(二)使用数组长度实现ADT bag(java)
目录
1.使用固定大小的数组实现ADT bag 包
1.1 一组核心方法
1.2 实现核心方法
1.3 让实现安全
1.4 测试核心方法
1.5 实现更多的方法
1.6 删除项的方法
1.7 测试
1.8 发现总结
2.使用可变大小的数组实现ADT包
2.1 可变大小数组
2.2 包的新实现
2.3 使用数组实现ADT包的优缺点
1. 使用固定大小的数组实现ADT bag包
1.1 一组核心方法
基于数组实现的ADT包ArrayBag,实现接口BagInterface,接口中定义了泛型T,在ArrayBag的定义中也用到了这个泛型。对于定义难懂的类(ArrayBag),有不少方法,不应该定义整个类,然后试图去测试它。而是先定义一组核心方法(core mehod)来实现并测试这些方法,然后再继续定义类中的其他部分。(可以集中注意力,简化任务)。核心方法:这样的方法应该是类的重要目的,且允许合理的测试。有时称一组核心方法为核心组(core group)。
对于Bag这样的集合,添加元素add方法是一个基本操作,如果add不成功,remove无从谈起。所以add方法去核心方法之一。测试add,需要能看见Bag内容的方法toArray,也是核心方法之一。构造方法也是基本的,另外,核心方法可能调用的任何方法也是核心组的一部分。比如,add需要判断是否bag已满isArrayFull。
核心方法:(在这些核心方法能正确工作之前,先不实现其余方法)
|
注:像add和remove这样能改变集合结构的方法,可能是与实现最紧密的方法。一般,这类方法的定义应该先于类中的其他方法。但因为add正确之前不能remove,所以将remove实现放在add完成后且进行充分测试后进行。
程序设计技巧:当定义一个类时,实现并测试一组核心方法。从向对象集合添加对象及与之相关的方法开始。
1.2 实现核心方法
数据域:对象数组,容量(默认容量或用户提供)
|
private final T[] bag; private int numberOfEntries; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 25; |
加入类ArrayBag的UML表示:
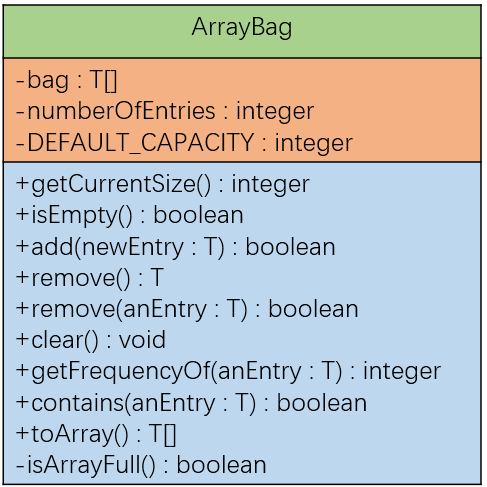
程序设计技巧:终态数组
通过声明bag是类ArrayBag的一个终态数据成员,可知变量bag中的引用不能改,但是数据元素bag[0]等可改,但是要防止客户直接修改bag元素,以防数组内容受到恶意毁坏。
构造方法:
注意:
|
数组bag的泛型问题: bag = new T[capacity]; // syntax error 分配数组时不能使用泛型 ---> 转为object: bag = new Object[capacity]; // imcompatible types不能将object数组赋给T型数组,两个类型不兼容 ----> 转型 bag = (T[])new Object[capacity]; // 编译警告,编译想保证将数组中的每项从类型object转为T都安全,有问题语句前写注释使编译忽略这个警告:@SuppressWarning(“unchecked”),该注释只能放在方法定义或变量声明之前 ---> 找个中间变量再声明一次 // The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries. @SuppressWarning(“unchecked”) T[] tempBag = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; bag = tempBag; |
注:禁止编译警告
要禁止编译程序给出的未检查转型警告,可以在标记的语句之前写
@SuppressWarning(“unchecked”)
注意,这条命令只能放在方法定义或变量声明之前。应该包含一条注释,对禁止编译程序警告做出解释。
类的框架:
/**
* A class of bags whose entries are stored in a fixed-size array.
* @author Administrator
*
* @param <T>
*/
public final class ArrayBag<T> implements BagInterface<T> {
private final T[] bag;
private int numberOfEntries;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 25; /**
* Creates an empty bag whose initial capacity is 25.
