在内核中针对的cpu的操作,比如arm_cpuidle_init、arm_cpuidle_suspend、boot_secondary、secondary_start_kernel、op_cpu_disable、op_cpu_kill、cpu_die、smp_cpu_setup、smp_prepare_cpus的都会回落到对cpu_ops的调用。
cpu_ops将针对底层cpu的操作抽象为一系列回调函数,以统一的形式向上层提供API。
cpu_psci_ops作为cpu_ops的一个特殊实现,将cpu_ops关联到PSCI的psci_ops。
psci_ops的函数在PSCI Firmware中实现,提供一系列基于Function ID的调用。
这种分层思想将内核通用cpu_operations和硬件相关部分分隔开。
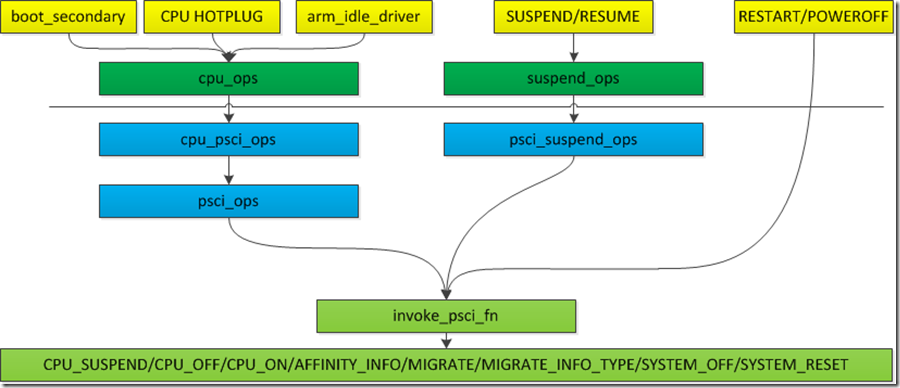
从上图可知,cpu_ops和suspend_ops将内核通用API和底层arch-specific代码区隔开;cpu_ops和suspend_ops分别调用cpu_psci_ops和psci_suspend_ops,这些回调函数最终都会回落到PSCI Firmware提供的接口。machine_restart/machine_power_off直接调用PSCI提供的接口。
cpu_operations及应用场景
首先分析一些cpu_operations这个结构体:
|
struct cpu_operations {
const char *name;
int (*cpu_init)(unsigned int); 读取必要的数据准备初始化。
int (*cpu_prepare)(unsigned int); 启动前准备工作
int (*cpu_boot)(unsigned int); 启动一个CPU
void (*cpu_postboot)(void); 执行boot后的清理工作
#ifdef CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU
int (*cpu_disable)(unsigned int cpu); 关闭CPU之前的准备工作
void (*cpu_die)(unsigned int cpu); 关闭CPU
int (*cpu_kill)(unsigned int cpu); 确认是否关闭
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_IDLE
int (*cpu_init_idle)(unsigned int); 读取CPU idle状态的参数
int (*cpu_suspend)(unsigned long); suspend一个CPU,并且保存上下文
#endif
};
|
cpu_init
|
static int __init smp_cpu_setup(int cpu)
{
if (cpu_read_ops(cpu))
return -ENODEV;
if (cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_init(cpu))
return -ENODEV;
set_cpu_possible(cpu, true);
return 0;
}
|
获取指定cpu的cpu_ops,执行cpu_init回调函数进行初始化。并将此cpu设置为possible。
cpu_prepare
|
void __init smp_prepare_cpus(unsigned int max_cpus)
{
int err;
unsigned int cpu, ncores = num_possible_cpus();
init_cpu_topology(); 填充cpu_topology结构体数组
smp_store_cpu_info(smp_processor_id());
/*
* are we trying to boot more cores than exist?
*/
if (max_cpus > ncores) 不能超过possible cpu数目
max_cpus = ncores;
/* Don't bother if we're effectively UP */
if (max_cpus <= 1)
return;
/*
* Initialise the present map (which describes the set of CPUs
* actually populated at the present time) and release the
* secondaries from the bootloader.
*
* Make sure we online at most (max_cpus - 1) additional CPUs.
