树的总结(遍历,BST,AVL原型,堆,练习题)
树
@
一.抽象数据类型
1.顺序存储
使用数组存储
父亲索引为 n
左孩子 2*n 右孩子 2*n+1
2.链式存储
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree; /* 二叉树类型 */
struct TNode{ /* 树结点定义 */
ElementType Data; /* 结点数据 */
BinTree Left; /* 指向左子树 */
BinTree Right; /* 指向右子树 */
};
二、二叉树的性质
1.二叉树第i层最大结点数为:2^(i-1),i>=1
2.深度为k的二叉树最大结点总数为:2^k-1,k>=1
3.对任何非空二叉树T,若n0表示叶子结点个数、n2是度为2的非叶子结点个数,那么二者满足关系n0=n2+1
三、二叉树的遍历
3.1.递归
void PreOrderTraversal(BinTree BT){
if(BT){
printf("%d",BT->Data);
PreOrderTraversal(BT->Left);
PreOrderTraversal(BT->Right);
}
}
中序后序同理,把打印放在中间和后面,这里不加以赘述。
3.2.非递归
以链式中序为例
void InOrderTraversal(BinTree BT){
BinTree T=BT;
Stack S=CreatSatck(MaxSize);
while(T||!IsEmpty(S)){
Push(S,T);
T=T->Left;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S)){
T=Pop(S);
printf("%5d",T->Data);
T=T->Right;
}
}
3.3.利用队列进行层序遍历
void levelOrderTraversal(Tree *tr){
queue<Tree*> que;
Tree *t=tr;
if(t==NULL) return;
que.push(t);
while(!que.empty()){
t=que.front();
que.pop();
printf("%d\n",t->val);
if(t->left!=NULL) que.push(t->left);
if(t->right!=NULL) que.push(t->right);
}
}
3.4.已知先序中序求后序
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int post[] = {3, 4, 2, 6, 5, 1};
int in[] = {3, 2, 4, 1, 6, 5};
void pre(int root, int start, int end) {
if(start > end) return ;
int i = start;
while(i < end && in[i] != post[root]) i++;
printf("%d ", post[root]);
pre(root - 1 - end + i, start, i - 1);
pre(root - 1, i + 1, end);
}
int main() {
pre(5, 0, 5);
return 0;
}
3.5.已知中序后序求先序
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int pre[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int in[] = {3, 2, 4, 1, 6, 5};
void post(int root, int start, int end) {
if(start > end)
return ;
int i = start;
while(i < end && in[i] != pre[root]) i++;
post(root + 1, start, i - 1);
post(root + 1 + i - start, i + 1, end);
printf("%d ", pre[root]);
}
int main() {
post(0, 0, 5);
return 0;
}
3.6.先序构建树
TreeNode* buildTree(int root, int start, int end) {
if(start > end) return NULL;
int i = start;
while(i < end && in[i] != pre[root]) i++;
TreeNode* t = new TreeNode();
t->left = buildTree(root + 1, start, i - 1);
t->right = buildTree(root + 1 + i - start, i + 1, end);
t->data = pre[root];
return t;
}
三、活用树的遍历
3.1.PAT Advanced 1020 Tree Traversals
参考 https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805485033603072
这是一道考察树的构成,后序中序转前序,前序构造树,树层序遍历的一道题目,知识点考察很多
原题翻译:
已知后序遍历,中序遍历,求层序遍历
输入:一共有多少值
第一行为后序遍历,第二行为中序遍历
输出:层序遍历
Sample Input:
7
2 3 1 5 7 6 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Sample Output:
4 1 6 3 5 7 2
根据二中的方法,我们可以进行活用
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode{//树的抽象类型
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
};
vector<int> pre,in,post,ans;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
void preOrder(int root,int start,int end){//由中序后序建立前序
if(start>end) return;
int i=0;
while(i<=end&&in[i]!=post[root]) i++;
pre.push_back(post[root]);
preOrder(root-1-end+i,start,i-1);
preOrder(root-1,i+1,end);
}