*/
public ArrayBag() {
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
} // end default constructor /**
* Creats an empty bag having a given initial capacity.
* @param capacity: The integer capacity desired.
*/
public ArrayBag(int capacity) {
// The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] tempBag = (T[])new Object[capacity]; // Unchecked entries.
bag = tempBag;
numberOfEntries = 0;
} // end constructor /**
* Gets the current number of entries in this bag.
* @return: The integer number of entries currently in the bag.
*/
@Override
public int getCurrentSize() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
} // end getCurrentSize /**
* Sees whether this bag is empty.
* @return: True if the bag is empty, or false if not.
*/
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
} // end isEmpty /**
* Adds a new entry to this bag.
* @param newEntry: The object to be added as a new entry.
* @return: True if the addition is successful, or false if not.
*/
@Override
public boolean add(T newEntry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
} // end add /**
* Removes one unspecified entry from this bag, if possible.
* @return: Either the removed entry, if the removel was successful, or null.
*/
@Override
public T remove() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
} // end remove /**
* Removes one occurrence of a given entry from this bag, if possible.
* @param anEntry: The entry to be removed.
* @return: True if the removal was successful, or false if not.
*/
@Override
public boolean remove(T anEntry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
} // end remove /**
* Removes all entries from this bag.
*/
@Override
public void clear() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
} // end clear /**
* Counts the number of times a given entry appears in this bag.
* @param anEntry: The entry to counted.
* @return: The number of times anEntry appears in the bag.
*/
@Override
public int getFrequencyOf(T anEntry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
} // end getFrequencyOf /**
* Tests whether this bag contains a given entry.
* @param anEntry: The entry to locate.
* @return: True if the bag contains anEntry, or false if not.
*/
@Override
public boolean contains(T anEntry) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
} // end contains /**
* Retrieves all entries that are in this bag.
* @return: A newly allocated array of all the entries in the bag.
* Note: If the bag is empty, the returned array is empty.
*/
@Override
public T[] toArray() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
} // end toArray // Returns true if the arraybag is full, or false if not.
private boolean isArrayFull() {
return numberOfEntries == 0;
} // end isArrayFull
} // end class ArrayBag
程序设计技巧:当定义实现接口的类时,从接口中复制它们来添加类中公有方法的注释和头。使用这种方式,方便在实现时检查每个方法的规格说明。另外,维护代码的人也容易访问这些规格说明。
|
设计决策:当数组中装了一部分数据时,包的项应该放在数组的哪些位置? 添加第一个项:数组中第一个,下标为0; 项是否连续:关于计划中的实现方案,必须确定某些事实或断言,以便每个方法的动作不会对其他方法产生不利。(toArray必须知道add将项放在哪里)(remove需要保证项连续吗?) |
方法add:如果包满了,则不添加,返回false;否则,将新元素添加到最后一个元素后面。
/**
* Adds a new entry to this bag.
* @param newEntry: The object to be added as a new entry.
* @return: True if the addition is successful, or false if not.
*/
@Override
public boolean add(T newEntry) {
if(isArrayFull()) {
return false;
}
else {
// Assertion : result is true here
bag[numberOfEntries++] = newEntry;
return true;
} // end if
} // end add
方法isArrayFull:包中项数与包容量相等时,包满返回true。
// Returns true if the arraybag is full, or false if not.
private boolean isArrayFull() {
return numberOfEntries >= bag.length;
} // end isArrayFull
方法toArray:获取包中的项,将它们返回到客户新分配的数组内。分配数组处理与构造方法相同。
/**
* Retrieves all entries that are in this bag.
* @return: A newly allocated array of all the entries in the bag.
* Note: If the bag is empty, the returned array is empty.
*/
@Override
public T[] toArray() {
// The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] result = (T[])new Object[numberOfEntries]; // Unchecked cast
for(int i = 0; i < numberOfEntries; i++) {
result[i] = bag[i];
} // end for
return result;
} // end toArray
1.3 让实现安全
程序中检查可能出现的错误来练习有安全机制的程序设计(fail-safe programming)。安全可靠程序设计(safe and secure programming)通过验证输入给方法的数据和参数的合法性,消除方法的副作用,对客户和使用者的行为不做任何假设。
安全说明:保护ADT实现的完整性
两个问题:
- 若构造方法没有完全执行,可能发生什么?完成初始化之前抛异常,入侵者捕获异常或错误,试图使用部分初始化的对象;
- 客户试图创建一个容量超出给出范围的包,会发生什么?
