool> insert_pairl; //insert 1 and check
insert_pairl = mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(,"Christal"));
if(insert_pairl.second == true)
cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl; //insert 2 and check
insert_pairl = mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(,"Carl"));
if(insert_pairl.second == true)
cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl; //insert 3 and check
insert_pairl = mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(,"Jerry"));
if(insert_pairl.second == true)
cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl<<endl;
else
cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl<<endl; //print
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for(it=mapStudent.begin();it!=mapStudent.end();it++)
cout<<(*it).first<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl; return ;
}
map_insert_check
正如上面所说,当要插入的关键字已经存在,是插入失败的,所以输出结果为:

而采用数组插入方式会直接覆盖
mapStudent[] = "Christal";
mapStudent[] = "Carl";
mapStudent[] = "Jerry";
输出结果为:

(4)数据的遍历,当然分为用迭代器遍历的方式和用数组遍历的方式,其中以迭代器遍历中又分为正向遍历和反向遍历,正向遍历就是我们所熟知的迭代器遍历方式,反向遍历如下:
map<int,string>::iterator it; //print
2 for(it=mapStudent.begin();it!=mapStudent.end();it++)
3 cout<<(*it).first<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl;
4
5 map<int,string>::reverse_iterator rit; //reverse print
6 for(rit=mapStudent.rbegin();rit!=mapStudent.rend();rit++)
7 cout<<(*rit).first<<" "<<(*rit).second<<endl;
输出结果为:
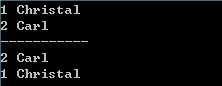
(5)查找数据,一是用count()函数查找,存在返回1,否者返回0;二是用find()函数来定位数据出现的位置;
find()函数返回一个迭代器,如果找到数据,则返回数据所在位置的迭代器;如果不存在,则返回值与end()函数的返回值相同;
1 map<int,string>::iterator _iter;
2 _iter = mapStudent.find();
if(_iter != mapStudent.end())
4 cout<<"Find Successfully"<<endl;
5 else
6 cout<<"Find Failure"<<endl;
(6)删除数据,clear()和erase()
清空map中的所有数据用clear()函数,判定map中是否有数据用empty()函数,为空返回true。
选择性的删除用erase()函数,可以实现三种方式的删除,
用迭代器删除:
1 map<int,string>::iterator _iter;
2 _iter = mapStudent.find();
3 mapStudent.erase(_iter);
用关键字删除:
int n = mapStudent.erase();
if(n == )
3 cout<<"Erase Successfully"<<endl;
else
5 cout<<"Erase Failure"<<endl;
用迭代器成片删除,删除区间是一个前闭后开[ )的集合:
1 mapStudent.erase(mapStudent.begin(),mapStudent.end());
set
4、set:用来存储同一数据类型的数据,内部每个元素都是唯一的,且自动排序;数据结构为红黑树(RB-Tree)
(1)构造函数,set<int> c;
(2)查找函数,find()函数和count()函数;
(3)数据访问函数,begin()、end()、rbegin()、rend();
(4)插入数据,insert(element)、insert(position,element)、insert(begin,end);
(5)删除数据,erase(position)、erase(element)、erase(begin,end);
hash_map&hash_set
5、hash_map和hash_set:底层数据结构是哈希表
hash_map与map用法类似,只是内部数据结构不同,hash_map提供内部数据随机、更快的访问;hash_set同理。
总结
6、总结:
(1)vector封装数组,list封装链表,map和set封装了二叉树;
(2)对于这些STL,应当掌握基本的插入、删除、排序、查找等操作;
(3)对于结构体类型的vector、map、set、hash_map、hash_set等,需要对运算符 ‘ < ’ 进行重载。
例如在map中引入结构体,对 ‘ < ’ 运算符进行重载:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std; struct Student
{
int num;
string name;
Student(int nu,string na) //constructor
{
name = na;
num = nu;
}
public:
bool operator< (const Student& stu) const //operator the <
{
return stu.num<num;
}
}; int main()
{
map<Student,double> mapStudent;
//student information
Student stu1(,"Christal");
Student stu2(,"Carl");
Student stu3(,"Jerry");
//insert
mapStudent.insert(pair<Student,double>(stu1,9.9));
mapStudent.insert(pair<Student,double>(stu2,8.8));
mapStudent.insert(pair<Student,double>(stu3,7.7));
map<Student,double>::iterator it;
for(it=mapStudent.begin();it!=mapStudent.end();it++)
cout<<(*it).first.num<<" "<<(*it).first.name<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl; return ;
}
STL的使用和背后数据结构的更多相关文章
- 转载:STL常用容器的底层数据结构实现
转载至:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28584889/article/details/88763090 vector :底层数据结构为数组,支持快速随机访问 list:底层数据结 ...