TreeNode* buildTree(int root,int start,int end){//由前序中序构建树
if(start>end) return NULL;
int i=0;
TreeNode *t=new TreeNode();
while(i<=end&&in[i]!=pre[root]) i++;
t->val=pre[root];
t->left=buildTree(root+1,start,i-1);
t->right=buildTree(root+1+i-start,i+1,end);
return t;
}
void levelOrder(TreeNode *tree){//层序遍历树
que.push(tree);
while(!que.empty()){
TreeNode *tmp=que.front();
ans.push_back(tmp->val);
que.pop();
if(tmp->left!=NULL) que.push(tmp->left);
if(tmp->right!=NULL) que.push(tmp->right);
}
}
int main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
post.resize(N);in.resize(N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) scanf("%d",&post[i]);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) scanf("%d",&in[i]);
preOrder(N-1,0,N-1);
TreeNode *tree=buildTree(0,0,N-1);
levelOrder(tree);
for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++)
if(i!=ans.size()-1) cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
else cout<<ans[i];
system("pause");
return 0;
}
查看柳婼大神的博客,我们可以知道,有更简单的方法,仅仅加一个索引值,便可以达到相同的效果,代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int index;
int val;
};
bool cmp(node n1,node n2){
return n1.index<n2.index;
}
vector<int> in,post;
vector<node> ans;
void preOrder(int root,int start,int end,int index){
if(start>end) return;
int i=0;
while(i<=end&&in[i]!=post[root]) i++;
ans.push_back({index,post[root]});
preOrder(root-1-end+i,start,i-1,2*index+1);
preOrder(root-1,i+1,end,2*index+2);
}
int main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
post.resize(N);in.resize(N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) scanf("%d",&post[i]);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) scanf("%d",&in[i]);
preOrder(N-1,0,N-1,0);
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end(),cmp);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
if(i!=N-1) printf("%d ",ans[i].val);
else printf("%d",ans[i].val);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.2.PAT Advanced 1086 Tree Traversals Again 参考PAT官网原题
这道题比上面一题简单,简单叙述
给先序遍历的进栈出栈过程,求后序遍历。
输入:数量 进栈出栈过程
输出:后序遍历
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
我们可以知道,先序遍历的出栈就是中序遍历打印,于是代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
vector<int> pre,in,post,val;
void postorder(int root,int start,int end){//中序,后序找前序
if(start>end) return ;
int root_index=0;
while(root_index<=end&&in[root_index]!=pre[root]) root_index++;
postorder(root+1,start,root_index-1);
postorder(root+1+root_index-start,root_index+1,end);
post.push_back(pre[root]);
}
int main()
{
stack<int> sta;
int k=0,N;
char ch[5];int num;
scanf("%d",&N);
while(~scanf("%s",&ch)){
if(strlen(ch)==4) {
scanf("%d",&num);
pre.push_back(num);
sta.push(num);
}else{
in.push_back(sta.top());
sta.pop();
//if(in.size()==N) break;//测试代码的时候,可以把这句加上,因为官方使用的是文件测,所以支持~scanf的写法
}
}
postorder(0,0,N-1);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
if(i!=N-1) printf("%d ",post[i]);
else printf("%d",post[i]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
四、BST树
原型以及增删