如果这两个动作可能会导致问题,则必须阻止。
增加两个数据域:
private boolean initialized = false;
private static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 10000;
修改构造方法:
判断客户参数和最大容量,大于抛出异常;
内存不足,小于等于最大容量,系统是否能够分配成功?错误OutOfMemoryError,黑客捕获这个异常,使用部分初始化的数据 ---> 利用initialized的状态判断是否执行方法。
public ArrayBag(int capacity) {
if(capacity <= MAX_CAPACITY) {
// The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] tempBag = (T[])new Object[capacity]; // Unchecked entries.
bag = tempBag;
numberOfEntries = 0;
initialized = true; // Last action
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Attempt to create a bag whose "
+ "capacity exceeds allowed maximum.");
}
} // end constructor
方法如何利用intialized变量:任何方法执行前都要确保数据域initialized的值为真。若为假,方法可以抛出一个异常。
public boolean add(T newEntry) {
if(initialized) {
boolean result = true;
if(isArrayFull()) {
result = false;
}
else {
// Assertion : result is true here
bag[numberOfEntries++] = newEntry;
} // end if
return result;
}
else {
throw new SecurityException("ArrayBag object is not initialized properly.");
}
} // end add
多个方法都要判断initialized,所以包装为方法:
// Throws an exception if this ovject is not initialized.
private void checkInitialized() {
if(!initialized) {
throw new SecurityException("ArrayBag object is not initialized properly.");
}
} // end checkInitialized public boolean add(T newEntry) {
checkInitialized();
boolean result = true;
if(isArrayFull()) {
result = false;
}
else {
// Assertion : result is true here
bag[numberOfEntries++] = newEntry;
} // end if
return result;
} // end add public T[] toArray() {
checkInitialized();
// The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] result = (T[])new Object[numberOfEntries]; // Unchecked cast
for(int i = 0; i < numberOfEntries; i++) {
result[i] = bag[i];
} // end for
return result;
} // end toArray
安全说明:
- 将类的大多数数据域声明为私有的,如果不是全部。任何公有数据域都应该是静态和终态的,且有常量值;
- 避免那些掩盖代码安全性的所谓聪明的逻辑;
- 避免重复代码。相反,将这样的代码封装为一个可供其他方法调用的私有方法;
- 当构造方法调用一个方法时,确保这个方法不能被重写。
安全说明:终态类(ArrayBag是一个终态类final class,不会被继承,确保程序员不能继承来改变它的行为,比非终态类安全)
1.4 测试核心方法
准备。已经实现三个核心方法,进行测试。其他需要实现的方法设为存根(stub),即一个不完整定义的方法。仅需要让语法检查器通过即可,return一个哑值,Boolean返回false,对象返回null,void方法为空方法体。如果想在测试程序中调用存根,应该显示一条信息来报告它被调用过。
测试程序。(默认容量和超容量)
/**
* A test of the constructors and the methods add and toArray,
* as defined in the first draft of the class ArrayBag.
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ArrayBagDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Adding to an initially empty bag with sufficient capacity
System.out.println("Testing an initially empty bag with the capacity to hold at least 6 strings:");
BagInterface<String> aBag = new ArrayBag<>();
String[] contentsBag1 = {"A", "B", "A", "D", "B", "C"};
testAdd(aBag, contentsBag1); System.out.println("\nTesting an initially empty bag that will be filled to capacity:");
aBag = new ArrayBag<>(7);
String[] contentsOfBag2 = {"A", "B", "A", "C", "B", "C", "D", "another string"};
testAdd(aBag, contentsOfBag2); } // end main // Tests the method add.
public static void testAdd(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] content) { System.out.println("Adding the following " + content.length + " strings to the bag: ");
for(int index = 0; index < content.length; index++) {
if(aBag.add(content[index])) {
System.out.print(content[index] + " ");
}
else {
System.out.print("\nUnable to add " + content[index] + " to the bag.");
}
} // end for
System.out.println(); displayBag(aBag); } // end testAdd // Tests the method thArray while displaying the bag.