*/
max_cpus--;
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
if (max_cpus == 0)
break;
if (cpu == smp_processor_id())
continue;
if (!cpu_ops[cpu])
continue;
err = cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_prepare(cpu); 执行.cpu_prepare回调函数,将指定cpu设置为present。
if (err)
continue;
set_cpu_present(cpu, true);
max_cpus--;
}
}
|
cpu_boot
|
static int boot_secondary(unsigned int cpu, struct task_struct *idle)
{
if (cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_boot)
return cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_boot(cpu);
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
|
cpu_postboot
|
asmlinkage void secondary_start_kernel(void) 被汇编调用,作为secondary CPU的启动入口
{
struct mm_struct *mm = &init_mm;
unsigned int cpu = smp_processor_id();
/*
* All kernel threads share the same mm context; grab a
* reference and switch to it.
*/
atomic_inc(&mm->mm_count);
current->active_mm = mm;
set_my_cpu_offset(per_cpu_offset(smp_processor_id()));
/*
* TTBR0 is only used for the identity mapping at this stage. Make it
* point to zero page to avoid speculatively fetching new entries.
*/
cpu_set_reserved_ttbr0();
local_flush_tlb_all();
cpu_set_default_tcr_t0sz();
preempt_disable();
trace_hardirqs_off();
/*
* If the system has established the capabilities, make sure
* this CPU ticks all of those. If it doesn't, the CPU will
* fail to come online.
*/
verify_local_cpu_capabilities();
if (cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_postboot)
cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_postboot();
/*
* Log the CPU info before it is marked online and might get read.
*/
cpuinfo_store_cpu();
/*
* Enable GIC and timers.
*/
notify_cpu_starting(cpu);
smp_store_cpu_info(cpu);
/*
* OK, now it's safe to let the boot CPU continue. Wait for
* the CPU migration code to notice that the CPU is online
* before we continue.
*/
pr_info("CPU%u: Booted secondary processor [%08x]\n",
cpu, read_cpuid_id());
set_cpu_online(cpu, true); 至此CPU可以设置为online状态
complete(&cpu_running);
local_dbg_enable();
local_irq_enable();
local_async_enable();
/*
* OK, it's off to the idle thread for us
*/
cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE);
}
|
cpu_disable
|
static int op_cpu_disable(unsigned int cpu)
{
/*
* If we don't have a cpu_die method, abort before we reach the point
* of no return. CPU0 may not have an cpu_ops, so test for it.
*/
if (!cpu_ops[cpu] || !cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_die)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
/*
* We may need to abort a hot unplug for some other mechanism-specific
* reason.
*/
if (cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_disable)
return cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_disable(cpu);
return 0;
}
|
cpu_die
|
void cpu_die(void)
{
unsigned int cpu = smp_processor_id();
idle_task_exit();
local_irq_disable();
/* Tell __cpu_die() that this CPU is now safe to dispose of */
(void)cpu_report_death();
/*
* Actually shutdown the CPU. This must never fail. The specific hotplug
* mechanism must perform all required cache maintenance to ensure that
* no dirty lines are lost in the process of shutting down the CPU.
*/
cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_die(cpu);
BUG();
}
|
cpu_kill
|
static int op_cpu_kill(unsigned int cpu)
{
/*
* If we have no means of synchronising with the dying CPU, then assume
* that it is really dead. We can only wait for an arbitrary length of
* time and hope that it's dead, so let's skip the wait and just hope.
*/
if (!cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_kill)
return 0;
return cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_kill(cpu);
}
|
cpu_init_idle和cpu_suspend
这两个回调函数主要用于idle初始化和进入idle状态。
arm_idle_init解析DeviceTree的"arm,idle-state",注册ARM的cpuidle驱动arm_idle_driver,
|
static int __init arm_idle_init(void)
{
int cpu, ret;
struct cpuidle_driver *drv = &arm_idle_driver;
struct cpuidle_device *dev;
/*
* Initialize idle states data, starting at index 1.
* This driver is DT only, if no DT idle states are detected (ret == 0)
* let the driver initialization fail accordingly since there is no
* reason to initialize the idle driver if only wfi is supported.
*/
ret = dt_init_idle_driver(drv, arm_idle_state_match, 1);
if (ret <= 0)
return ret ? : -ENODEV;
ret = cpuidle_register_driver(drv); 注册arm_idle_driver驱动函数
if (ret) {
pr_err("Failed to register cpuidle driver\n");
return ret;
}
/*
* Call arch CPU operations in order to initialize
* idle states suspend back-end specific data
*/
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
ret = arm_cpuidle_init(cpu); 获取arch-specific的idle处理参数,这里对应cpu_psci_cpu_init_idle。
/*
* Skip the cpuidle device initialization if the reported
* failure is a HW misconfiguration/breakage (-ENXIO).