C语言BST树原型,BST树在进行增删的时候效率没有链表高,但是在查找的时候比较快,这边以BST原型,用C程序构造一个BST树。
#ifndef BSTTREE_H_INCLUDED
#define BSTTREE_H_INCLUDED
#define ElementType int
#define Position BSTTree*
typedef struct BSTTree{
ElementType Data;
struct BSTTree *Left;
struct BSTTree *Right;
}BSTTree;
Position FindMin(BSTTree *bstTree){//递归查找
if(!bstTree) return NULL;
else if(!bstTree->Left) return bstTree;
else return FindMin(bstTree->Left);
}
Position FindMax(BSTTree *bstTree){//循环查找
if(bstTree)
while(bstTree->Right) bstTree=bstTree->Right;
return bstTree;
}
BSTTree* Insert(ElementType x,BSTTree *bstTree){
if(bstTree){
bstTree=malloc(sizeof(struct BSTTree));
bstTree->Data=x;
bstTree->Left=NULL;
bstTree->Right=NULL;
}else{
if(x<bstTree->Data) bstTree->Left=Insert(x,bstTree->Left);
else if(x>bstTree->Data) bstTree->Right=Insert(x,bstTree->Right);
//else 啥也不做
}
return bstTree;
}
BSTTree* Delete(ElementType x,BSTTree *bstTree){
Position Tmp;
if(!bstTree) printf("not find");
else if(x<bstTree->Data) bstTree->Left=Delete(x,bstTree->Left);//左递归删除
else if(x>bstTree->Data) bstTree->Right=Delete(x,bstTree->Right);//右递归删除
else
if(bstTree->Left&&bstTree->Right){//左右两个孩子
Tmp=FindMin(bstTree->Right);//右子树找最小元素填充删除节点
bstTree->Data=Tmp->Data;
bstTree->Right=Delete(bstTree->Data,bstTree->Right);//继续删除右子树最小元素
}else{//有一个孩子或者没有孩子
Tmp=bstTree;
if(!bstTree->Left)
bstTree=bstTree->Right;//直接赋值有孩子
else if(!bstTree->Left)
bstTree=bstTree->Left;//直接赋值左孩子
free(Tmp);//进行释放
}
return bstTree;
}
#endif // BSTTREE_H_INCLUDED
五、AVL树
5.1.AVL树概念
什么是AVL树,比BST树多了一个平衡因子(Balance Factor),简称BF:BF(T)=hl-hr,其中hl和hr为左右子树的高度。
当平衡因子大于1的时候,我们就可以进行旋转操作
1.RR旋转(右单旋)
2.LL旋转(左单旋)
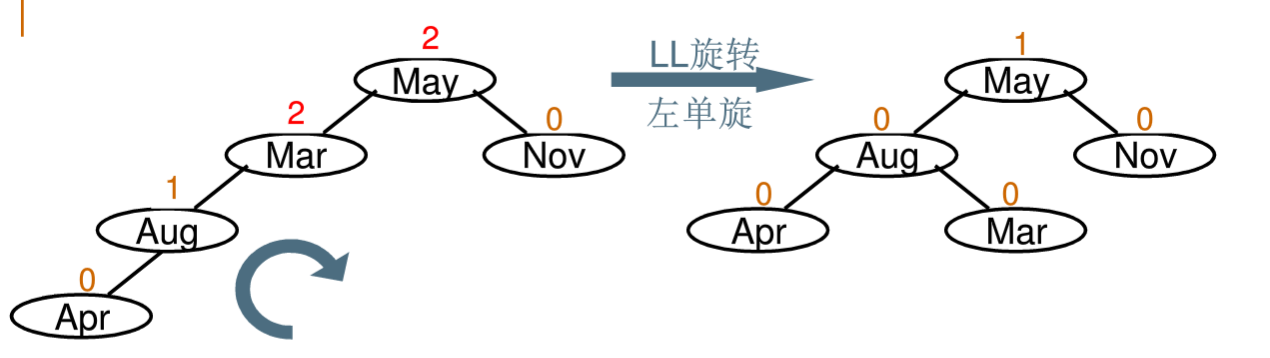
3.LR旋转(左右双旋)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-46YFPG97-1571396745491)(C:\Users\74302\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1571053306116.png)]
5.2.AVL树原型
#define ElementType int
typedef struct AVLNode *Position;
typedef Position AVLTree; /* AVL树类型 */
struct AVLNode{
ElementType Data; /* 结点数据 */
AVLTree Left; /* 指向左子树 */
AVLTree Right; /* 指向右子树 */
int Height; /* 树高 */
};
5.3.AVL树LL旋转
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A){
/* 注意:A必须有一个左子结点B */
/* 将A与B做左单旋,更新A与B的高度,返回新的根结点B */
AVLTree B = A->Left;
A->Left = B->Right;
B->Right = A;
A->Height = Max( GetHeight(A->Left), GetHeight(A->Right) ) + 1;
B->Height = Max( GetHeight(B->Left), A->Height ) + 1;
return B;
}
5.4.AVL树LR旋转
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation ( AVLTree A )
{ /* 注意:A必须有一个左子结点B,且B必须有一个右子结点C */
/* 将A、B与C做两次单旋,返回新的根结点C */
/* 将B与C做右单旋,C被返回 */
A->Left=SingleRightRotation(A->Left);
/* 将A与C做左单旋,C被返回 */
return SingleLeftRotation(A);
}
5.5.AVL树插入函数
AVLTree Insert( AVLTree T, ElementType X )
{ /* 将X插入AVL树T中,并且返回调整后的AVL树 */
if ( !T ) { /* 若插入空树,则新建包含一个结点的树 */
T = (AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct AVLNode));
T->Data = X;
T->Height = 0;
T->Left = T->Right = NULL;
} /* if (插入空树) 结束 */
else if ( X < T->Data ) {
/* 插入T的左子树 */
T->Left = Insert( T->Left, X);
/* 如果需要左旋 */