private static void displayBag(BagInterface<String> aBag) { System.out.println("The bag contains the following string(s):");
Object[] bagArray = aBag.toArray();
for(int index = 0; index < bagArray.length; index++) {
System.out.print(bagArray[index] + " ");
} // end for System.out.println(); } // end displayBag
} // end ArrayBagDemo1
output:
|
Testing an initially empty bag with the capacity to hold at least 6 strings: Adding the following 6 strings to the bag: A B A D B C The bag contains the following string(s): A B A D B C Testing an initially empty bag that will be filled to capacity: Adding the following 8 strings to the bag: A B A C B C D Unable to add another string to the bag. The bag contains the following string(s): A B A C B C D |
程序设计技巧:方法的全貌测试还应该包括实参取值范围在合理范围内外的情况。
1.5 实现更多的方法
方法isEmpty和getCurrentSize
可以更早的定义它们,而不是为它们写存根。
public int getCurrentSize() {
return numberOfEntries;
} // end getCurrentSize
public boolean isEmpty() {
return numberOfEntries == 0;
} // end isEmpty
方法getFrequencyOf.(比较对象使用equals)
public int getFrequencyOf(T anEntry) {
checkInitialization();
int count = 0;
for(int index = 0; index < numberOfEntries; index++) {
if(bag[index].equals(anEntry)) {
count++;
} // end if
} // end for
return count;
} // end getFrequencyOf
方法contains。
public boolean contains(T anEntry) {
checkInitialization();
boolean found = false;
for(int index = 0; index < numberOfEntries; index++) {
if(bag[index].equals(anEntry)) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
return found;
} // end contains
测试:
public class ArrayBagDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BagInterface<String> aBag = new ArrayBag<>();
boolean created = aBag.isEmpty();
System.out.println(created);
aBag.add("wang");
aBag.add("pu");
aBag.add("wang");
int size = aBag.getCurrentSize();
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(aBag.contains("pu"));
System.out.println(aBag.contains("he"));
int count = aBag.getFrequencyOf("wang");
System.out.println(count);
}
}
output:
|
true 3 true false 2 |
1.6 删除项的方法
方法clear(remove方法将调用checkInitialization,所以clear不需要显式地调用它)
public void clear() {
while(!isEmpty()) {
remove();
}
} // end clear
删除不确定项remove。只要bag不空,就删除一个项并将项返回
public T remove() {
checkInitialization();
T temp = null;
if(numberOfEntries > 0) {
temp = bag[numberOfEntries - 1];
bag[numberOfEntries - 1] = null;
numberOfEntries--;
} // end if
return temp;
} // end remove
安全说明:将数组元素bag[numberOfEntries-1]设置为null,标记被删除对象可进行垃圾回收,并防止恶意代码来访问它。
安全说明:在正确计数后更新计数器。删除数组最后一项后才将numberOfEntries减1,虽然刚开始减1会避免重复,但时间上微不足道的节省不值得冒太早减小计数器带来的不安全风险。
删除给定项,remove。多次只删除第一次,删除后需要将该位置补上,因为不需要维护包中项的具体次序,所以只需要将最后一项移过来即可。
public boolean remove(T anEntry) {
checkInitialization();
boolean result = false;
if(numberOfEntries > 0) {
for(int index = 0; index < numberOfEntries; index++) {
if(bag[index].equals(anEntry)) {
bag[index] = bag[numberOfEntries - 1];
bag[numberOfEntries - 1] = null;
numberOfEntries--;
result = true;
break;
} // if
} // end for
} // end if
return false;
} // end remove
删除最后一项和remove相同,抽出共同部分removeEntry
// Removes and returns the entry at a given index within the array bag.
// If no such entry exists, return null.
// Preconditions: 0 <= givenIndex < numberOfEntries;
// checkInitialization has been called.
private T removeEntry(int givenIndex) {
T result = null;
if (!isEmpty() && (givenIndex >= 0)) {
result = bag[givenIndex]; // Entry to remove
bag[givenIndex] = bag[numberOfEntries - 1]; // Replace entry with last entry
bag[numberOfEntries - 1] = null; // Remove last entry
numberOfEntries--;
} // end if
return result;
} // end removeEntry
此时remove
public T remove() {
checkInitialization();
T result = removeEntry(numberOfEntries - 1);
return result;
} // end remove
public boolean remove(T anEntry) {
checkInitialization();
int index = getIndexOf(anEntry);
T result = removeEntry(index);
return anEntry.equals(result);
} // end remove
需要索引函数,返回项的位置索引
// Locates a given entry within the array bag.