*/
if (ret == -ENXIO)
continue;
if (ret) {
pr_err("CPU %d failed to init idle CPU ops\n", cpu);
goto out_fail;
}
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev) {
pr_err("Failed to allocate cpuidle device\n");
goto out_fail;
}
dev->cpu = cpu;
ret = cpuidle_register_device(dev);
if (ret) {
pr_err("Failed to register cpuidle device for CPU %d\n",
cpu);
kfree(dev);
goto out_fail;
}
}
return 0;
out_fail:
while (--cpu >= 0) {
dev = per_cpu(cpuidle_devices, cpu);
cpuidle_unregister_device(dev);
kfree(dev);
}
cpuidle_unregister_driver(drv);
return ret;
}
|
arm_cpuidle_init调用.cpu_init_idle回调函数。
|
int __init arm_cpuidle_init(unsigned int cpu)
{
int ret = -EOPNOTSUPP;
if (cpu_ops[cpu] && cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_init_idle)
ret = cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_init_idle(cpu);
return ret;
}
|
arm_enter_idle_state根据参数idx使CPU进入特定的idle状态,
|
static int arm_enter_idle_state(struct cpuidle_device *dev,
struct cpuidle_driver *drv, int idx)
{
int ret;
if (!idx) {
cpu_do_idle(); 如果idx为0,则cpu_do_idle。
return idx;
}
ret = cpu_pm_enter();
if (!ret) {
/*
* Pass idle state index to cpu_suspend which in turn will
* call the CPU ops suspend protocol with idle index as a
* parameter.
*/
ret = arm_cpuidle_suspend(idx); 调用底层arch-specific处理函数。
cpu_pm_exit();
}
return ret ? -1 : idx;
}
|
cpu_do_idle使CPU进入WFI状态。
|
ENTRY(cpu_do_idle)
dsb sy // WFI may enter a low-power mode
wfi
ret
ENDPROC(cpu_do_idle)
|
|
int arm_cpuidle_suspend(int index)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
/*
* If cpu_ops have not been registered or suspend
* has not been initialized, cpu_suspend call fails early.
*/
if (!cpu_ops[cpu] || !cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_suspend)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
return cpu_ops[cpu]->cpu_suspend(index);
}
|
cpu_ops到arch-dependent的关联
以start_kernel为起点,查看从内核开始到获取cpu_ops的路径如下:
start_kernel
-->setup_arch
-->cpu_read_bootcpu_ops 只获取bootcpu的cpu_ops
-->cpu_read_bootcpu_ops
-->cpu_read_ops(0)
-->smp_init_cpus 获取nonboot cpu的cpu_ops
-->smp_cpu_setup
-->cpu_read_ops |
cpu_read_ops是获取cpu_ops的关键,参数是cpu的序列号,输出是cpu_ops[cpu]。
|
int __init cpu_read_ops(int cpu)
{
const char *enable_method = cpu_read_enable_method(cpu); 从DeviceTree获取enable_method字符串
if (!enable_method)
return -ENODEV;
cpu_ops[cpu] = cpu_get_ops(enable_method); 根据enable_method字符串在supported_cpu_ops获取指针
if (!cpu_ops[cpu]) {
pr_warn("Unsupported enable-method: %s\n", enable_method);
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
return 0;
}
|
通过cpu0的DeviceTree可以看出enable-method为pcsi。
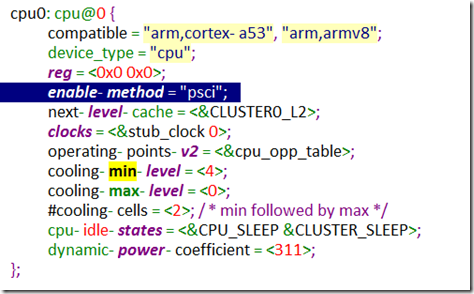
支持的cpu_operations有:
|
static const struct cpu_operations *supported_cpu_ops[] __initconst = {
