聊聊ReentrantLock的内部实现
大家都用过ReentrantLock,但是大家对内部实现是否足够了解呢,下面我就简单说一下其中的实现原理。
ReentrantLock是可重入锁,也就是同一个线程可以多次获取锁,每获取一次就会进行一次计数,解锁的时候就会递减这个计数,直到计数变为0。
它有两种实现,一种是公平锁,一种是非公平锁,那么默认是什么锁呢?看完如下代码想必你也知道了。
- /**
- * Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
- * This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.
- */
- public ReentrantLock() {
- sync = new NonfairSync();
- }
它的内部结构的实现是如何的呢? 首先NonFairSync类是静态内部类,它继承了Sync。
- /**
- * Sync object for non-fair locks
- */
- static final class NonfairSync extends Sync
Sync继承了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,简称AQS。同时Sync里边实现了tryRelease方法,因为公平锁和非公平锁都可以用这个方法释放锁。
- /**
- * Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
- * into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to
- * represent the number of holds on the lock.
- */
- abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
继续看非公平锁的lock方法,采用CAS进行当前状态的设置state=0,表示没有线程占用,state=1表示已经有现成占用了,设置成功了,将当前线程设置为线程拥有者,并且是排他的。如果有现成占用了,那么需要进入acquire(1),需要获取一个锁。
- /**
- * Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
- * acquire on failure.
- */
- final void lock() {
- if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
- setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
- else
- acquire(1);
- }
acquire方法首先进行tryAcquire,尝试获取锁,即调用nonfairTryAcquire,判断当前锁是否state=0, 则没有现成占用,则进行设置。如果被占用了判断该线程是否是当前线程占用的,如果是的话,那么可以进行重入,即当前可以获取锁,计数器进行加1。否则的话返回失败。返回失败后执行addWaiter方法,也就是添加到等待的队列。Node是一个双向列表,也就是把需要等待的线程放到放到Node,并且链接起来。
- /**
- * Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
- * by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},
- * returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
- * repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
- * #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used
- * to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.
- *
- * @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
- * {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
- * can represent anything you like.
- */
- public final void acquire(int arg) {
- if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
- acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
- selfInterrupt();
- }
- /**
- * Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in
- * subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.
- */
- final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
- final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
- int c = getState();
- if (c == 0) {
- if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
- setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
- return true;
- }
- }
- else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
- int nextc = c + acquires;
- if (nextc < 0) // overflow
- throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
- setState(nextc);
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- /**
- * Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
- *
- * @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
- * @return the new node
- */
- private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
- Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
- // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
- Node pred = tail;
- if (pred != null) {
- node.prev = pred;
- if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
- pred.next = node;
- return node;
- }
- }
- enq(node);
- return node;
- }
接下来看一下Node的大致内容,有两个指针,一个是prev,一个是next,还保存着当前的线程。同时里边还有一个共享锁和独占锁,SHARED和EXCLUSIVE。ReentrantLock采用的就是独占锁。Semaphore,CountDownLatch等采用的是共享锁,即有多个线程可以同时获取锁。
- static final class Node {
- /** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */
- static final Node SHARED = new Node();
- /** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode */
- static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
- /**
- * Link to predecessor node that current node/thread relies on
- * for checking waitStatus. Assigned during enqueuing, and nulled
- * out (for sake of GC) only upon dequeuing. Also, upon
- * cancellation of a predecessor, we short-circuit while
- * finding a non-cancelled one, which will always exist
- * because the head node is never cancelled: A node becomes
- * head only as a result of successful acquire. A
- * cancelled thread never succeeds in acquiring, and a thread only
- * cancels itself, not any other node.
- */
- volatile Node prev;
- /**
- * Link to the successor node that the current node/thread
- * unparks upon release. Assigned during enqueuing, adjusted
- * when bypassing cancelled predecessors, and nulled out (for
- * sake of GC) when dequeued. The enq operation does not
- * assign next field of a predecessor until after attachment,
- * so seeing a null next field does not necessarily mean that
- * node is at end of queue. However, if a next field appears
- * to be null, we can scan prev's from the tail to
- * double-check. The next field of cancelled nodes is set to
- * point to the node itself instead of null, to make life
- * easier for isOnSyncQueue.
- */
- volatile Node next;
- /**
- * The thread that enqueued this node. Initialized on
- * construction and nulled out after use.
- */
- volatile Thread thread;
- /**
- * Link to next node waiting on condition, or the special
- * value SHARED. Because condition queues are accessed only
- * when holding in exclusive mode, we just need a simple
- * linked queue to hold nodes while they are waiting on
- * conditions. They are then transferred to the queue to
- * re-acquire. And because conditions can only be exclusive,
- * we save a field by using special value to indicate shared
- * mode.