if ( GetHeight(T->Left)-GetHeight(T->Right) == 2 )
if ( X < T->Left->Data )
T = SingleLeftRotation(T); /* 左单旋 */
else
T = DoubleLeftRightRotation(T); /* 左-右双旋 */
} /* else if (插入左子树) 结束 */
else if ( X > T->Data ) {
/* 插入T的右子树 */
T->Right = Insert( T->Right, X );
/* 如果需要右旋 */
if ( GetHeight(T->Left)-GetHeight(T->Right) == -2 )
if ( X > T->Right->Data )
T = SingleRightRotation(T); /* 右单旋 */
else
T = DoubleRightLeftRotation(T); /* 右-左双旋 */
} /* else if (插入右子树) 结束 */
/* else X == T->Data,无须插入 */
/* 别忘了更新树高 */
T->Height = Max( GetHeight(T->Left), GetHeight(T->Right) ) + 1;
return T;
}
六、BST树和AVL树练习
6.1.浙大习题7-4 是否是同一棵二叉搜索树
给定一个插入序列就可以唯一确定一棵二叉搜索树。然而,一棵给定的二叉搜索树却可以由多种不同的插入序列得到。例如分别按照序列{2, 1, 3}和{2, 3, 1}插入初始为空的二叉搜索树,都得到一样的结果。于是对于输入的各种插入序列,你需要判断它们是否能生成一样的二叉搜索树。
输入格式:
输入包含若干组测试数据。每组数据的第1行给出两个正整数N (≤10)和L,分别是每个序列插入元素的个数和需要检查的序列个数。第2行给出N个以空格分隔的正整数,作为初始插入序列。最后L行,每行给出N个插入的元素,属于L个需要检查的序列。
简单起见,我们保证每个插入序列都是1到N的一个排列。当读到N为0时,标志输入结束,这组数据不要处理。
输出格式:
对每一组需要检查的序列,如果其生成的二叉搜索树跟对应的初始序列生成的一样,输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
输入样例:
4 2
3 1 4 2
3 4 1 2
3 2 4 1
2 1
2 1
1 2
0
输出样例:
Yes
No
No
这道题,仅仅需要进行构造一棵BST树,然后进行判断先序遍历的打印即可,AC代码如下。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string traver_ini,traver_cmp;
struct BST{
int val;
BST *left;
BST *right;
};
BST *ini,*cmp;
BST* BST_insert(BST *b,int val){
if(b==NULL) {
b=new BST();
b->val=val;
return b;
}
if(val<b->val) b->left=BST_insert(b->left,val);
else if(val>b->val) b->right=BST_insert(b->right,val);
return b;
}
void pre(BST *b,string& str){
if(b==NULL) return;
str+=(b->val+'0');
pre(b->left,str);
pre(b->right,str);
}
int main()
{
int M,N,tmp;
while(1){
scanf("%d",&M);
if(M==0) break;
scanf("%d\n",&N);
ini=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
scanf("%d",&tmp);
ini=BST_insert(ini,tmp);
}
traver_ini="";
pre(ini,traver_ini);
while(N--){
cmp=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
scanf("%d",&tmp);
cmp=BST_insert(cmp,tmp);
}
traver_cmp="";
pre(cmp,traver_cmp);
if(traver_cmp==traver_ini) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
6.2.PAT Advanced 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25 分) 参考PAT官网
简单叙述:
给定插入元素个数n
插入n个元素后,输出根节点元素值
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
解题方法,构造一棵AVL树,然后插入,求根即可
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node{//AVL节点原型
int val;
node *left,*right;
};
node *rotateRight(node *root){//右多,进行RR旋转
node *t=root->right;
root->right=t->left;
t->left=root;
return t;
}
node *rotateLeft(node *root){//左多,进行LL旋转
node *t=root->left;
root->left=t->right;
t->right=root;
return t;
}
node *rotateLeftRight(node *root){//左多,进行LR旋转
root->left=rotateRight(root->left);
return rotateLeft(root);
}
node *rotateRightLeft(node *root){//右多,进行RL旋转
root->right=rotateLeft(root->right);
return rotateRight(root);
}
int getHeight(node *root){//获得高度
if(root==NULL) return 0;
return max(getHeight(root->left),getHeight(root->right))+1;
}
node *insert(node *root,int val){
if(root==NULL){//空的时候
root=new node();