&smp_spin_table_ops,
&cpu_psci_ops,
NULL,
};
|
所以cpu_ops=&cpu_psci_ops。
suspend_ops
在enter_state—>suspend_devices_and_enter—>suspend_enter有针对suspend_ops->enter的调用,suspend_ops的赋值在psci_init_system_suspend中:
|
static void __init psci_init_system_suspend(void)
{
int ret;
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SUSPEND))
return;
ret = psci_features(PSCI_FN_NATIVE(1_0, SYSTEM_SUSPEND));
if (ret != PSCI_RET_NOT_SUPPORTED)
suspend_set_ops(&psci_suspend_ops); suspend_ops指向psci_suspend_ops
}
|
psci_suspend_ops是platform_suspend_ops类型的函数结构体,这里只有两个成员。
|
static const struct platform_suspend_ops psci_suspend_ops = {
.valid = suspend_valid_only_mem, 返回系统支持的suspend类型
.enter = psci_system_suspend_enter, 进入suspend状态,参数是状态值,这里只能有mem
};
|
psci_system_suspend_enter调用cpu_suspend并且给出结束回调函数。
cpu_suspend调用__cpu_suspend_enter,并进行TTBR0、TLB、TCR、MM等的操作,这些都涉及到汇编处理。
__cpu_suspend_enter保存当前CPU状态,其中x0保存结束回调函数的参数,x1是结束回调函数指针地址。
|
ENTRY(__cpu_suspend_enter)
stp x29, lr, [sp, #-96]!
stp x19, x20, [sp,#16]
stp x21, x22, [sp,#32]
stp x23, x24, [sp,#48]
stp x25, x26, [sp,#64]
stp x27, x28, [sp,#80]
/*
* Stash suspend finisher and its argument in x20 and x19
*/
mov x19, x0
mov x20, x1
mov x2, sp
sub sp, sp, #CPU_SUSPEND_SZ // allocate cpu_suspend_ctx
mov x0, sp
/*
* x0 now points to struct cpu_suspend_ctx allocated on the stack
*/
str x2, [x0, #CPU_CTX_SP]
ldr x1, =sleep_save_sp
ldr x1, [x1, #SLEEP_SAVE_SP_VIRT]
mrs x7, mpidr_el1
ldr x9, =mpidr_hash
ldr x10, [x9, #MPIDR_HASH_MASK]
/*
* Following code relies on the struct mpidr_hash
* members size.
*/
ldp w3, w4, [x9, #MPIDR_HASH_SHIFTS]
ldp w5, w6, [x9, #(MPIDR_HASH_SHIFTS + 8)]
compute_mpidr_hash x8, x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x10
add x1, x1, x8, lsl #3
bl __cpu_suspend_save
/*
* Grab suspend finisher in x20 and its argument in x19
*/
mov x0, x19 将备份的arg和fn恢复到x0, x1
mov x1, x20
/*
* We are ready for power down, fire off the suspend finisher
* in x1, with argument in x0
*/
blr x1 执行suspend结束函数回调,这里指的是psci_system_suspend。
/*
* Never gets here, unless suspend finisher fails.
* Successful cpu_suspend should return from cpu_resume, returning
* through this code path is considered an error
* If the return value is set to 0 force x0 = -EOPNOTSUPP
* to make sure a proper error condition is propagated
*/
cmp x0, #0
mov x3, #-EOPNOTSUPP
csel x0, x3, x0, eq
add sp, sp, #CPU_SUSPEND_SZ // rewind stack pointer
ldp x19, x20, [sp, #16]
ldp x21, x22, [sp, #32]
ldp x23, x24, [sp, #48]
ldp x25, x26, [sp, #64]
ldp x27, x28, [sp, #80]
ldp x29, lr, [sp], #96
ret
ENDPROC(__cpu_suspend_enter)
|
psci_system_suspend作为cpu_suspend收尾函数,调用psci的suspend函数,让CPU进入suspend。
|