- */
- Node nextWaiter;
大致的思路我们看了一下,总体的流程图我画了一下。ReentrankLock内核采用的是AQS实现的,AQS里边采用的是双向链表,即如果当前线程未获取到锁将会加入到链表中。
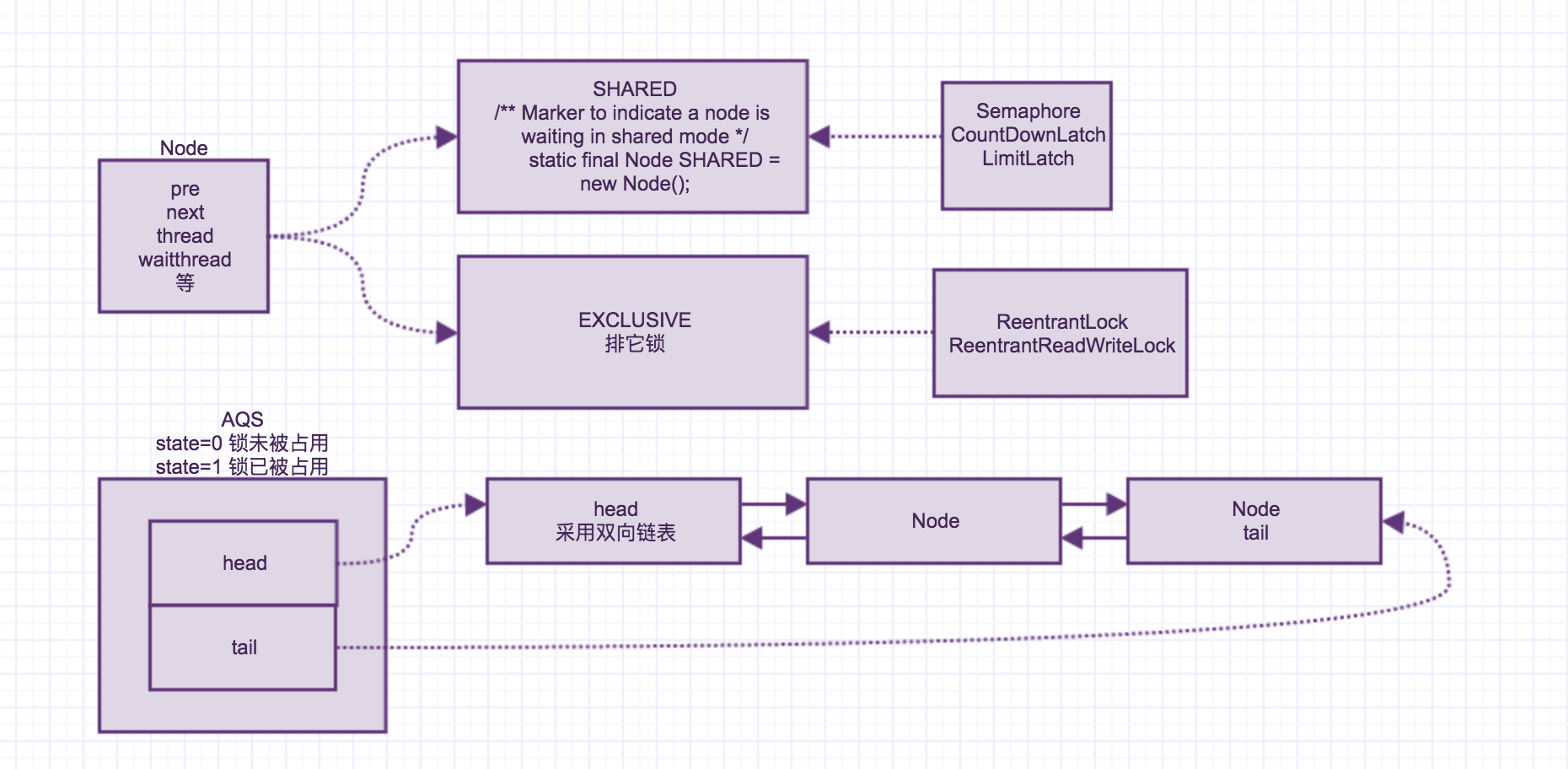
那么公平锁和非公平锁的实现的不同点在哪里呢?公平锁和非公平锁就差在 !hasQueuedPredecessors() ,也就是前边没有排队者的话,我就可以获取锁了。
- /**
- * Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
- * recursive call or no waiters or is first.