root->val=val;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
}else if(val<root->val){//插左边
root->left=insert(root->left,val);
if(getHeight(root->left)-getHeight(root->right)==2)
root=val<root->left->val?rotateLeft(root):rotateLeftRight(root);
//如果比左还要小,只需要进行LL旋转,否则需要LR旋转
}else{//插右边
root->right=insert(root->right,val);
if(getHeight(root->right)-getHeight(root->left)==2)
root=val>root->right->val?rotateRight(root):rotateRightLeft(root);
//如果比右还要打,只需进行RR旋转,否则需要RL旋转
}
return root;
}
int main()
{
int n,tmp;cin>>n;
node* root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>tmp;
root=insert(root,tmp);
}
cout<<root->val;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
七、堆
7.1.创建堆
void createHeap(){
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--)
downAjust(i,n);
}
7.2.向下调整
思想是,low代表孩子,high代表极限。我们在[low,high]范围进行调整,low和low+1为2*low的孩子。如果没有交换,那就break掉,交换了还要和上面父亲去比较。
void downAdjust(int low,int high){
int i=low,j=i*2;//i为要调整的节点,j为左孩子
while(j<=high){
if(j+1<=high && heap[j+1]>heap[j]) j=j+1;
if(heap[j]>heap[i]){
swap(heap[j],heap[i]);
i=j;j=i*2;
}else break;
}
}
7.3.删除堆顶元素
void deleteTop(){
heap[1]=heap[n--];//用第n个数进行覆盖
downAdjust(1,n);//之后进行向下调整第一个数
}
7.4.增加一个元素
void insert(int x){
heap[++n]=x;
upAdjust(1,n);
}
7.5.向上调整
void upAdjust(int low,int high){
int i=high,j=i/2;
while(j>=low){
if(heap[j]<heap[i]){
swap(heap[j],heap[i]);
i=j;j=i/2;
}else break;
}
}
7.6.堆排序
void heapSort(){
createHeap();
for(int i=n;i>=2;i--){
swap(heap[i],heap[1]);
downAdjust(1,i-1);
}
}
7.7.复用型heap.h文件
#ifndef HEAP_H_INCLUDED
#define HEAP_H_INCLUDED
#define maxn 1000
using namespace std;//这里面有swap函数
int heap[maxn];
void upAdjust(int low,int high){
int i=high,j=i/2;
while(j>=low){
if(heap[j]<heap[i]){
swap(heap[j],heap[i]);
i=j;j=i/2;
}else break;
}
}
void downAdjust(int low,int high){
int i=low,j=i*2;//i为要调整的节点,j为左孩子
while(j<=high){
if(j+1<=high && heap[j+1]>heap[j]) j=j+1;
if(heap[j]>heap[i]){
swap(heap[j],heap[i]);
i=j;j=i*2;
}else break;
}
}
void createHeap(int n){
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--)
downAdjust(i,n);
}
void deleteTop(int n){
heap[1]=heap[n--];//用第n个数进行覆盖
downAdjust(1,n);//之后进行向下调整第一个数
}
void insert(int x,int n){
heap[++n]=x;
upAdjust(1,n);
}
void heapSort(int n){
createHeap(n);
for(int i=n;i>=2;i--){
swap(heap[i],heap[1]);
downAdjust(1,i-1);
}
}
#endif // HEAP_H_INCLUDED
7.8.测试文件
#include <iostream>
#include "heap.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
extern int heap[maxn];
extern int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
/**我们的堆序列是从[1,n]的*/
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&heap[i]);
createHeap();//生成大根堆
insert(4);//插入堆顶元素
deleteTop();//删除堆顶
heapSort();//排序
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) printf("%d%s",heap[i],i==n?"\n":" ");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
树的总结(遍历,BST,AVL原型,堆,练习题)的更多相关文章
- 算法设计和数据结构学习_5(BST&AVL&红黑树简单介绍)
前言: 节主要是给出BST,AVL和红黑树的C++代码,方便自己以后的查阅,其代码依旧是data structures and algorithm analysis in c++ (second ed ...