// Returns the index of the entry, if bocated, or -1 otherwise.
private int getIndexOf(T anEntry) {
int getIndex = -1;
if (numberOfEntries > 0) {
for (int index = 0; index < numberOfEntries; index++) {
if (bag[index].equals(anEntry)) {
getIndex = index;
break;
} // if
} // end for
} // end if
return getIndex;
} // end getIndexOf /* 正向思考
private int getIndexOf(T anEntry) {
int where = -1;
boolean stillLooking = true;
int index = 0;
while (stillLooking && (index < numberOfEntries)){
if (anEntry.equals(bag[index])){
stillLooking = false;
where = index;
} // end if
index++;
} // end while
return where;
} // end getIndexOf
*/
利用getIndexOf方法修改contains方法需要索引函数,返回项的位置索引
public boolean contains(T anEntry) {
checkInitialization();
return getIndexOf(anEntry) > -1;
} // end contains
因为已经修改了contains,所以需要再次测试。
设计决策:什么方法应该调用checkInitialization?
可以在直接涉及数组bag的每个方法都调用,不过更灵活的是,私有方法getIndexOf和removeEntry直接访问bag,但它们不调用,为什么?若调用,则在共有方法中被调两次,所以规定在共有方法中调用,并为这两个私有方法添加一个前置条件来说明checkInitialization必须要先调用(只给实现者和维护者使用)。私有方法只实现一个已定的任务,不再为第二任务负责。
程序设计技巧:即使可能已经有了方法的正确定义,但如果想到了一个更好的实现,也不要犹豫地取修改它。肯定要再次测试方法!
1.7 测试
/**
* A demostration of the class ArrayBag
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ArrayBagDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] contentsOfBag = {"A", "A", "B", "A", "C", "A"}; // Tests on an empty bag
BagInterface<String> aBag = new ArrayBag<>(contentsOfBag.length);
System.out.println("Testing an initially empty bag:");
testIsEmpty(aBag, true);
String[] testStrings1 = {"", "B"};
testFrequency(aBag, testStrings1);
testContains(aBag, testStrings1);
testRemove(aBag, testStrings1); // Adding strings
System.out.println("Adding " + contentsOfBag.length + " strings to an initially empty bag "
+ "with the capacity to hold more than " + contentsOfBag.length + " strings:");
testAdd(aBag, contentsOfBag); // Tests on a bag that is not empty
testIsEmpty(aBag, false);
String[] testStrings2 = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "A"};
testFrequency(aBag, testStrings2);
testContains(aBag, testStrings2); // Removing strings
String[] testStrings3 = {"", "B", "A", "C", "Z"};
testRemove(aBag, testStrings3); System.out.println("\nClearing the bag:");
aBag.clear();
testIsEmpty(aBag, true);
displayBag(aBag);
} // Tests the method add.
public static void testAdd(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] content) { System.out.println("Adding ");
for(int index = 0; index < content.length; index++) {
aBag.add(content[index]);
System.out.print(content[index] + " ");
} // end for
System.out.println(); displayBag(aBag); } // end testAdd private static void testRemove(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] tests) {
for (int index = 0; index < tests.length; index++) {
String aString = tests[index];
if (aString.equals("") || (aString == null)) {
// test remove()
System.out.println("\nRemoving a string from the bag:");
String removedString = aBag.remove();
System.out.println("remove() returns " + removedString);
}
else {
// test remove(aString)
System.out.println("\nRemoving \"" + aString + "\" from the bag:");
boolean result = aBag.remove(aString);
System.out.println("remove(\"" + aString + "\") returns " + result);
} // end if displayBag(aBag);
} // end for } // end testRemove // Tests the method toArray while displaying the bag.
private static void displayBag(BagInterface<String> aBag) {
System.out.println("The bag contains " + aBag.getCurrentSize() +
" string(s), as follows:");
Object[] bagArray = aBag.toArray();
for (int index = 0; index < bagArray.length; index++) {
System.out.print(bagArray[index] + " ");
} // end for System.out.println();
} // end diaplayBag // Tests the method contains.
private static void testContains(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] tests) {
System.out.println("\nTesting the method contains:");
for (int index = 0; index < tests.length; index++) {
String aString = tests[index];
if (!aString.equals("") && (aString != null)) {
System.out.println("Does this bag contain " + tests[index] +
" ? " + aBag.contains(aString));
} // end if
} // end for
} // end testContains // Tests the method getFrequencyOf
private static void testFrequency(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] tests) {
System.out.println("\nTesting the method getFrequencyOf:");
for (int index = 0; index < tests.length; index++) {
String aString = tests[index];
if (!aString.equals("") && (aString != null)) {
System.out.println("In this bag, the count of " + tests[index] +
" is " + aBag.getFrequencyOf(aString));
} // end if
} // end for
} // end testFrequency // Tests the method isEmpty
// correctResult indicates what isEmpty should return.