static int psci_system_suspend(unsigned long unused)
{
return invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_FN_NATIVE(1_0, SYSTEM_SUSPEND),
virt_to_phys(cpu_resume), 0, 0);
}
|
psci的SYSTEM_SUSPEND entry_point参数是cpu_resume,这个函数会在CPU唤醒之后执行的入口点。
cpu_resume在arc/arm64/kernel/sleep.S中定义,和__cpu_suspend_enter是相反的过程,恢复sp指针、pc指针、MMU等。
|
ENTRY(cpu_resume)
bl el2_setup // if in EL2 drop to EL1 cleanly
mrs x1, mpidr_el1
adrp x8, mpidr_hash
add x8, x8, #:lo12:mpidr_hash // x8 = struct mpidr_hash phys address
/* retrieve mpidr_hash members to compute the hash */
ldr x2, [x8, #MPIDR_HASH_MASK]
ldp w3, w4, [x8, #MPIDR_HASH_SHIFTS]
ldp w5, w6, [x8, #(MPIDR_HASH_SHIFTS + 8)]
compute_mpidr_hash x7, x3, x4, x5, x6, x1, x2
/* x7 contains hash index, let's use it to grab context pointer */
ldr_l x0, sleep_save_sp + SLEEP_SAVE_SP_PHYS
ldr x0, [x0, x7, lsl #3]
/* load sp from context */
ldr x2, [x0, #CPU_CTX_SP]
/* load physical address of identity map page table in x1 */
adrp x1, idmap_pg_dir
mov sp, x2
/*
* cpu_do_resume expects x0 to contain context physical address
* pointer and x1 to contain physical address of 1:1 page tables
*/
bl cpu_do_resume // PC relative jump, MMU off
b cpu_resume_mmu // Resume MMU, never returns
ENDPROC(cpu_resume)
|
cpu_psci_ops分析
cpu_psci_ops结构体可以说是cpu_operations和psci_operations的桥梁,他讲cpu_operations的一些列回调函数,映射到psci_operations。
|
const struct cpu_operations cpu_psci_ops = {
.name = "psci",
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_IDLE
.cpu_init_idle = cpu_psci_cpu_init_idle, 从DeviceTree获取CPU idle状态数据
.cpu_suspend = cpu_psci_cpu_suspend, 根据是否丢失上下文来选择是psci_ops.cpu_suspend还是cpu_suspend
#endif
.cpu_init = cpu_psci_cpu_init, 为空
.cpu_prepare = cpu_psci_cpu_prepare, 只是判断psci_ops.cpu_on是否存在,不存在则返回错误。
.cpu_boot = cpu_psci_cpu_boot, 调用psci_ops.cpu_on
#ifdef CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU
.cpu_disable = cpu_psci_cpu_disable, 检查是否支持psci_ops.cpu_off。
.cpu_die = cpu_psci_cpu_die, 调用psci_ops.cpu_off
.cpu_kill = cpu_psci_cpu_kill, 检查指定cpu是否已经被kill
#endif
}
|
cpu_psci_cpu_boot
|
static int cpu_psci_cpu_boot(unsigned int cpu)
{
int err = psci_ops.cpu_on(cpu_logical_map(cpu), __pa(secondary_entry));
if (err)
pr_err("failed to boot CPU%d (%d)\n", cpu, err);
return err;
}
|
CPU_ON用于secondary boot、hotplug或者big.LITTLE迁移。如果需要从一个核启动另一个核,通过CPU_ON提供一个入口地址和上下文标识。
PCSI提供必要的操作启动一个核,并且在提供的入口地址开始执行,上下文标识必须存在R0或者W0中。这里的入口地址就对应secondary_entry。
在arch/arm64/kernel/head.S中:
| secondary_entry—>secondary_startup—>__secondary_switched—>secondary_start_kernel
ENTRY(secondary_entry)
bl el2_setup // Drop to EL1
bl set_cpu_boot_mode_flag
b secondary_startup
ENDPROC(secondary_entry)
ENTRY(secondary_startup)
/*
* Common entry point for secondary CPUs.