- BST&AVL&红黑树简单介绍
(BST&AVL&红黑树简单介绍) 前言: 节主要是给出BST,AVL和红黑树的C++代码,方便自己以后的查阅,其代码依旧是data structures and algorithm ...
- B树、B+树、红黑树、AVL树
定义及概念 B树 二叉树的深度较大,在查找时会造成I/O读写频繁,查询效率低下,所以引入了多叉树的结构,也就是B树.阶为M的B树具有以下性质: 1.根节点在不为叶子节点的情况下儿子数为 2 ~ M2. ...
- 多级树的深度遍历与广度遍历(Java实现)
目录 多级树的深度遍历与广度遍历 节点模型 深度优先遍历 广度优先遍历 多级树的深度遍历与广度遍历 深度优先遍历与广度优先遍历其实是属于图算法的一种,多级树可以看做是一种特殊的图,所以多级数的深/广遍 ...
- 树和二叉树->遍历
文字描述 二叉树的先根遍历 若二叉树为空,则空操纵,否则 (1) 访问根结点 (2) 先根遍历左子树 (3) 先根遍历右子树 二叉树的中根遍历 若二叉树为空,则空操纵,否则 (1) 中根遍历左子树 ( ...
- List Leaves 树的层序遍历
3-树2 List Leaves (25 分) Given a tree, you are supposed to list all the leaves in the order of top do ...
- 树的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历的原理和java实现代码
import java.util.ArrayDeque; public class BinaryTree { static class TreeNode{ int value; TreeNode le ...
- Tree(树的还原以及树的dfs遍历)
紫书:P155 uva 548 You are to determine the value of the leaf node in a given binary tree that is th ...
- PAT树_层序遍历叶节点、中序建树后序输出、AVL树的根、二叉树路径存在性判定、奇妙的完全二叉搜索树、最小堆路径、文件路由
03-树1. List Leaves (25) Given a tree, you are supposed to list all the leaves in the order of top do ...
随机推荐
- MySQL创建用户、授权、删除
1.在MySQL中创建新用户 使用具有shell访问权限的root用户登录MySQL服务器并创建名为“rahul”的新用户.下面的命令只允许从localhost系统访问用户rahul的MySQL服务器 ...
- Linux 之 awk文本分析工具
AWK是一种处理文本文件的语言,是一个强大的文本分析工具.Linux环境中自带. awk调用方法 命令行 awk [-F field-separator] 'commands' input-file( ...
- Centos7服务器环境搭建
1.Apache安装 yum install httpd systemctl start httpd.service #启动 systemctl stop httpd.service#停止 syste ...
- linux命令帮助 man bash
BASH(1) BASH(1) NAME bash - GNU Bourne-Again SHell (GNU 命令解释程序 “Bourne二世”) 概述(SYNOPSIS) bash [option ...
- 【ARM-Linux开发】 uboot启动阶段修改启动参数方法及分析
作者:围补 本来启动方式这节不是什么复杂的事儿,不过想简单的说清楚明白,还真是不知道怎么组织.毕竟文字跟有声语言表达有别.但愿简单的东西别让我讲的太复杂! Arm板系统文件一般有三个--bootloa ...
- ue-cli3 取消eslint校验代码
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/sjie/p/9884362.html
- *#【Python】【基础知识】【运算符】【Python的几类运算符】
Python的运算符分为以下几类: 算术运算符比较(关系)运算符赋值运算符逻辑运算符位运算符成员运算符身份运算符 以及需要考虑的:运算符优先级 一.算术运算符: 需要注意的,上图是Python 2.0 ...
- html当中如何引用js文件
3)html当中如何引用js文件 如果需要javascript工程师和html美工各干各的工作,需要分开写文件. 例 1.2 <html><head> <scrip ...
- SQLite进阶-15.触发器
目录 触发器(Trigger) 触发器(Trigger)的要点: 触发器应用 查看触发器 删除触发器 触发器(Trigger) 触发器(Trigger)是数据库的回调函数,它会在指定的数据库事件发生时 ...
- (十二)springMvc 处理图片,视频等文件的上传
文章目录 导包 修改表单类型 配置解析器 处理上传的图片 补充一个自己写的工具类 导包 需要导入如下的包 commons-fileupload-1.3.3.jar commons-io-2.6.jar ...