private static void testIsEmpty(BagInterface<String> aBag, boolean correctResult) {
System.out.println("Testing isEmpty with ");
if(correctResult) {
System.out.println("an empty bag:");
}
else {
System.out.println("a bag that is not empty:");
} // end if System.out.print("isEmpty finds the bag ");
if(correctResult && aBag.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("empty: OK.");
}
else if(correctResult) {
System.out.println("not empty, but it is empty: ERROR.");
}
else if(!correctResult && aBag.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("empty, but it is not empty: ERROR.");
}
else {
System.out.println("not empty: OK.");
} // if else System.out.println();
} // end testIsEmpty }
1.8 发现总结
|
2.使用可变大小的数组实现ADT包
2.1 可变大小数组
一般新数组要两倍于原始数组的大小。数组复制可以使用Arrays.copyOf(sourceArray, newLength)
程序设计技巧:当增大数组时,将它的项复制到更大的数组中。应该充分地扩展数组,以减少复制代价的影响。常用的办法是倍增数组大小。
2.2 包的新实现
方法:修改ADT包的前一个实现,通过调整数组大小使包的容量仅由计算机可用的内存量来限定。
|
方法add:
public boolean add(T newEntry) {
checkInitialization();
if(isArrayFull()) {
doubleCapacity();
} // end if
// Assertion : result is true here
bag[numberOfEntries++] = newEntry;
return true;
} // end add
// Doubles the size of the array bag.
private void doubleCapacity() {
}
增加容量需要检查是否超出最大容量MAX_CAPACITY.构造方法中也需要同样检查,定义私有方法checkCapacity。
// Doubles the size of the array bag.
private void doubleCapacity() {
int newLength = 2 * bag.length;
checkCapacity(newLength);
bag = Arrays.copyOf(bag, newLength);
} // end doubleCapacity private void checkCapacity(int capacity) {
if (capacity > MAX_CAPACITY) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Attempt to create a bag whose "
+ "capacity exeeds allowed maximun of " + MAX_CAPACITY);
} // end if
} // end checkCapacity
构造方法:
public ResizableArrayBag(int capacity) {
checkCapacity(capacity);
// The cast is safe because the new array contains null entries.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] tempBag = (T[])new Object[capacity]; // Unchecked entries.
bag = tempBag;
numberOfEntries = 0;
initialized = true; // Last action
} // end constructor
增加构造方法:
/**
* Creates a bag containing given entries.
* @param contents: An array of objects.
*/
public ResizableArrayBag(T[] contents) {
checkCapacity(contents.length);
bag = Arrays.copyOf(contents, contents.length);
numberOfEntries = contents.length;
initialized = true;
} // end constructor
设计决策:
方法add布尔方法而不是void:要和接口定义保持一致
定义私有方法,只被add使用一次:一个方法只执行一个动作的哲学理念。
程序设计技巧:实现了声明ADT操作的单一接口的类,应该将定义在接口中的方法声明为公有方法。但是,类还可以定义私有方法和保护方法。
测试类:(把测试当做写代码的一部分,得学得改!!!)
/** A demonstration of the class ResizableArrayBag
@author Frank M. Carrano
@version 4.0
*/
public class ResizableArrayBagDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// A bag whose initial capacity is small
BagInterface<String> aBag = new ResizableArrayBag<String>(3);
testIsEmpty(aBag, true); System.out.println("Adding to the bag more strings than its initial capacity.");
String[] contentsOfBag = {"A", "D", "B", "A", "C", "A", "D"};
testAdd(aBag, contentsOfBag); testIsEmpty(aBag, false);
String[] testStrings2 = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "Z"};
testFrequency(aBag, testStrings2);
testContains(aBag, testStrings2); // Removing strings
String[] testStrings3 = {"", "B", "A", "C", "Z"};
testRemove(aBag, testStrings3); System.out.println("\nClearing the bag:");
aBag.clear();
testIsEmpty(aBag, true);
displayBag(aBag);
} // end main // Tests the method add.