*/
adrp x25, idmap_pg_dir
adrp x26, swapper_pg_dir
bl __cpu_setup // initialise processor
ldr x21, =secondary_data
ldr x27, =__secondary_switched // address to jump to after enabling the MMU
b __enable_mmu
ENDPROC(secondary_startup)
ENTRY(__secondary_switched)
ldr x0, [x21] // get secondary_data.stack
mov sp, x0
mov x29, #0
b secondary_start_kernel
ENDPROC(__secondary_switched)
|
在secondary_start_kernel将CPU设置为online,并调用.cpu_postboot回调函数,进行boot后处理。然后cpu_startup_entry启动idle线程。
cpu_psci_cpu_init_idle
|
static int __maybe_unused cpu_psci_cpu_init_idle(unsigned int cpu)
{
int i, ret, count = 0;
u32 *psci_states;
struct device_node *state_node, *cpu_node;
cpu_node = of_get_cpu_node(cpu, NULL);
if (!cpu_node)
return -ENODEV;
/*
* If the PSCI cpu_suspend function hook has not been initialized
* idle states must not be enabled, so bail out
*/
if (!psci_ops.cpu_suspend)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
/* Count idle states */
while ((state_node = of_parse_phandle(cpu_node, "cpu-idle-states",
count))) {
count++;
of_node_put(state_node);
}
if (!count)
return -ENODEV;
psci_states = kcalloc(count, sizeof(*psci_states), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!psci_states)
return -ENOMEM;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
u32 state;
state_node = of_parse_phandle(cpu_node, "cpu-idle-states", i);
ret = of_property_read_u32(state_node,
"arm,psci-suspend-param",
&state);
if (ret) {
pr_warn(" * %s missing arm,psci-suspend-param property\n",
state_node->full_name);
of_node_put(state_node);
goto free_mem;
}
of_node_put(state_node);
pr_debug("psci-power-state %#x index %d\n", state, i);
if (!psci_power_state_is_valid(state)) {
pr_warn("Invalid PSCI power state %#x\n", state);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto free_mem;
}
psci_states[i] = state;
}
/* Idle states parsed correctly, initialize per-cpu pointer */
per_cpu(psci_power_state, cpu) = psci_states;
return 0;
free_mem:
kfree(psci_states);
return ret;
}
|
1.解析DeviceTree中cpu下的cpu-idle-states属性
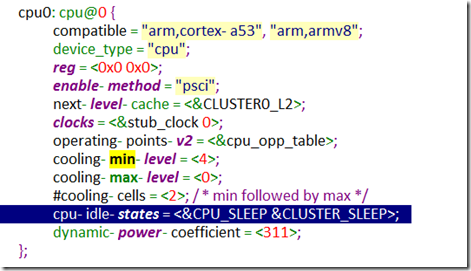
2.从每个state中获取arm,psci-suspend-param的参数,并验证是否有效。

3.初始化per-CPU类型的指针psci_power_state。
cpu_psci_cpu_suspend
|
static int __maybe_unused cpu_psci_cpu_suspend(unsigned long index)
{
int ret;
u32 *state = __this_cpu_read(psci_power_state); 从psci_power_state中读取suspend的state参数。
/*
* idle state index 0 corresponds to wfi, should never be called
* from the cpu_suspend operations
*/
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!index))
return -EINVAL;
if (!psci_power_state_loses_context(state[index - 1]))
ret = psci_ops.cpu_suspend(state[index - 1], 0);
else
ret = cpu_suspend(index, psci_suspend_finisher);
return ret;
}
|
psci_ops
由于acpi_disabled,所以psci通过DeviceTree获取相关参数。
start_kernel
-->setup_arch
-->psci_dt_init 这个函数在cpu_ops之前,因为cpu_ops依赖psci_ops |
psci有不同版本,需要通过DeviceTree获取版本信息和使用的method(是smc还是)。
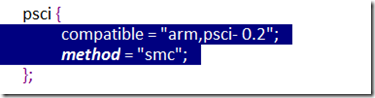
通过查看DeviceTree可以看到对应的是psci_0_2_init。
|
static const struct of_device_id const psci_of_match[] __initconst = {
{ .compatible = "arm,psci", .data = psci_0_1_init},
{ .compatible = "arm,psci-0.2", .data = psci_0_2_init},
{ .compatible = "arm,psci-1.0", .data = psci_0_2_init},
{},
};
|
psci_dt_init解析DeviceTree执行对应psci版本的初始化函数。
|
int __init psci_dt_init(void)
{
struct device_node *np;
const struct of_device_id *matched_np;
psci_initcall_t init_fn;
np = of_find_matching_node_and_match(NULL, psci_of_match, &matched_np);
if (!np)
return -ENODEV;
init_fn = (psci_initcall_t)matched_np->data;
return init_fn(np);
