ROS actionlib学习(三)
下面这个例子将展示用actionlib来计算随机变量的均值和标准差。首先在action文件中定义goal、result和feedback的数据类型,其中goal为样本容量,result为均值和标准差,feedback为样本编号、当前样本数据、均值和标准差。
#goal definition
int32 samples
---
#result definition
float32 mean
float32 std_dev
---
#feedback
int32 sample
float32 data
float32 mean
float32 std_dev
按照之前例程中的步骤修改CMakeLists.txt后进行编译,生成相关的消息文件和头文件。
Writing a Simple Server
参考 C++ SimpleActionServer 文档,SimpleActionServer类的构造函数有多种重载形式:
SimpleActionServer (std::string name, ExecuteCallback execute_callback, bool auto_start) SimpleActionServer (std::string name, bool auto_start) SimpleActionServer (ros::NodeHandle n, std::string name, ExecuteCallback execute_callback, bool auto_start) SimpleActionServer (ros::NodeHandle n, std::string name, bool auto_start)
在Writing a Simple Action Server using the Execute Callback的例子中,SimpleActionServer就使用了上面第3种构造函数,参数为节点句柄、action名称以及ExecuteCallback回调函数。在本例中没有使用这种来创建action server,而是在action server创建后通过注册 goal callback 和 preempt callback这两个回调函数来处理事件。
void registerGoalCallback (boost::function< void()> cb) // Allows users to register a callback to be invoked when a new goal is available void registerPreemptCallback (boost::function< void()> cb) // Allows users to register a callback to be invoked when a new preempt request is available
服务端代码averaging_server.cpp如下:
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
#include <actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h> // actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h is the action library used from implementing simple actions
#include <actionlib_tutorials/AveragingAction.h> // This includes action message generated from the Averaging.action file class AveragingAction
{
public: AveragingAction(std::string name) :
as_(nh_, name, false),
action_name_(name)
{
//register the goal and feeback callbacks
as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this)); //subscribe to the data topic of interest
sub_ = nh_.subscribe("/random_number", , &AveragingAction::analysisCB, this);
as_.start();
} ~AveragingAction(void)
{
} void goalCB()
{
// reset helper variables
data_count_ = ;
sum_ = ;
sum_sq_ = ;
// accept the new goal
goal_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->samples;
// acceptNewGoal: Accepts a new goal when one is available. The status of this goal is set to active upon acceptance, and the status of any previously active goal is set to preempted
} void preemptCB()
{
ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
// set the action state to preempted
as_.setPreempted();
} void analysisCB(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg)
{
// make sure that the action hasn't been canceled
if (!as_.isActive())
return; data_count_++;
feedback_.sample = data_count_;
feedback_.data = msg->data;
//compute the std_dev and mean of the data
sum_ += msg->data;
feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, );
feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, )));
as_.publishFeedback(feedback_); if(data_count_ > goal_)
{
result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev; if(result_.mean < 5.0)
{
ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
//set the action state to aborted
as_.setAborted(result_);
}
else
{
ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
// set the action state to succeeded
as_.setSucceeded(result_);
}
}
} protected: ros::NodeHandle nh_;
actionlib::SimpleActionServer<actionlib_tutorials::AveragingAction> as_;
std::string action_name_;
int data_count_, goal_;
float sum_, sum_sq_;
actionlib_tutorials::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
actionlib_tutorials::AveragingResult result_;
ros::Subscriber sub_;
}; int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "averaging"); AveragingAction averaging(ros::this_node::getName());
ros::spin(); return ;
}
程序中标准差是根据下面的公式计算的:
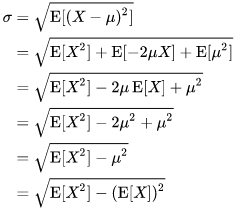
服务端程序会订阅/random_number话题,并执行回调函数analysisCB。注意在消息回调函数的开头会调用SimpleActionServer类中的isActive()来检测goal的状态,如果不是处于active状态(The goal is currently being processed by the action server)则退出程序,直到客户端发起请求,goal开始被server处理。
Goals请求由ActionClient发出,ActionServer接收后会创建一个有限状态机来跟踪goal的状态:

goal状态的转变主要由server端程序发起,可以使用下面一系列的命令:
setAccepted - After inspecting a goal, decide to start processing it
setRejected - After inspecting a goal, decide to never process it because it is an invalid request (out of bounds, resources not available, invalid, etc)
setSucceeded - Notify that goal has been successfully processed
setAborted - Notify that goal encountered an error during processsing, and had to be aborted
setCanceled - Notify that goal is no longer being processed, due to a cancel request
客户端也能异步发起状态转变:
CancelRequest: The client notifies the action server that it wants the server to stop processing the goal.