private static void testAdd(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] content)
{
System.out.print("Adding to the bag: ");
for (int index = 0; index < content.length; index++)
{
aBag.add(content[index]);
System.out.print(content[index] + " ");
} // end for
System.out.println(); displayBag(aBag);
} // end testAdd // Tests the two remove methods.
private static void testRemove(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] tests)
{
for (int index = 0; index < tests.length; index++)
{
String aString = tests[index];
if (aString.equals("") || (aString == null))
{
// test remove()
System.out.println("\nRemoving a string from the bag:");
String removedString = aBag.remove();
System.out.println("remove() returns " + removedString);
}
else
{
// test remove(aString)
System.out.println("\nRemoving \"" + aString + "\" from the bag:");
boolean result = aBag.remove(aString);
System.out.println("remove(\"" + aString + "\") returns " + result);
} // end if displayBag(aBag);
} // end for
} // end testRemove // Tests the method isEmpty.
// correctResult indicates what isEmpty should return.
private static void testIsEmpty(BagInterface<String> aBag, boolean correctResult)
{
System.out.print("Testing isEmpty with ");
if (correctResult)
System.out.println("an empty bag:");
else
System.out.println("a bag that is not empty:"); System.out.print("isEmpty finds the bag ");
if (correctResult && aBag.isEmpty())
System.out.println("empty: OK.");
else if (correctResult)
System.out.println("not empty, but it is empty: ERROR.");
else if (!correctResult && aBag.isEmpty())
System.out.println("empty, but it is not empty: ERROR.");
else
System.out.println("not empty: OK.");
System.out.println();
} // end testIsEmpty // Tests the method getFrequencyOf.
private static void testFrequency(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] tests)
{
System.out.println("\nTesting the method getFrequencyOf:");
for (int index = 0; index < tests.length; index++)
System.out.println("In this bag, the count of " + tests[index] +
" is " + aBag.getFrequencyOf(tests[index]));
} // end testFrequency // Tests the method contains.
private static void testContains(BagInterface<String> aBag, String[] tests)
{
System.out.println("\nTesting the method contains:");
for (int index = 0; index < tests.length; index++)
System.out.println("Does this bag contain " + tests[index] +
"? " + aBag.contains(tests[index]));
} // end testContains // Tests the method toArray while displaying the bag.
private static void displayBag(BagInterface<String> aBag)
{
System.out.println("The bag contains " + aBag.getCurrentSize() +
" string(s), as follows:");
Object[] bagArray = aBag.toArray();
for (int index = 0; index < bagArray.length; index++)
{
System.out.print(bagArray[index] + " ");
} // end for System.out.println();
} // end displayBag
} // end ResizableArrayBagDemo /*
Testing isEmpty with an empty bag:
isEmpty finds the bag empty: OK. Adding to the bag more strings than its initial capacity.
Adding to the bag: A D B A C A D
The bag contains 7 string(s), as follows:
A D B A C A D
Testing isEmpty with a bag that is not empty:
isEmpty finds the bag not empty: OK. Testing the method getFrequencyOf:
In this bag, the count of A is 3
In this bag, the count of B is 1
In this bag, the count of C is 1
In this bag, the count of D is 2
In this bag, the count of Z is 0 Testing the method contains:
Does this bag contain A? true
Does this bag contain B? true
Does this bag contain C? true
Does this bag contain D? true
Does this bag contain Z? false Removing a string from the bag:
remove() returns D
The bag contains 6 string(s), as follows:
A D B A C A Removing "B" from the bag:
remove("B") returns true
The bag contains 5 string(s), as follows:
A D A A C Removing "A" from the bag:
remove("A") returns true
The bag contains 4 string(s), as follows:
C D A A Removing "C" from the bag:
remove("C") returns true
The bag contains 3 string(s), as follows:
A D A Removing "Z" from the bag:
remove("Z") returns false
The bag contains 3 string(s), as follows:
A D A Clearing the bag:
Testing isEmpty with an empty bag:
isEmpty finds the bag empty: OK. The bag contains 0 string(s), as follows:
*/
2.3 使用数组实现ADT包的优缺点
数组易于使用,知道下标就能立即访问。
|
使用数组来实现ADT包时:
|
(二)使用数组长度实现ADT bag(java)的更多相关文章
- java 获取数组(二维数组)长度实例程序
我们可能知道 js有个length函数,java也有啊length函数 例 如果数组是data[],则data.length 代码如下 复制代码 byte[] phone =new byte[81]; ...