- */
- protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
- final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
- int c = getState();
- if (c == 0) {
- if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
- compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
- setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
- return true;
- }
- }
- else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
- int nextc = c + acquires;
- if (nextc < 0)
- throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
- setState(nextc);
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
如果当前线程之前还有线程等待就会返回true,如果当前节点是头结点,或者当前队列为空就会返回false。非公平锁没有这句话的判断,所以直接去竞争锁。
- /**
- * Queries whether any threads have been waiting to acquire longer
- * than the current thread.
- *
- * <p>An invocation of this method is equivalent to (but may be
- * more efficient than):
- * <pre> {@code
- * getFirstQueuedThread() != Thread.currentThread() &&
- * hasQueuedThreads()}</pre>
- *
- * <p>Note that because cancellations due to interrupts and
- * timeouts may occur at any time, a {@code true} return does not
- * guarantee that some other thread will acquire before the current
- * thread. Likewise, it is possible for another thread to win a
- * race to enqueue after this method has returned {@code false},
- * due to the queue being empty.
- *
- * <p>This method is designed to be used by a fair synchronizer to
- * avoid <a href="AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#barging">barging</a>.
- * Such a synchronizer's {@link #tryAcquire} method should return
- * {@code false}, and its {@link #tryAcquireShared} method should
- * return a negative value, if this method returns {@code true}
- * (unless this is a reentrant acquire). For example, the {@code
- * tryAcquire} method for a fair, reentrant, exclusive mode
- * synchronizer might look like this:
- *
- * <pre> {@code
- * protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
- * if (isHeldExclusively()) {
- * // A reentrant acquire; increment hold count
- * return true;
- * } else if (hasQueuedPredecessors()) {
- * return false;
- * } else {
- * // try to acquire normally
- * }
- * }}</pre>
- *
- * @return {@code true} if there is a queued thread preceding the
- * current thread, and {@code false} if the current thread
- * is at the head of the queue or the queue is empty
- * @since 1.7
- */
- public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
- // The correctness of this depends on head being initialized
- // before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current
- // thread is first in queue.
- Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
- Node h = head;
- Node s;
- return h != t &&
- ((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
- }
这个就是ReentrantLock的基本原理,接下来咱们继续看看与之一块使用的Condition。Condition是一个接口,它的实现类是ConditionObject。调用await的时候也会将当前线程的一些信息加入到队列当中。ConditionObject中有一个firstWaiter和LastWaiter分别指向的了等待队列的头和尾。
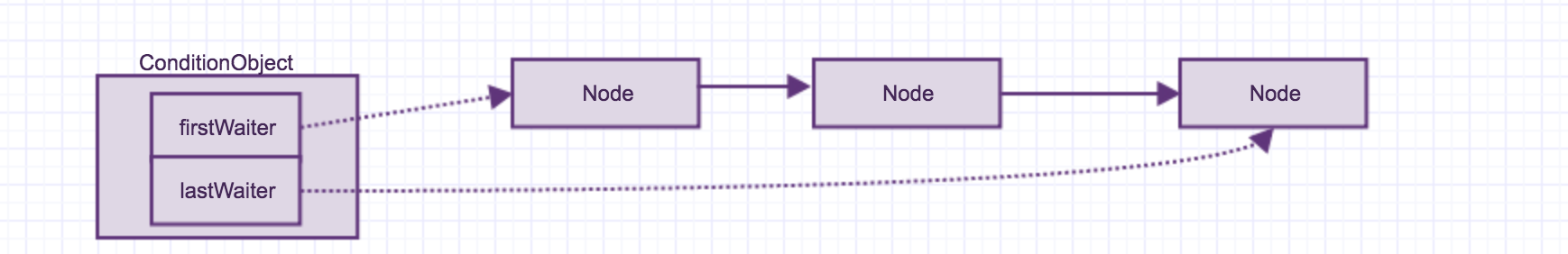
当调用Condition的signal方法是,则会将第一个Node转换到同步队列,如下图所示。
好了,总结一下:
1. ReentrankLock默认是非公平锁。
2.ReentrankLock的内部实现采用的AQS的双向链表实现。获取锁的线程会被封装成Node里边,供后续使用。
3.公平锁采用判断当前Node是不是头结点,如果是的话就获取锁并做业务处理,不是头结点的不能获取所。
4.非公平锁没有判断当前结点,采用CAS,谁第一个拿到了state=0,则视为获取锁。
5.Condition的await和notify也采用类似的机制,当执行await是,会将当前线程信息的相关信息放入到Node的列表,记录firstWaiter和lastWaiter指向的信息。
希望对大家有所帮助,如果有问题的请及时指出。
聊聊ReentrantLock的内部实现的更多相关文章
- 聊聊ReentrantLock实现原理
ReentrantLock 是常用的锁,相对于Synchronized ,lock锁更人性化,阅读性更强 从LOCK切入 考虑下面的场景如果有A,B线程,同时去执行lock.lock(Lock loc ...