状态机有下面多种状态:
中间状态:
Pending - The goal has yet to be processed by the action server
Active - The goal is currently being processed by the action server
Recalling - The goal has not been processed and a cancel request has been received from the action client, but the action server has not confirmed the goal is canceled
Preempting - The goal is being processed, and a cancel request has been received from the action client, but the action server has not confirmed the goal is canceled
最终状态:
Rejected - The goal was rejected by the action server without being processed and without a request from the action client to cancel
Succeeded - The goal was achieved successfully by the action server
Aborted - The goal was terminated by the action server without an external request from the action client to cancel
Recalled - The goal was canceled by either another goal, or a cancel request, before the action server began processing the goal
Preempted - Processing of the goal was canceled by either another goal, or a cancel request sent to the action server
Writing the Data Node
发布随机数节点的代码 gen_numbers.py如下。Python中的random.normalvariate(mu, sigma)函数会返回服从正态分布的随机数,均值为mu,标准差为sigma.
#!/usr/bin/env python import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import Float32
import random
def gen_number():
pub = rospy.Publisher('random_number', Float32)
rospy.init_node('random_number_generator', log_level=rospy.INFO)
rospy.loginfo("Generating random numbers") while not rospy.is_shutdown():
pub.publish(Float32(random.normalvariate(5, 1)))
rospy.sleep(0.05) if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
gen_number()
except Exception, e:
print "done"
注意不要忘记给文件添加可执行权限:
chmod +x gen_numbers.py
Writing a Threaded Simple Action Client
SimpleActionClient的构造函数如下,注意参数spin_thread的设置。如果spin_thread为false则需要自行开启线程。
// Constructs a SingleGoalActionClient
actionlib::SimpleActionClient< ActionSpec >::SimpleActionClient ( const std::string & name, bool spin_thread = true ) /*
Parameters
name: The action name. Defines the namespace in which the action communicates
spin_thread: If true, spins up a thread to service this action's subscriptions.
If false, then the user has to call ros::spin() themselves. Defaults to True
*/
客户端程序averaging_client.cpp如下:
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <actionlib/client/simple_action_client.h> // the action library used from implementing simple action clients
#include <actionlib/client/terminal_state.h> // defines the possible goal states
#include <actionlib_tutorials/AveragingAction.h> // This includes action message generated from the Averaging.action file
#include <boost/thread.hpp> // the boost thread library for spinning the thread void spinThread()
{
ros::spin();
} int main (int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "test_averaging"); // create the action client
actionlib::SimpleActionClient<actionlib_tutorials::AveragingAction> ac("averaging", false); boost::thread spin_thread(&spinThread); // the thread is created and the ros node is started spinning in the background ROS_INFO("Waiting for action server to start.");
// Since the action server may not be up and running, the action client will wait for the action server to start before continuing.