- c++面试题【转】
语言部分: 虚函数,多态.这个概念几乎是必问. STL的使用和背后数据结构,vector string map set 和hash_map,hash_set 实现一个栈类,类似STL中的栈.这个题目初 ...
- STL中经常使用数据结构
STL中经常使用的数据结构: [1] stack.queue默认的底层实现为deque结构. [2] deque:用map管理多个size大小的连续内存块,方便头尾插入. [3] vector: ...
- C++的标准模板库STL中实现的数据结构之顺序表vector的分析与使用
摘要 本文主要借助对C++的标准模板库STL中实现的数据结构的学习和使用来加深对数据结构的理解.即联系数据结构的理论分析和详细的应用实现(STL),本文是系列总结的第一篇,主要针对线性表中的顺序表(动 ...
- C++的标准模板库STL中实现的数据结构之链表std::list的分析与使用
摘要 本文主要借助对C++的标准模板库STL中实现的数据结构的学习和使用来加深对数据结构的理解,即联系数据结构的理论分析和详细的应用实现(STL),本文是系列总结的第二篇.主要针对线性表中的链表 ST ...
- STL学习小结
STL就是Standard Template Library,标准模板库.这可能是一个历史上最令人兴奋的工具的最无聊的术语.从根本上说,STL是一些"容器"的集合,这些" ...
- STL学习总结
STL就是Standard Template Library,标准模板库.这可能是一个历史上最令人兴奋的工具的最无聊的术语.从根本上说,STL是一些"容器"的集合.这些" ...
- STL 较详尽总结
STL就是Standard Template Library,标准模板库.这可能是一个历史上最令人兴奋的工具的最无聊的术语.从根本上说,STL是一些"容器"的集合,这些" ...
- stl 迭代器(了解)
STL 主要是由 containers(容器),iterators(迭代器)和 algorithms(算法)的 templates(模板)构成的. 对应于它们所支持的操作,共有五种 iterators ...
随机推荐
- LAMP的搭建与简易配置(apache,php已module方式结合)
测试所用环境:centos7.2 apache php 所在主机IP:9.110.187.120 mariadb 所在主机IP:9.110.187.121 第一部分:环境搭建 yum安装软件包 其中a ...
- 选择排序——Python实现
选择排序: 选择排序(Selection sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法.它的工作原理如下.首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,然后,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小( ...
- php处理表单中的复选框问题以及js实现全选
做的一个项目中遇到了全选和取消全选的问题,这是一个很普遍的功能,,虽然我们经常用到,但是真正做起来却发现行不通,在网上找了些,大部分都是ie,但是谷歌内核浏览器不能正常实现,所以经过小小的调整,今天就 ...
- 设计模式一:关于C++写观察者模式的一些收获
先贴上部分代码: #include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<v ...
- java设计模式之 装饰器模式
装饰器模式 装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构. 这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的类的一个包装. 这种模式创建了一个装 ...
- BOM(2)
Window 子对象 (1)Location 对象 Location 对象包含有关当前 URL(统一资源定位符) 的信息.(Uniform Resource Location) Location 对象 ...
- Spring学习(2)---IOC
1.接口及面向接口编程 2.什么是IOC 3.Spring的Bean配置 4.Bean的初始化 5.Spring的常用注入方式 (一)接口 用于沟通的中介物的抽象化 实体把自己提供给我外接的一种抽象化 ...
- win8安装sql2008及设置登陆名问题
1. .net3.5安装 使用win8系统自带的升级功能无法成功安装.其实Windows8安装文件中已经集了.Net3.5, (1)此时只需要使用虚拟光驱加载Windows8 ...
- Oracle exp/imp数据导入导出工具基本用法
一.获取帮助 exp/imp help=y 二.数据导出 1.将数据库完全导出,设置full选项exp system/manager@orcl file=d:\db.dmp full=y 2.导出数据 ...
- Log4PHP 配置和使用
Log4PHP2.3.0使用解释 1. 什么是Log4PHP Log4php它为apche组织维护项目,是Log4xx系列日志组件之一,log4j在JAVA中可算是大名鼎鼎的日志开发包.Log4PHP ...