- 聊聊ReentrantLock基于AQS的公平锁和非公平锁的实现区别
ReentrantLock锁的实现是基于AQS实现的,所以先简单说下AQS: AQS是AbstractQueuedSynchronizer缩写,顾名思义:抽象的队列同步器,它是JUC里面许多同步工具类 ...
- 【JUC】JDK1.8源码分析之ReentrantLock(三)
一.前言 在分析了AbstractQueuedSynchronier源码后,接着分析ReentrantLock源码,其实在AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的分析中,已经提到过Ree ...
- java分析源码-ReentrantLock
一.前言 在分析了 AbstractQueuedSynchronier 源码后,接着分析ReentrantLock源码,其实在 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的分析中,已经提到 ...
- Java中可重入锁ReentrantLock原理剖析
本文由码农网 – 吴极心原创,转载请看清文末的转载要求,欢迎参与我们的付费投稿计划! 一. 概述 本文首先介绍Lock接口.ReentrantLock的类层次结构以及锁功能模板类AbstractQue ...
- ReentrantLock源码分析与理解
在上面一篇分析ThreadExecutedPool的文章中我们看到线程池实现源码中大量使用了ReentrantLock锁,那么ReentrantLock锁的优势是什么?它又是怎么实现的呢? Reent ...
- 5.Lock接口及其实现ReentrantLock
jdk1.7.0_79 在java.util.concurrent.locks这个包中定义了和synchronized不一样的锁,重入锁——ReentrantLock,读写锁——ReadWriteLo ...
- ReentrantLock和synchronized的性能对比
详见:http://blog.yemou.net/article/query/info/tytfjhfascvhzxcytpo8 ReentrantLock和内部锁的性能对比 Reentran ...
- 并发编程(五)——AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 之 ReentrantLock源码分析
本文将从 ReentrantLock 的公平锁源码出发,分析下 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 这个类是怎么工作的,希望能给大家提供一些简单的帮助. AQS 结构 先来看看 AQ ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript学习 - 基础(五) - string/array/function/windows对象
String对象 更详细转:http://www.w3school.com.cn/jsref/jsref_obj_string.asp //------------------------------ ...
- Dubbo高可用
高可用:通过设计减少系统不能提供服务的时间 (1).zookeeper宕机 原因:zookeeper宕机 现象:zookeeper注册中心宕机,还可以消费dubbo暴露的服务. 健壮性: 监控中心宕掉 ...
- python3之协程
1.协程的概念 协程,又称微线程,纤程.英文名Coroutine. 线程是系统级别的它们由操作系统调度,而协程则是程序级别的由程序根据需要自己调度.在一个线程中会有很多函数,我们把这些函数称为子程序, ...
- mysql系列三、mysql开启缓存、设置缓存大小、缓存过期机制
一.开启缓存 mysql 开启查询缓存可以有两种方法来开启一种是使用set命令来进行开启,另一种是直接修改my.ini文件来直接设置都是非常的简单的哦. 开启缓存,设置缓存大小,具体实施如下: 1.修 ...
- Python3学习笔记16-错误和异常
使用try...except可以处理异常 异常处理 import sys try: print('try...') r = 10/0 print('result:',r) except ZeroDiv ...
- Bootstrap3.0学习第四轮(排版)
详情请查看http://aehyok.com/Blog/Detail/10.html 个人网站地址:aehyok.com QQ 技术群号:206058845,验证码为:aehyok 本文文章链接:ht ...
- Windows CreateFont:创建自己的字体
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/softn/article/details/51718347 前面无论是使用文本输出函数还是 static 控件,字体都是默认的,比较丑陋,我们完全 ...
- 802.11 af 要点
(1)TVWS工作在 VHF/UHF 频段,欧洲为 470-790MHZ, 美国为 54-698MHZ. (2)GDB(Geolocation Database):地理位置数据库,与其他802.11协 ...
- 破解idea
2019最新注册码 地址: http://idea.lanyus.com/ https://blog.csdn.net/best_luxi/article/details/81479820
- Redis Windows上下载安装
其它的默认就可. public class RedisTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Jedis jedis = RedisPool.g ...