ac.waitForServer(); ROS_INFO("Action server started, sending goal.");
// send a goal to the action
actionlib_tutorials::AveragingGoal goal;
goal.samples = ;
ac.sendGoal(goal); // The action client now waits for the goal to finish before continuing
bool finished_before_timeout = ac.waitForResult(ros::Duration(30.0)); if (finished_before_timeout)
{
actionlib::SimpleClientGoalState state = ac.getState();
ROS_INFO("Action finished: %s",state.toString().c_str());
}
else
ROS_INFO("Action did not finish before the time out."); // shutdown the node and join the thread back before exiting
ros::shutdown(); spin_thread.join(); //exit
return ;
}
下面是boost::thread线程管理的一个例子:
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
#include <iostream> void wait(int seconds)
{
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::seconds(seconds));
} void thread()
{
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
{
wait();
std::cout << i << std::endl;
}
} int main()
{
boost::thread t(thread);
t.join(); return ;
}
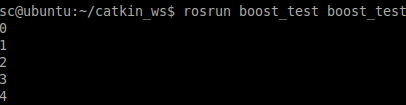
上述示例中的变量t 一旦被创建,该thread()函数就在其所在线程中被立即执行。为了防止程序终止,就需要对新建线程调用 join() 方法。 join() 方法是一个阻塞调用:它可以暂停当前线程,直到调用 join() 的线程运行结束。 这就使得main() 函数一直会等待到 thread() 运行结束。程序输出如下图所示,如果没有用join方法,则会直接退出。
Running an Action Server and Client with Other Nodes
运行server:
rosrun actionlib_tutorials averaging_server
运行随机数发生器节点:
rosrun actionlib_tutorials gen_numbers.py
运行client:
rosrun actionlib_tutorials averaging_client
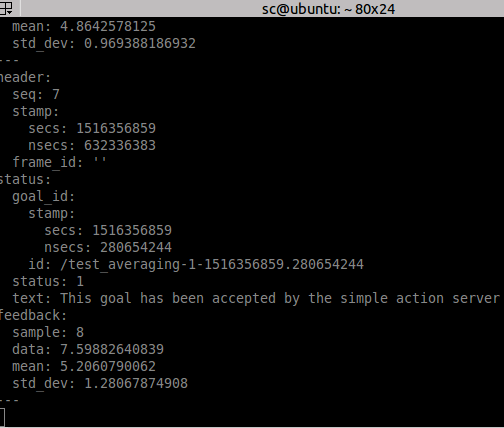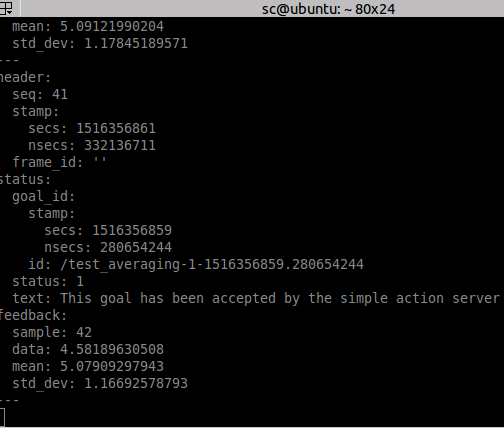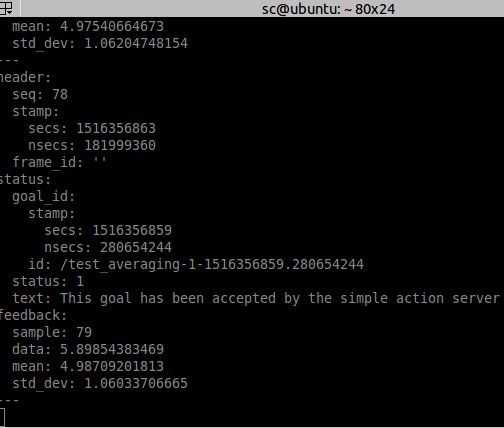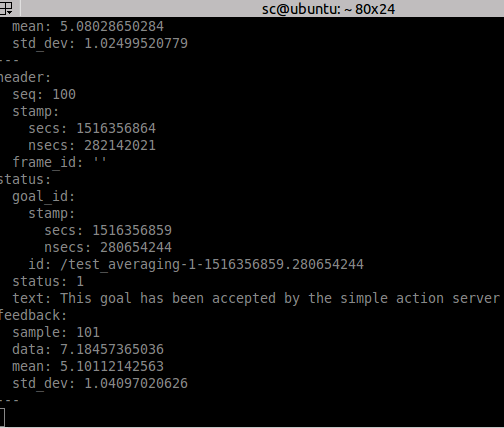
计算平均数时查看feedback:
rostopic echo /averaging/feedback
参考:
actionlib-Detailed Description
ROS actionlib学习(三)的更多相关文章
- ROS actionlib学习(二)
在ROS actionlib学习(一)中的例子展示了actionlib最基本的用法,下面我们看一个稍微实际一点的例子,用actionlib计算斐波那契数列,并发布反馈(feedback)和结果(res ...
- ROS actionlib学习(一)
actionlib是ROS中一个很重要的功能包集合,尽管在ROS中已经提供了srevice机制来满足请求—响应式的使用场景,但是假如某个请求执行时间很长,在此期间用户想查看执行的进度或者取消这个请求的 ...