}
|
psci_0_2_init设置method,然后调用psci_probe:
|
static int __init psci_0_2_init(struct device_node *np)
{
int err;
err = get_set_conduit_method(np); 从DeviceTree可知invoke_psci_fn = __invoke_psci_fn_smc
if (err)
goto out_put_node;
/*
* Starting with v0.2, the PSCI specification introduced a call
* (PSCI_VERSION) that allows probing the firmware version, so
* that PSCI function IDs and version specific initialization
* can be carried out according to the specific version reported
* by firmware
*/
err = psci_probe();
out_put_node:
of_node_put(np);
return err;
}
|
psci_probe设置版本高于0.2的PSCI回调函数,以及arm_pm_restart和pm_power_off。
|
static void __init psci_0_2_set_functions(void)
{
pr_info("Using standard PSCI v0.2 function IDs\n");
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND] =
PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, CPU_SUSPEND);
psci_ops.cpu_suspend = psci_cpu_suspend;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_OFF] = PSCI_0_2_FN_CPU_OFF;
psci_ops.cpu_off = psci_cpu_off;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_ON] = PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, CPU_ON);
psci_ops.cpu_on = psci_cpu_on;
psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_MIGRATE] = PSCI_FN_NATIVE(0_2, MIGRATE);
psci_ops.migrate = psci_migrate;
psci_ops.affinity_info = psci_affinity_info;
psci_ops.migrate_info_type = psci_migrate_info_type;
arm_pm_restart = psci_sys_reset;
pm_power_off = psci_sys_poweroff;
}
|
这些函数都有一个共性invoke_psci_fn(PSCI_0_2_FN_SYSTEM_OFF, 0, 0, 0),着这里invoke_psci_fn指向__invoke_psci_fn_smc 。
__invoke_psci_fn_smc指向arch/arm64/kernel/psci-call.S定义的函数:
|
/* int __invoke_psci_fn_smc(u64 function_id, u64 arg0, u64 arg1, u64 arg2) */
ENTRY(__invoke_psci_fn_smc)
smc #0
ret
ENDPROC(__invoke_psci_fn_smc)
|
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0022c/DEN0022C_Power_State_Coordination_Interface.pdf Chapter5有PSCI函数圆形和相关参数返回值的介绍。
第一个参数是Function ID,后面三个参数作为Function ID的参数。如果使用的是32位的参数,后三个参数通过r0-r3传递给Function ID,r0存放返回值;如果使用64位的参数,后三个参数通过W0-W3传递,w0存放返回值。这些Function ID的实现,在对应的Firmware中,但是可以通过上述pdf查看输入输出细节。
PSCI除了提供psci_ops的回调函数之外,还提供以restart和power off的arch-dependent函数arm_pm_restart和pm_power_off
比如machine_power_off和machine_restart调用:
|
void machine_power_off(void)
{
local_irq_disable();
smp_send_stop();
if (pm_power_off)
pm_power_off();
}
void machine_restart(char *cmd)
{
/* Disable interrupts first */
local_irq_disable();
smp_send_stop();
/*
* UpdateCapsule() depends on the system being reset via
* ResetSystem().
*/
if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES))
efi_reboot(reboot_mode, NULL);
/* Now call the architecture specific reboot code. */
if (arm_pm_restart)
arm_pm_restart(reboot_mode, cmd);
else
do_kernel_restart(cmd);
/*
* Whoops - the architecture was unable to reboot.
*/
printk("Reboot failed -- System halted\n");
while (1);
}
|
参考文档
Linux CPU core的电源管理(3)_cpu ops:http://www.wowotech.net/pm_subsystem/cpu_ops.html
- List-LinkedList、set集合基础增强底层源码分析
List-LinkedList 作者 : Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 继上一章继续讲解,上章内容: List-ArreyLlist集合基础增强底层源码分析:https:// ...
- List-ArrayList集合基础增强底层源码分析
List集合基础增强底层源码分析 作者:Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 集合分为三个系列,分别为:List.set.map List系列 特点:元素有序可重复 有序指的是元素的 ...
- LInkedList总结及部分底层源码分析
LInkedList总结及部分底层源码分析 1. LinkedList的实现与继承关系 继承:AbstractSequentialList 抽象类 实现:List 接口 实现:Deque 接口 实现: ...
- Vector总结及部分底层源码分析
Vector总结及部分底层源码分析 1. Vector继承的抽象类和实现的接口 Vector类实现的接口 List接口:里面定义了List集合的基本接口,Vector进行了实现 RandomAcces ...