- 剑指offer面试题3 二维数组中的查找 (java)
注:java主要可以利用字符串的length方法求出长度解决这个问题带来方便 public class FindNum { public static void main(String[] args) ...
- 剑指Offer-1.二维数组中的查找(C++/Java)
题目: 在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数. ...
- php获取一维,二维数组长度的方法(有实例)
在php中获取数组长度方法很简单,php为我们提供了两个函数可以计算一维数组长度,如count,sizeof都可以直接统计数组长度哦,下面我们来看几个实例吧.php如何获取数组的长度,使用php函数c ...
- 11、增强型for循环对二维数组的输出(test8.java)
由于笔者原因,这部分知识,尚不能整理出代码,笔者会好好学习增强型for循环中迭代起的相关知识,在笔者有能力,书写好这段代码后,将对本篇文章,进行二次修改,也同时欢迎大家与笔者交流,共同学习,共同进步. ...
- 10、二维数组的申请(test7.java)
我个人认为,二维数组的构造就是在一位数组中存入一个地址,这个地址指向另一个一位数组,这样通过这种排列组合便构造成了二维数组. 二维数组的形状,有的时候二维数组看起来像是一个矩阵,所以一般情况下如果涉及 ...
- 剑指Offer:面试题3——二维数组中的查找(java实现)
问题描述:在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数. 思路:取数组中的元素与 ...
- 剑指offer第二版面试题3:二维数组中的查找(JAVA版)
题目: 在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数. 1 2 8 9 2 4 ...
- 二维数组模拟实现酒店管理系统-java
业务分析 1.需要一个房间类,包含房间的属性,比如房间编号.房间类型.是否占用. 2.需要一个旅馆类,旅馆有房间,提供的方法需要有 预订房间.打印房间信息.初始化房间.退房. 3.测试类,测试预订房间 ...
随机推荐
- 【Hadoop 分布式部署 一 :分布式部署准备虚拟机 】
一.将IP配置为静态 按照 下面的操作将IP配置为静态IP 这个静态的IP地址 是你自己设置的,只要符合虚拟机的IP段就可以.最后点击 Apply 需要root密码 将网络断开 (在网络图标左键 ...
- -第3章 jQuery方法实现下拉菜单显示和隐藏
知识点 jquery 的引入方式 本地下载引入 在线引入 children 只获取子元素,不获取孙元素 show() 显示. hide() 隐藏. 完整代码 <!-- Author: XiaoW ...
- ECharts配置项之title(标题)
1.标题居中 //left的值为'left', 'center', 'right' title:{ left:'center' } 2.主副标题之间的间距 title:{ //默认为10 itemGa ...
- C#Listview添加数据,选中最后一行,滚屏
this.listView.Items.Add(lvi); this.listView.EnsureVisible(this.listView.Items.Count - 1); this.listV ...
- 【Python】【有趣的模块】【Requests】无状态 & 无连接
无状态:原来的Web是静态,后来换成动态的就需要保存一些上下文信息,session和cookie应运而生 无连接:原来为了请求结束后赶紧把资源让出去,后来发现每次请求中有相同的小请求时候再重复执行(而 ...
- React生命周期执行顺序详解
文章内容转载于https://www.cnblogs.com/faith3/p/9216165.html 一.组件生命周期的执行次数是什么样子的??? 只执行一次: constructor.compo ...
- codeforces 767C - Garland
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/767/problem/C 问能否将一棵带点权的书分成点权$3$块,求任意方案. 其实考虑一棵以$x$为根的子树权值为${\fra ...
- Centos7默认自带了Python2.7版本,但是因为项目需要使用Python3.x,这里提供一种比较快捷方便的安装方式
安装必要工具 yum-utils: $ sudo yum install yum-utils 使用yum-builddep为Python3构建环境,安装缺失的软件依赖,使用下面的命令会自动处理.$ s ...
- MySQL学习(十五)
索引的概念 索引是数据的目录,能快速定位数据的位置.索引提高了查询速度,降低了增删改的速度.并非加的越多越好. 一般在查询频率高的列上加,而且在重复度低的列上加效果更好.如在性别列上不用加索引,但是身 ...
- Qt5鼠标事件及实例
mainwindow.h #ifndef MAINWINDOW_H #define MAINWINDOW_H #include <QMainWindow> #include <QLa ...