- ROS入门学习
ROS学习笔记 ROS入门网站; ROS入门书籍 ROS主要包含包括功能包.节点.话题.消息类型和服务; ROS功能包/软件包(Packages) ROS软件包是一组用于实现特定功能的相关文件的集合, ...
- HTTP学习三:HTTPS
HTTP学习三:HTTPS 1 HTTP安全问题 HTTP1.0/1.1在网络中是明文传输的,因此会被黑客进行攻击. 1.1 窃取数据 因为HTTP1.0/1.1是明文的,黑客很容易获得用户的重要数据 ...
- TweenMax动画库学习(三)
目录 TweenMax动画库学习(一) TweenMax动画库学习(二) TweenMax动画库学习(三) ...
- Struts2框架学习(三) 数据处理
Struts2框架学习(三) 数据处理 Struts2框架框架使用OGNL语言和值栈技术实现数据的流转处理. 值栈就相当于一个容器,用来存放数据,而OGNL是一种快速查询数据的语言. 值栈:Value ...
- 4.机器学习——统计学习三要素与最大似然估计、最大后验概率估计及L1、L2正则化
1.前言 之前我一直对于“最大似然估计”犯迷糊,今天在看了陶轻松.忆臻.nebulaf91等人的博客以及李航老师的<统计学习方法>后,豁然开朗,于是在此记下一些心得体会. “最大似然估计” ...
- DjangoRestFramework学习三之认证组件、权限组件、频率组件、url注册器、响应器、分页组件
DjangoRestFramework学习三之认证组件.权限组件.频率组件.url注册器.响应器.分页组件 本节目录 一 认证组件 二 权限组件 三 频率组件 四 URL注册器 五 响应器 六 分 ...
- [ZZ] 深度学习三巨头之一来清华演讲了,你只需要知道这7点
深度学习三巨头之一来清华演讲了,你只需要知道这7点 http://wemedia.ifeng.com/10939074/wemedia.shtml Yann LeCun还提到了一项FAIR开发的,用于 ...
随机推荐
- 步步为营-30-AES加密与解密
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; usin ...
- 2018-2019-2 20165333 《网络对抗技术》 Exp5:MSF基础应用
2018-2019-2 20165333 <网络对抗技术> Exp5:MSF基础应用 实践内容(3.5分) 本实践目标是掌握metasploit的基本应用方式,重点常用的三种攻击方式的思路 ...
- Asp.Net构架(Http请求处理流程)、(Http Handler 介绍)、(HttpModule 介绍)
Asp.Net构架(Http请求处理流程) Http请求处理流程概述 对于普通访问者来说,这就像每天太阳东边升起西边落下一样是理所当然的:对于很多程序员来说,认为这个与己无关,不过是系统管理员或者网管 ...
- python访问百度地图接口并返回信息
import urllib.parse import urllib.request data = urllib.parse.urlencode({'address': '广东省湛江市霞山区', 'ou ...
- [转] React 是什么
用脚本进行DOM操作的代价很昂贵.有个贴切的比喻,把DOM和JavaScript各自想象为一个岛屿,它们之间用收费桥梁连接,js每次访问DOM,都要途径这座桥,并交纳“过桥费”,访问DOM的次数越多, ...
- python全栈开发day29-网络编程之socket常见方法,socketserver模块,ftp作业
一.昨日内容回顾 1.arp协议含义 2.子网,子网掩码 3.两台电脑在网络中怎么通信的? 4.tcp和udp socket编码 5.tcp和udp协议的区别 6.tcp三次握手和四次挥手,syn洪攻 ...
- Codeforces Round #317 (div 2)
Problem A Arrays 思路:水一水. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; int n1,n2,k,m,a[N],b[N ...
- Codeforces 757D - Felicity's Big Secret Revealed
757D - Felicity's Big Secret Revealed 题目大意:给你一串有n(n<=75)个0或1组成的串,让你划最多n+1条分割线,第一条分割线的前面和最后一条分割线的后 ...
- 【Java】 剑指offer(16) 打印1到最大的n位数
本文参考自<剑指offer>一书,代码采用Java语言. 更多:<剑指Offer>Java实现合集 题目 输入数字n,按顺序打印出从1最大的n位十进制数.比如输入3,则打印 ...
- input禁止输入空格
<input name="" onkeyup="this.value=this.value.replace(/^\s+|\s+$/g,'')" value ...