- mybatis底层源码分析之--配置文件读取和解析
现在企业级开发中ssm是很常见的技术标配,mybatis比hibernate轻量了很多,而且学习成本相对较低,简单易上手. 那么,问题来了,简单好用的mybatis底层到底是如何实现的呢?都使用了什么 ...
- Unity3d底层数据传递分析
WeTest 导读 这篇文章主要分析了在Mono框架下,非托管堆.运行时.托管堆如何关联,以及通过哪些方式调用.内存方面,介绍了什么是封送,以及类和结构体的关系和区别. 一.托管交互(Interop) ...
- SpringData ES中一些底层原理的分析
之前写过一篇SpringData ES 关于字段名和索引中的列名字不一致导致的查询问题,顺便深入学习下Spring Data Elasticsearch. Spring Data Elasticsea ...
- 持久层Mybatis3底层源码分析,原理解析
Mybatis-持久层的框架,功能是非常强大的,对于移动互联网的高并发 和 高性能是非常有利的,相对于Hibernate全自动的ORM框架,Mybatis简单,易于学习,sql编写在xml文件中,和代 ...
- 【Flink】Flink 底层RPC框架分析
1. 前言 对于Flink中各个组件(JobMaster.TaskManager.Dispatcher等),其底层RPC框架基于Akka实现,本文着重分析Flink中的Rpc框架实现机制及梳理其通信流 ...
随机推荐
- mongos-sharding连接池配置
ShardingTaskExecutorPoolMaxSize Maximum number of outbound connections each TaskExecutor connection ...
- LeetCode专题-Python实现之第21题:Merge Two Sorted Lists
导航页-LeetCode专题-Python实现 相关代码已经上传到github:https://github.com/exploitht/leetcode-python 文中代码为了不动官网提供的初始 ...
- RDIFramework.NET ━ .NET快速信息化系统开发框架 V3.2-新增锁定用户与解除锁定用户的功能
锁定用户功能在现实应用场景中得到了大量的应用,当我们需要限制某用户的登录,又不能删除这个用户时就可以使用锁定功能,如:未授权的用户尝试错误密码错误过多可以尝试的用户进行锁定,又如ATM机上取钱时密码错 ...
- selenium加载配置参数,让chrome浏览器不出现‘Chrome正在受到自动软件的控制’的提示语,以及后台静默模式启动自动化测试,不占用桌面的方法
一:自动化测试的时候,启动浏览器出现‘Chrome正在受到自动软件的控制’,怎么样隐藏,今天学习分享: 在浏览器配置里加个参数,忽略掉这个警告提示语,disable_infobars option = ...
- 第52章 撤销端点(Revocation Endpoint) - Identity Server 4 中文文档(v1.0.0)
此端点允许撤消访问令牌(仅限引用令牌)和刷新令牌.它实现了令牌撤销规范(RFC 7009). token 要撤销的令牌(必填) token_type_hint access_token或refresh ...
- 【Parallel】.Net 并行执行程序的使用心得
一.摘要 官方介绍:提供对并行循环和区域的支持. 命名空间:using System.Threading.Tasks 三个静态方法:Parallel.Invoke,Parallel.For,Paral ...
- Java 由浅入深GUI编程实战练习(二)
一,项目简介 1.利用Java GUI 绘制图像界面,设置整体布局 2.编写一个随机数生成1~100的随机数 3.编写一个验证类,用于验证用户输入值与生成随机数是否相等并记录用户猜测次数,当用户猜测成 ...
- Dubbo+ZK与Eureka注册中心比较
Eureka可以很好的应对网络故障导致部分节点失去联系的情况,而不会像zk那样因为选举导致整个集群不可用 dubbo + zk 当向注册中心查询服务注册列表时,可以容忍注册中心返回的是几分钟以前的注册 ...
- 关于mybatis条件查询 报错:元素内容必须由格式正确的字符数据或标记组成
原查询 select sum(case when age<=16 then 1 else 0 end ) age1, sum(case when age>16 and age<=25 ...
- Vue CLI 3.0脚手架如何在本地配置mock数据
前后端分离的开发模式已经是目前前端的主流模式,至于为什么会前后端分离的开发我们就不做过多的阐述,既然是前后端分离的模式开发肯定是离不开前端的数据模拟阶段. 我们在开发的过程中,由于后台接口的没有完成或 ...





